Esophageal Disorders: Esophagitis and Esophageal Cancer
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
infectious, compromised, endoscopy, friability, fluconazole
Candida Esophagitis
-Most common cause of __________ esophagitis
-Think ____________ host (HIV, diabetes, chronic disease, chemo)
-Need _________ to diagnose. Will see characteristic appearance of linear yellow-white plaques with _________
-Oral ___________ to treat
vesicles, deep, Acyclovir
Herpetic Esophagitis
-HSV type 1 or 2
-________ on nose and lips may coexist
-Endoscopic findings are vesicles and small, ______ ulcerations
-Treatment is __________
immunocompromised, superficial, Ganciclovir
CMV Esophagitis
-Primarily in ______________ patients, particularly organ transplant recipients or AIDS
-Endoscopic findings include large __________ shallow ulcers
-Treatment = ____________
chronic, genetic, asthma, dysphagia, GERD
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Background
-______, immune/antigen-mediated disease
-Pathogenesis → interplay between _______, environmental, and host immune system factors
-Associated Disorders → food allergies, environmental allergies, _______, and atopic dermatitis
-Symptoms → ___________ (especially solids), food impaction, chest pain, ____, upper abdominal pain
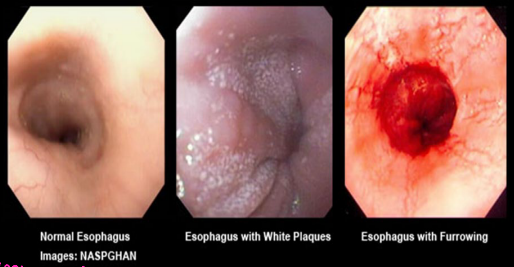
biopsy, ringed, linear, eosinophils, dietary, glucocorticoids
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Diagnosis and Treatment
-Diagnosis → EGD with _____ makes the diagnosis
______ appearance ('“feline” esophagus), strictures, attenuation of subepithelial vascular pattern, _____ furrows, whitish papules
Biopsy shows increased number of ____________
-Treatment → start with ________ therapy and avoiding known allergens
Pharmacologic therapy if dietary fails → PPI or topical _____________ (Fluticasone)
Esophageal dilation
medication, women, fluid, anatomy, tetracycline, bisphosphonates
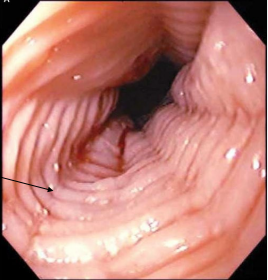
Pill Esophagitis: Background
-Direct esophageal mucosal injury due to ____________
-Epidemiology → mean age 41.5, higher prevalence in _______
-Risk → position of patient, size of medication, amount of _____ ingested with med, and altered esophageal __________
-Medications include → ___________/doxycycline (antibiotics), _____________ (alendronate), and NSAIDs
medication, barrier, heartburn, swallowing, without
Pill Esophagitis: Pathogenesis and Symptoms
-Pathogenesis → Direct irritant effect from prolonged contact of the ____________ with mucosa, causing a local acid burn or hyperosmolality. Can also cause disruption of cryoprotective _______
-Symptoms → retrosternal pain or _____________, odynophagia, dysphagia, and history of ___________ a pill _________ water (commonly at bedtime)
EGD, discrete, normal, discontinue, water
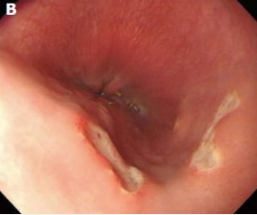
Pill Esophagitis: Diagnosis and Treatment
-Diagnosis
Clinical
___ → severe sx or sx that persist 1 week after discontinuation of med. Single-multiple, ________ ulcers with ______ surrounding mucosa
Air contrast barium study → suspect extrinsic compression
-Treatment
____________ likely medication (or substitute for liquid form)
Instruct on how to take medications properly → take with at least 8oz of _____ and stand/sit upright for at least 30 minutes after taking med
acid, stomach, ETOH, erosive, mucosa, GERD, injury
GERD: Background
-Reflux of ____ and pepsin or bile salts from _______ to esophagus, causing inflammation and symptoms
-Risk Factors → obesity, hiatal hernia, ____ use, tobacco use, and pregnancy
-________ esophagitis → visible breaks in the esophageal ______ with or without symptoms
-Nonerosive reflux disease → symptoms of ____ without visible esophageal mucosal ______
relaxation, reflux, smoking, laxity, delayed, lengthens
GERD: Pathogenesis
EGJ Incompetence
-Transient LES ____________ → increased relaxation associated with _____ of acid. Seen in obesity, pregnancy, and gastroparesis
-Hypotensive LES → gastric distention, pregnancy, _______, specific foods and meds
-Anatomic disruption of EGJ (hiatal hernia) → ______ in the LES/diaphragm attachment and increased EGJ distensibility
________ Gastric Emptying
-___________ period during which reflux is possible and increases acid content of chyme, like in gastroparesis
heartburn, gastric, dysphagia, substernally, globus
GERD: Symptoms
-_____________ → retrosternal burning sensation most commonly after eating
-Regurgitation → ______ contents flowing into mouth/throat
-_________
-Chest pain → mimic angina pectoris, squeezing or burning ___________. Usually postprandial, can awaken pt from sleep, can be exacerbated by stress
-______ sensation → perception of constant lump in throat
-Nausea
cough, asthma, respond, necrosis, ulcers, Barrett’s, adenocarcinoma
GERD: Extraesophageal Symptoms and Complications
-_____, hoarseness/laryngitis secondary to mucosal injury from gastric contents, wheezing/exacerbation of ______ due to microaspiration of gastric contents
Consider GERD in asthma pts whose symptoms don’t _______ well to asthma therapy
-Complications
Erosive esophagitis → ________ of esophageal mucosa leading to ______
_______’_ esophagus
Esophageal stricture → result of healing of erosive esophagitis
Esophageal ______________ (d/t Barrett’s esophagitis)
dyspepsia, bleeding, loss, vomiting
GERD: Alarm Symptoms for Malignancy
-New onset _________ in > 60 y/o
-GI __________ (hematemesis, melena, hematochezia)
-Iron deficiency anemia
-Anorexia
-Unexplained weight ____
-Dysphagia
-Odynophagia
-Persistent __________
-GI cancer in 1st degree relative
5-10, male, tobacco
GERD: Risk Factors for Barrett’s Esophagus
-Duration of GERD of at least _-__ years
-Age 50 or older
-____ sex
-White race
-Hiatal hernia
-Obesity
-Nocturnal reflux
-________ use
-1st degree relative with Barrett’s esophagus or adenocarcinoma
PPI, GERD, persistent, catheter
GERD: DIagnosis
-___ trial → classic symptoms without alarm symptoms or risk factors
-EGD (can be 1st line in certain situations) → indicated in pts with suspected ____ and alarm symptoms. Risk for Barrett’s esophagitis, fail PPI therapy
-Ambulatory esophageal pH monitoring → ___________ symptoms despite therapy and/or normal EGD. 24 hour transnasal pH ________ or 96 hour wireless capsule
lifestyle, loss, dietary, antacids, histamine
GERD: Mild and Intermittent Symptoms Treatment
-__________ and dietary modifications are first line → weight ____, elevation of head of bed, avoid late night meals or laying down directly after eating, elimination of _______ triggers, and tobacco/ETOH cessation
-_______ → usually contain combo of magnesium trisilicate, aluminum hydroxide, or calcium carbonate. Ex Tums
-Histamine 2 Receptor Antagonist → decrease the secretion of acid by inhibiting the __________ 2 receptor on the gastric parietal cell
PPI, 8, Nissen Fundoplication
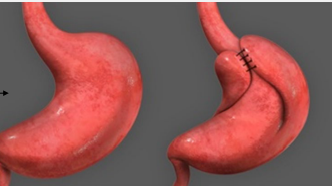
GERD: Severe or Frequent Symptoms or Erosive Esophagitis Treatment
-___ → block proton pumps to prevent release of gastric acid
Begin with standard dose of PPI once daily for _ weeks + lifestyle changes
-Reserved for refractory cases → surgical and endoscopic therapy
Laparoscopic _______ ___________
Thermocoagulation of LES
Suturing of LES
metaplastic, adenocarcinoma, distal, columnar, asymptomatic, GERD
Barrett’s Esophagus: Background
-________ change d/t chronic GERD, predisposes to ______________
-Epidemiology → more common in white males, mean age at dx is 55
-Pathophysiology → chronic GERD causes a metaplastic change, d/t inflammation, in the ______ esophagus from normal stratified squamous epithelium to a more acid-resistant _______ epithelium
-Symptoms → Barrett’s esophagus itself is ____________, usually found during investigation of ____ symptoms
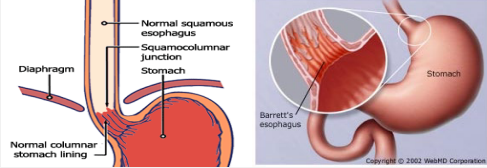
biopsy, columnar, metaplasia, goblet
Barrett’s Esophagus: Diagnosis
-EGD with ______
-Diagnostic criteria → ________ epithelium lines > 1 cm of distal esophagus. Biopsy reveals intestinal ___________ with ______ cells
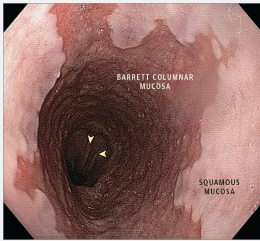
GERD, obesity, smoking
Barrett’s Esophagus: Screen for BE
-Men with chronic ____ (>5 yrs) and 2 or more risk factors like age > 50, Caucasian, central _______, hx of _______, and FHx of Barrett’s esophagus or esophageal carcinoma
3-5, 6-12, endoscopic
Barrett’s Esophagus: Surveillance in those with BE
-30 fold increase of developing esophageal cancer
-Barrett’s Esophagus with no dysplasia → EGD with biopsy every _-_ years
-Barrett’s Esophagus with low-grade dysplasia → EGD with biopsy every _-__ months or perform endoscopic eradication
-Barrett’s Esophagus with high-grade dysplasia → no surveillance, __________ eradication therapy
PPI, eradication, ablation
Barrett’s Esophagus: Treatment
-___ → all patients indefinitely, might prevent cancer
-Endoscopic __________ therapy (if dysplasia present)
________ therapy
Radiofrequency ablation, photodynamic therapy, cryotherapy
Resection
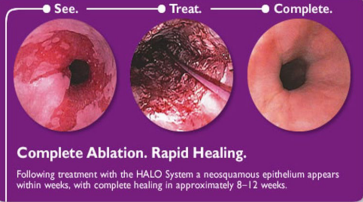
ETOH, tobacco, mid, upper, polyps, early
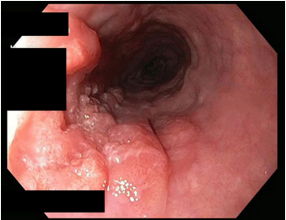
Esophageal Cancer: Squamous Cell Carcinoma
-Epidemiology → men > women
-Risk Factors → ____, _______, achalasia/strictures, and tylosis
-Pathogenesis → located in ___ to _____ esophagus
Arise from small ______, denuded epithelium, or plaques
Advanced lesions → infiltrating and ulcerated mass
______ lymph node invasion
Metastases → liver, bone, lung
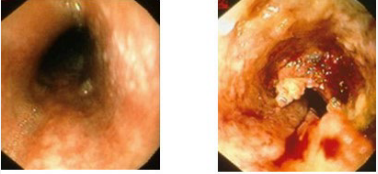
GERD, GEJ, Barrett’s, ulcer, early
Esophageal Cancer: Adenocarcinoma
-Epidemiology → men > women, Caucasian
-Risk Factors → ____/Barrett’s metaplasia, tobacco, obesity
-Pathogenesis → located near the ___ and associated with _______’_ esophagus. May present as _____, nodule, altered mucosal pattern. Lymph nodes involved _____
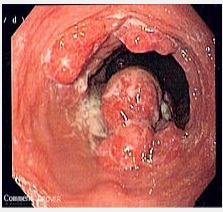
dysphagia, anemia, biopsy, US, PET
Esophageal Cancer: Symptoms and Diagnosis
-Symptoms: progressive _________, weight loss, odynophagia, iron deficiency ______
-Diagnosis: EGD with _______, contrast CT or ___ scan
-Staging Evaluation: endoscopic __ for locoregional staging. Can also do CT with contrast or ___ scan to look for distant metastasis.
fit, submucosa, invasion, chemotherapy, resection, surgery
Esophageal Cancer: Treatment
-Esophagectomy → preferred in ___ patients with involvement down to the ________/muscularis with or without lymphovascular ________. Some patients may need ____________ or chemoradiotherapy before surgery
If there is full-thickness involvement with or without nodal disease
Selected patients with full thickness involvement that invades adjacent structures
-Endoscopic __________ → alternative for selected patients
Cancers limited to the mucosa without lymphovascular invasion
Poor candidates for _______ (elderly with multiple comorbidities)
metastases, adjacent, cervical, unresectable, undergo
Esophageal Cancer: Treatment of Advanced/Unresectable EC
-Criteria for Unresectability
Distant __________ (peritoneal, lung, bone, adrenal, brain, liver, lymph nodes)
Invasion of ________ structures (aorta, trachea, vertebral body)
_________ esophageal cancer
-Chemotherapy with radiation therapy
Standard for fit pts with locally advanced, ____________ thoracic/abdominal EC
-Symptomatic treatment in those who can’t ________ other treatment (treat dysphagia)