The 4 Major Macromolecules (Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids) + Biology Basics
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Elements of Carbohydrate
Carbon (C)
Hydrogen (H)
Oxygen (O)
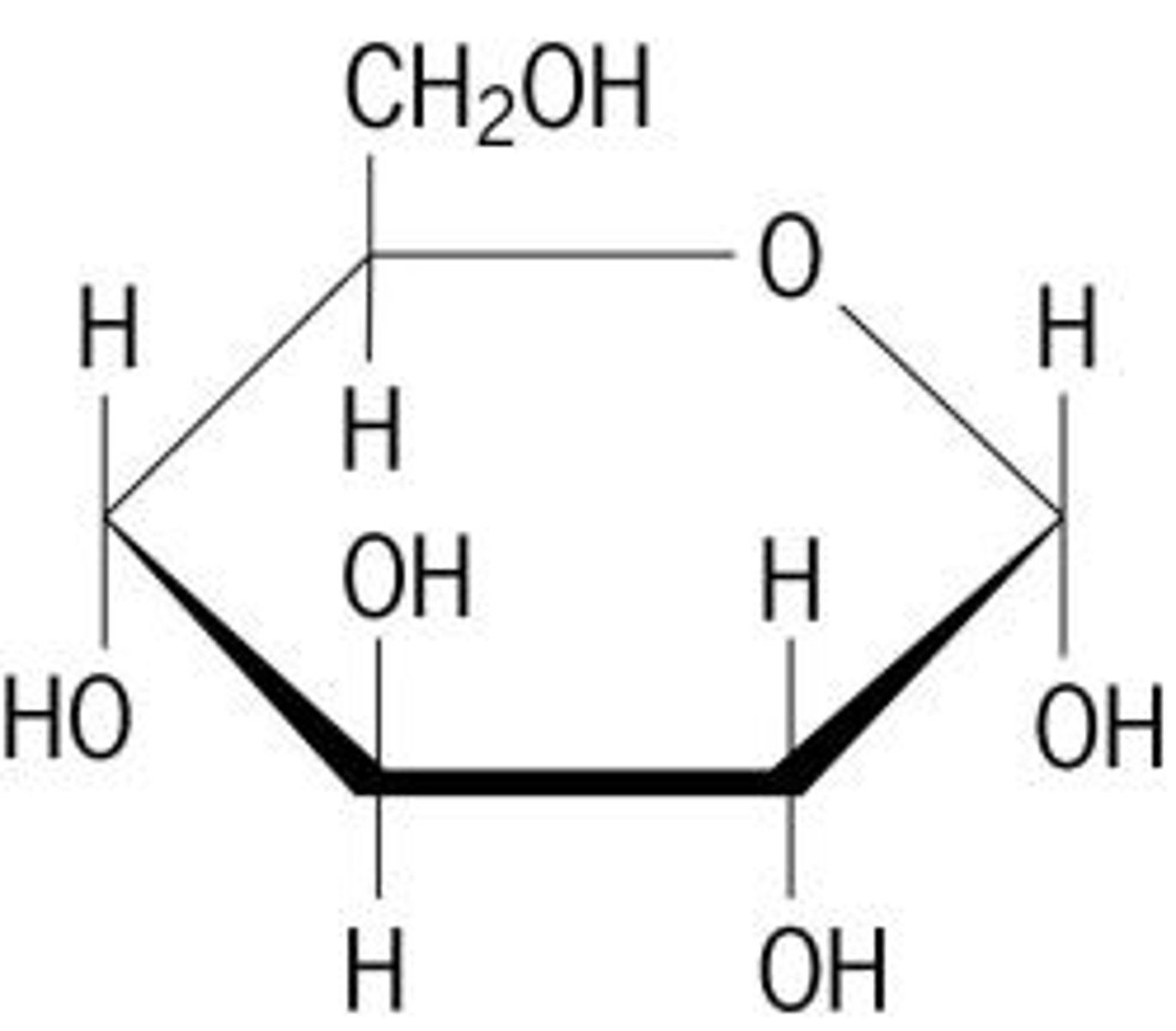
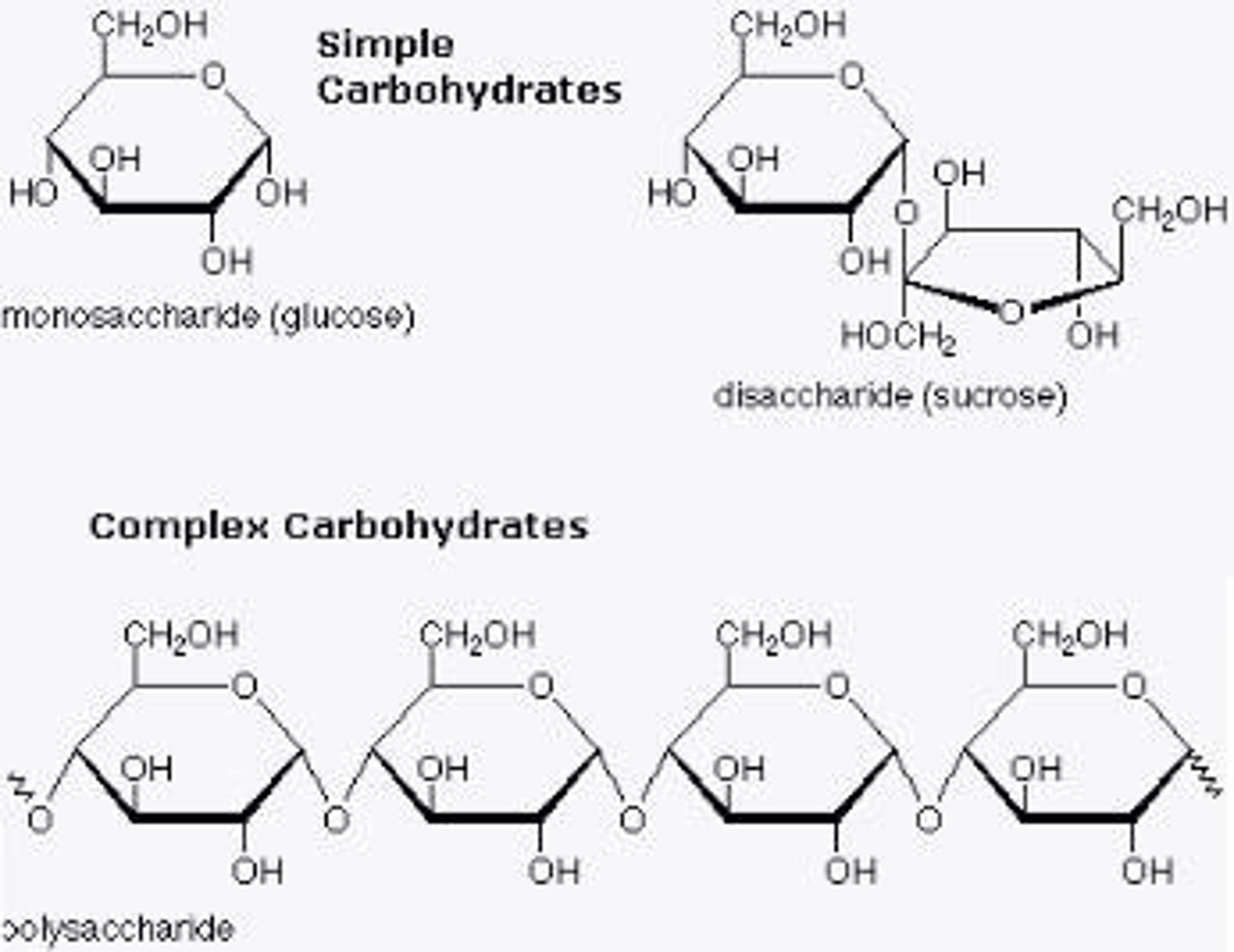
Building Blocks of Carbohydrates
Monosaccharides (simple sugar) - disaccharides polysaccharides
Elements of Lipids
Carbon (C)
Hydrogen (H)
Oxygen (O)
May contain: Phosphorus (phospholipid), Nitrogen (N), and Sulfur (S
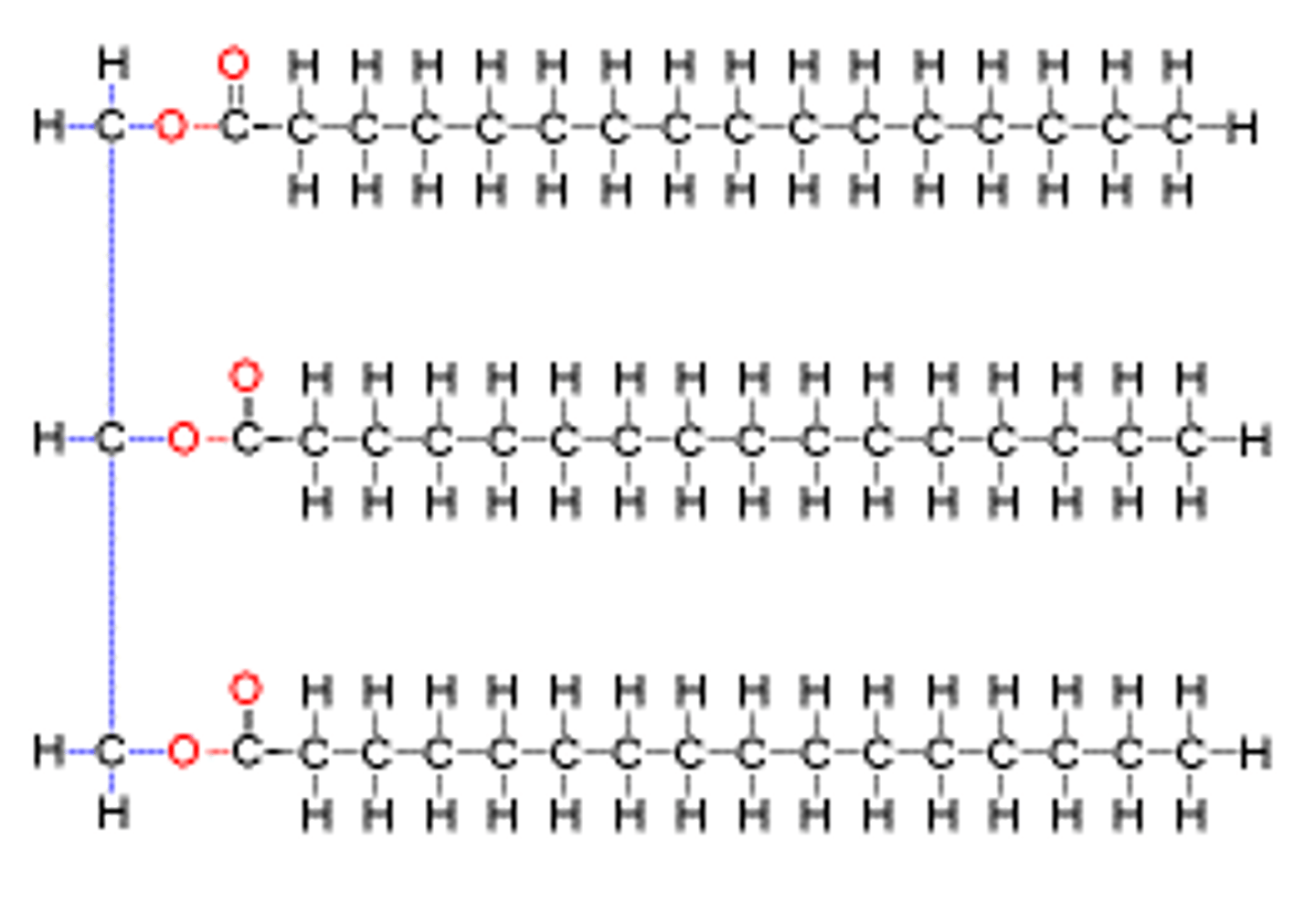
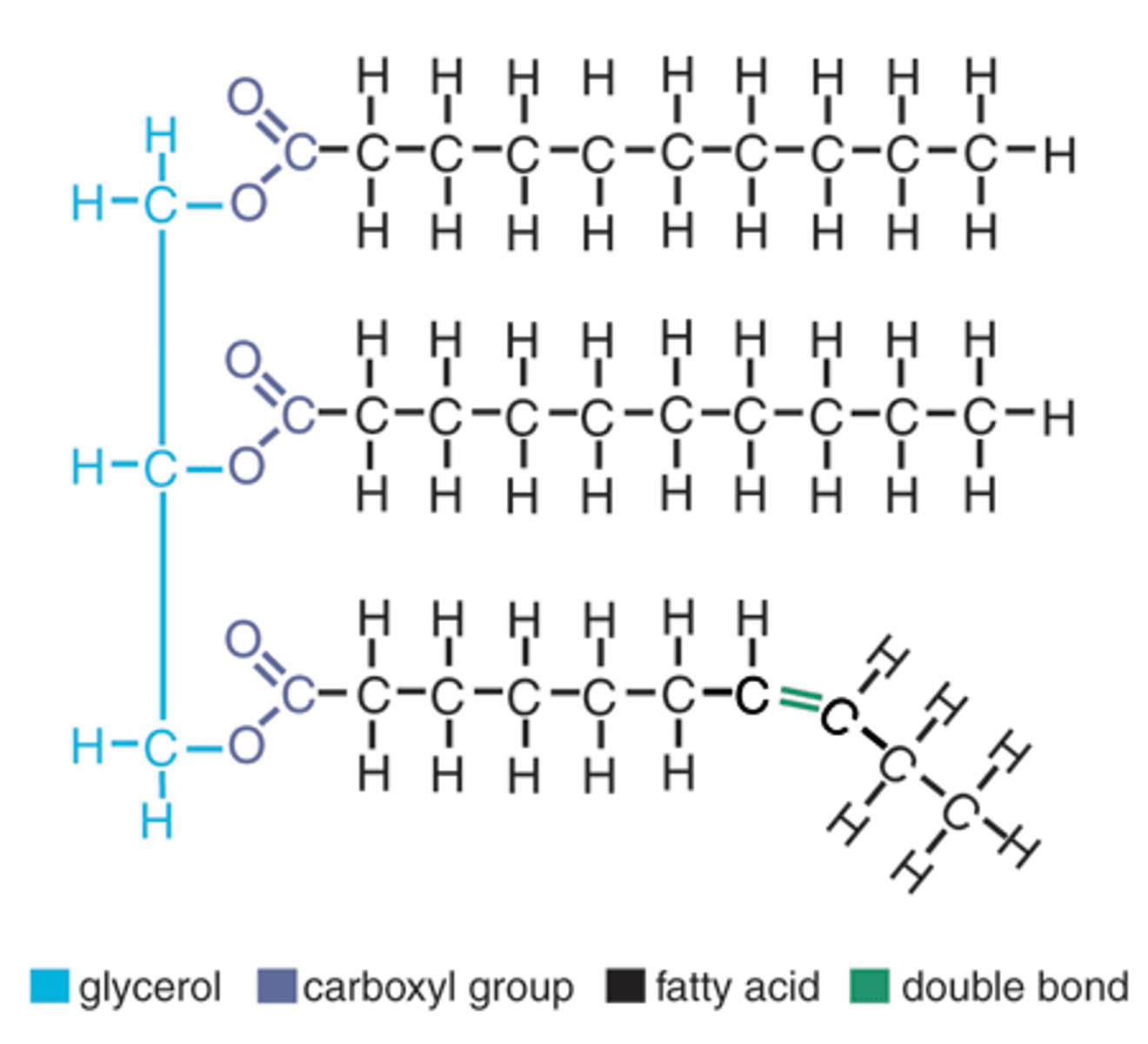
Building blocks of Lipids
Fatty acids and glycerol
Elements of Proteins
Carbon (C)
Hydrogen (H)
Oxygen (O)
Nitrogen (N)
May Contain: Sulfur (S), Phosphorus (P)
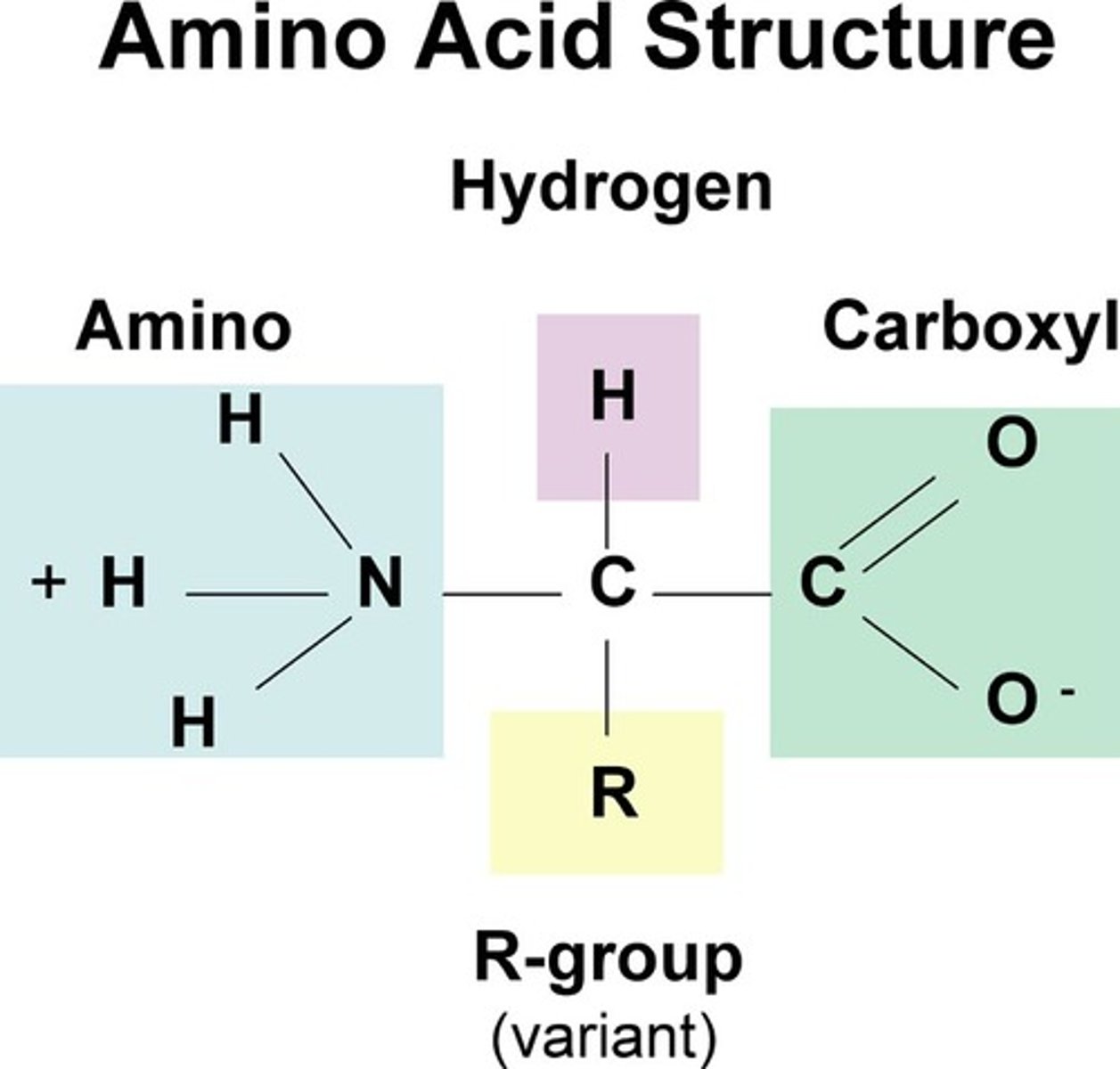
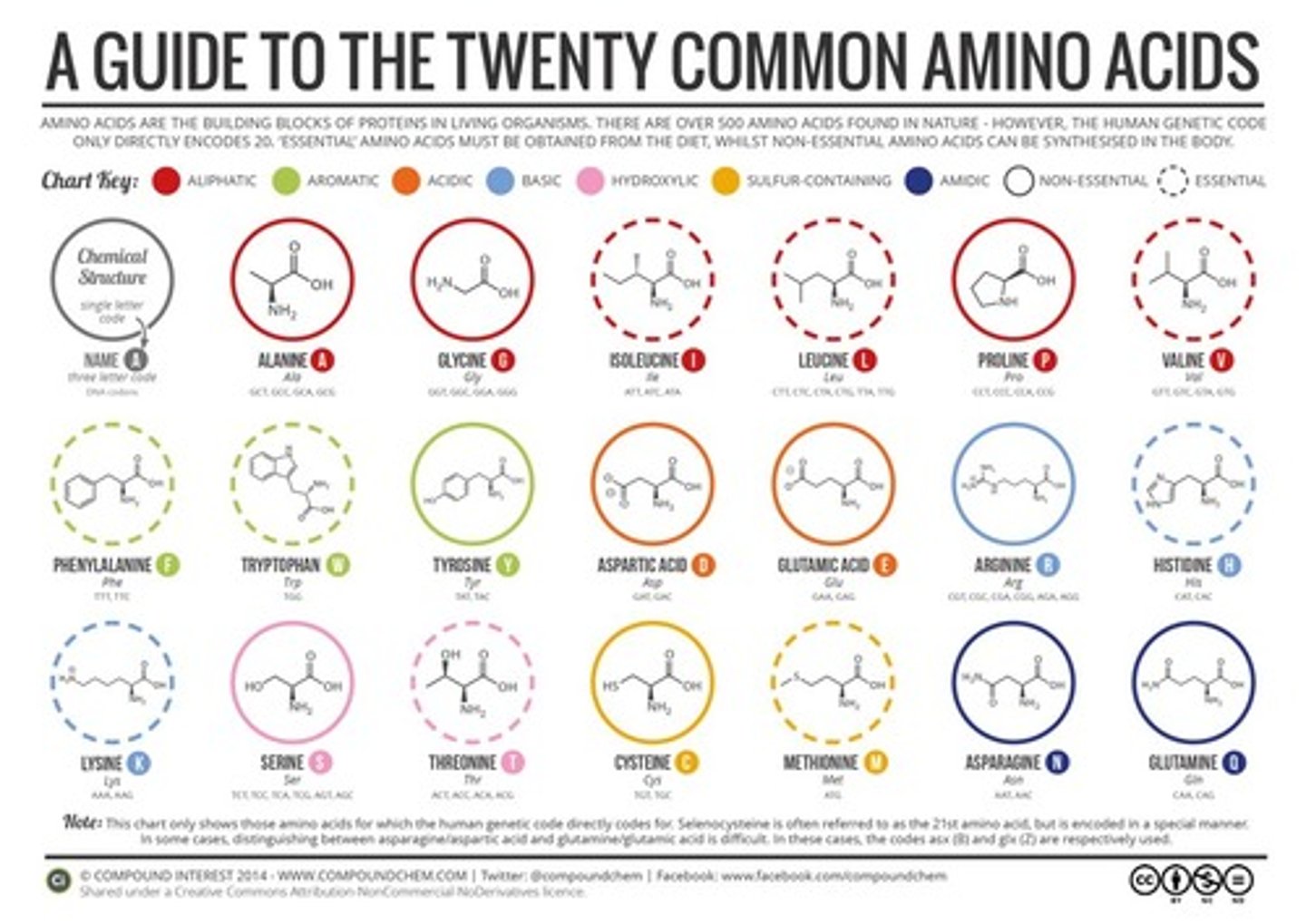
Building blocks of Proteins/Amino Acid
Amino Acids are the building blocks of proteins
Central Carbon Atom: Can make 4 bonds and is the core
Amino Group (NH2): Gives an amino acid its basic properties
Carboxyl Group (COOH): Acidic group which gives acidic properties
Hydrogen (H): Single H attached to core
R-Group: Unique part that determines its chemical properties and function
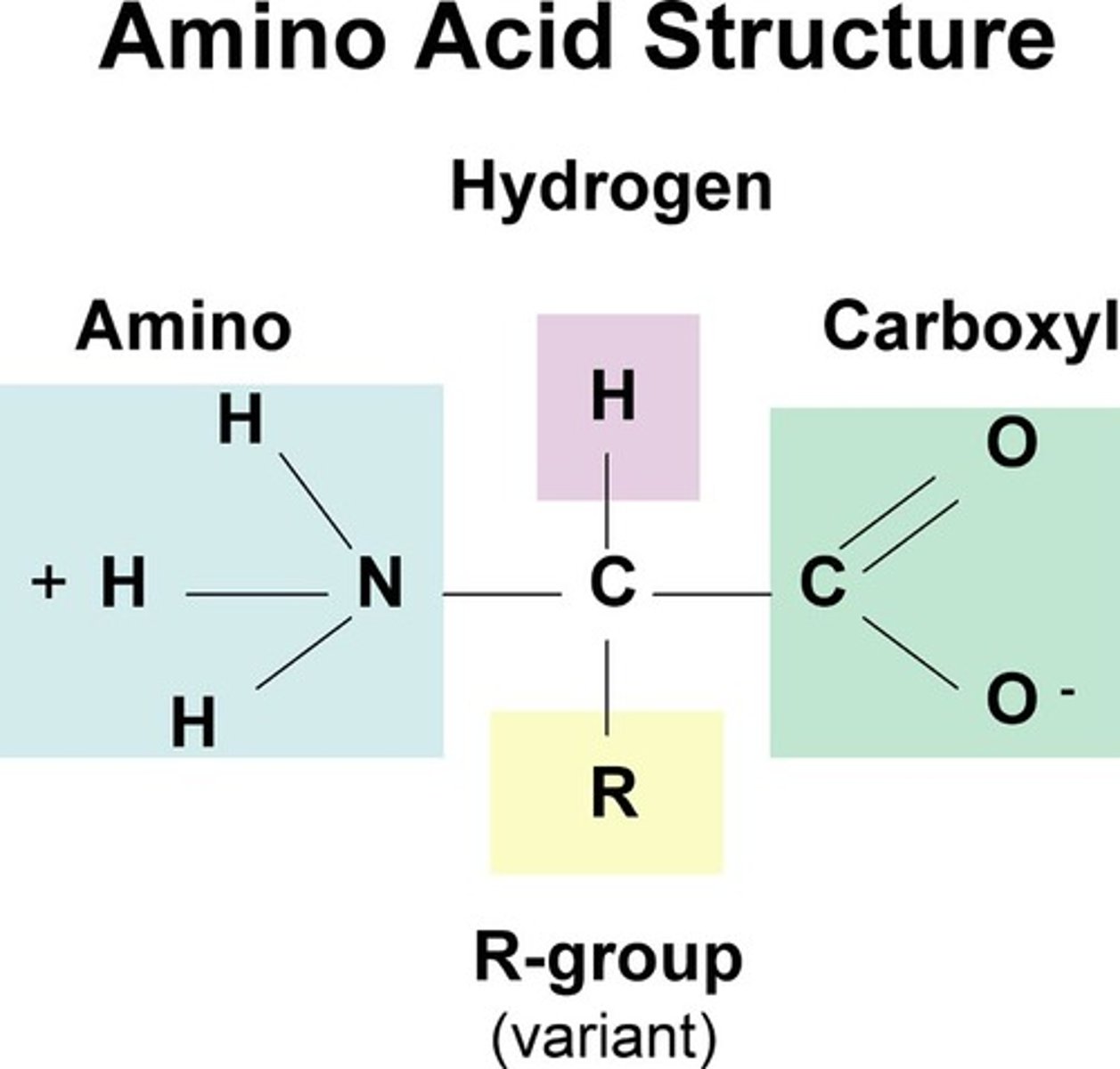
Functional groups in proteins include
Amino Group
Carboxyl group (COOH)
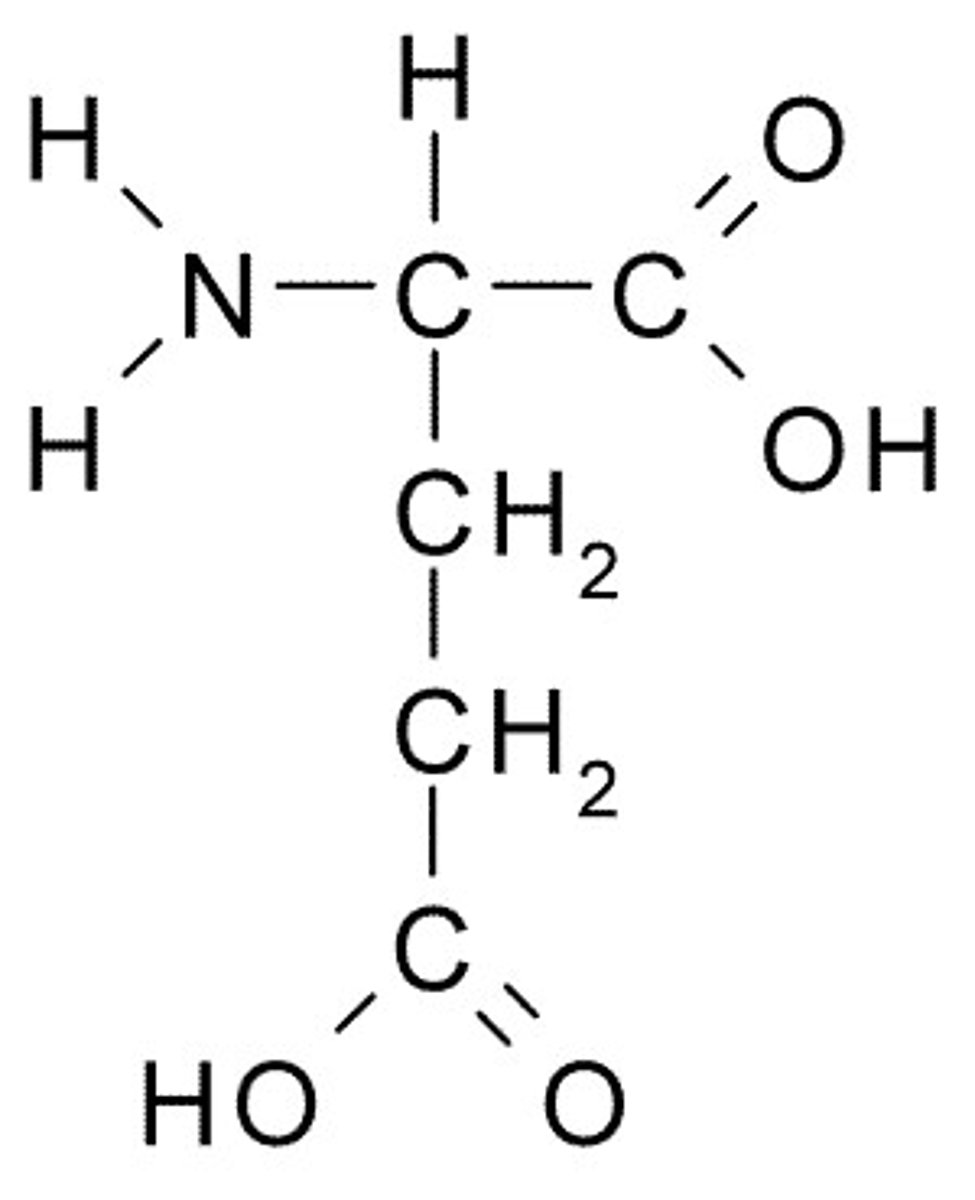
Order of amino acids determines...
Shape and function
What bonds are present in amino acids?
Hydrogen bonds
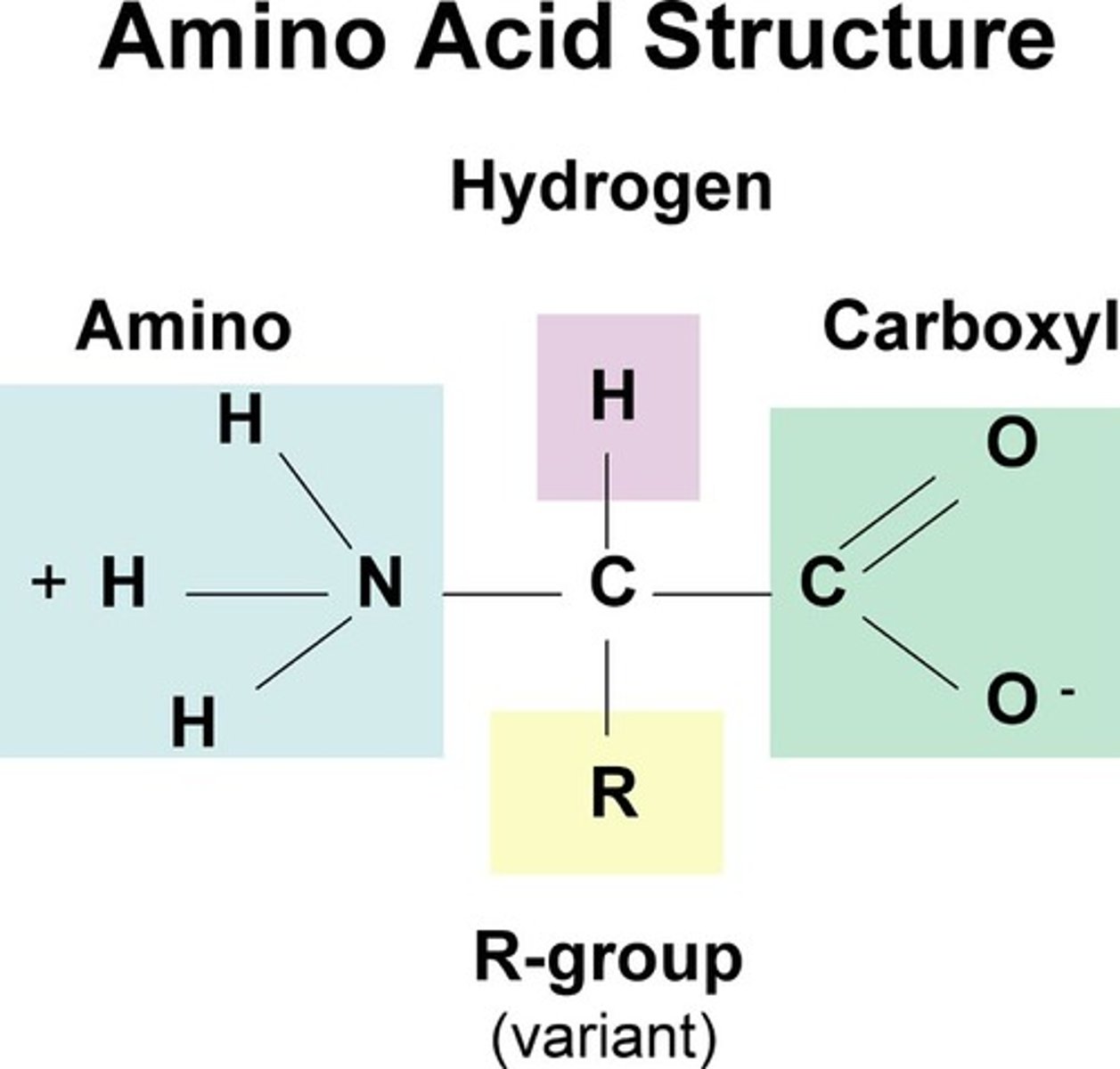
What bonds link amino acids?
Peptide Bonds (dehydration synthesis creates an H2O)
Amino acid (hydrogen bond) - Peptide bonds - Protein (polypeptide)
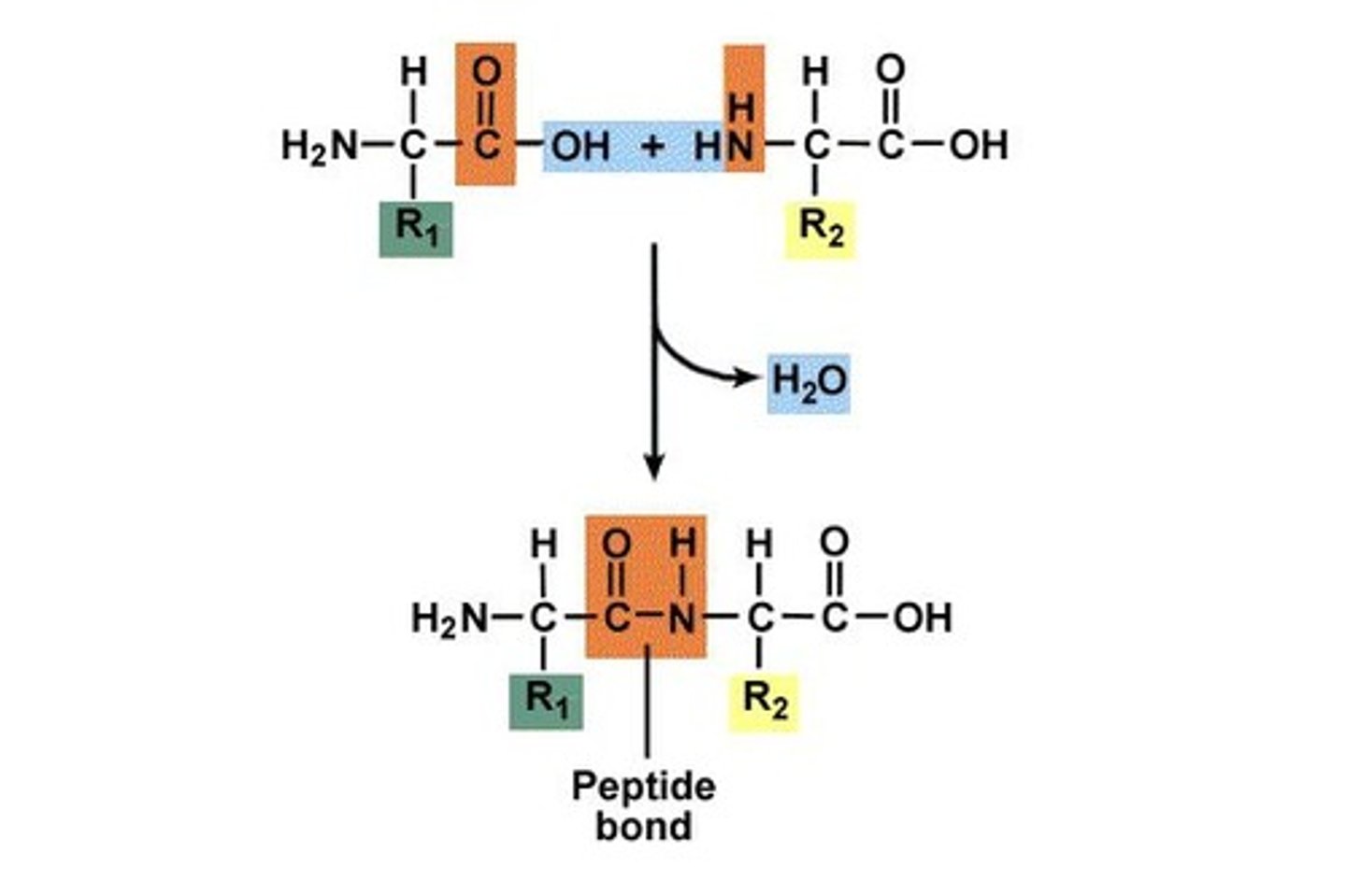
Protein order
Amino acid - Peptide/covalent bonds - hydrogen bonds - carbon/amino groups - sheets - R groups - disulfide bonds - ionic -hydrogen - van Der waals
Structure levels in proteins
Primary - Peptide Chain
Secondary - Alpha Helix, Beta Sheet
Tertiary - 3D shapes a polypeptide chain (interaction between polar/nonpolar R groups)
Quaternary - Two or more polypeptide chains
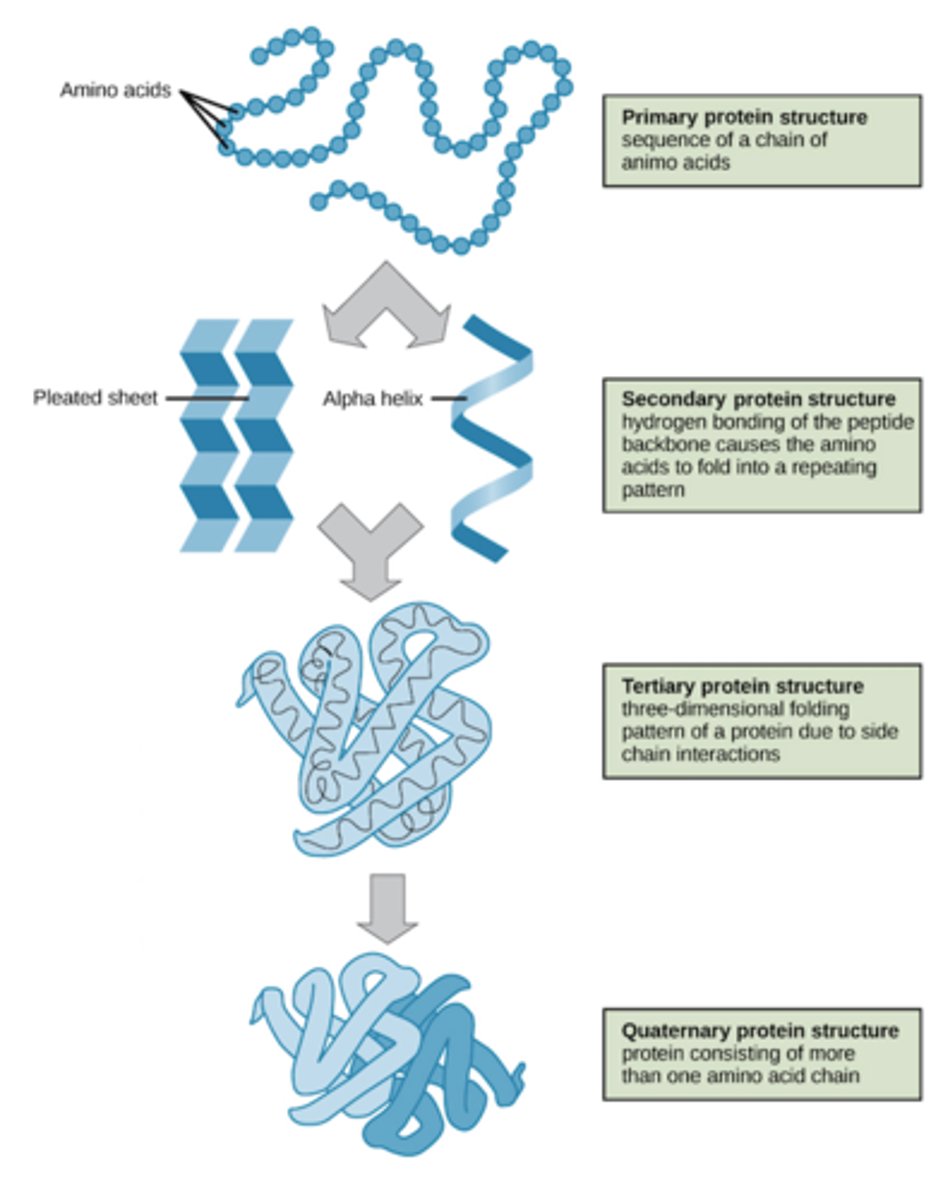
How many different amino acids are there?
20
Elements of Nucleic Acids
Carbon (C)
Hydrogen (H)
Oxygen (O)
Nitrogen (N)
Phosphorus (P)
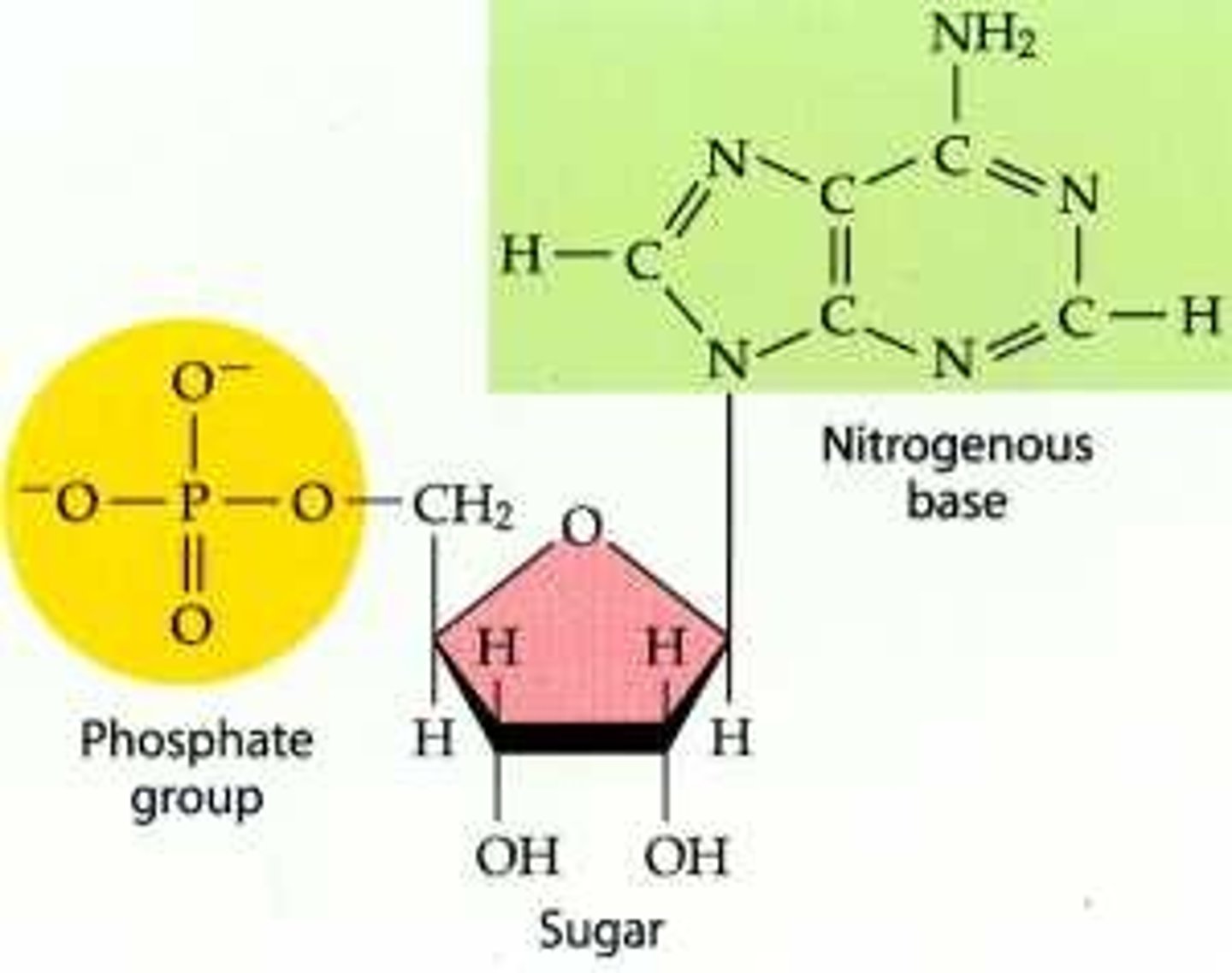
Building blocks of Nucleic acids
Nucleotides - Nucleic Acids
5-carbon sugar: Deoxyribose in DNA or ribose in RNA
Phosphate group
Nitrogenous base
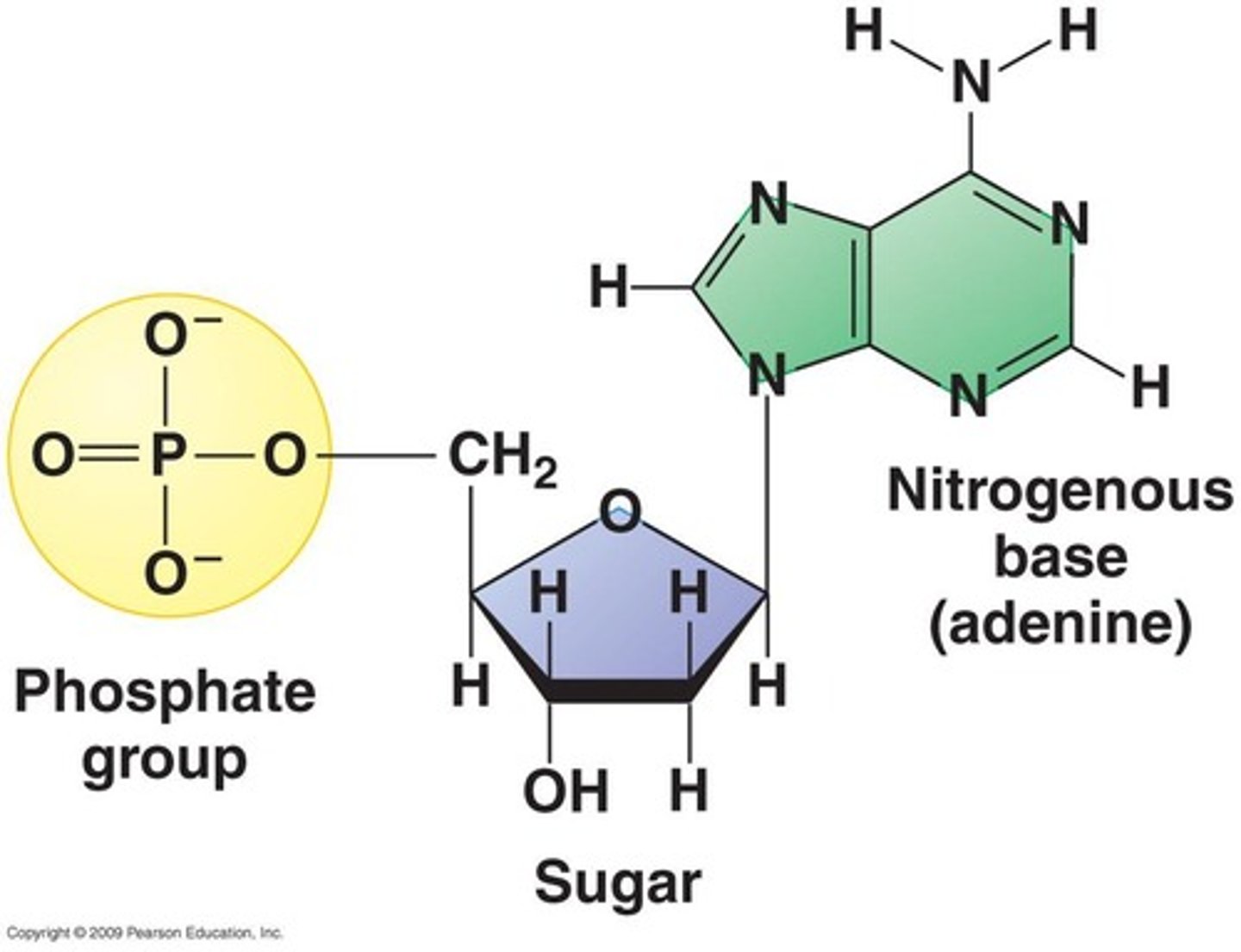
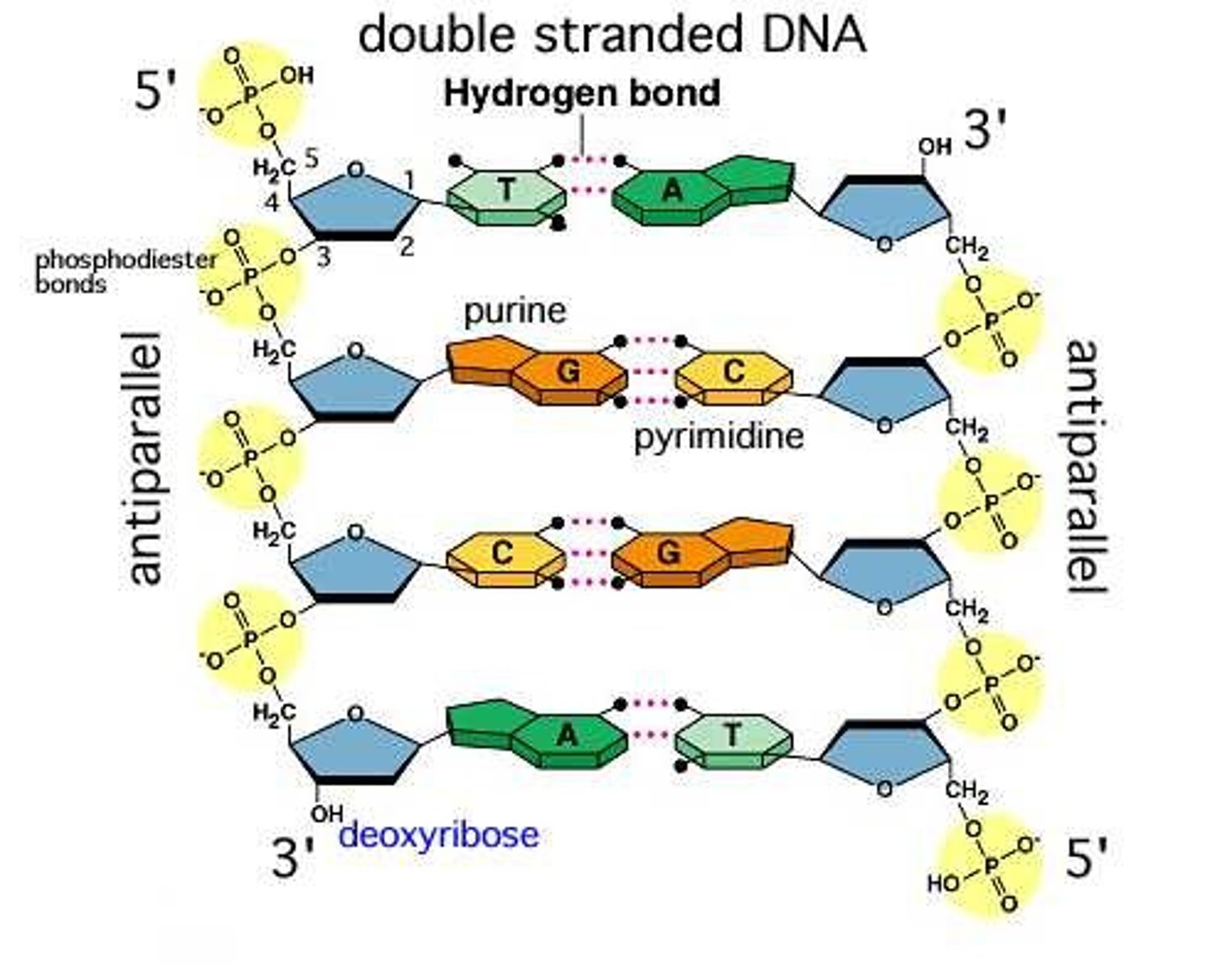
Nucleic Acid Bases (DNA vs. RNA)
DNA: A-T C-G
RNA: A-U C-G
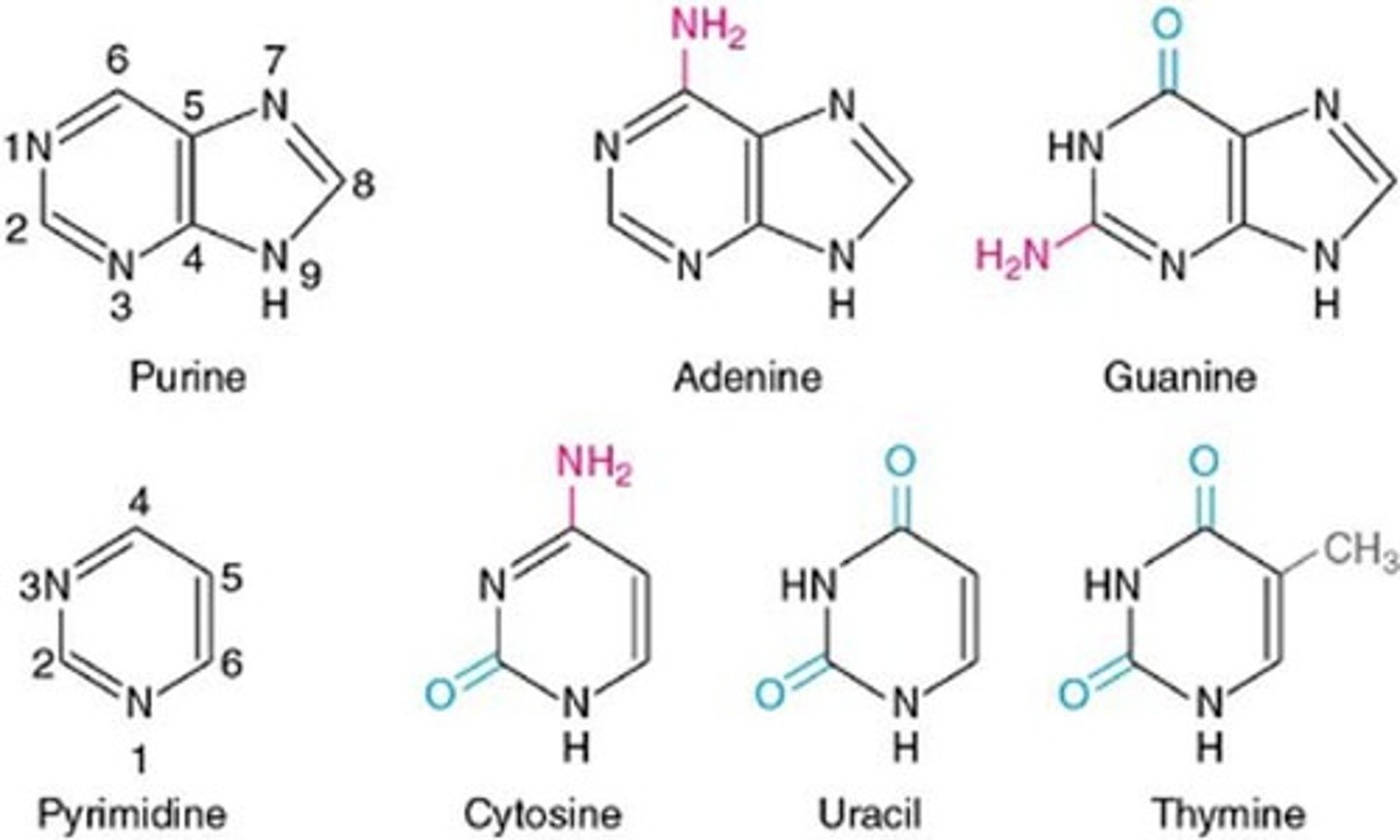
Purines VS. Pyrimidines
Purine: Double ring with 2 hydrogen bonds (Adenine and Guanine)
Pyrimidines: Single ring with 3 hydrogen bonds (Cytosine, Uracil, Thymine)
DNA function
DNA:
- Stores genetic information
- transmits genetic information
What bonds form nucleotides?
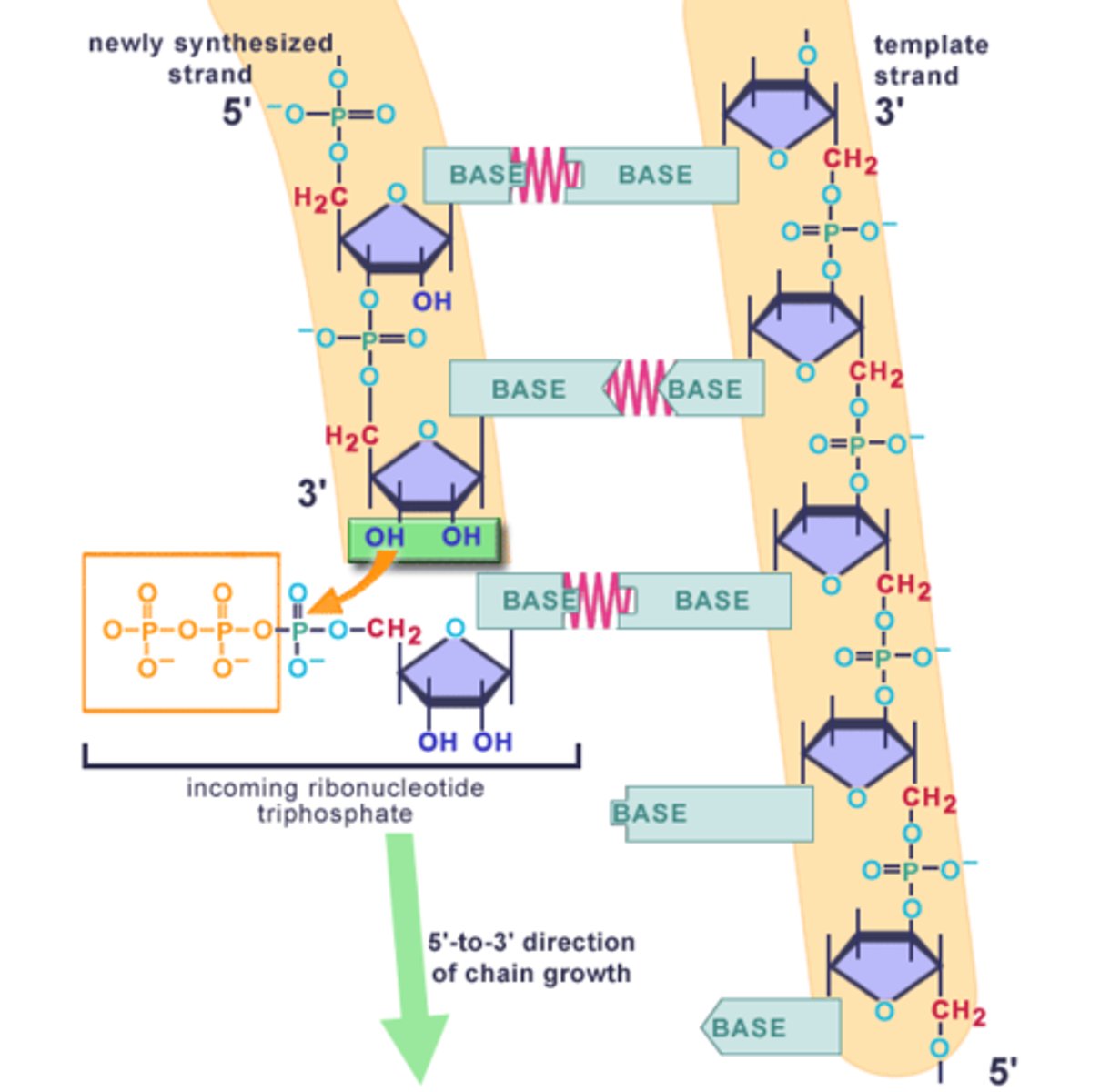
Phosphodiester bonds (think of phosphate group)
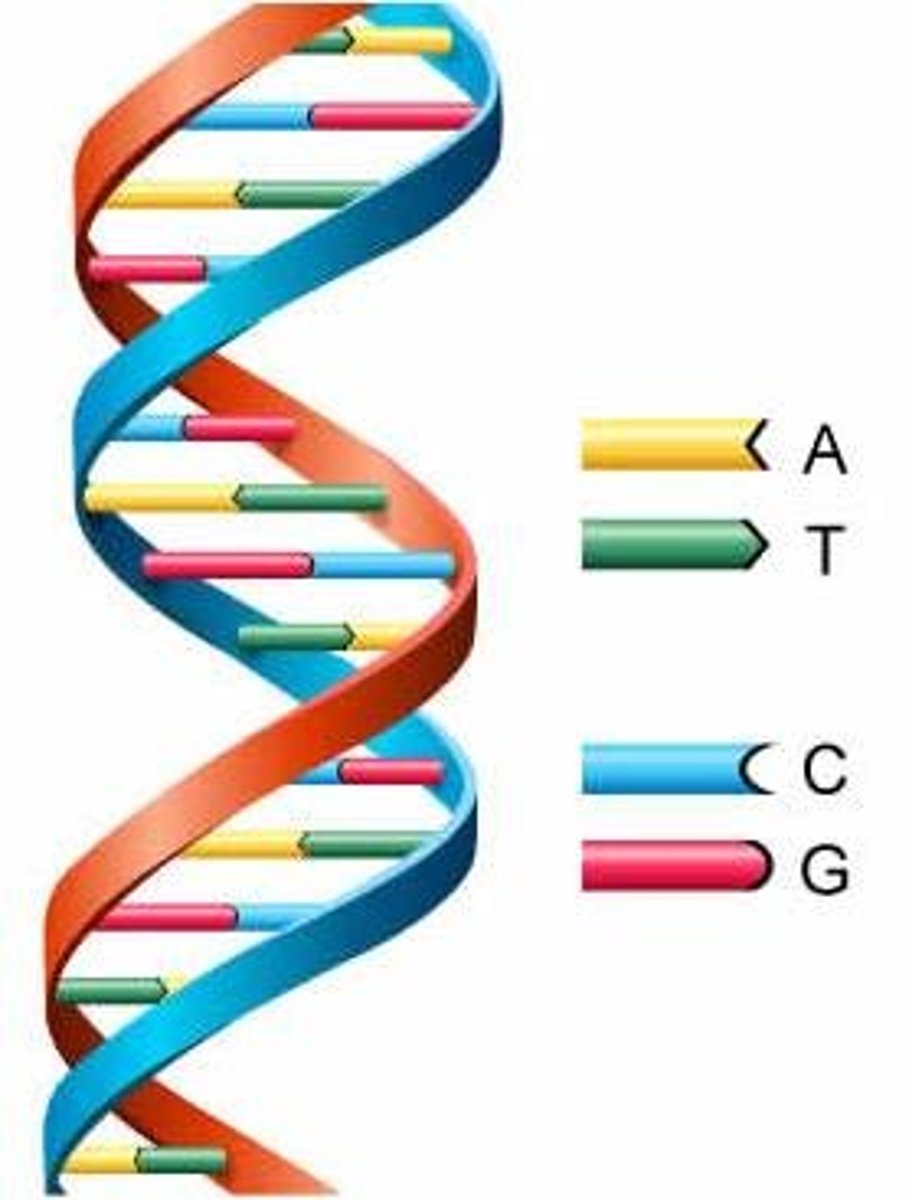
DNA strands have what type of arrangement?
Directionality Polarity (5'-3' and 3'-5')
DNA Synthesis
Nucleotide with 3 phosphate groups (nucleotide triphosphate) joins a growing chain
Structure of DNA
Double Helix (two chains) stands are antiparallel
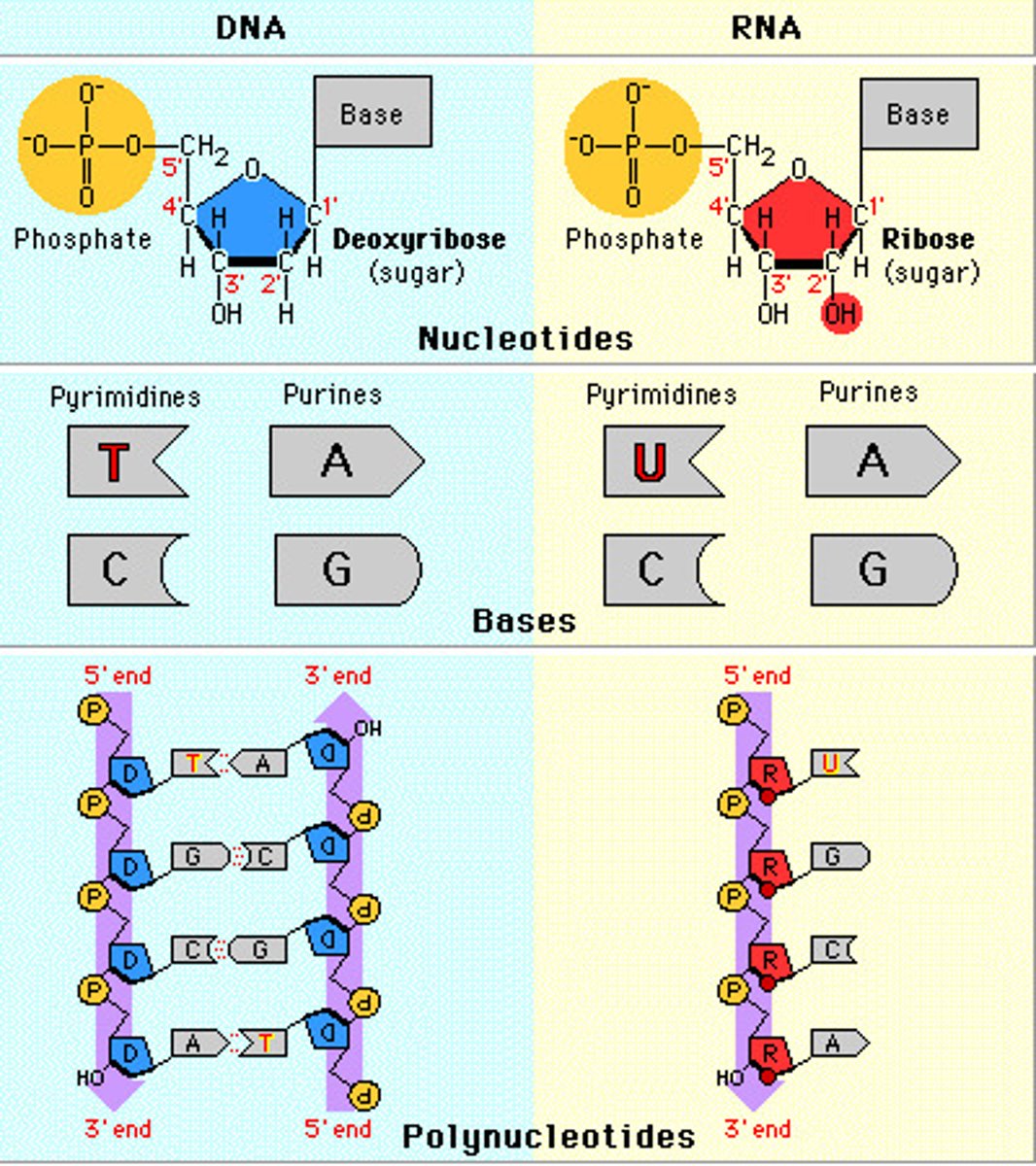
DNA vs RNA
DNA:
- Sugar is Deoxyribose
- Hydrogen (H) at 2'
- Double strand
- A-T C-G
- Longer
- Store/Transmit info
RNA:
- Sugar is Ribose
- Hydroxyl (OH) at 2'
- Single strand
- A-U C-G
- Shorter
- intermediate between DNA and protein
BOTH:
- Nucleic acids
- Directionality polarity
- Phosphodiester bonds
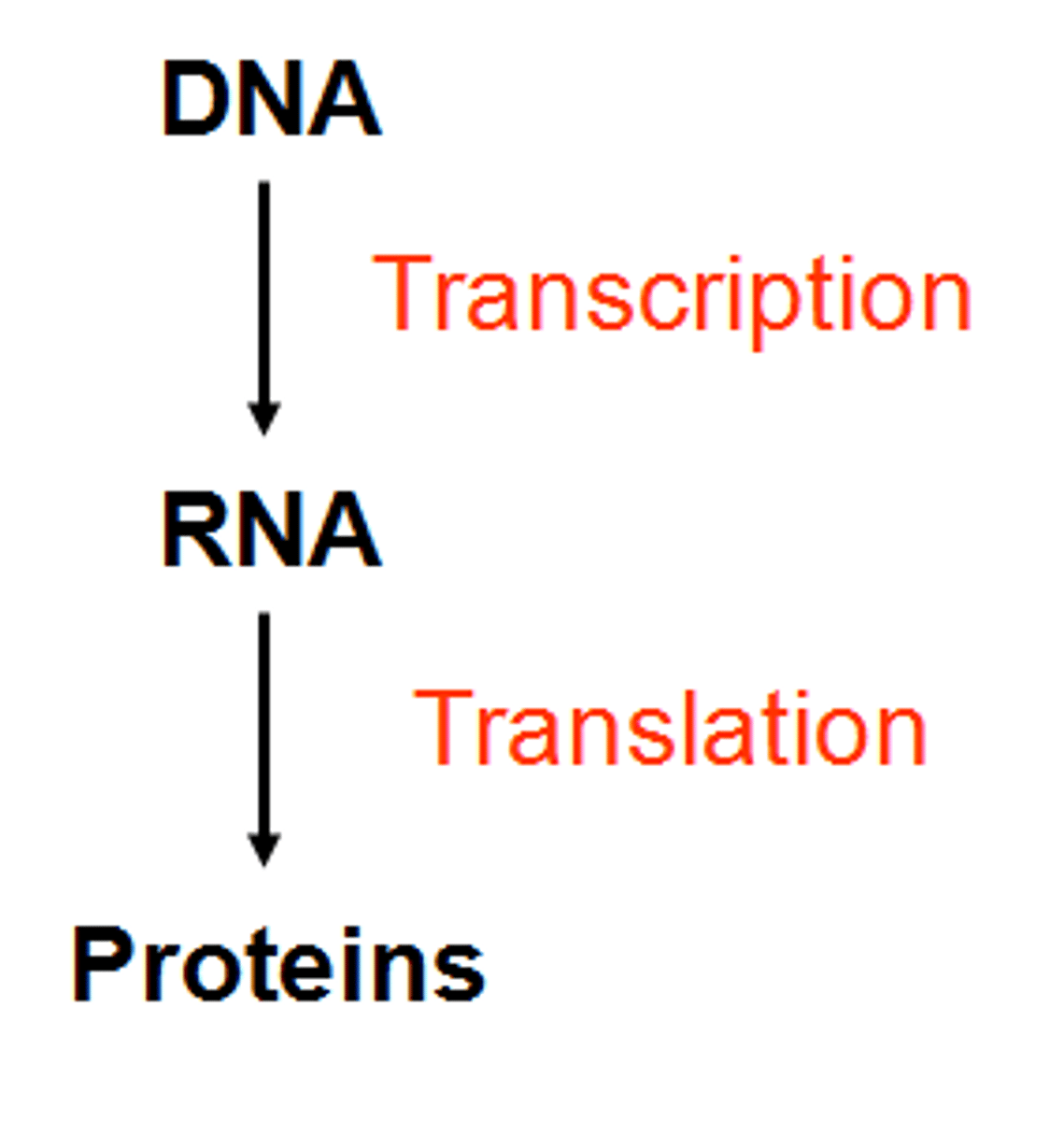
Central Dogma
Flow of info in a cell from DNA to RNA to
Protein
functional groups pg.68
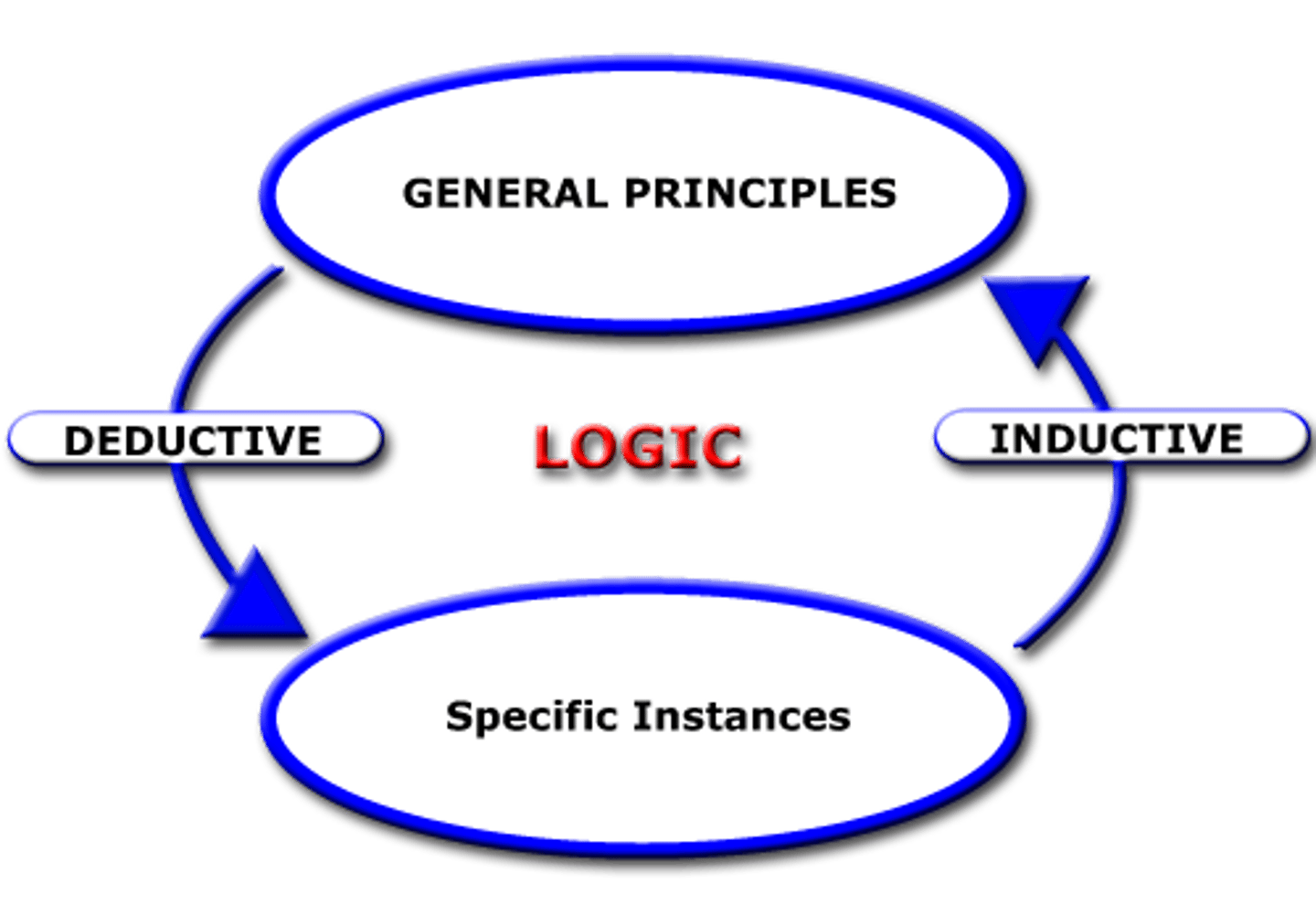
Inductive Reasoning
Use results to create principles
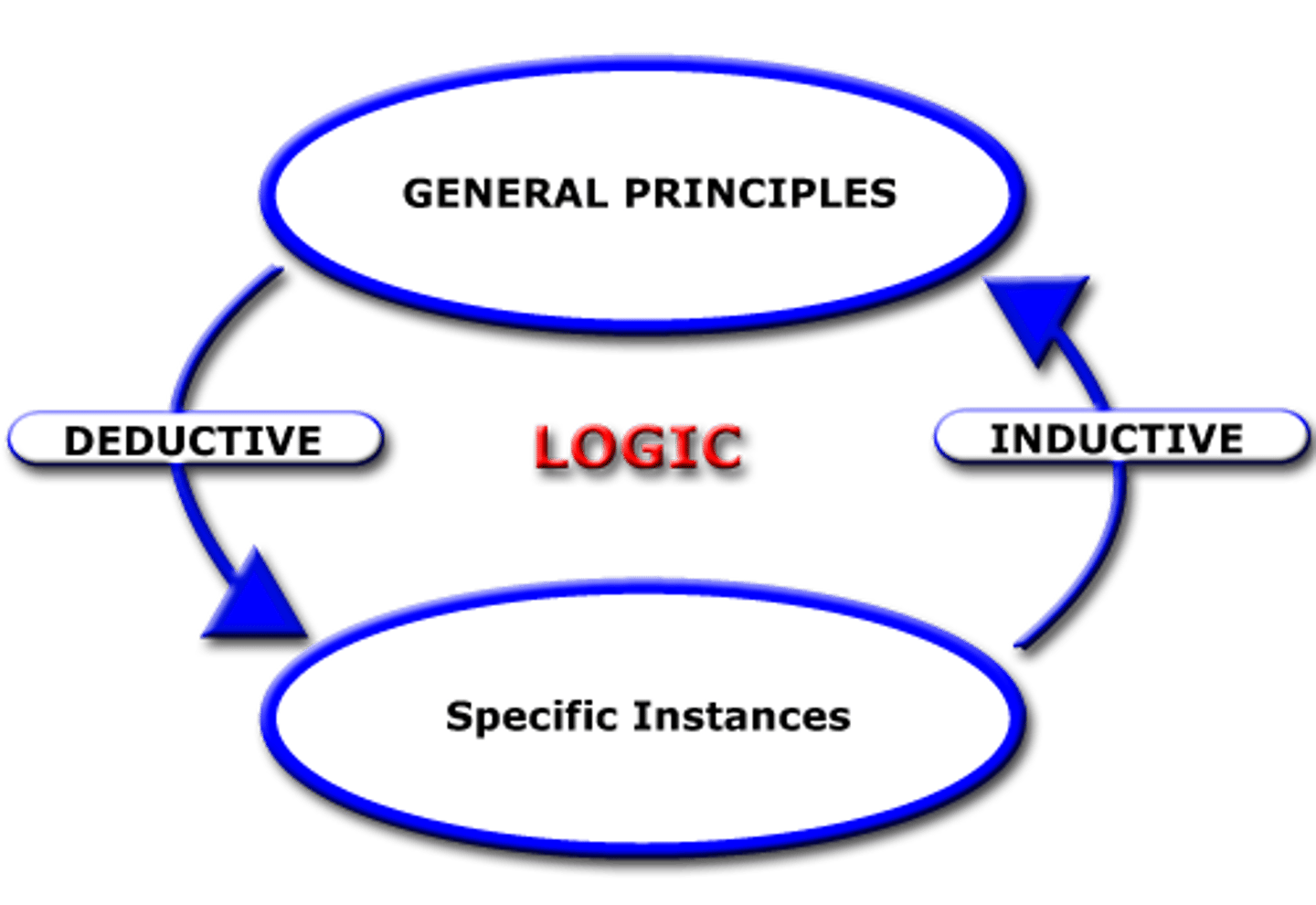
Deductive Reasoning
Logical reasoning to predict results by using principles
Control Group
Every feature of the experimental group except except what is hypothesized
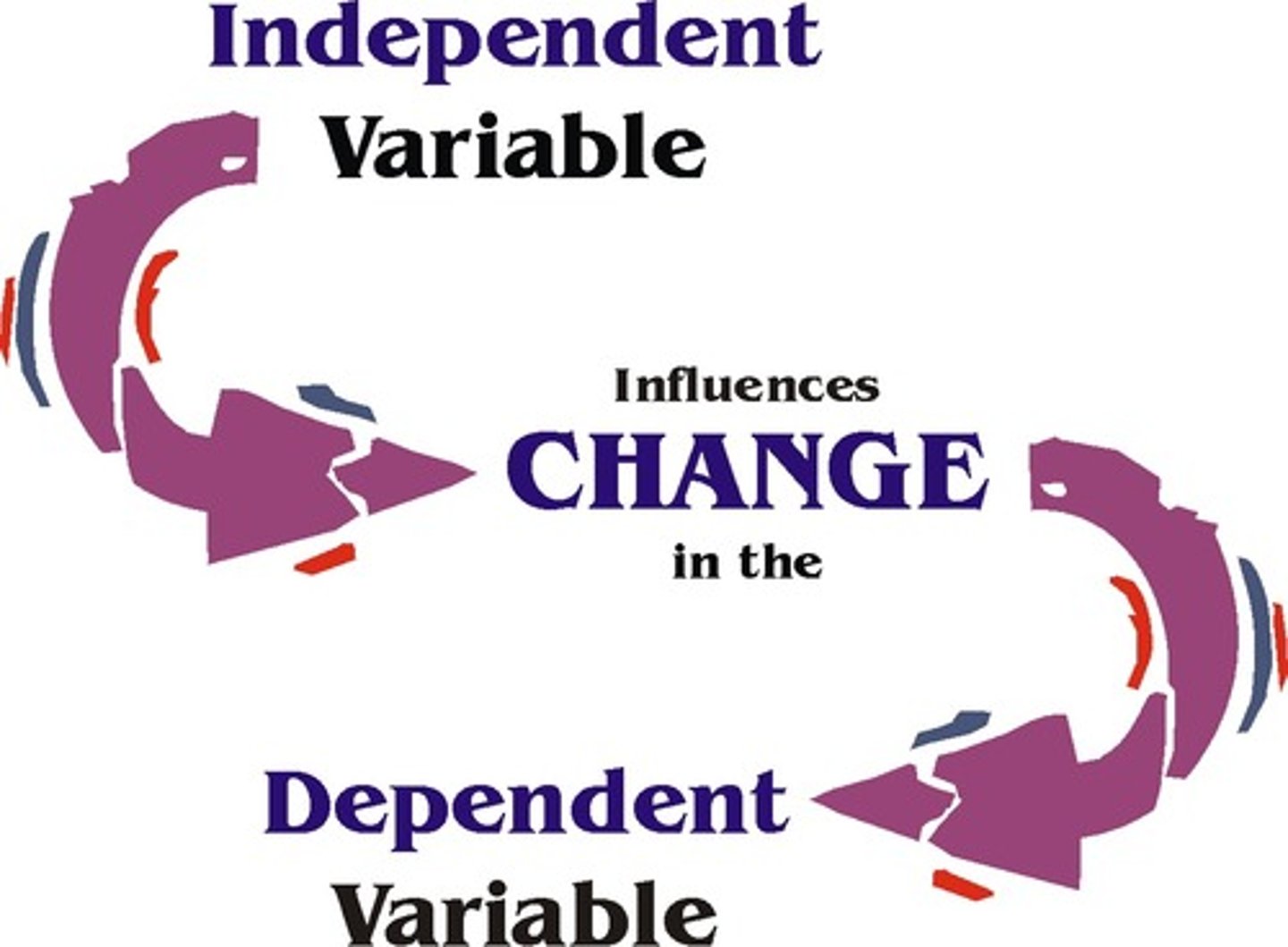
Variable (Independent/Dependent)
Part of the experiment that can vary or change
Theory
Tested and confirmed explanation for observations

Hypothesis
Suggested explanation for an event (can be tested)

Define Life
Order, Sensitivity, Response to stimuli, reproduction, adaptation, growth/development, homeostasis, energy processing, evolution
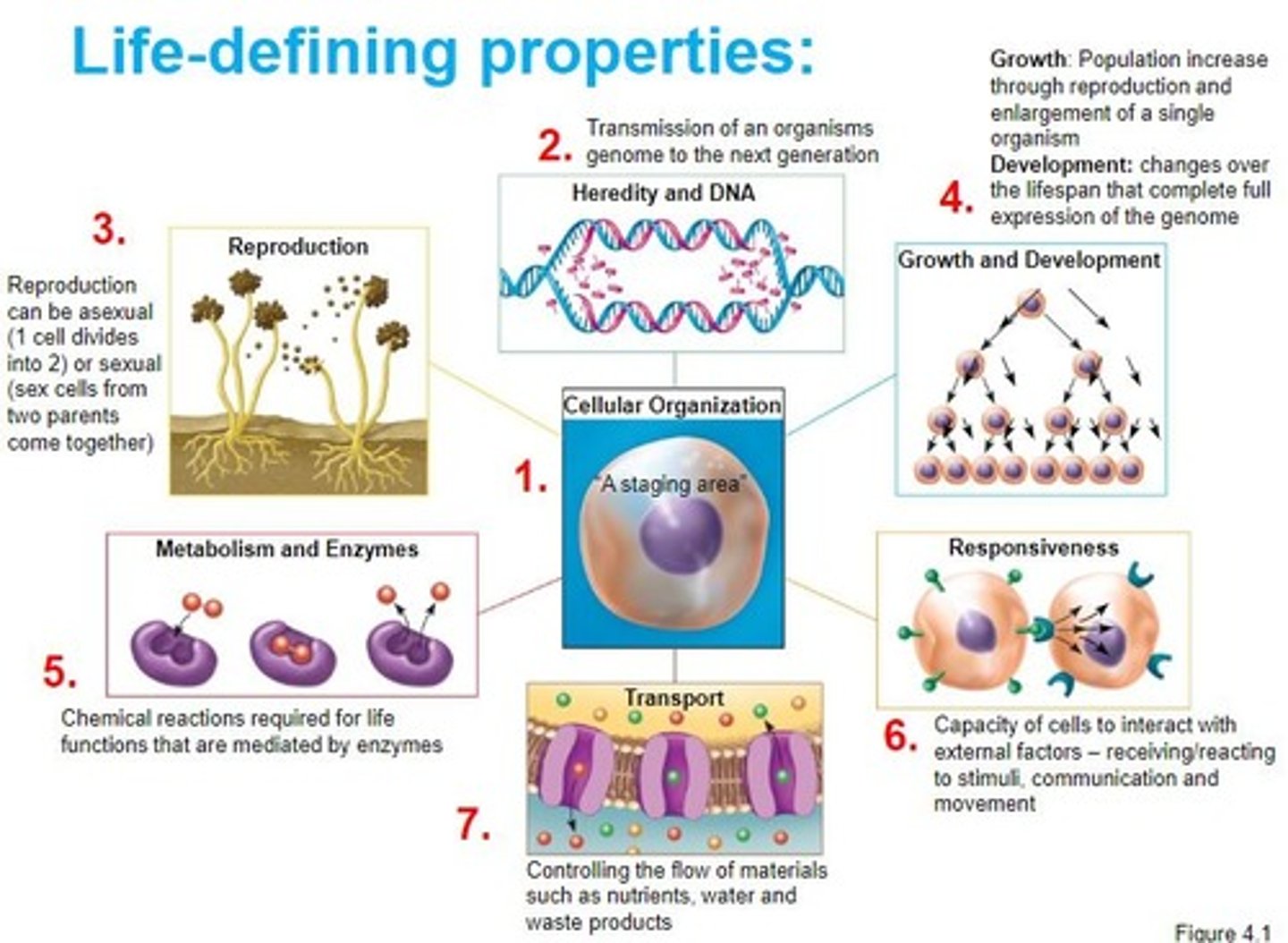
Order
Atom - Molecule - Cell - Cell organelle - Tissue - Organ - Organ system - Organisms - Population - Community - Ecosystem - Biome - Biosphere