Connective Tissue (loose, dense, & fluid)
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Loose connective tissue
a category of connective tissue that acts a soft, flexible packing for organs and other tissues - Each type contains cells (like fibroblasts, adipocytes, or reticular cells) and loosely arranged fibers (collagen, elastic, and reticular fibers) in a gel-like ground substance
loose: Areolar
soft, flexible, and cushion organs - provides support but permits independent movement
location: deep to the derms of skin and covered by the epitheial lining of the digestive, respiratory and urinary

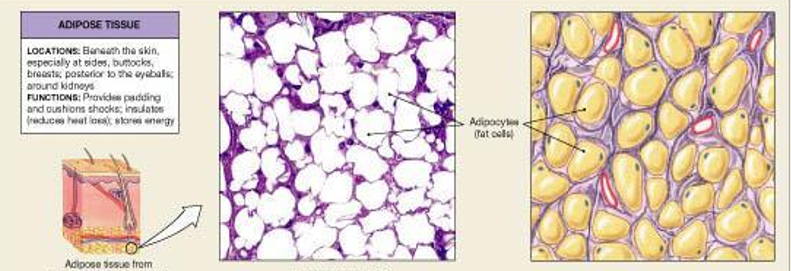
loose: Adipose
stores fat, insulates, and protects by providing padding and cushion shocks, stores energy
location: beneath the skin - sides, butt, breasts and posterior to the eyeballs and around kidneys
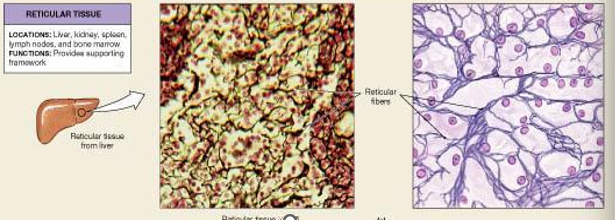
loose: Reticular
provides supportive framework especially in organs like the spleen and lymph nodes
location: spleen, lymph nodes, liver, and bone marrow
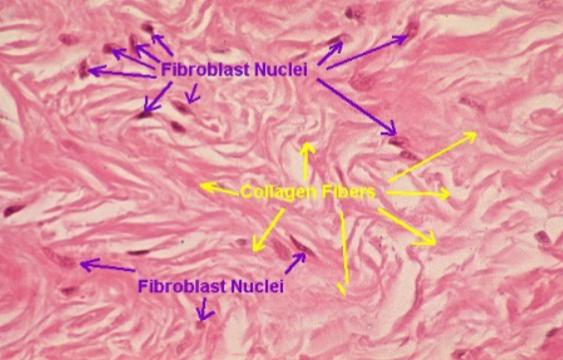
Dense connective tissue
Has a high amount of closely packed collagen fibers which makes it strong and able to resist stretching & it provides support and connects different tissues in the body
Dense regular connective tissue
Provides firm attachment; conducts pull of muscles; reduces friction between muscles; and stabilizes relative position of bones
fibers are arranged in parallel like in tendons and ligaments
location: between skeletal muscles and skeleton (tendon)

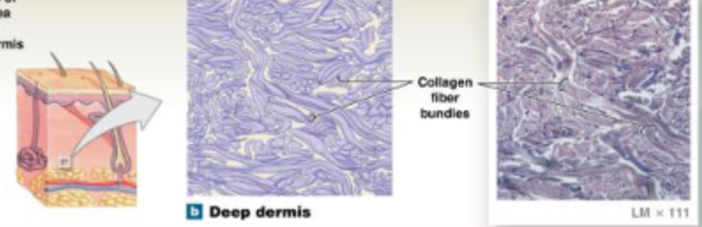
Dense irregular connective tissue
Provides strength to resist forces applied from many directions; helps prevent overexpansion of organs such as the urinary bladder
location: capsules of visceral organs; dermis; etc
fibers are arranged randomly and found in the dermis of the skin
(dense) Elastic connective tissue
Stabilizes positions of vertebrae and penis; cushions shocks; permits expansion and contraction of organs
location: between vertebrae of the spinal column; ligaments supporting penis, et
Fluid Connective Tisue: Blood
Contains red - carries and transport oxygen, account for half the volume of whole blood and give it its color & white blood cells - immune defense
platelets - membrane enclosed packets of cytoplasm that function in blood clotting
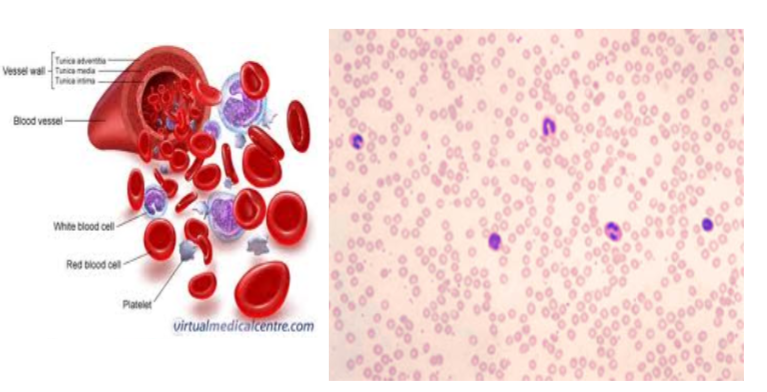
Fluid Connective Tisue: Plasma
Liquid part of blood (matrix for transport) and is made mostly of water with dissolved proteins, nutrients, hormones, and waste
Fluid Connective Tisue: Lymph
A clear fluid formed from plasma that leaves capillaries; contains white blood cells and is involved in immune responses and returning fluid to blood vessels.