Chapter #5 Virology Basics Brock 16th edition
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
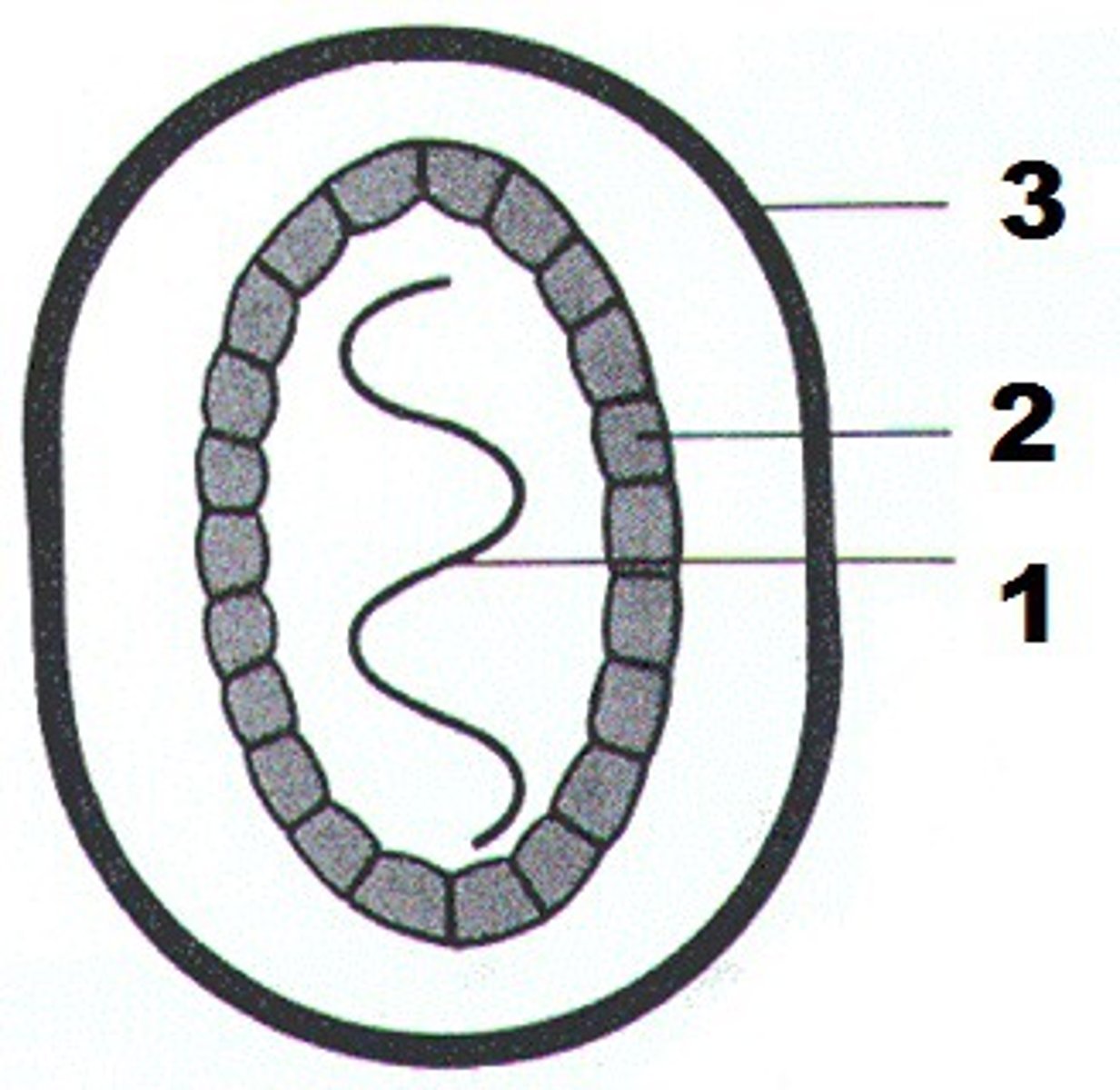
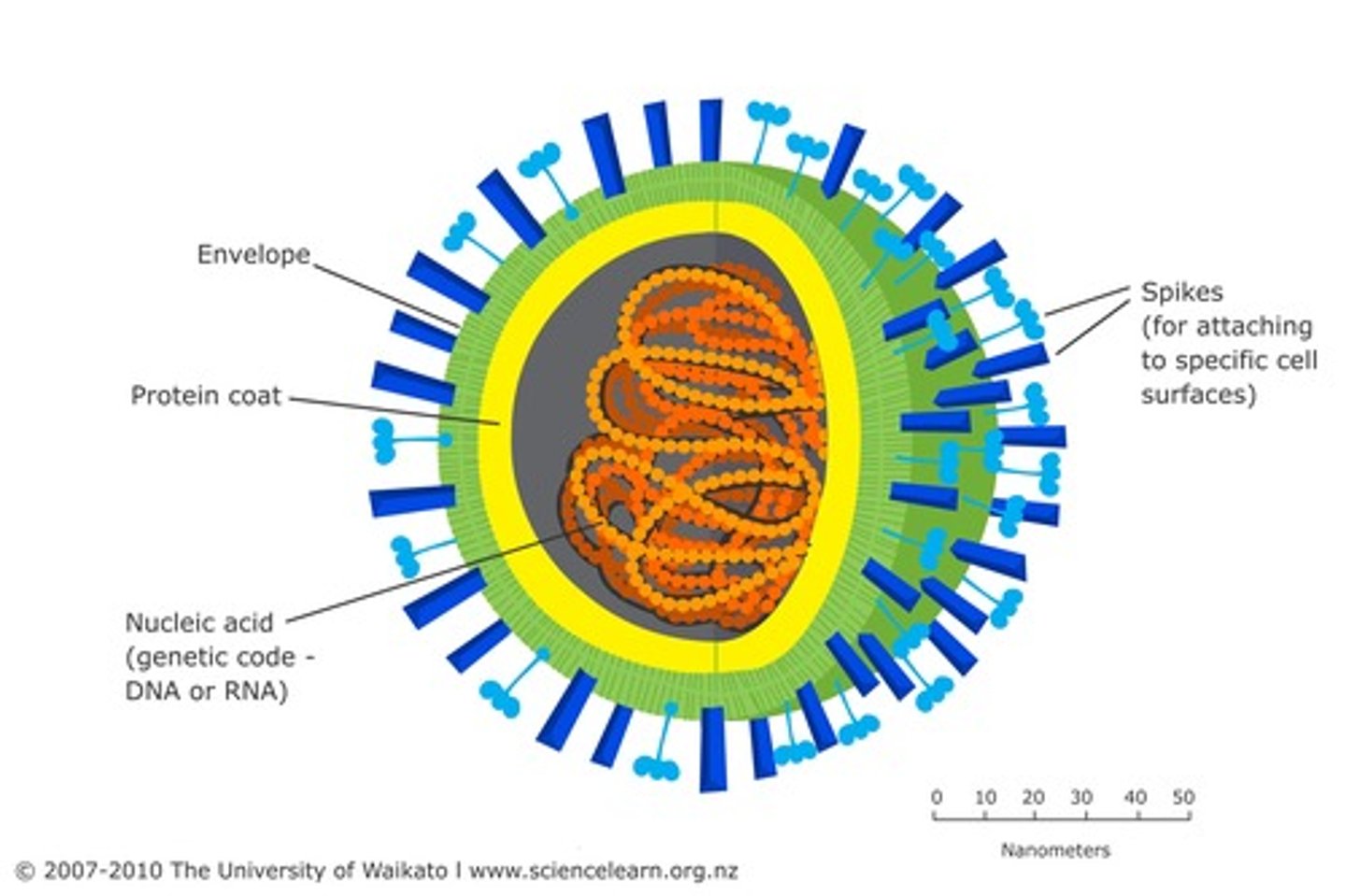
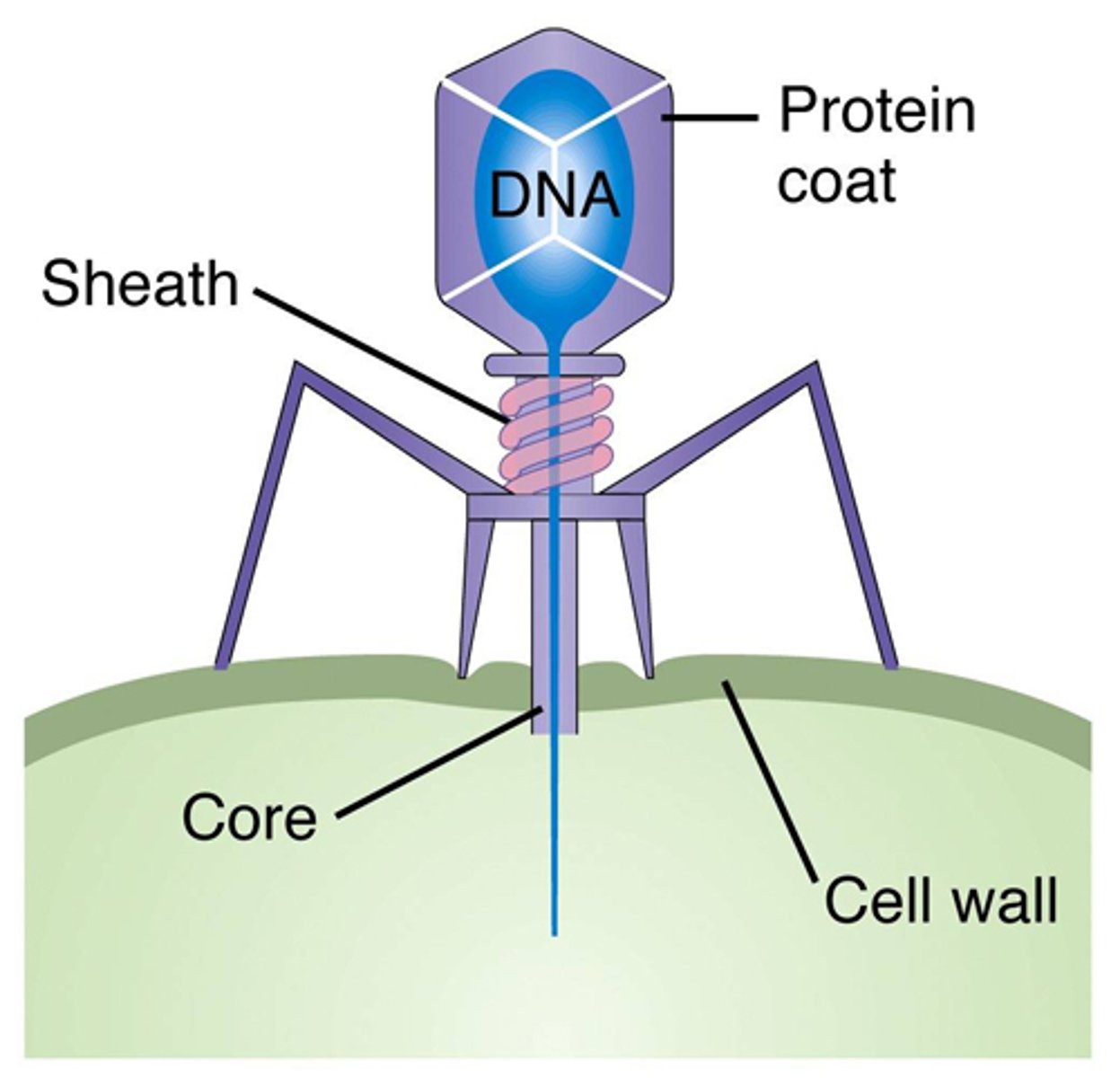
capsid
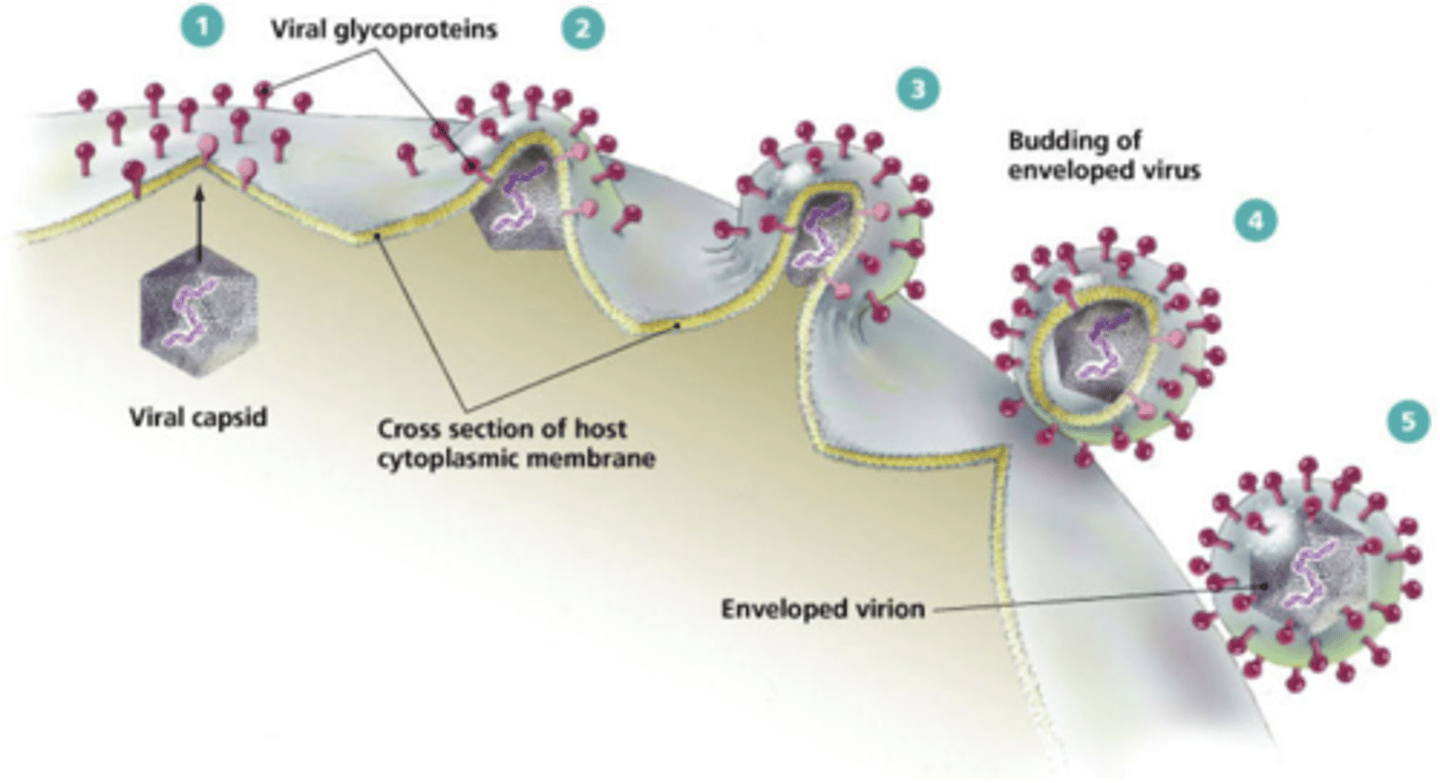
protein coat that surrounds the nucleic acid in a viral particle (#2 on the figure)
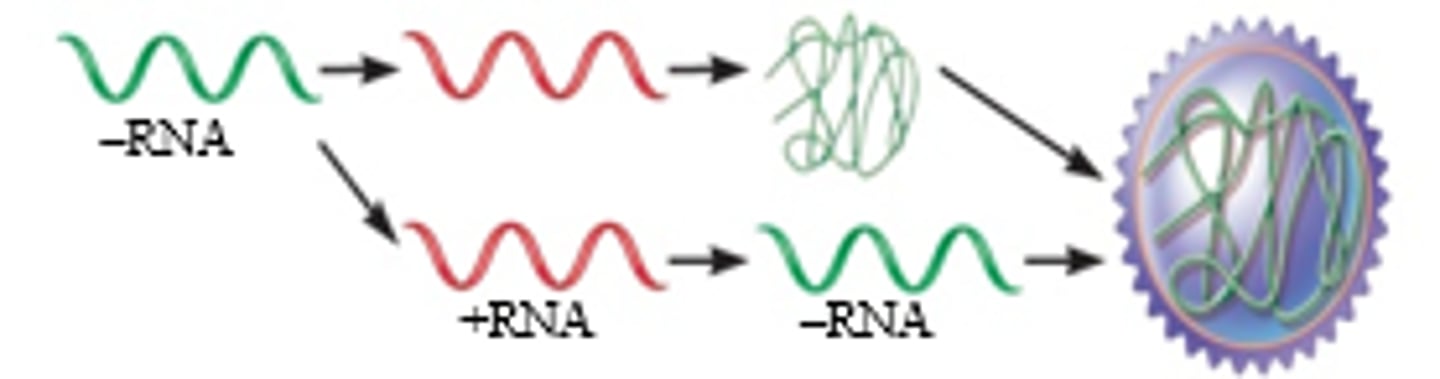
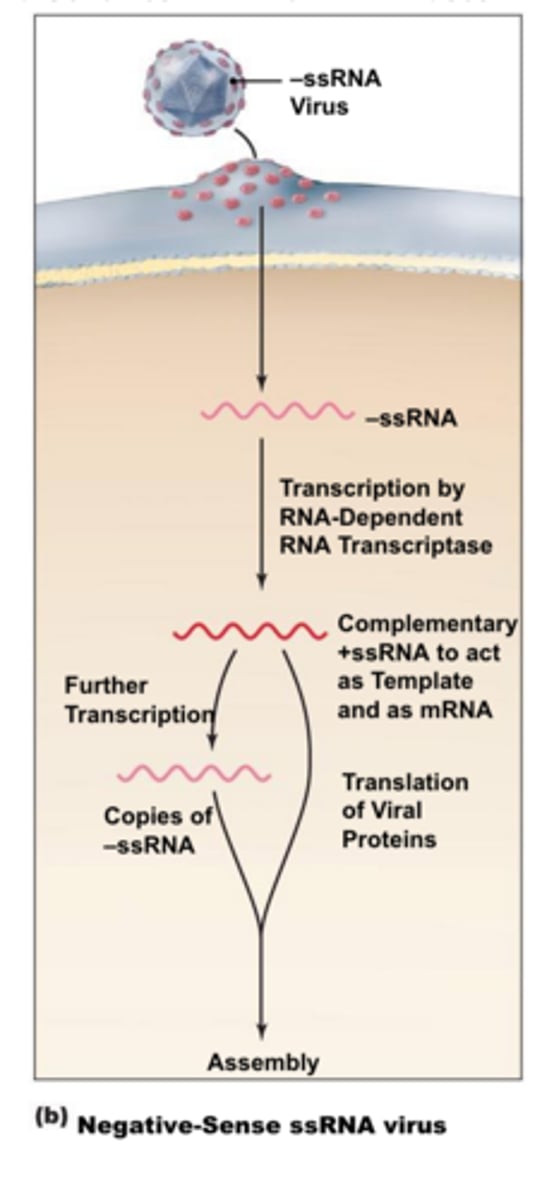
negative stranded
single stranded (DNA or RNA) virus whose genetic code is the complement of the coding strand, not directly encoding proteins
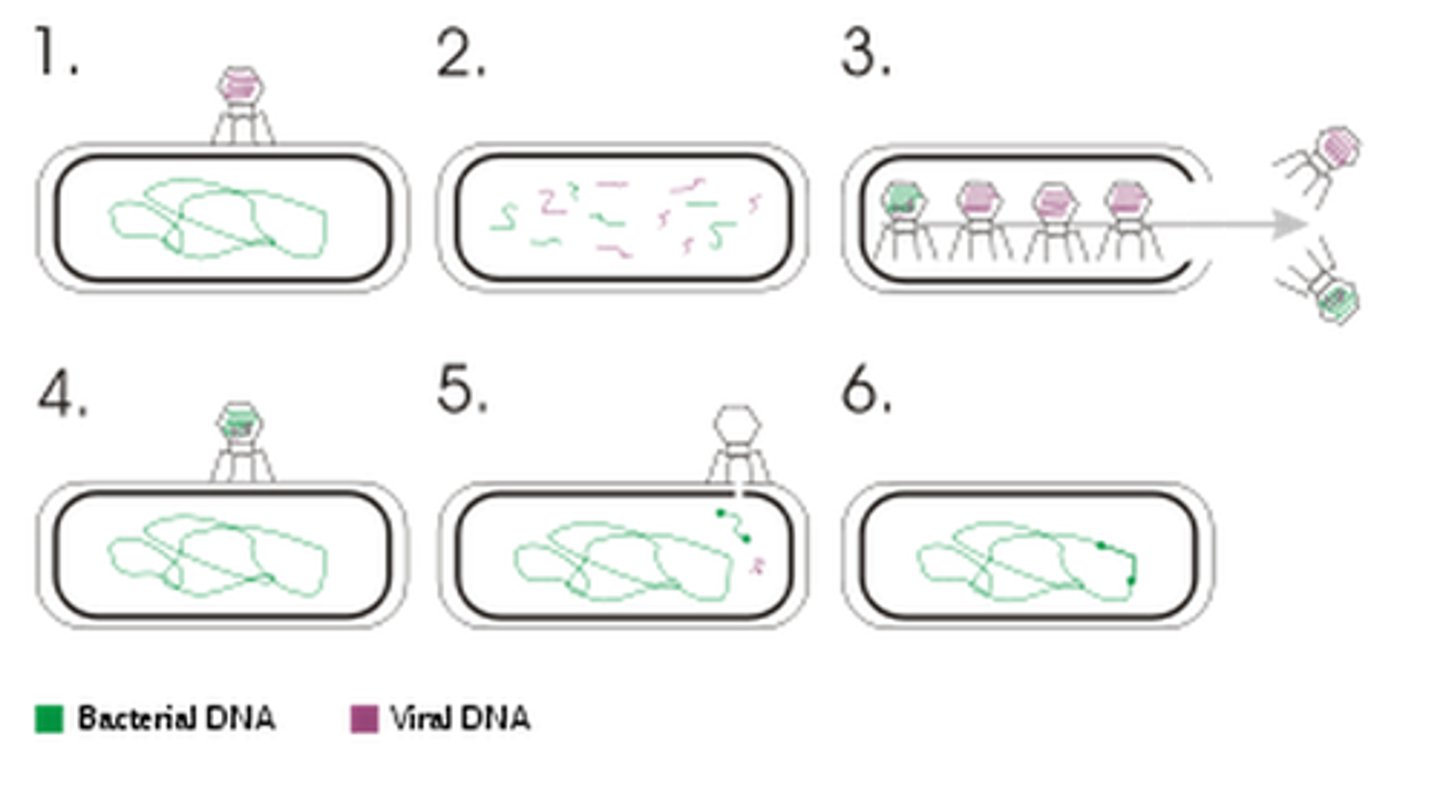
transduction
Most common means of horizontal gene transfer in between bacterial cells. This method uses a virus to move genes from one cell to another
smallpox
highly infectious and deadly viral disease. it was the first virus immunized against and the first viral disease eradicated.
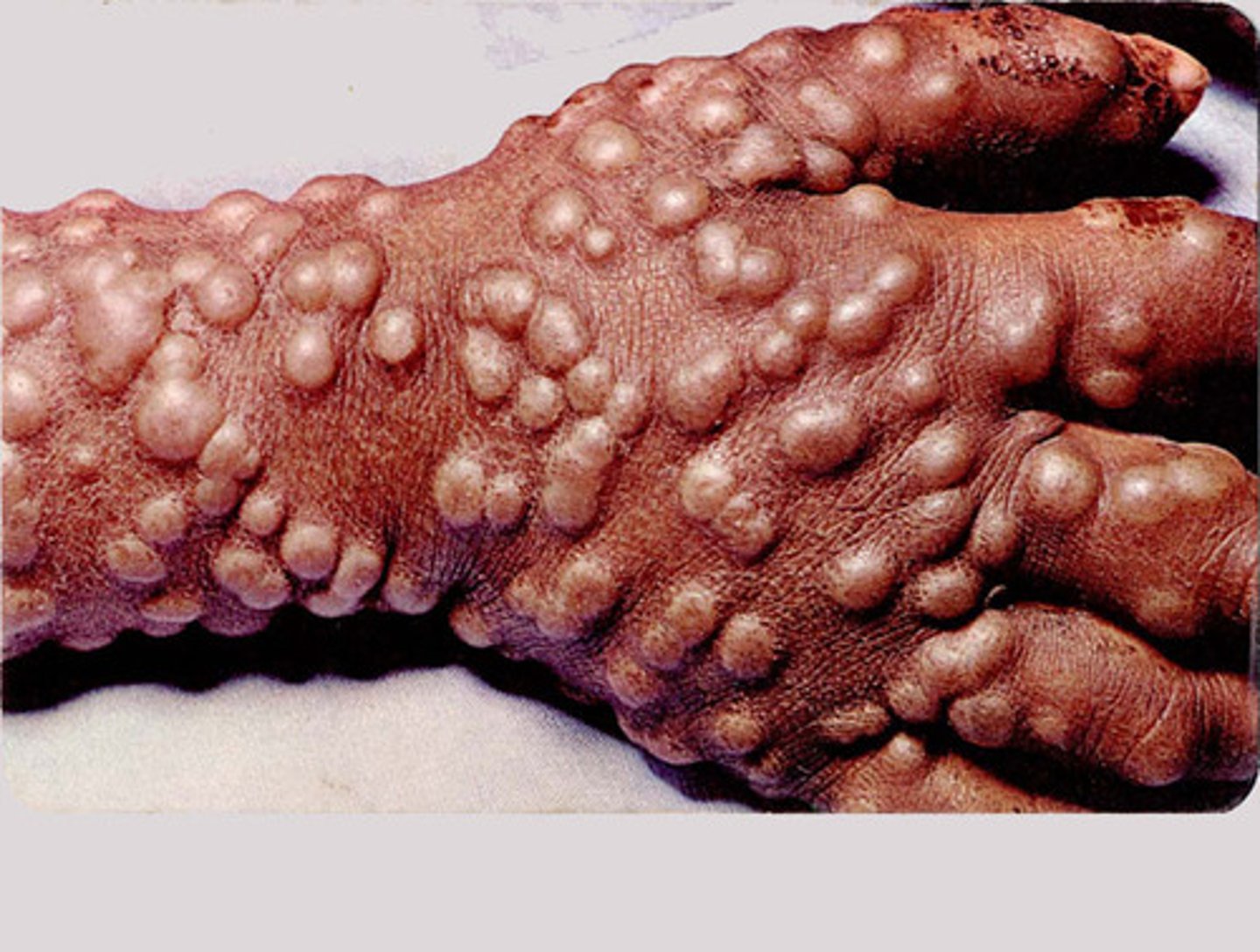
polio
viral disease that leads to temporary paralysis with potential for permanent damage to the body. it was widely vaccinated against and is no longer present in the US, but has not been eradicated.
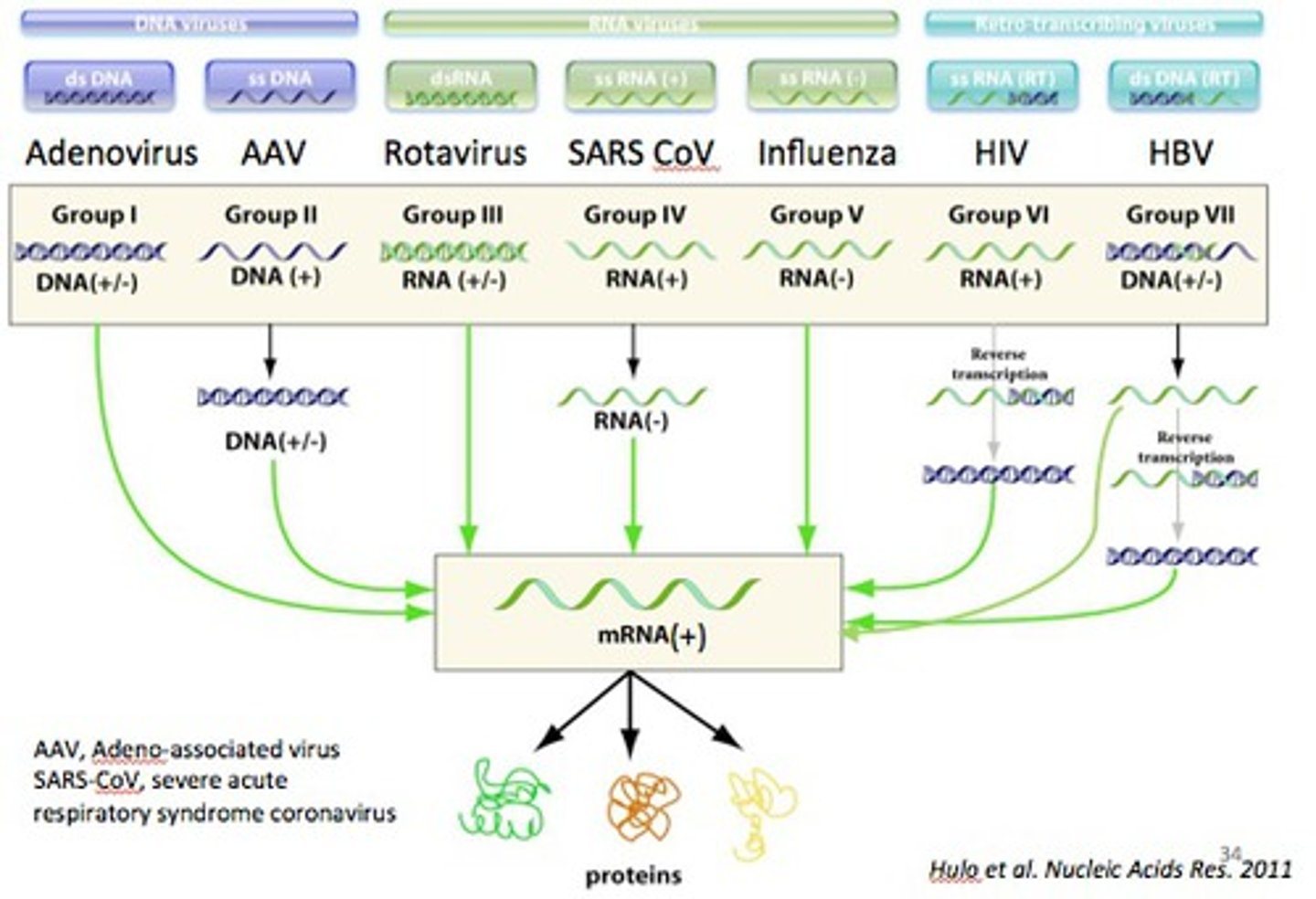
viral nucleic acids
can be DNA, RNA, single stranded or double stranded
envelope
outer layer that some viruses have, made of lipids and proteins (typically derived from the host cell's cytoplasmic membrane)
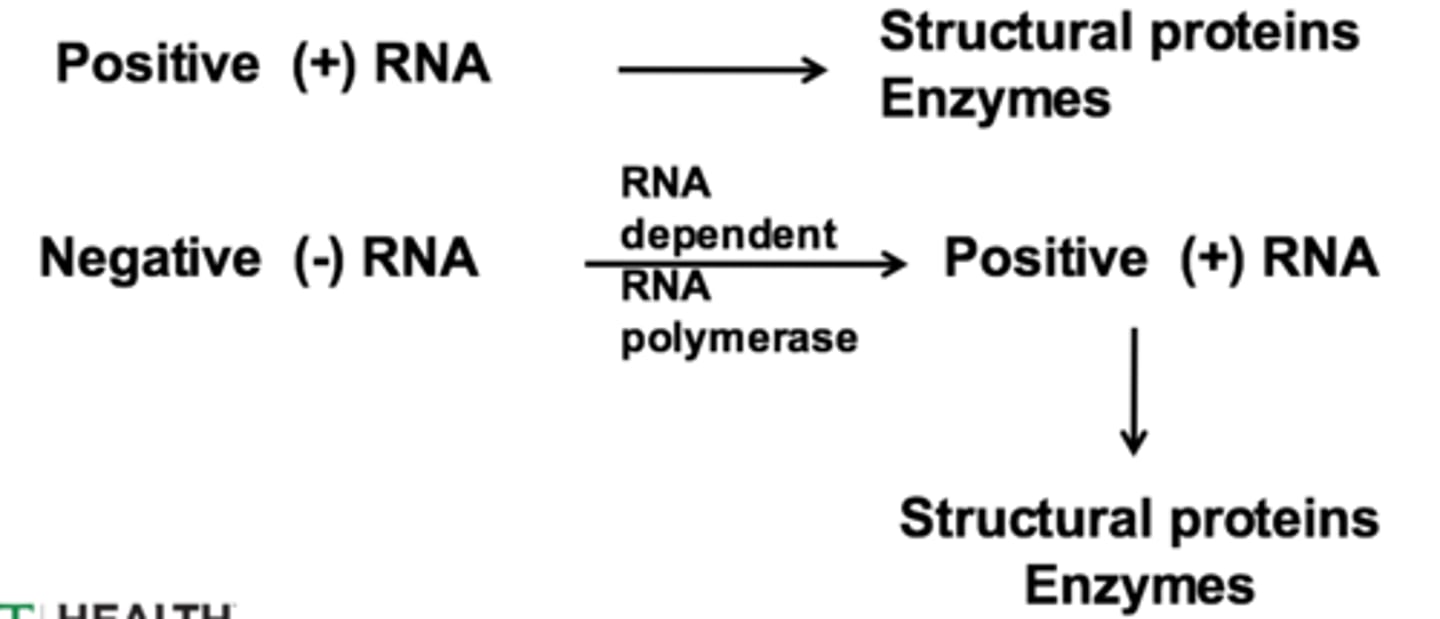
positive stranded
single stranded (DNA or RNA) virus whose genetic code is the coding strand, directly encoding proteins
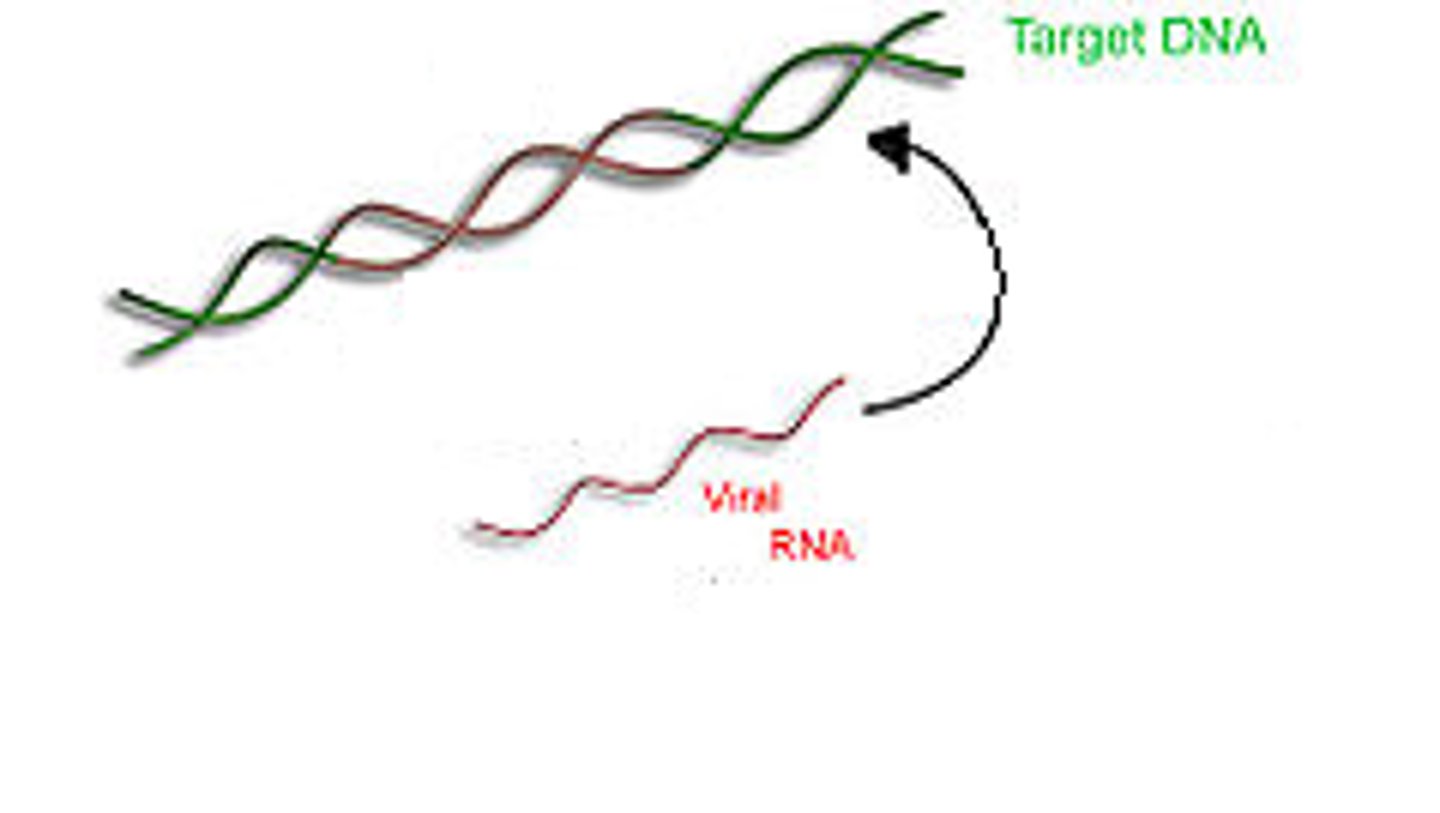
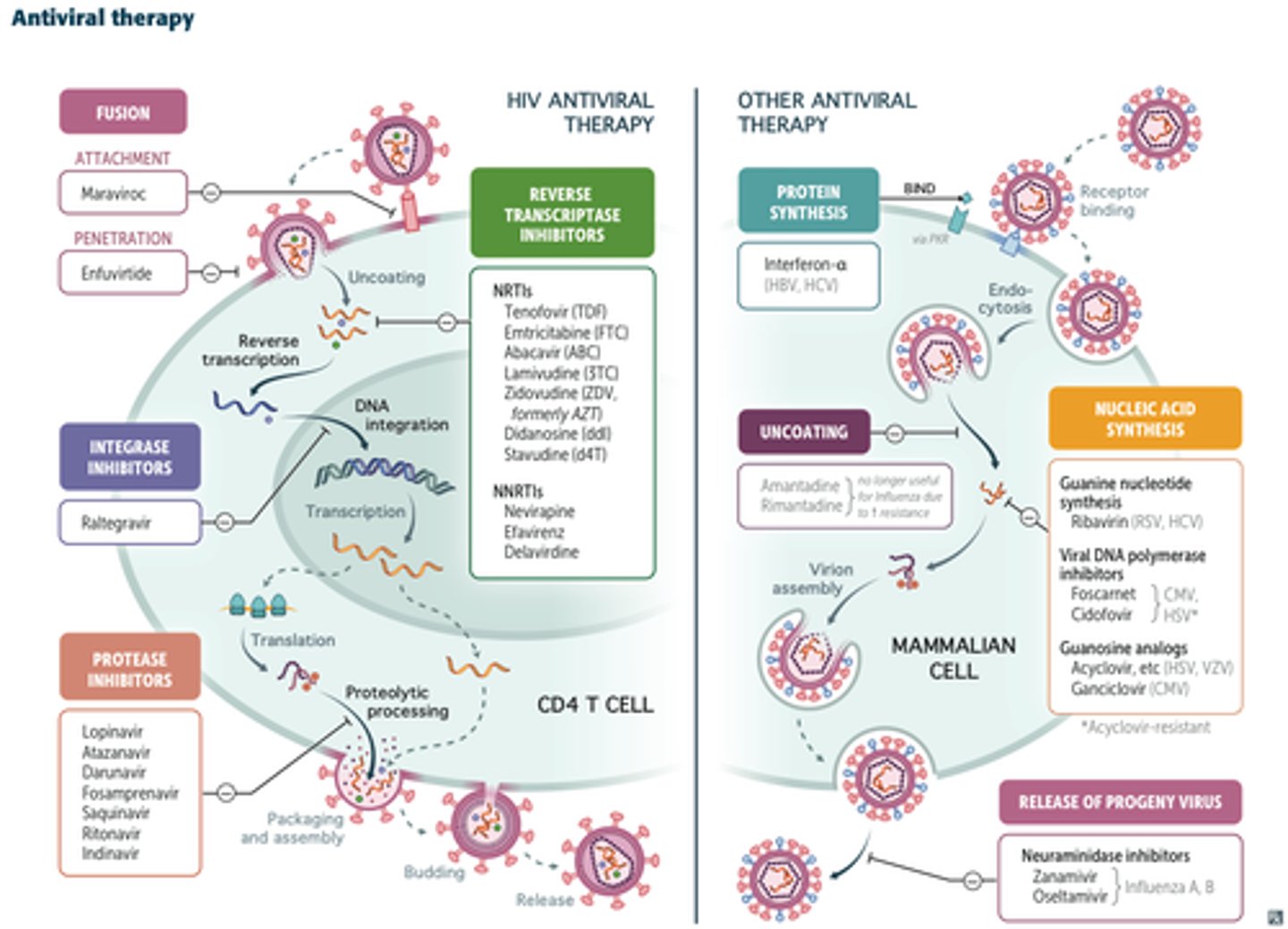
reverse transcriptase
virally encoded enzyme responsible for using an RNA template to make DNA
lysins
viral enzyme class (similar to lysozyme) that breaks down peptidoglycan by disrupting links between sugars

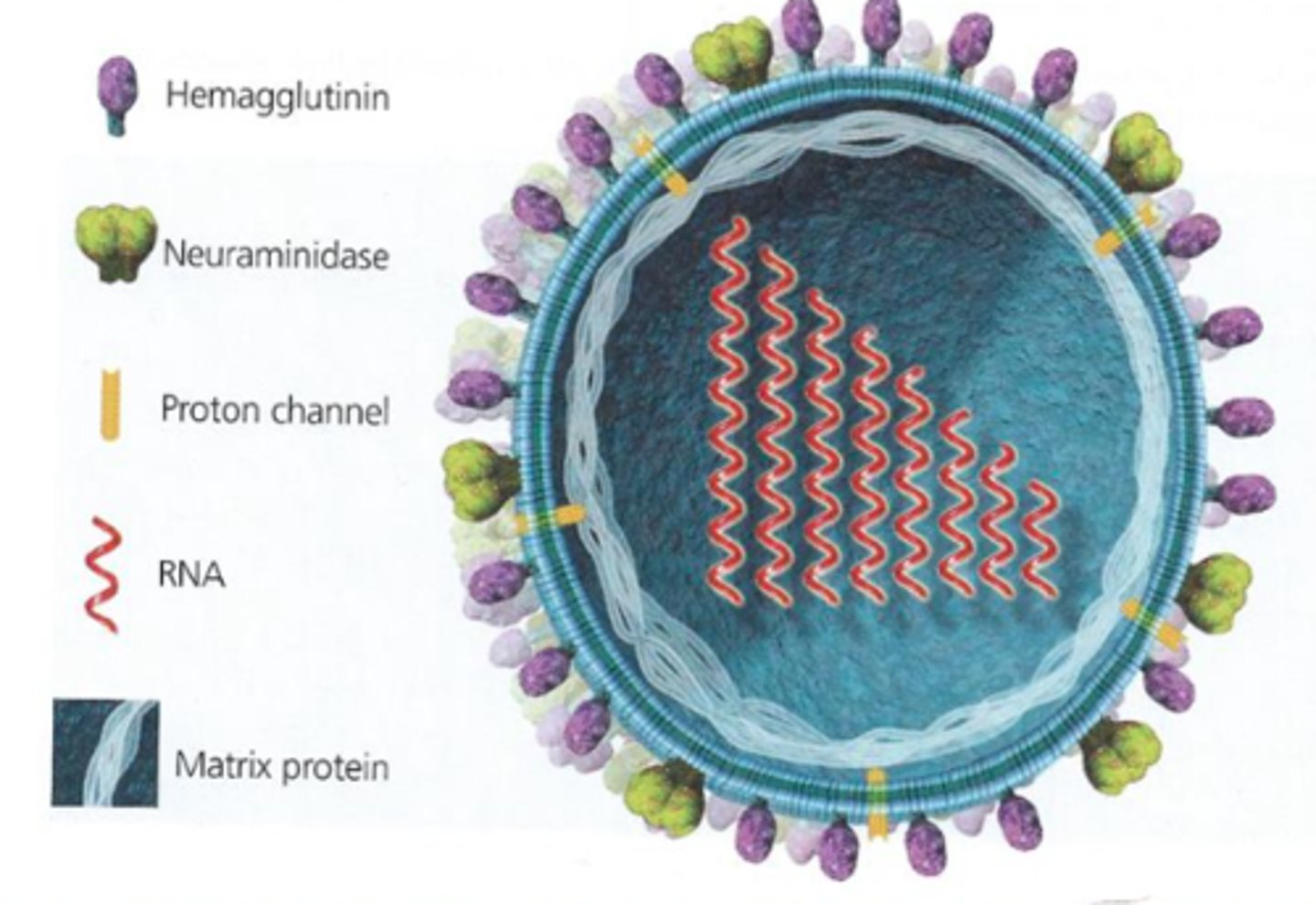
hemagglutinin
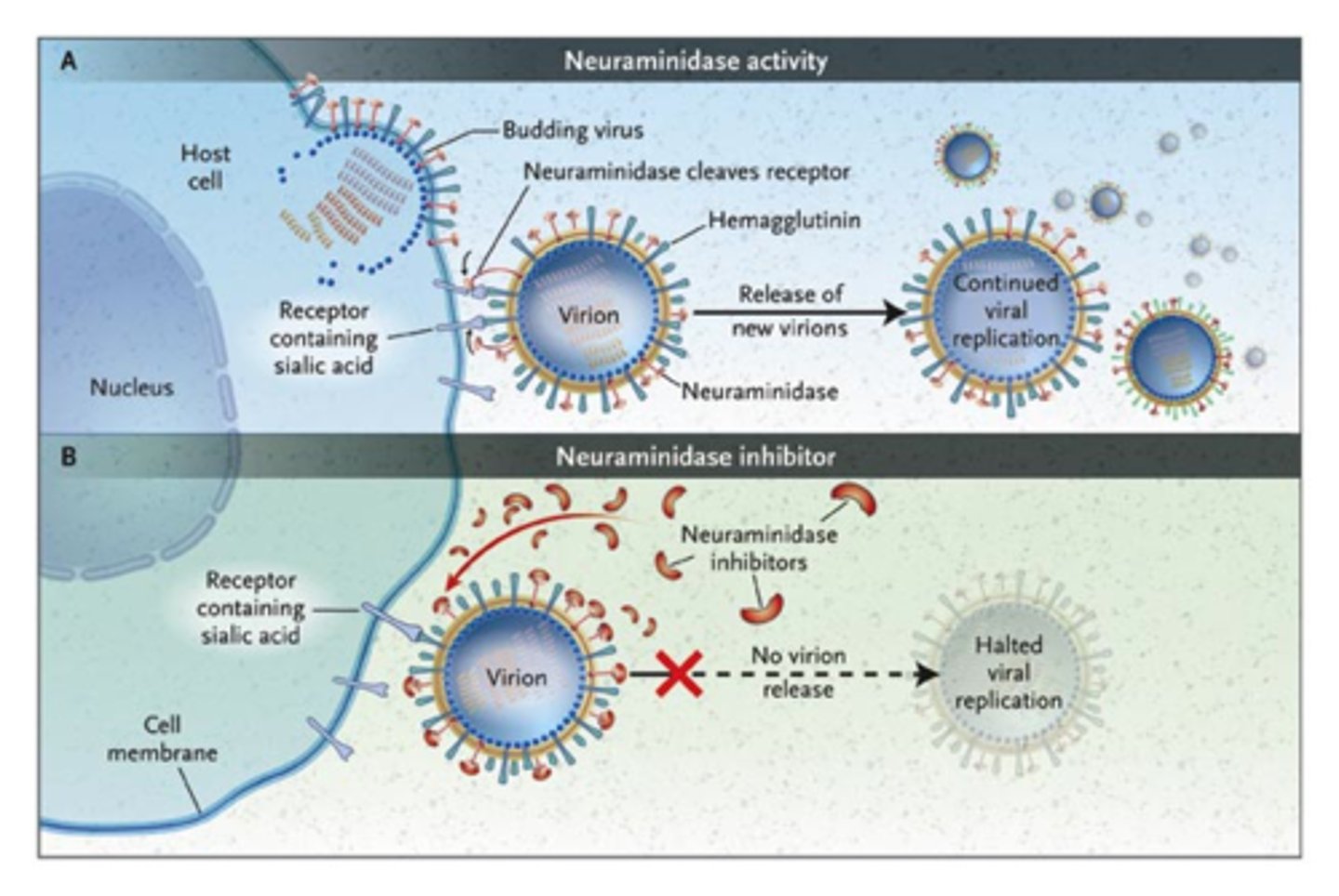
protein embedded in the envelope used by influenza to enter a cell (this is the H of H1N1)
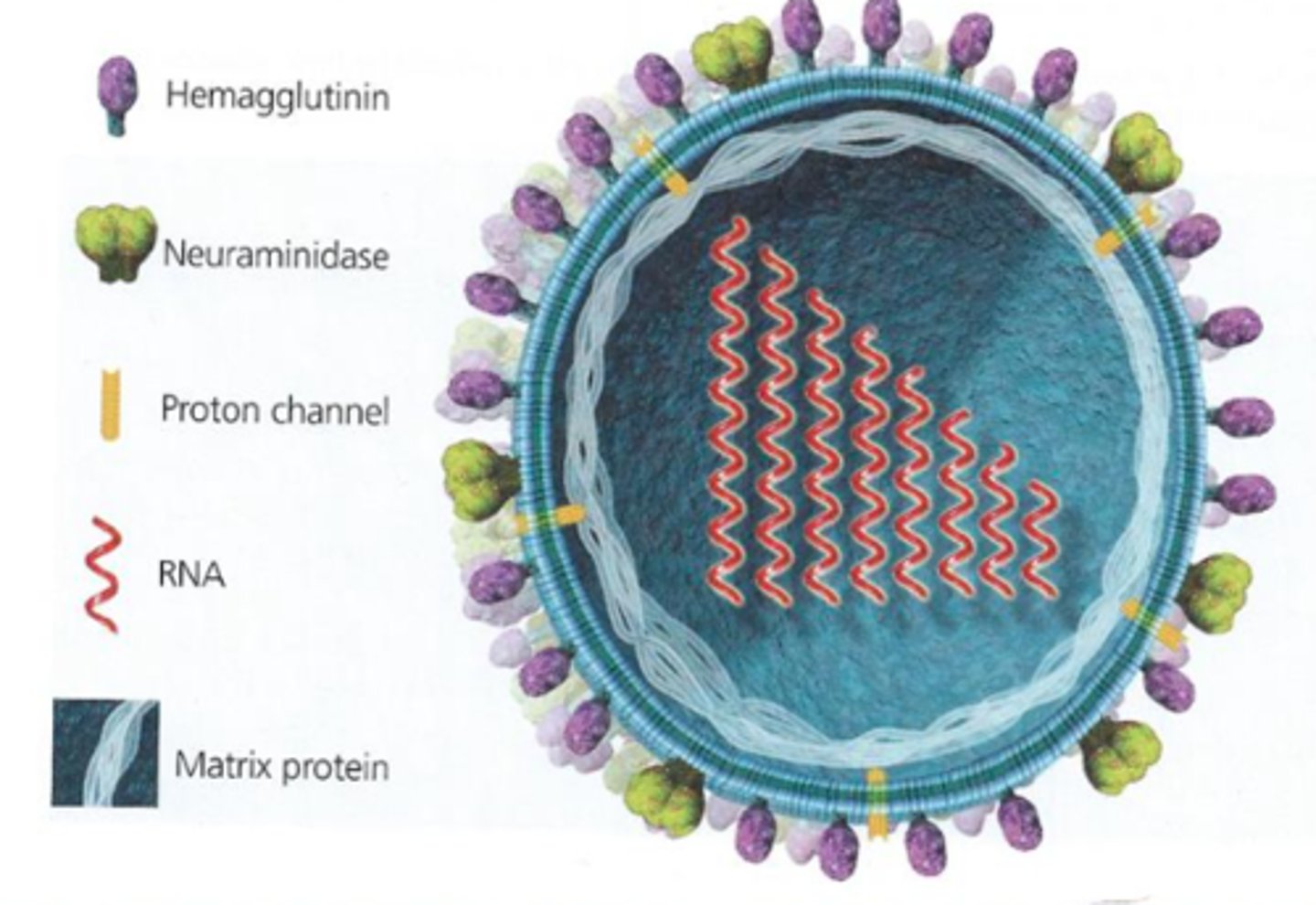
neuraminidase
protein embedded in a viral envelope that is used by influenza to leave a cell (this is the N of H1N1)
RNA replicase
Enzyme present in RNA viruses that creates the dsRNA intermediate they need for proceeding through cycle (RNA-dependent RNA polymerase)
Tamiflu
antiviral flu drug that treats flu by blocking virus from exiting the cell (neuraminidase inhibitor)
Ribavirin
antiviral drug that induces extra mutations, which are already common, in RNA viruses during replication
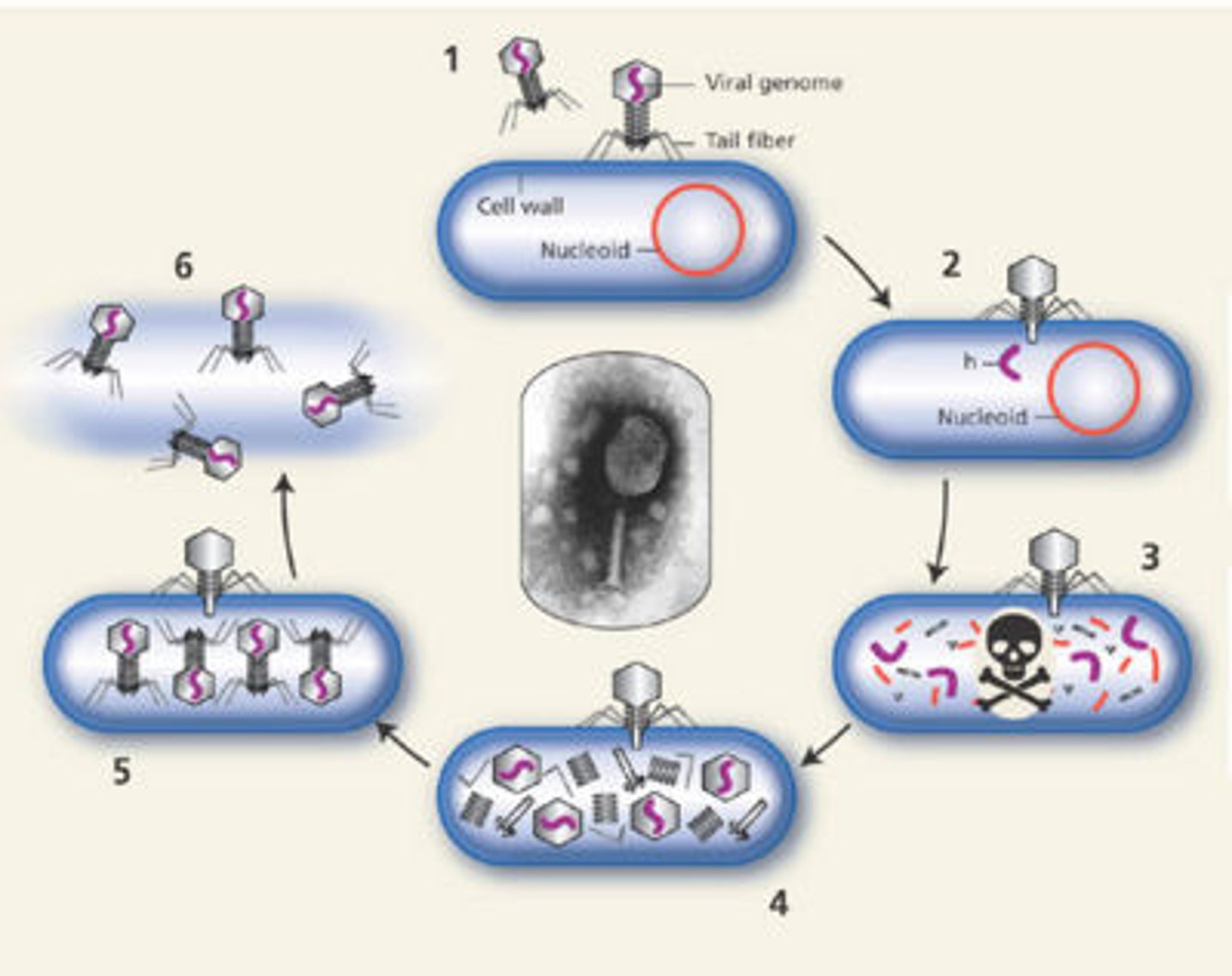
bacteriophage
viruses which infect bacteria. they do not enter a bacterial cell, just inject their genetic material.
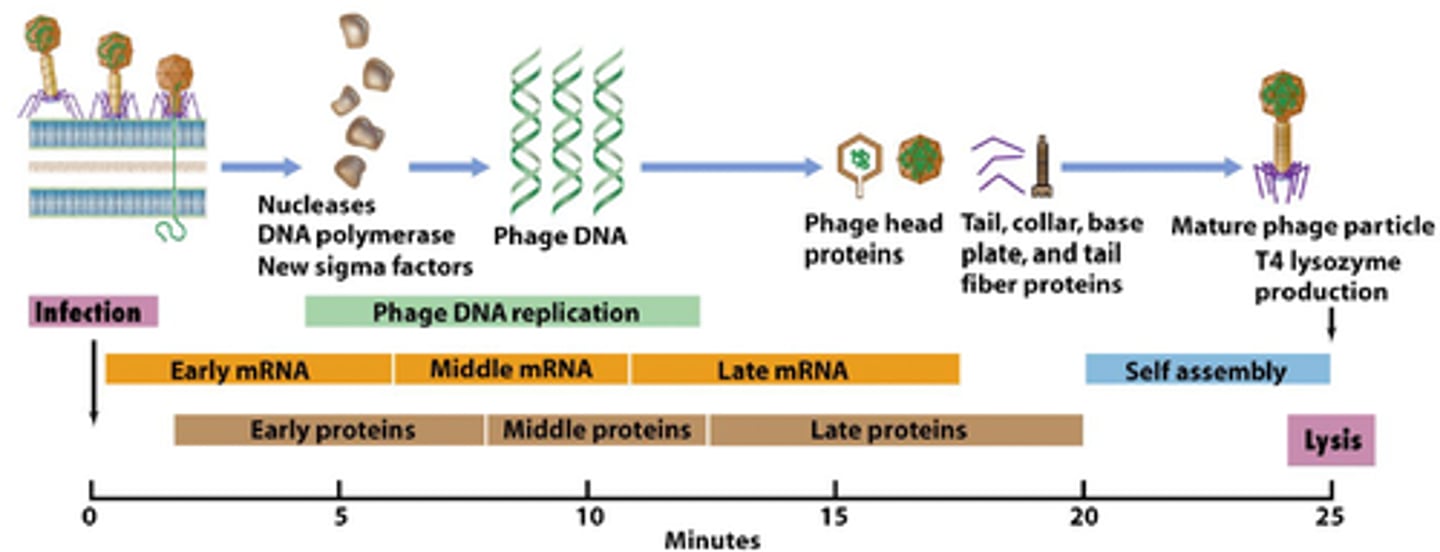
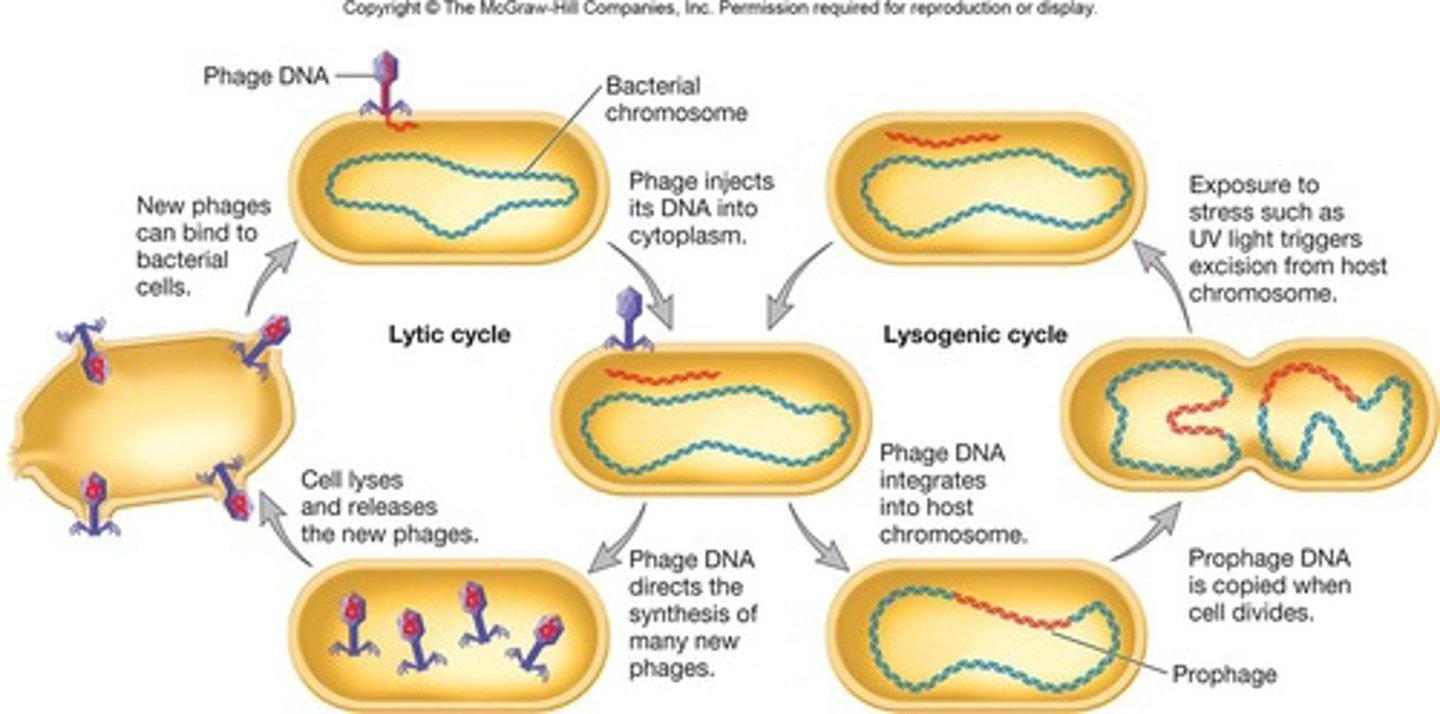
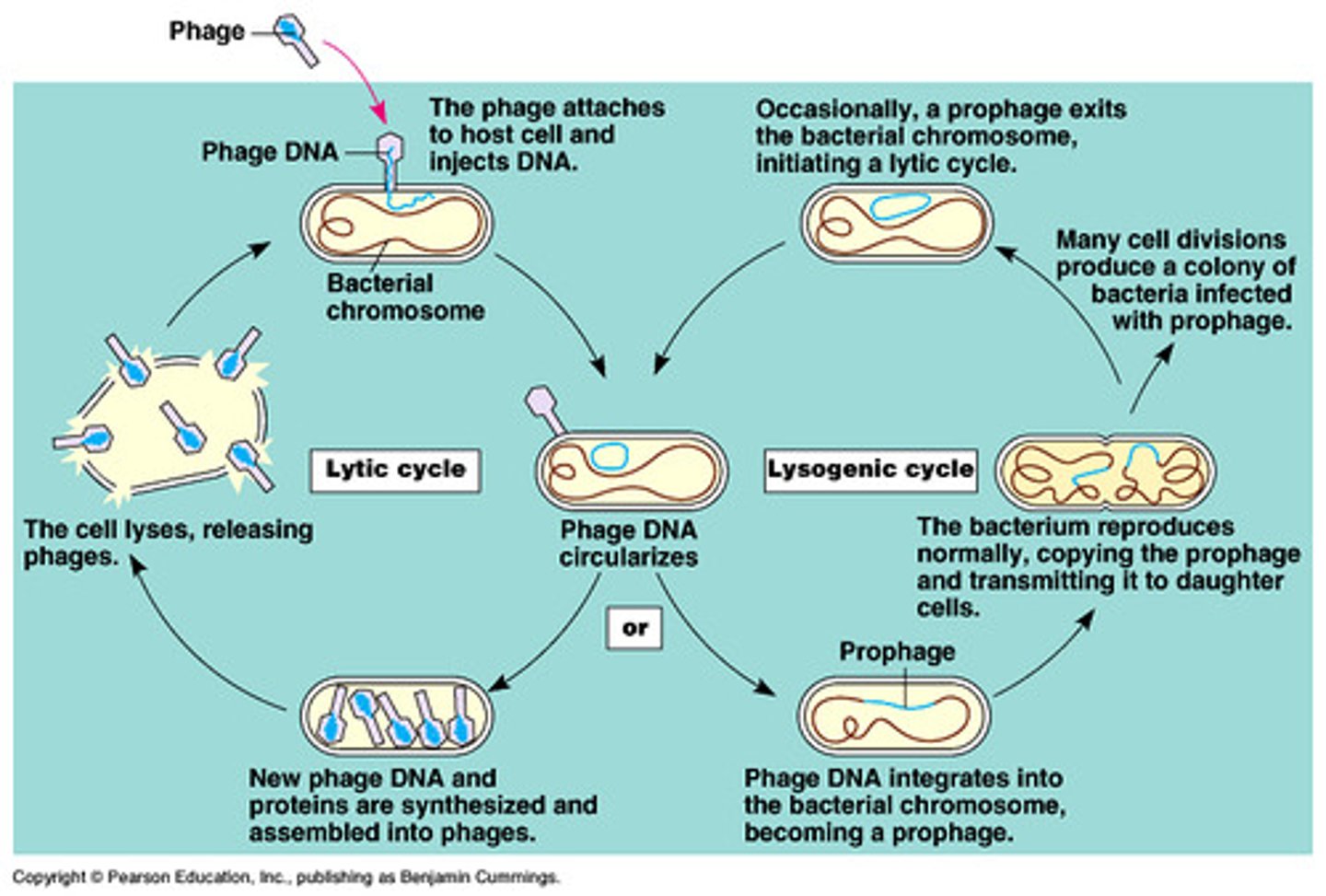
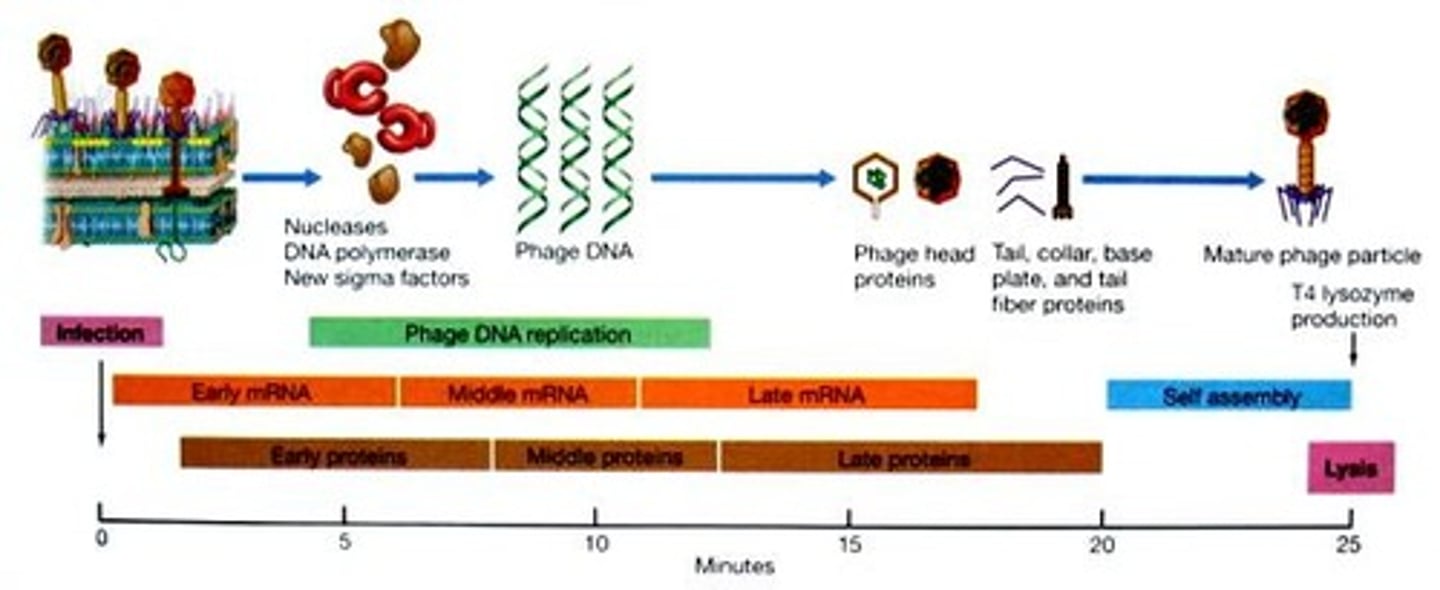
lytic life cycle
attachment, penetration, synthesis, assembly, release

attachment
virion fastens itself to bacterial cell
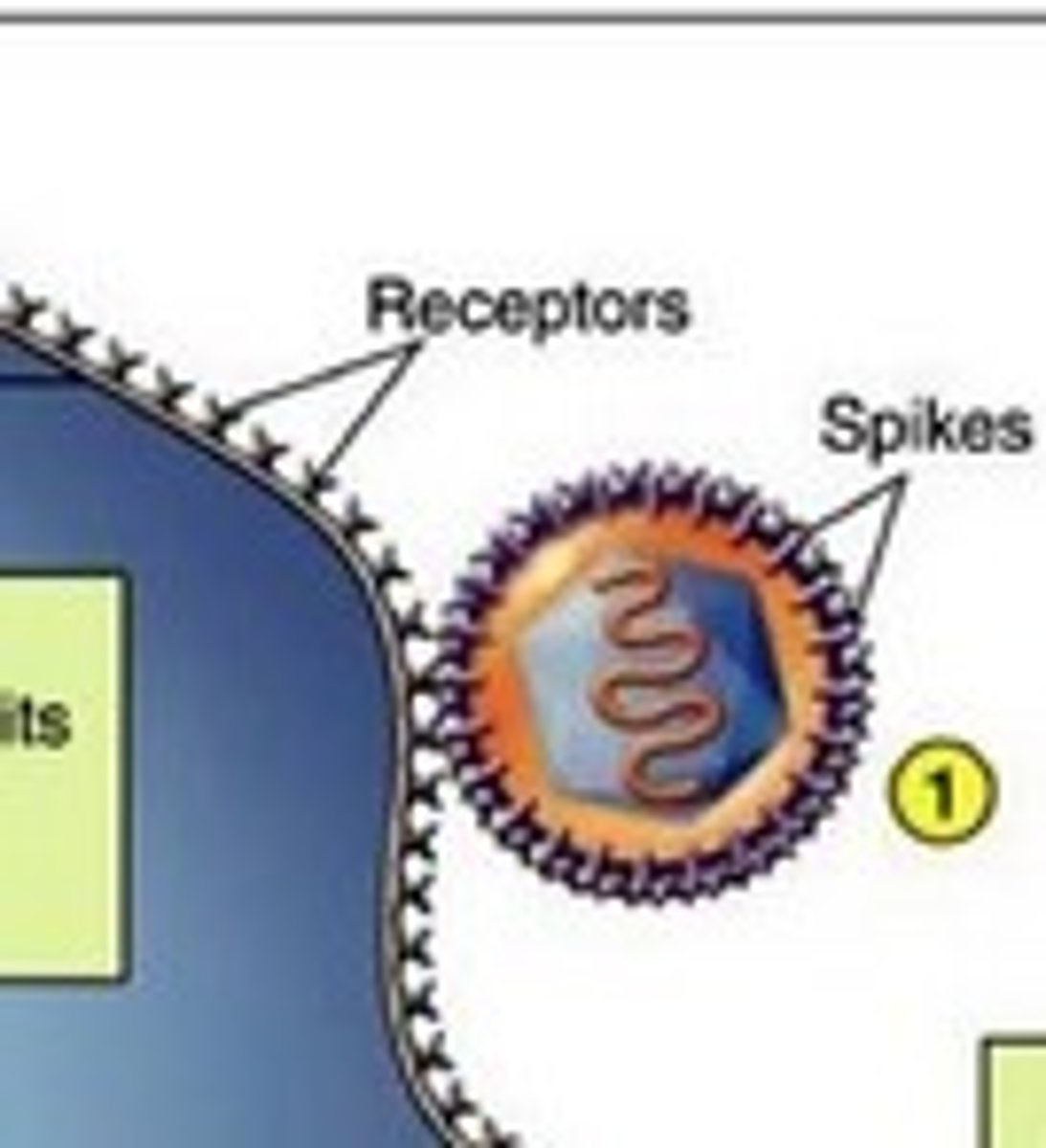
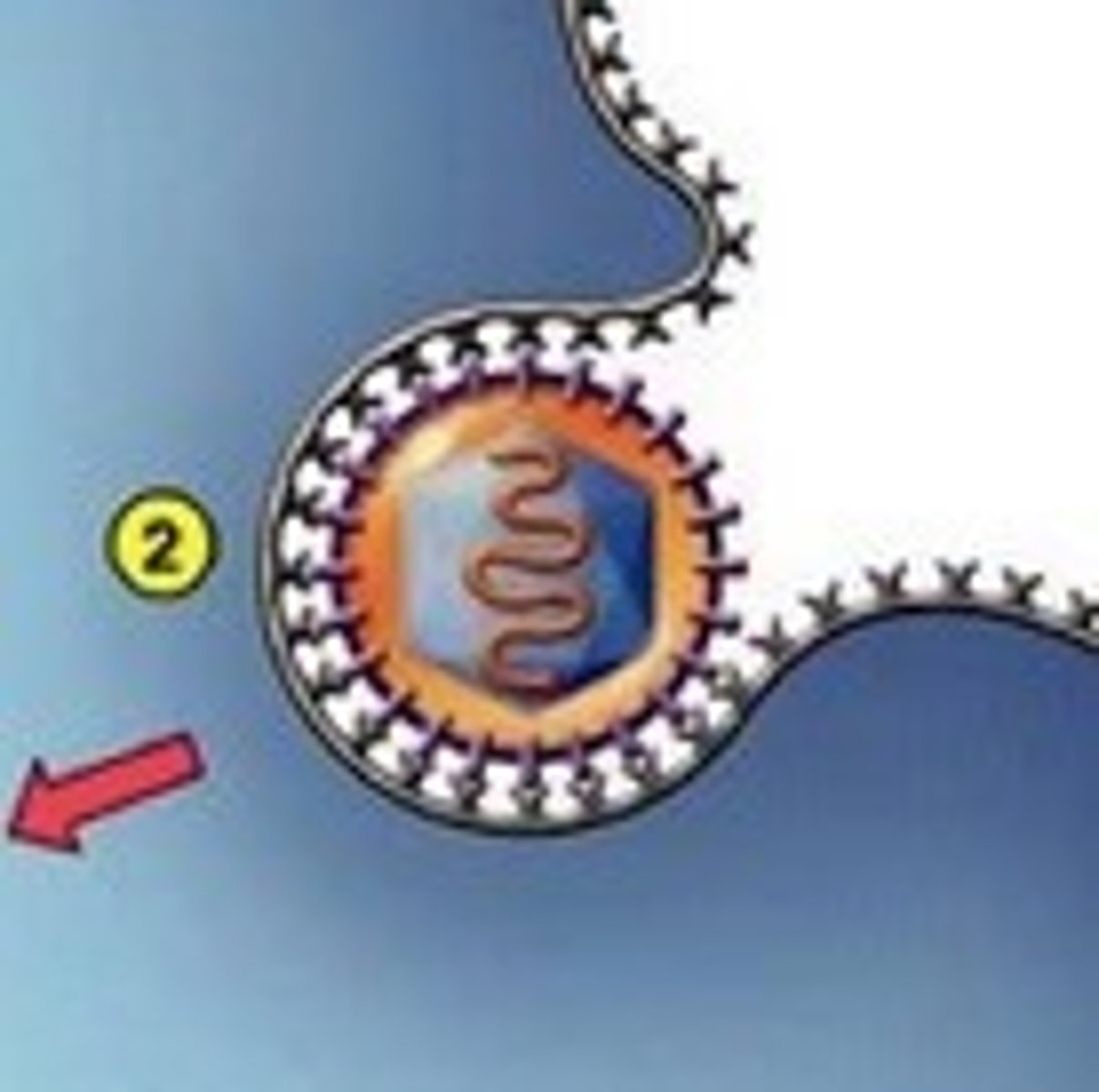
penetration
virion nucleic acid is injected into the cell
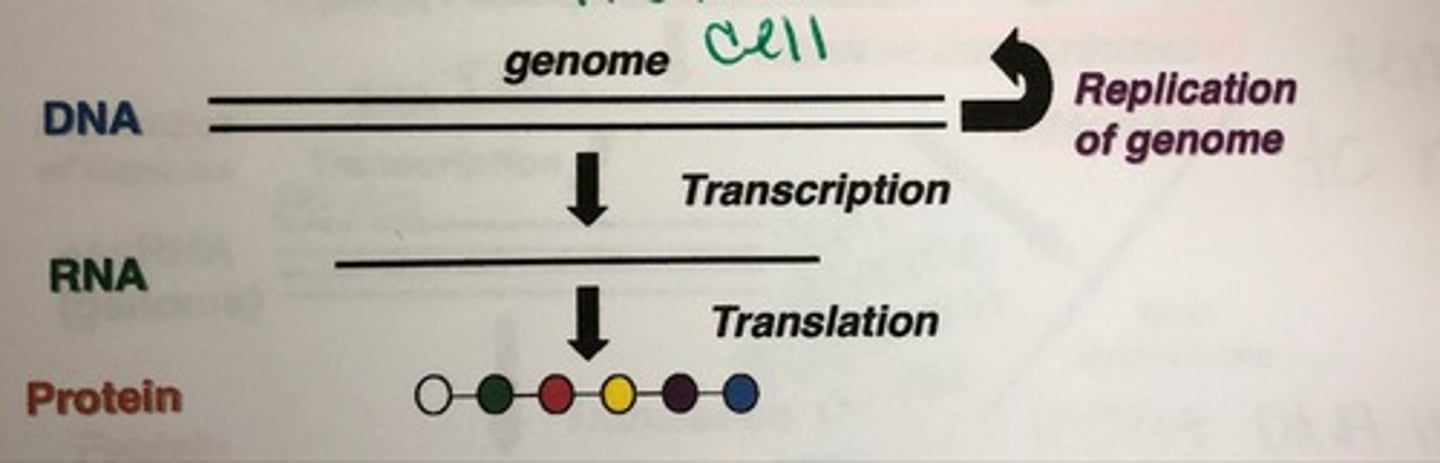
synthesis
virus nucleic acids and proteins are made by the host cell metabolism, which is being redirected by the virus
assembly
capsid forms and viral genome is packaged into new virions
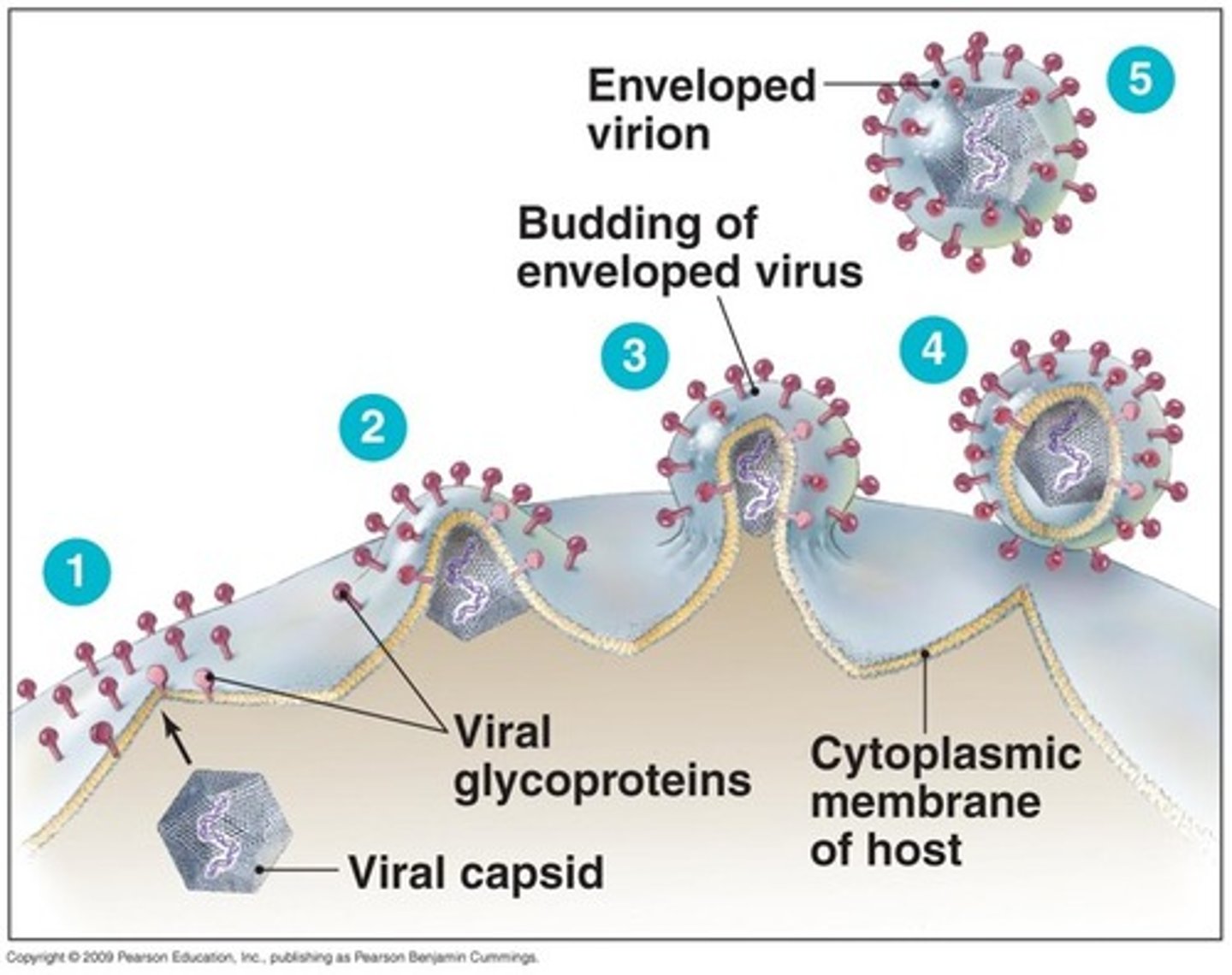
release
mature virions exit the host cell
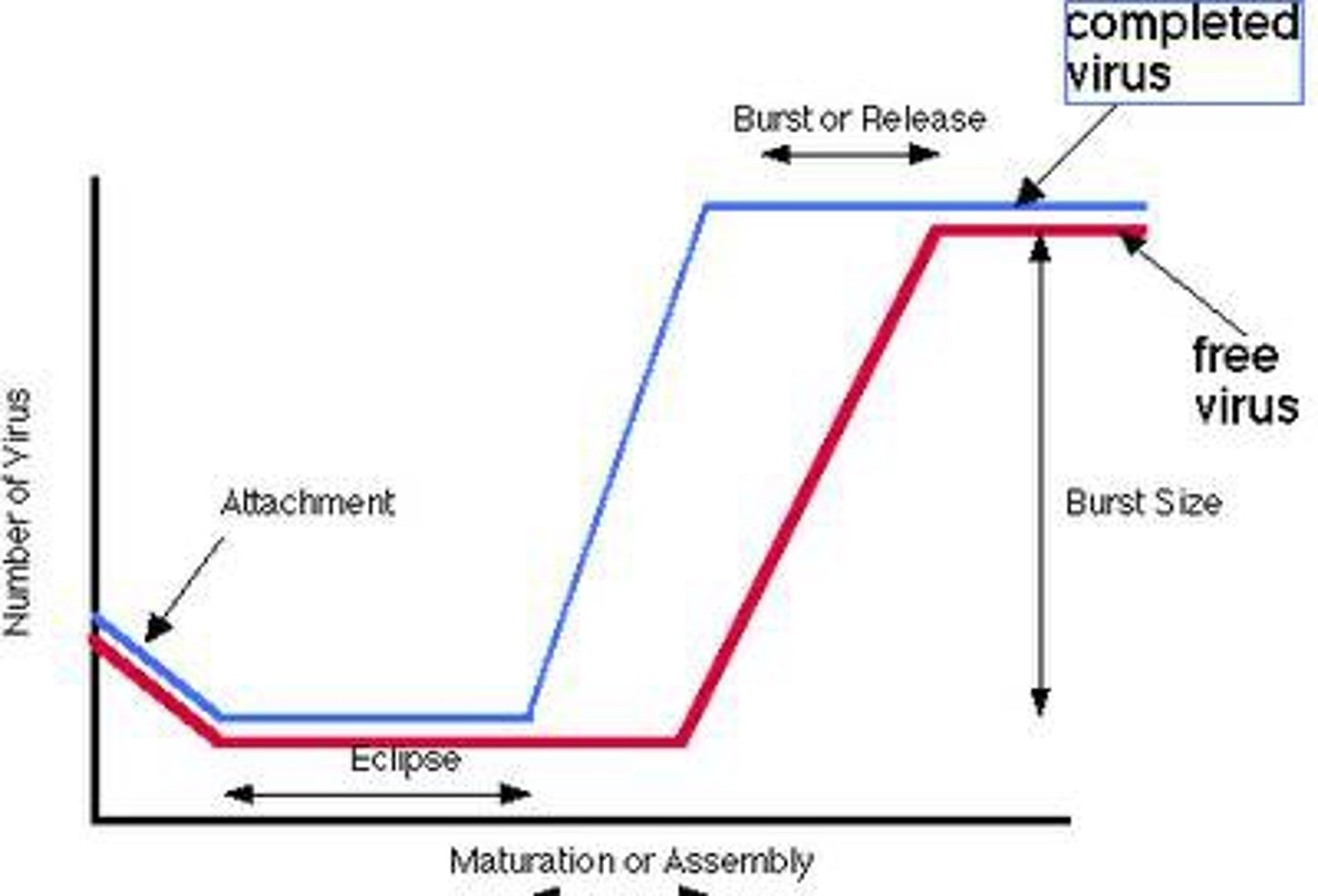
eclipse period
a period of time in which, if the infected cells are lysed, no viral particles will be found because all viruses are disassembled. (AKA latent period)
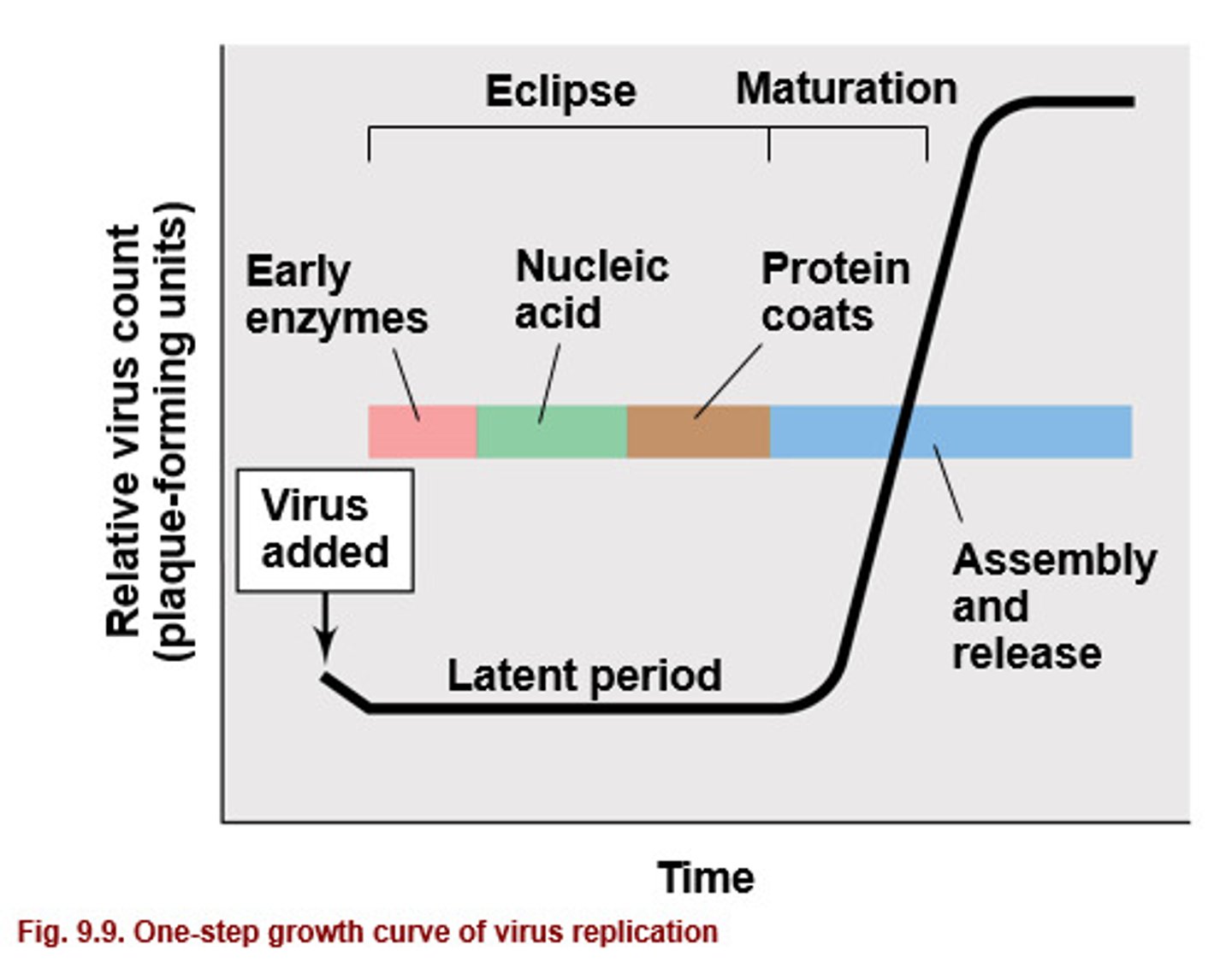
early enzymes
enzymes made at the beginning of the latent period that take over host cell machinery to facilitate viral reproduction
burst size
the number of viral particles that emerge upon release, assuming one virus acted per cell.
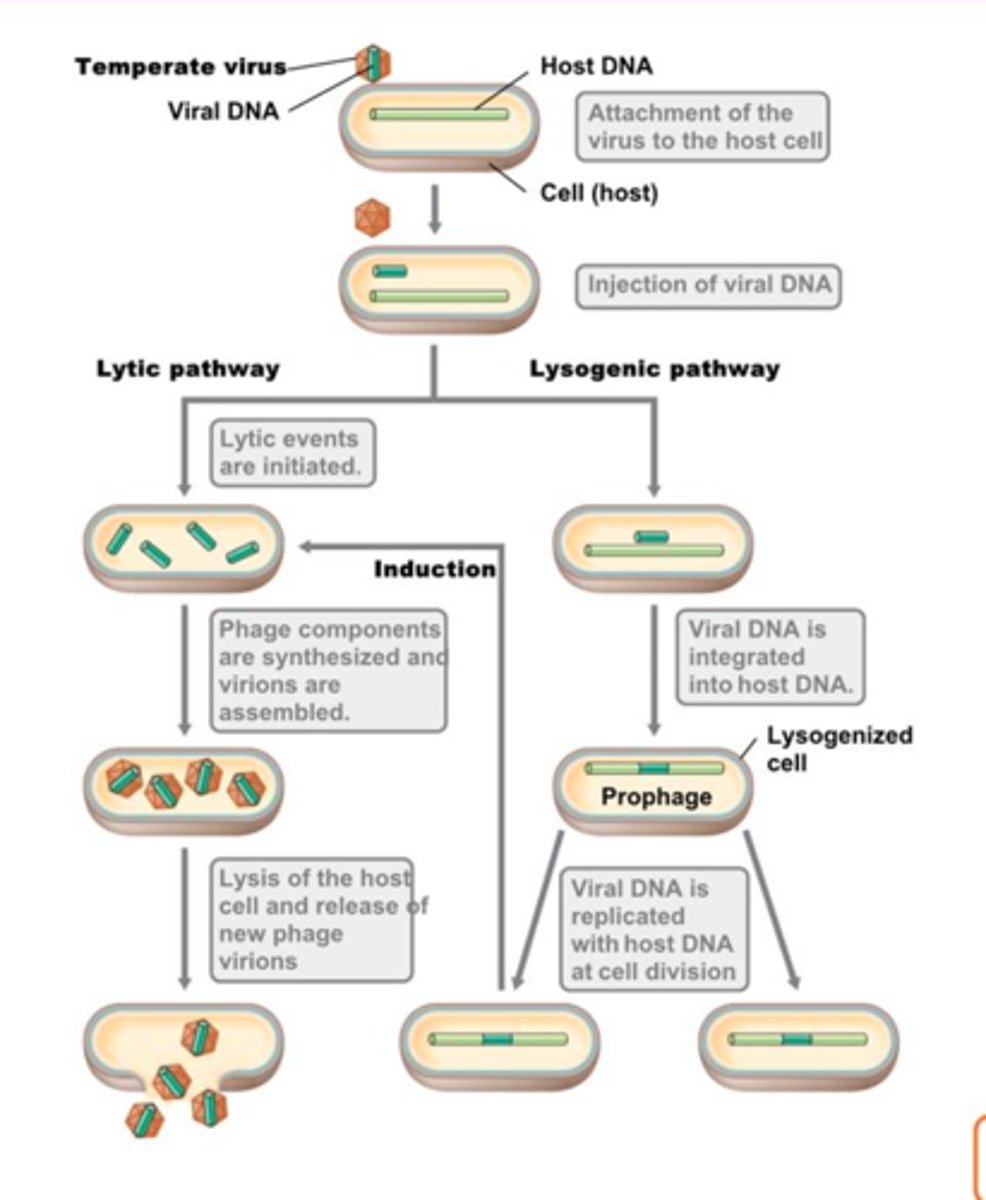
temperate phage
viruses that infect bacteria. These viruses insert their genome into the host chromosome as a prophage.
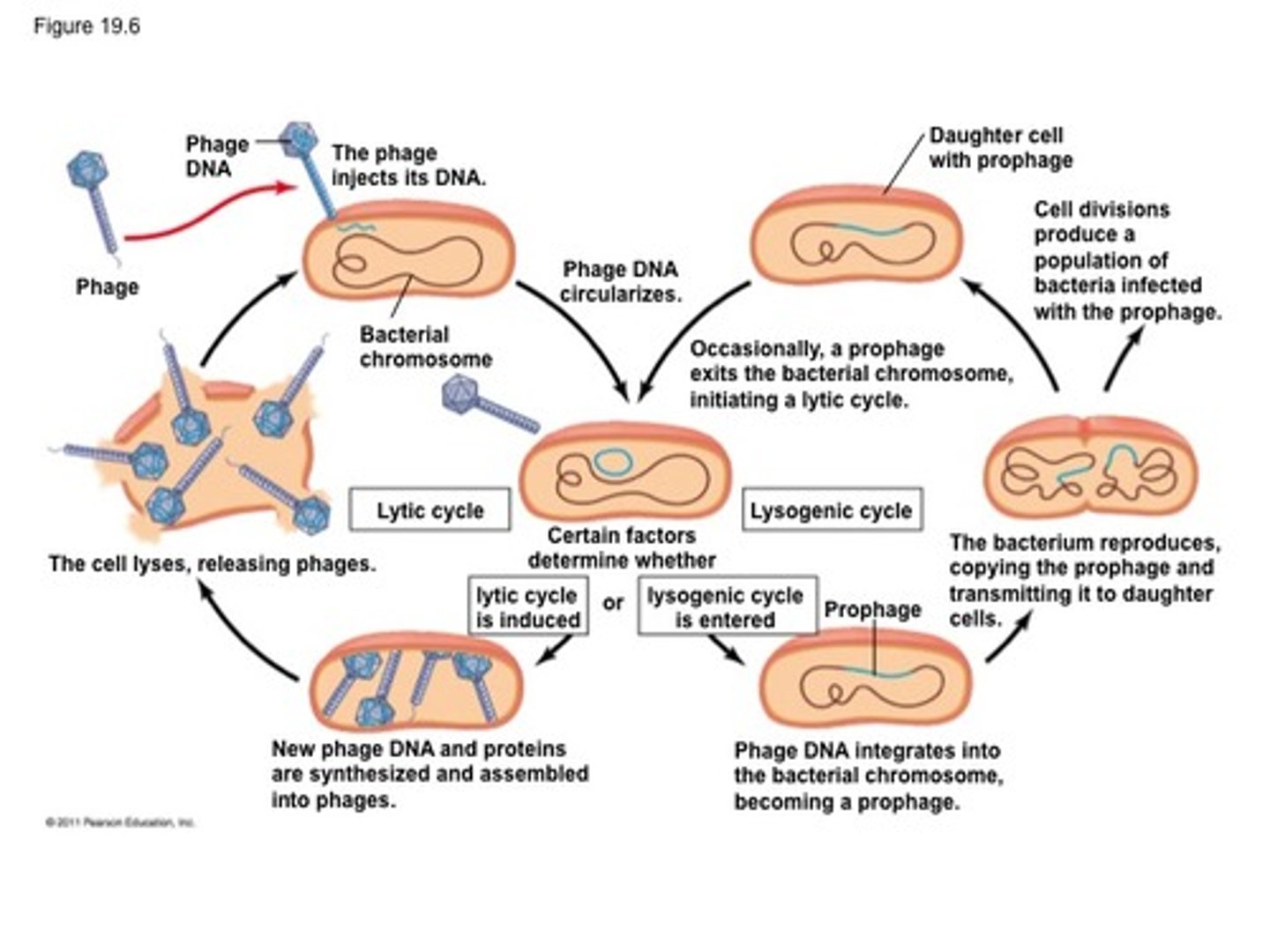
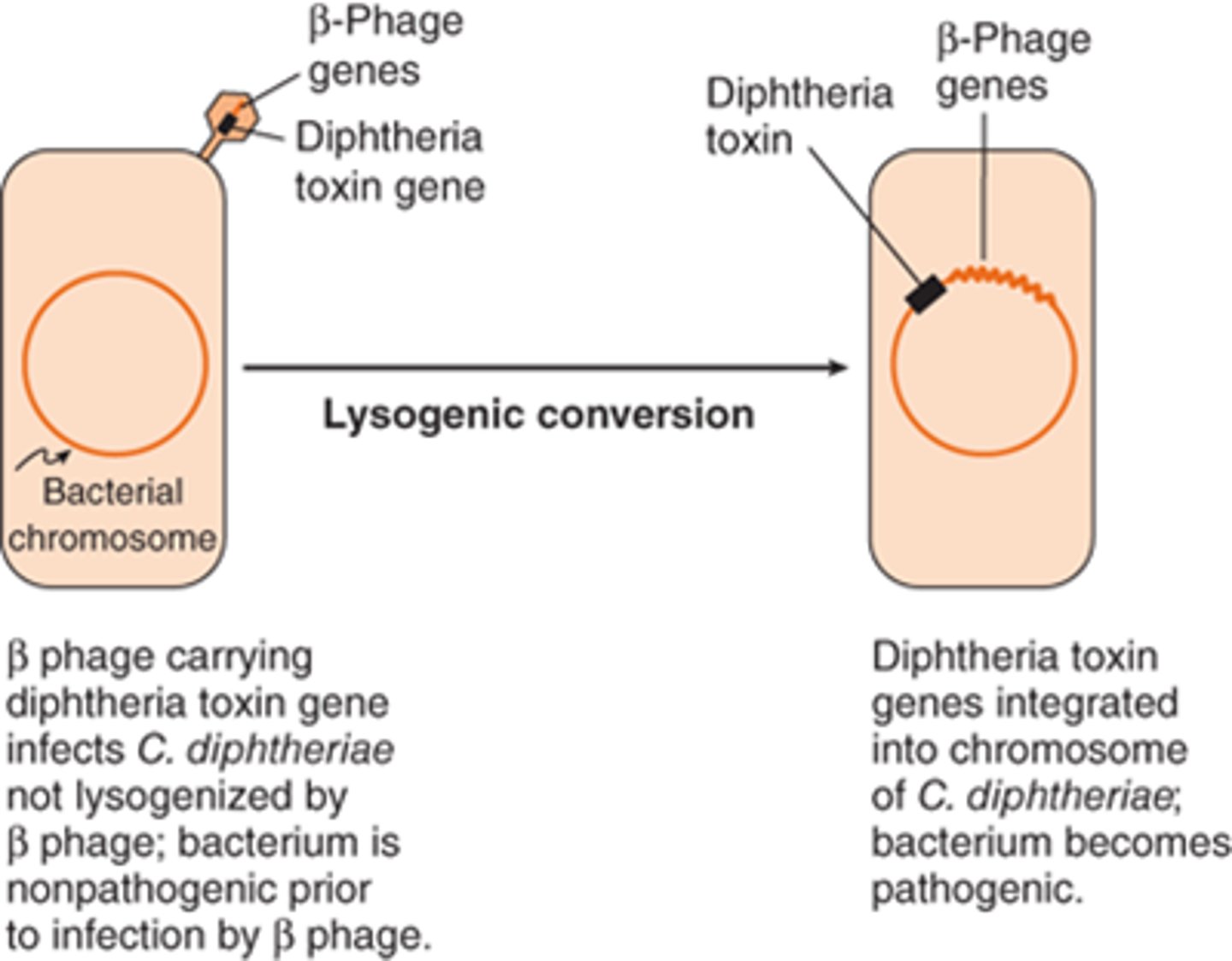
lysogenic conversion
Alteration of a bacterial cell's phenotype by the insertion of a prophage into its genome. This is responsible for several different bacterial species' ability to produce toxin (e.g. cholera, tetanus, etc. )
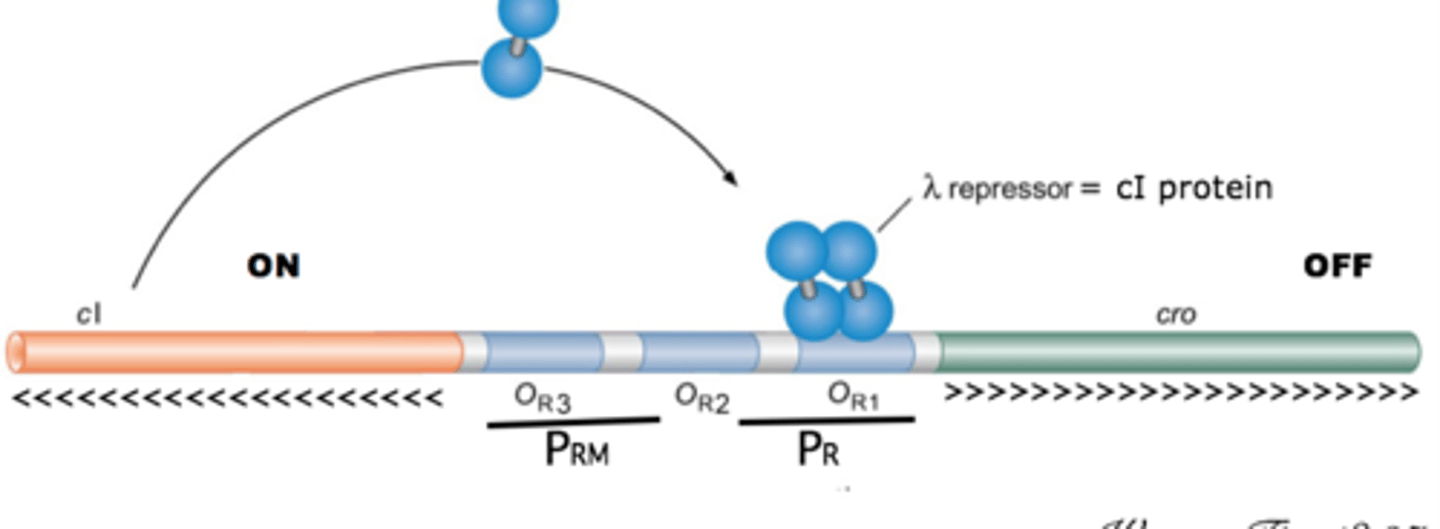
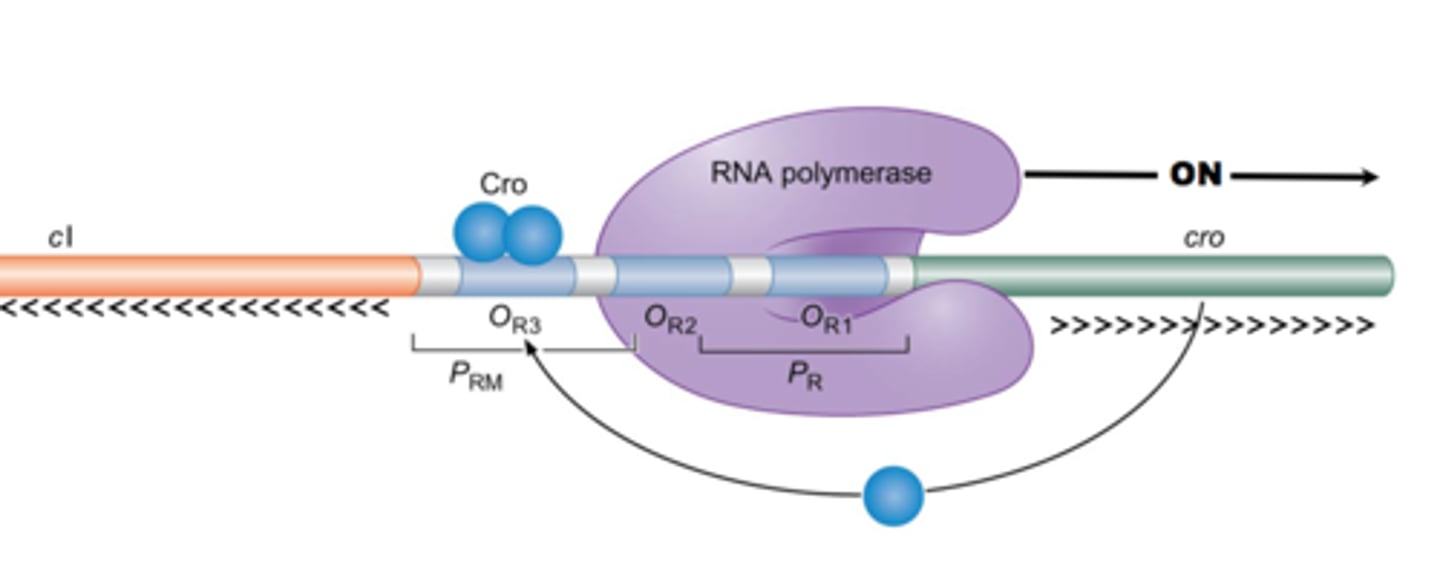
lambda repressor protein
protein that causes repression of lytic events, represses cro protein
lysogeny
most viral genes aren't transcribed but viral genome is replicated with host chromosome and passed to daughter cells
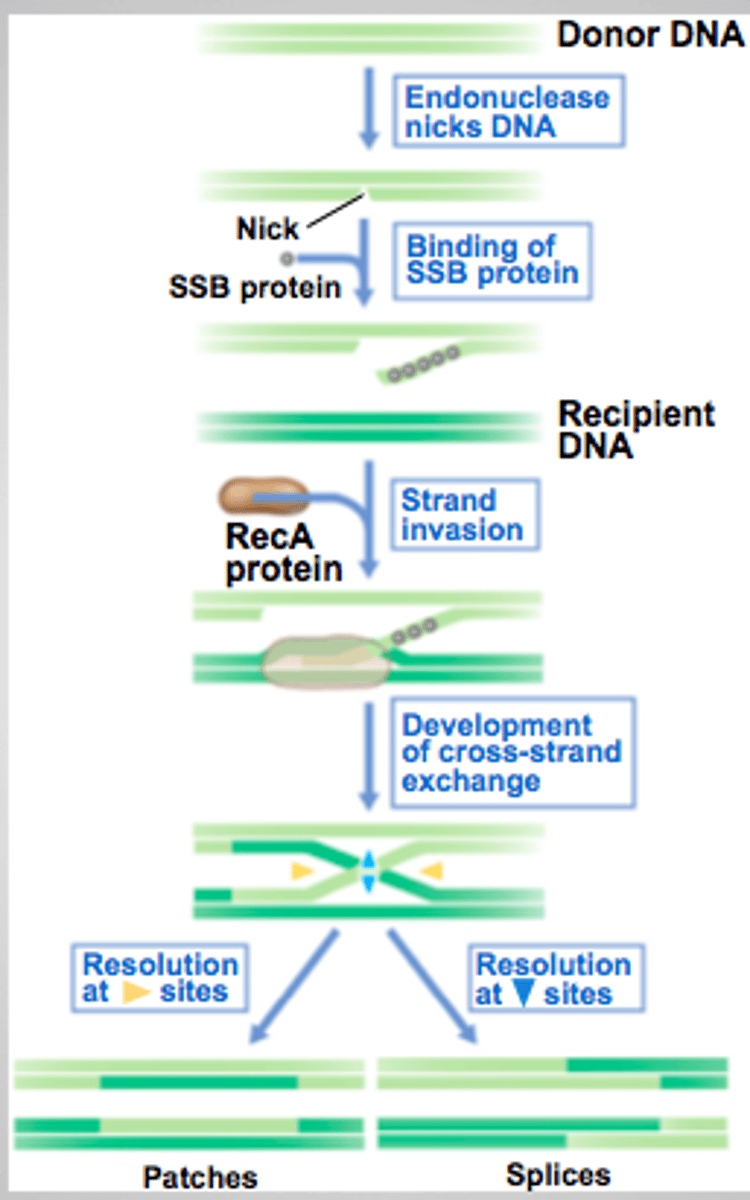
RecA
protein activated by cell stress that cleaves the lambda repressor protein, allowing balance to be tipped towards lysis
virulent
viruses that always lyse and kill host after infection
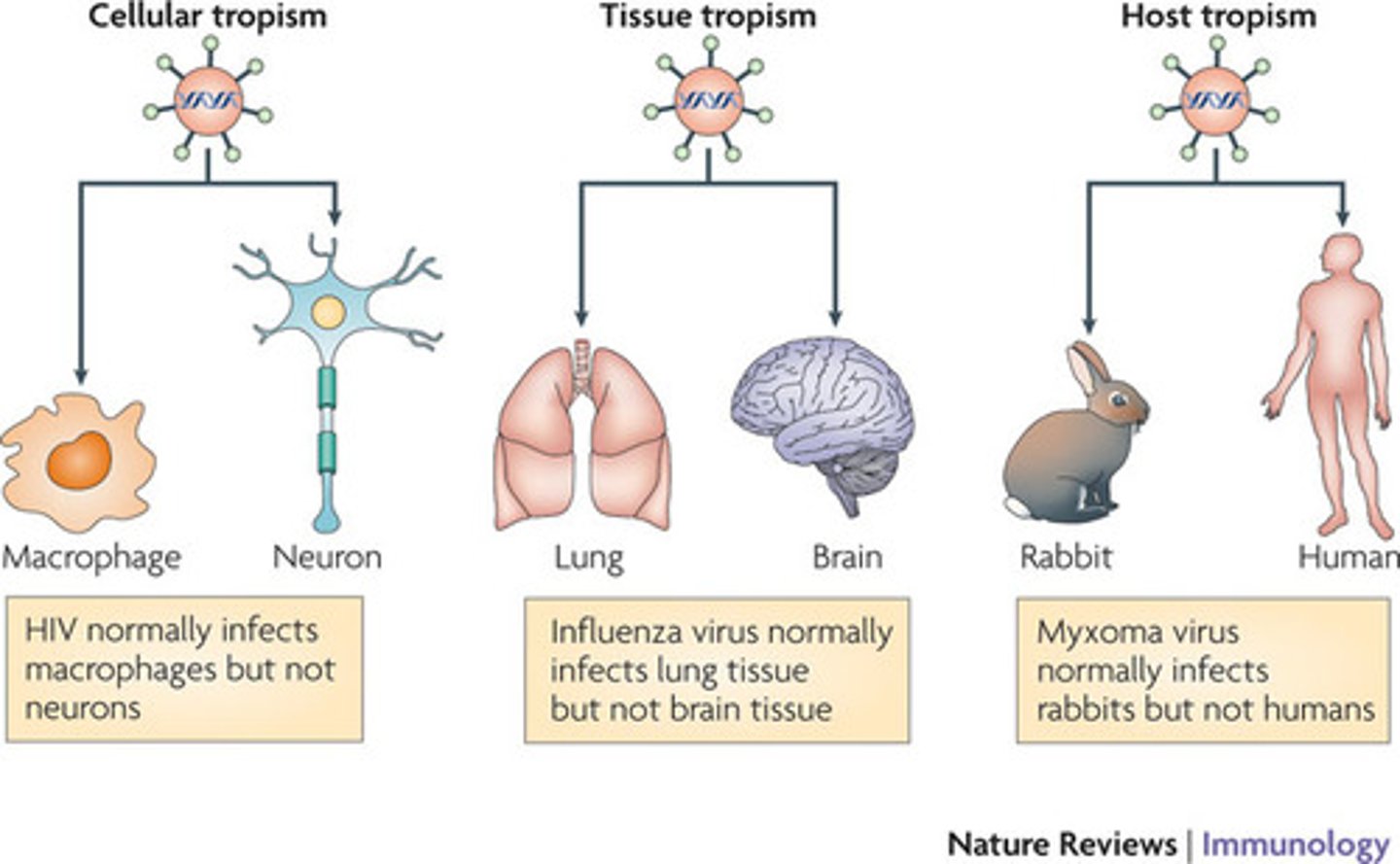
species specificity
a particular virus infects only particular species (based on presence of receptor for entry)
temperate
viruses that integrate and replicate their genomes with the host genome and without killing the host, establishing a long, stable relationship
Cro protein
protein that activates lytic events and represses lamba repressor protein
induction
the process causing a prophage to become virulent
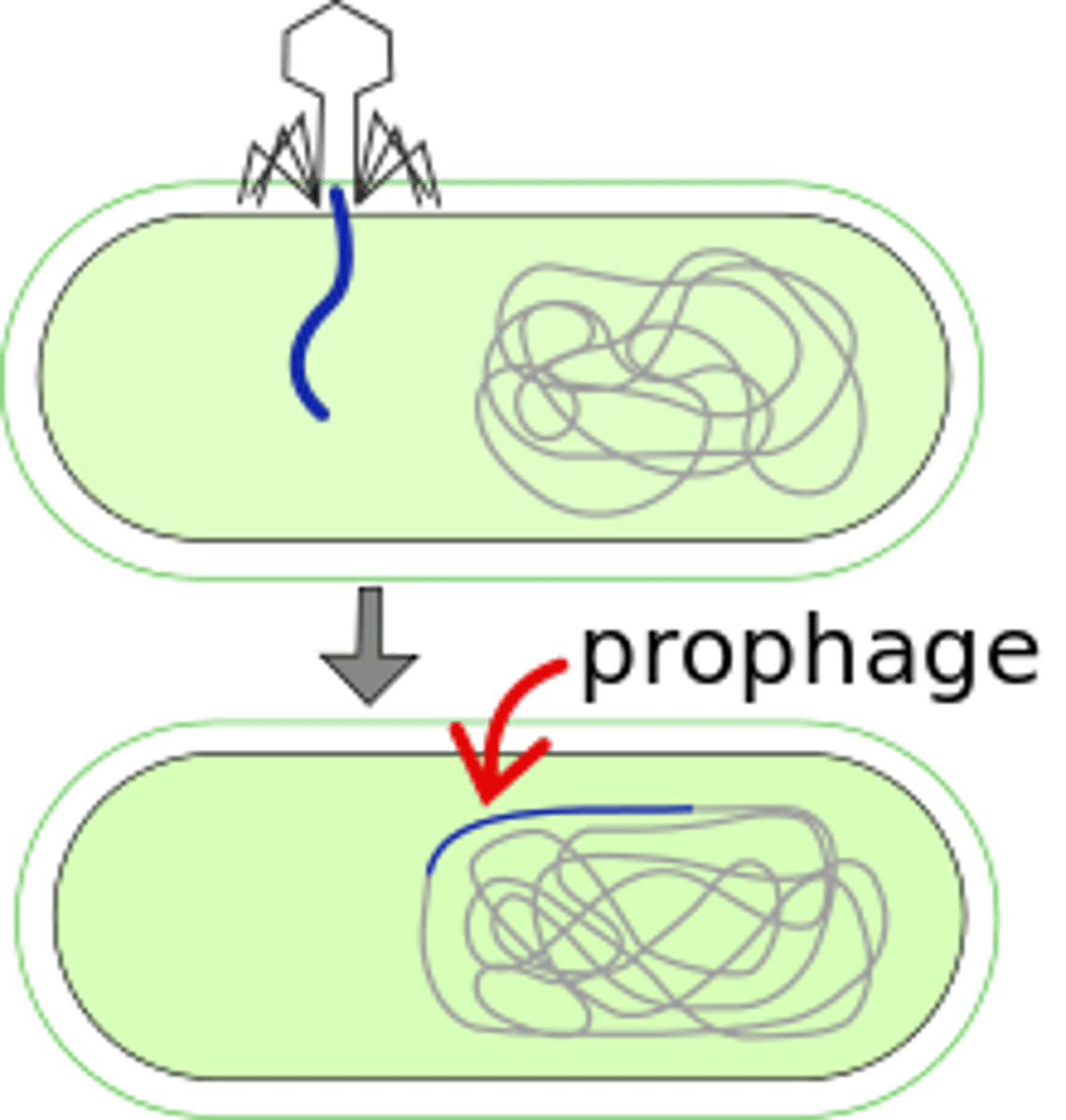
prophage
viral DNA integrated into host DNA
tissue tropism
a particular virus targeting a particular tissue (based on presence of receptor for entry)
late proteins
head and tail proteins, enzymes required to release mature phage particles
ICAM-1
immune protein found on surface of cells. receptor for the common cold.
CD4
molecule found on T-cells. receptor for HIV.
CCR5
co-receptor for HIV. people with very few of these are less susceptible to HIV.
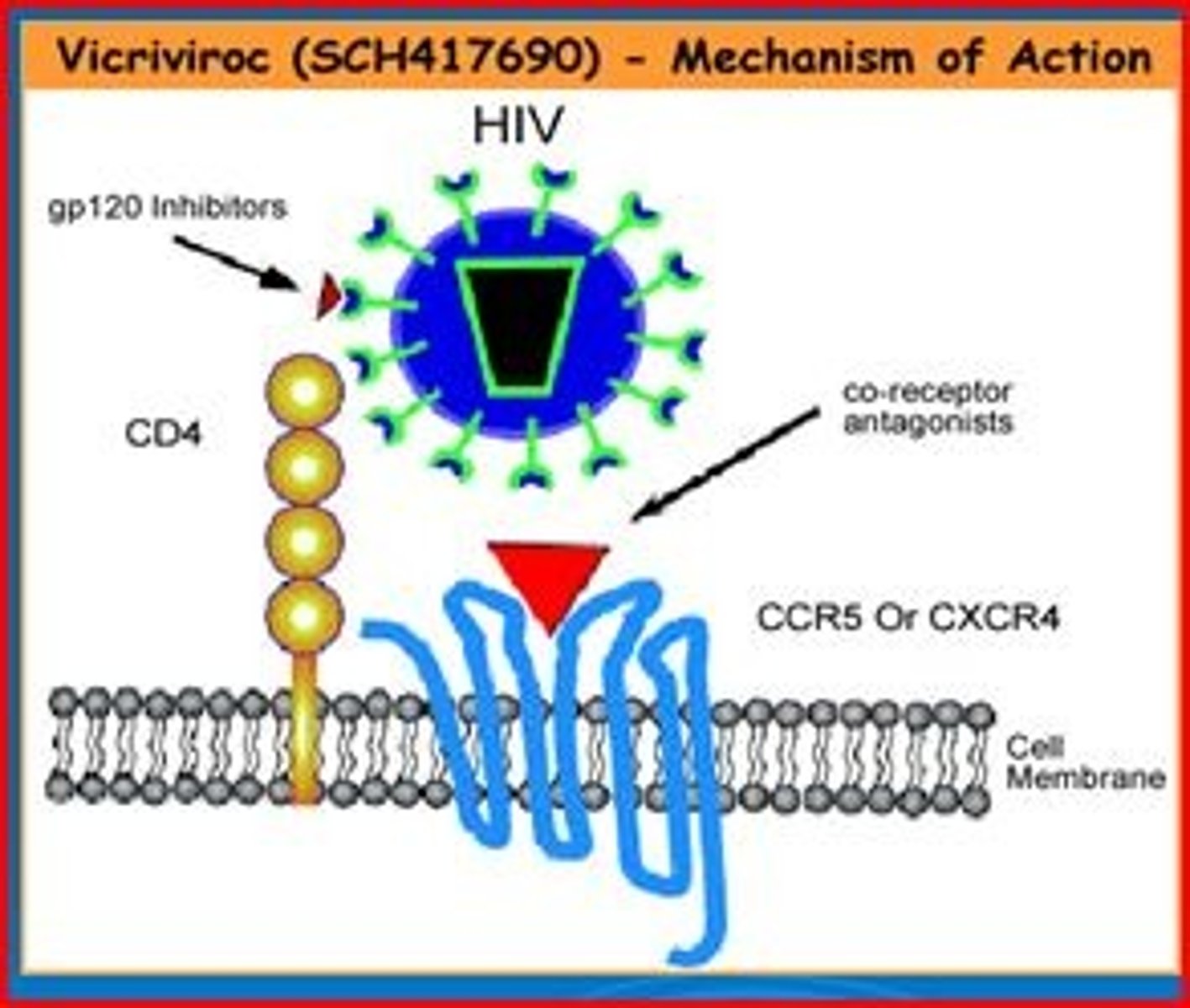
HAART
highly active antiretroviral therapy- use of combinations of drugs (e.g. RT, protease, integrase inhibitors) that are effective against AIDS

PrEP
Pre-exposure prophylaxis: can reduce the risk of HIV BEFORE exposure (RT inhibitors are particularly effective for this)

norovirus
naked ssRNA virus (positive strand) that causes the 24-48 hour stomach flu (diarrhea, vomiting, cramps). Very contagious (feared on cruise ships and other enclosed areas)

papillomavirus
Naked dsDNA virus that causes cervical cancer and warts. Sexually transmitted infections common prior to creation of HPV vaccine
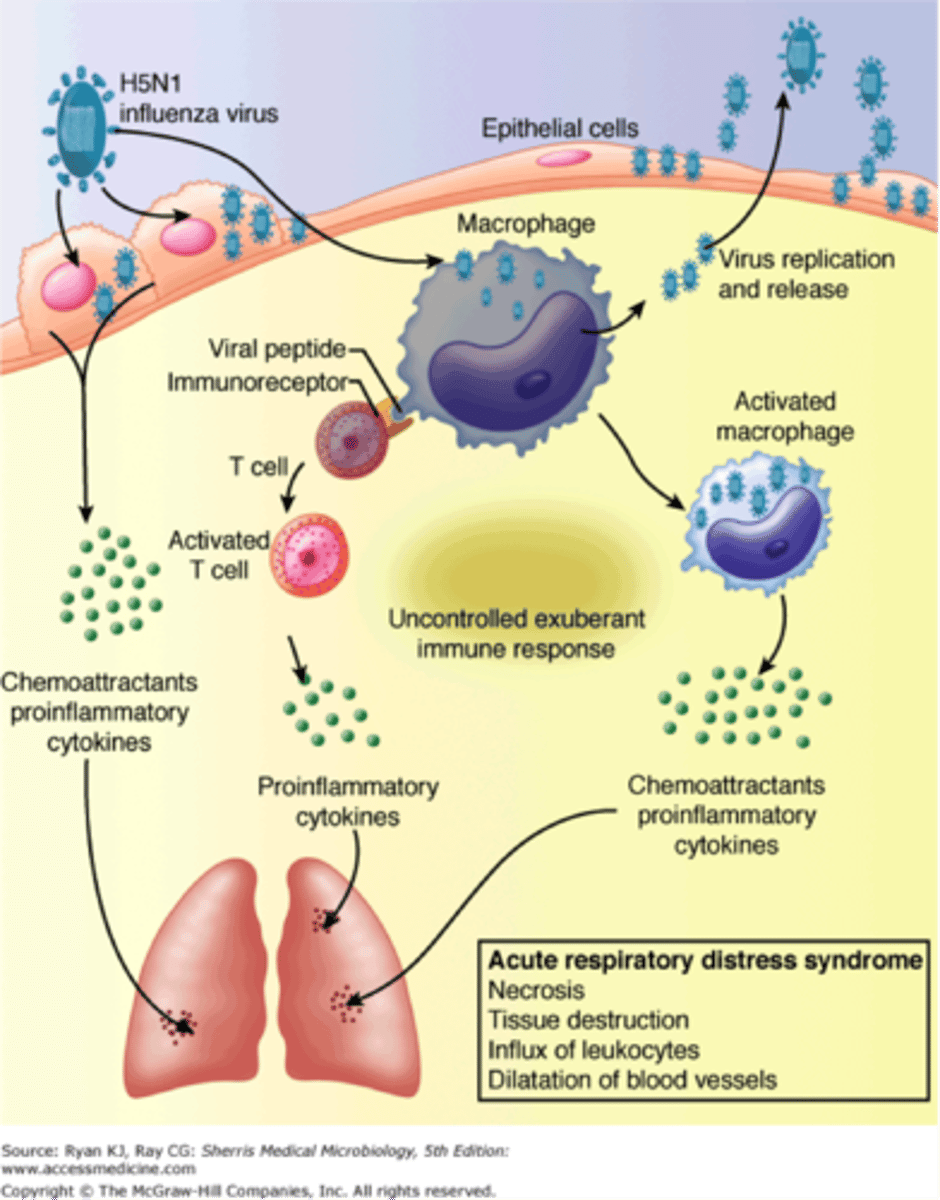
cytokine storm
A potentially fatal immune reaction caused by highly elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines
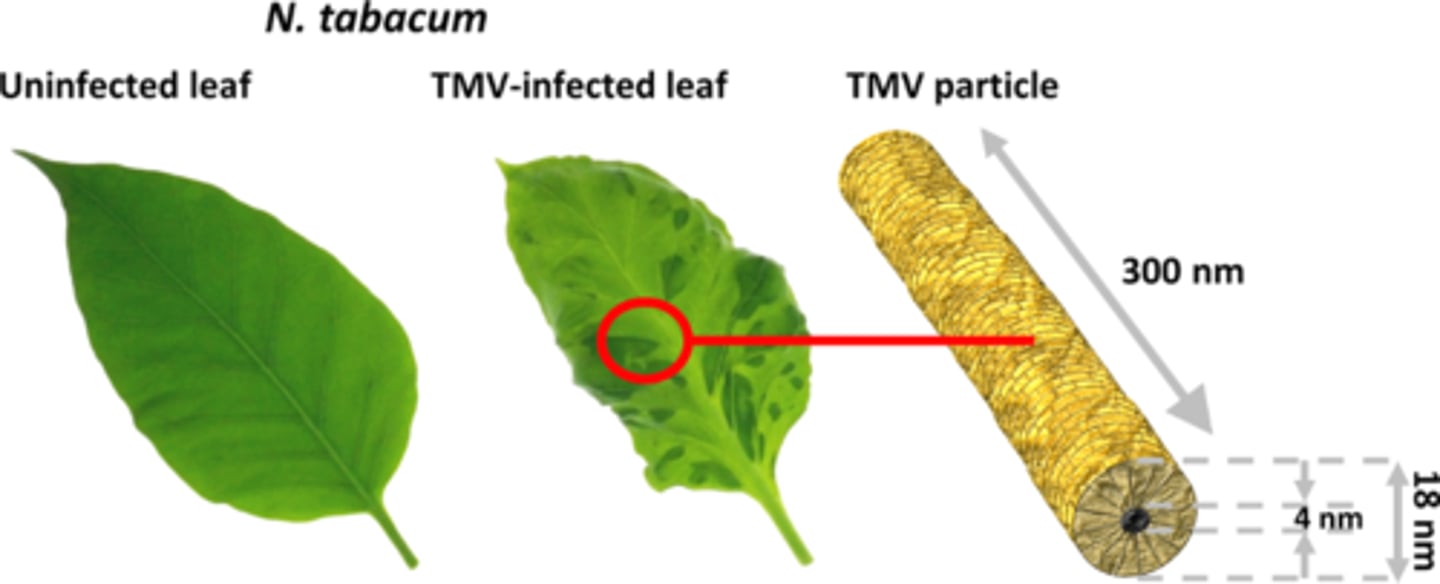
TMV
Virus affecting plants causing a mosaic pattern on leaves. This was the first virus ever discovered, using a filtration experiment - the disease was transmitted in the filtrate (too small to be bacteria)
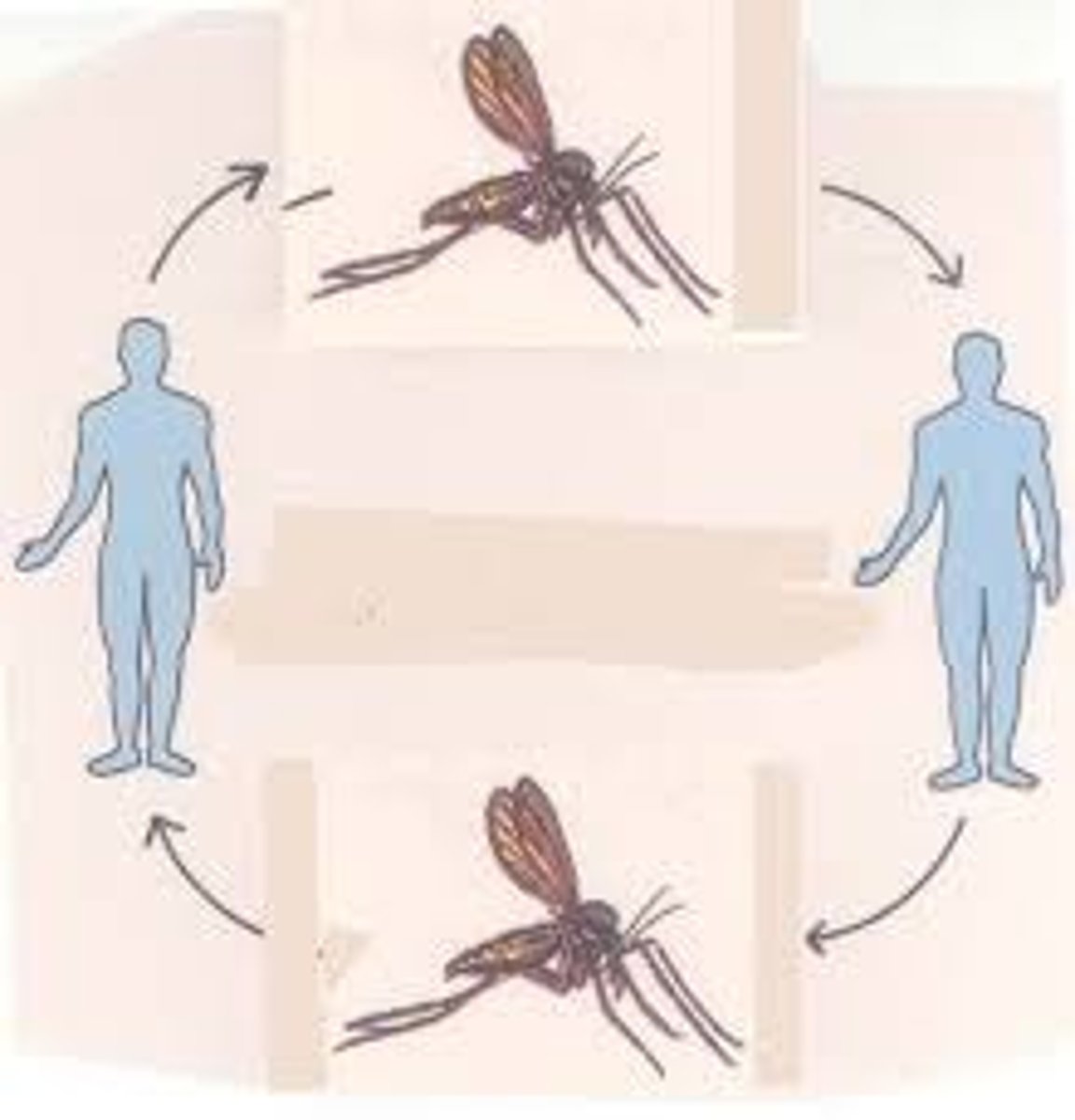
vector
Something that transfers things from one place to another, for example an organism that carries a pathogen from one infected person to another, such as the mosquito that carries the malaria protist.
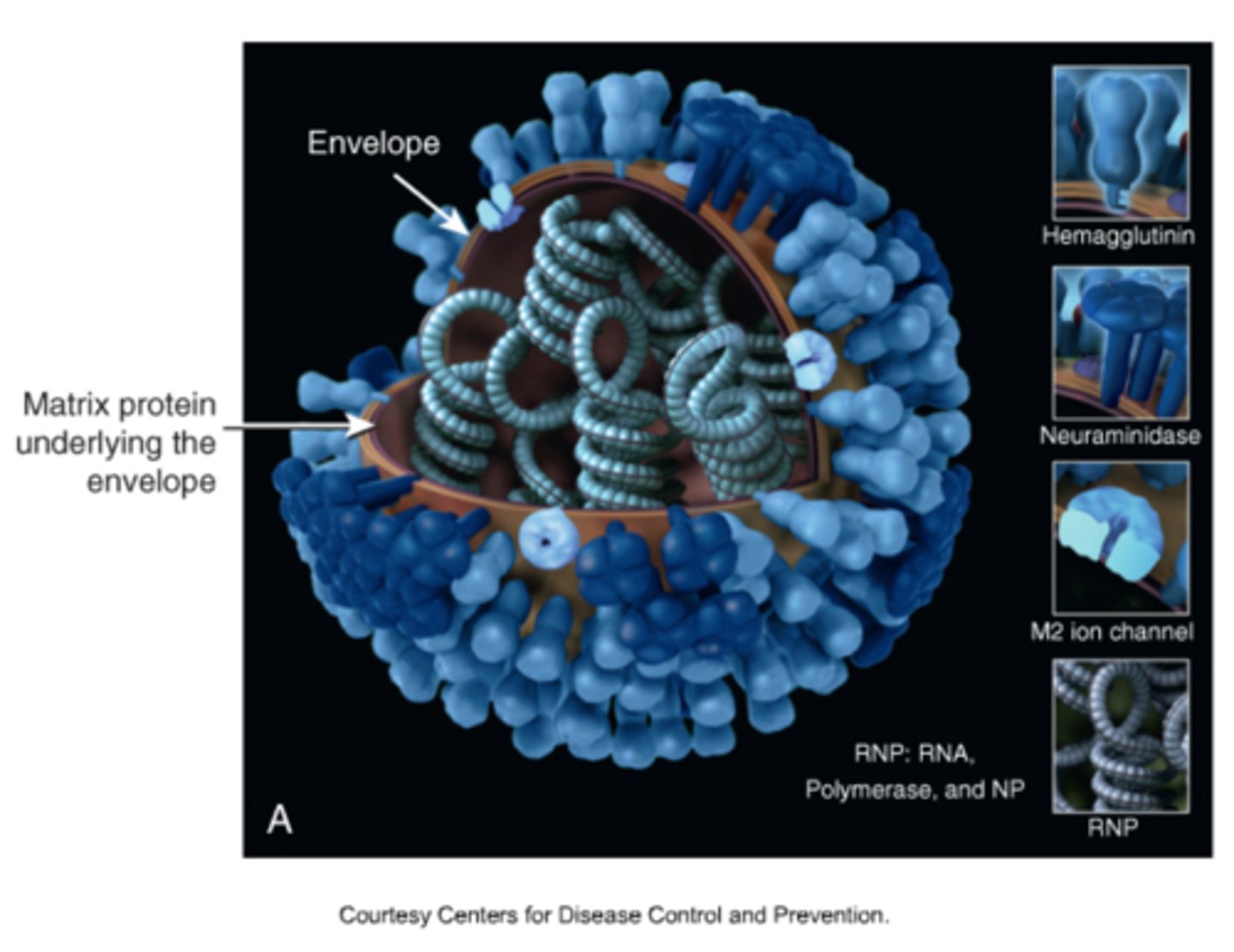
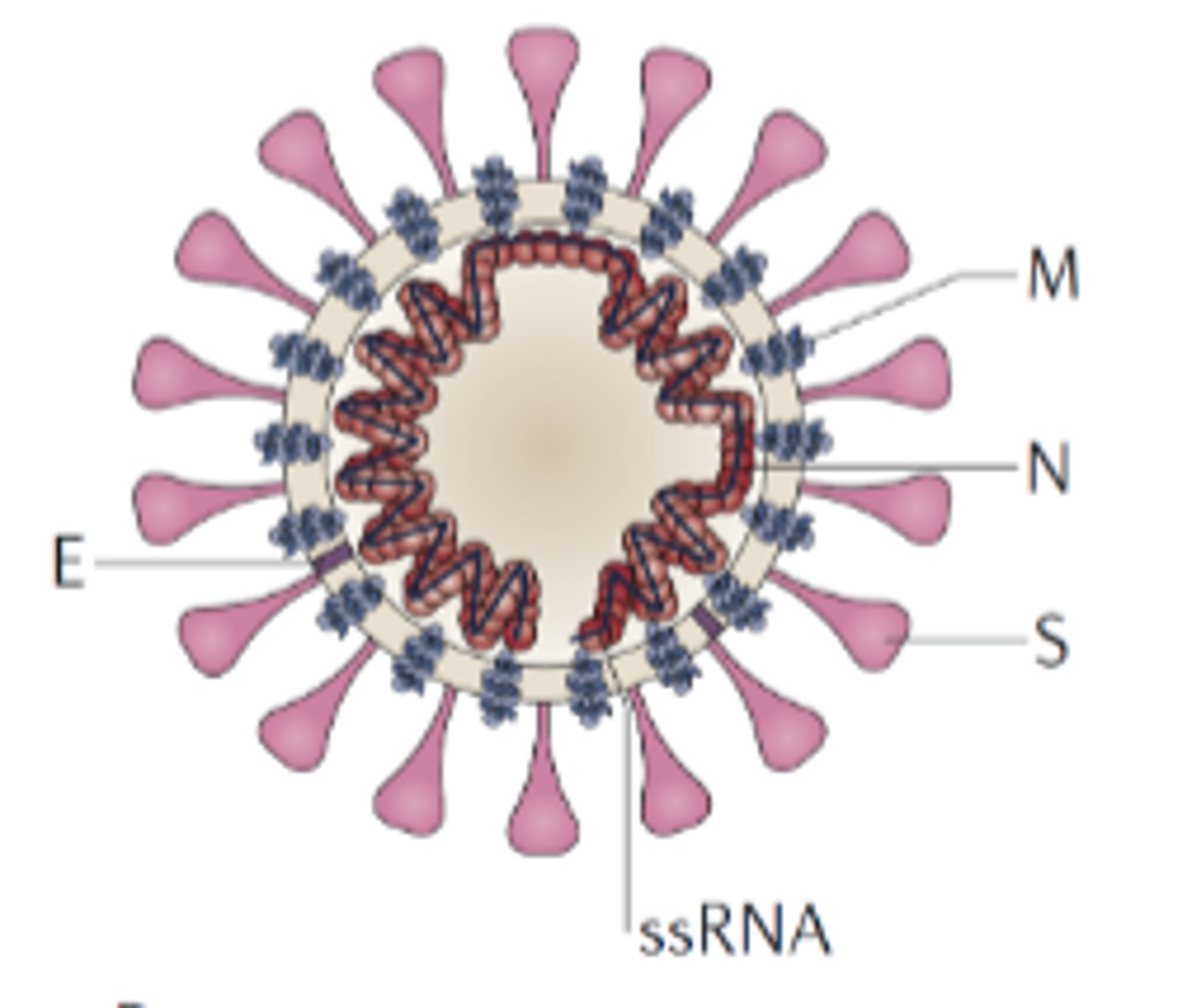
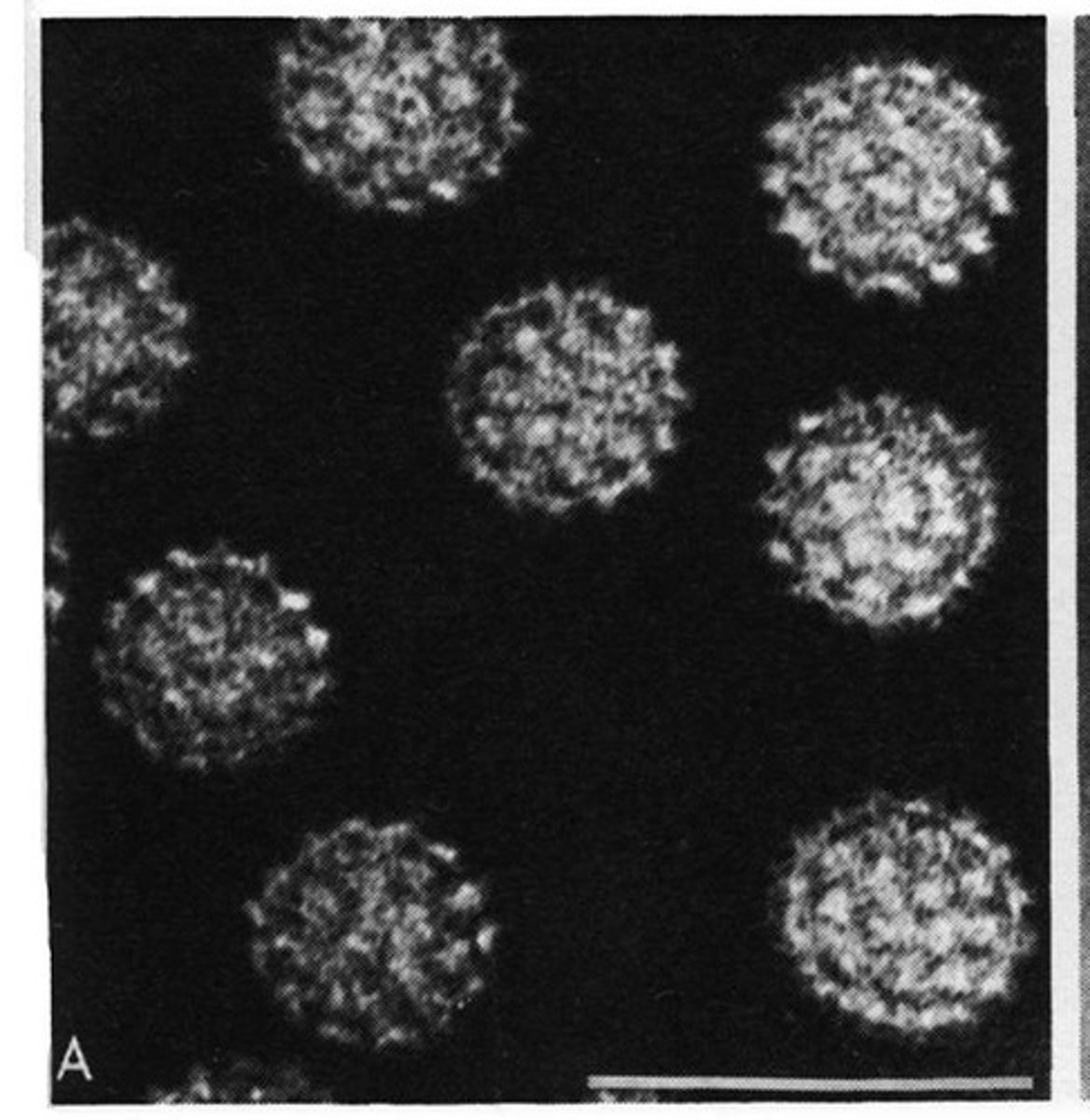
influenza
Segmented RNA virus (enveloped) made up of 8 segments (10 genes) that causes a lung infection (may lead to a cytokine storm). Key proteins are hemagglutinin and neuraminidase. (1918 H1N1 flu = 50 million dead in 2 years of the pandemic)
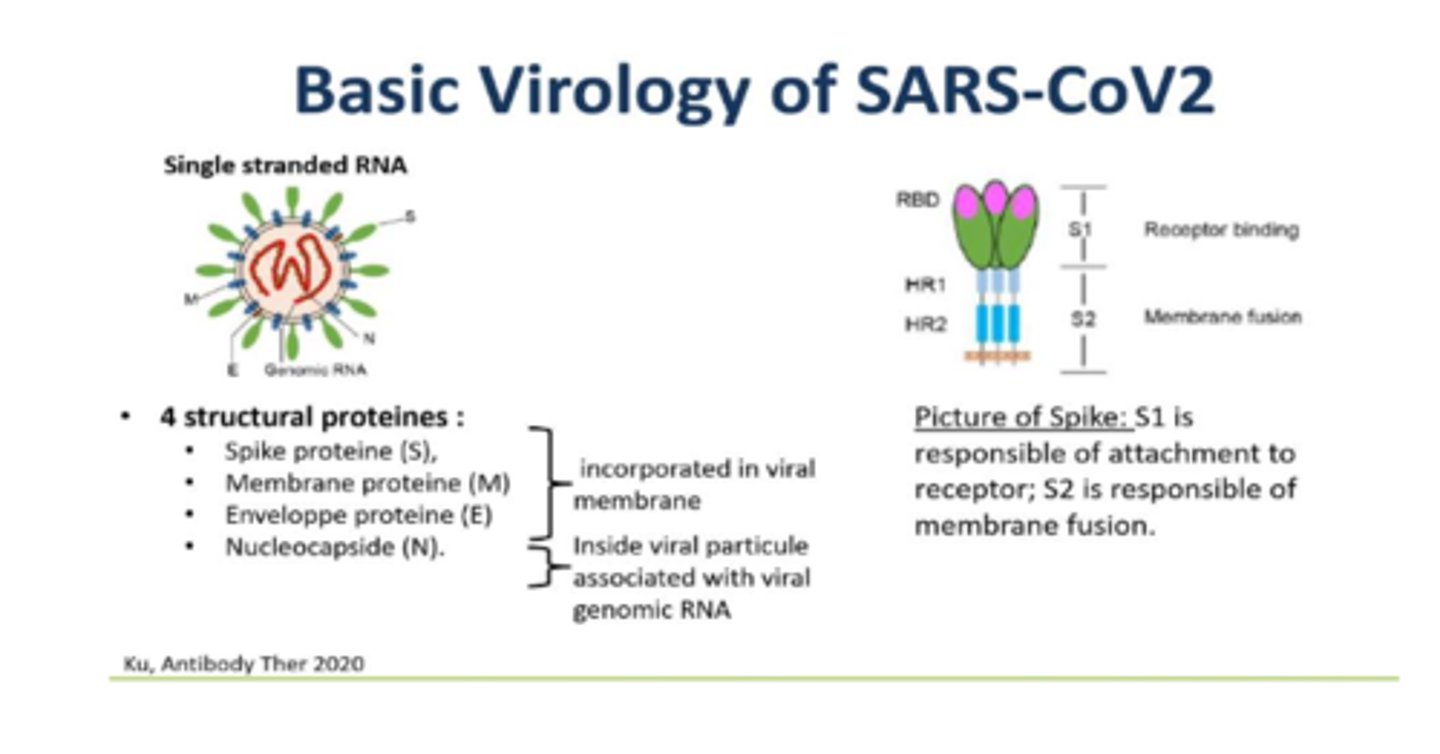
SARS-CoV2
Single stranded (+ strand) RNA virus that is the causative agent of COVID-19. This virus uses ACE2 as a receptor and infects lungs, causing pneumonia in severe cases.
COVID-19
Pandemic disease caused by SARS-CoV2. Symptoms are mild in 80% of the cases, severe in ~10%, with a 2-3% case fatality rate (due to pneumonia and multi-organ failure)
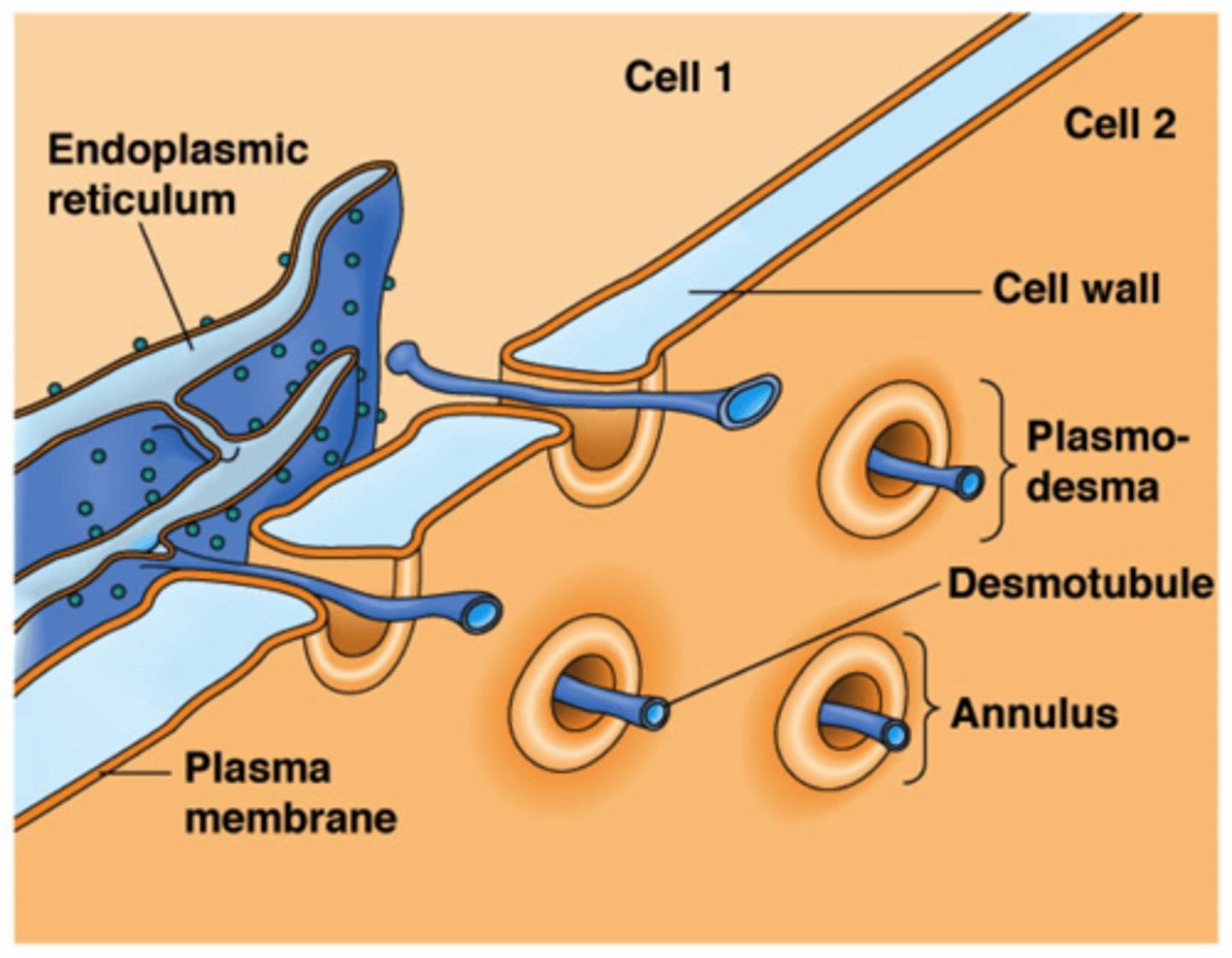
plasmodesma
An open channel in a plant cell wall through which strands of cytoplasm connect from adjacent cells. This is a typical route viruses use to move from one cell to the next