Hybrid Orbitals and Molecular Orbital Theory (Chapter 9)
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Nov 10, 12 and 14 Lectures
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Use ____ orbitals when you want to form a tetrahedral geometry from a central atom
sp³

to form trigonal planar geometry, hybridize
sp² orbitals

use ___ to form the sigma bond in all linear molecules
sp
the # of orbitals you hybridize for a geometry is related to the # of
sigma bonds
Kekule Structure
Lewis structure but without lone pairs
Condensed Structure
no bonds drawn in the core structure
ex: CH3CH2CH2CH3
Skeletal structures
Hydrogen atoms assumed, carbons represented by vertices
chirality
a property of a molecule that does NOT apply to its mirror image (optical isomerism)
structures with the same molecular formula can react differently due to their orientations in space
most common chiral molecule!!
4 different atoms (not hydrogen) attached to carbon
chiral molecules
their mirror images can NOT be superimposed upon themselves
Number of Molecular Orbitals always equals
the number of Atomic Orbitals used to make the Molecular Orbitals
Bond Order (predicts amt of bonds in a molecule)
Half of the number of (bonding electrons - antibonding electrons)
homonuclear diatomic
two of the same element
2pz direction
points directly at other atom
diamagnetic
all electrons are paired
weakly repelled in a magnetic field
paramagnetic
has unpaired electrons
attracted to a magnetic field
in MO theory, orbitals need the same ___ to be mixed
symmetry
related to whether sigma or pi bonds are formed
what p orbital forms sigma bonds?
2pz
which p orbitals form pi bonds?
2px and 2py
Valence Band
a band of orbitals that are filled or partially filled by valence electrons
Conduction Band
an unoccupied band higher in energy than a valence band, in which electrons are free to migrate
kind of the opposite of valence band
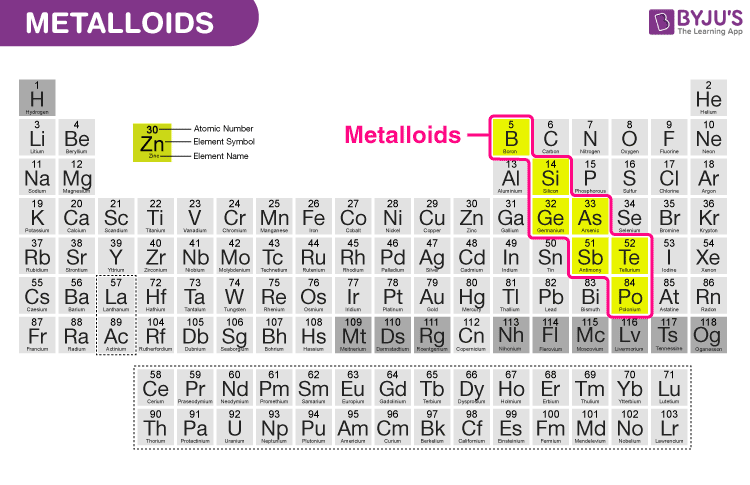
metalloids
elements with properties that are intermediate between metals and nonmetals, often appearing lustrous and brittle with variable electrical conductivity. Common metalloids include Boron (B), Silicon (Si), Germanium (Ge), Arsenic (As), Antimony (Sb), and Tellurium (Te)
band gap
the space between the conduction and valence bands
affects conductivity- larger gap= less conductive
Semi-Conductors
Metalloids
Critical for when we need to control the conductivity of a substance
Conductivity can be increased through doping
Doping
n-type: add electron-rich dopant atoms that contribute excess electrons
p-type: add electron-poor dopant atoms that cause a reduction in the number of electrons