Business Unit 1 (copy)
1/119
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
business
any organization that seeks to provide goods and services to others while operating at a profit. takes input, adds labour and materials to make an output
consumer goods
Tangible items produced for personal use. Can be durable or non durable (used once alone or more than once)
customer
people or organizations that buy a product or service
consumer
A person or organization who purchases goods and services to USE
consumer services
Non-tangible products that are sold to the general public and include hotel accommodation, insurance services and train journeys
capital goods
goods that are used in producing other goods, rather than being bought by consumers.
land/physical (factor of production)
the type and amount of resources, space and machinery, and natural resources needed to run a business
Labour (factor of production)
including skilled and unskilled labourers that make up the workforce
capital/finance (factor of production)
the money needed to set up a business/operate it on a daily basis
Enterprise (factor of production)
the driving force behind the 3 other factors, including the ability to manage, direct, communicate, coordinate and risk take
marketing (business function)
involves the process of creating, designing, promoting and selling their product. they appeal to consumer desires
finance (business function)
manages the org money; planning, organizing, auditing, accounting for, and controlling its company's dollars; and produces statements.
human resources ( business function)
recruits, selects, evaluates, trains, motivates, schedules and dismesses employees.
Operations Management/Production (business function)
A specialized area in management that converts or transforms resources (including human resources) into goods and services.
Primary sector
The portion of the economy concerned with the direct extraction of materials from Earth's surface, generally through agriculture, although sometimes by mining, fishing, and forestry.
Secondary Sector
The portion of the economy concerned with manufacturing useful products through processing, transforming, and assembling raw materials. Like clothing, construction and phones
Tertiary Sector
The portion of the economy concerned with transportation, communications, and utilities, sometimes extended to the provision of all goods and services to people in exchange for payment. Ex) retail, transport, tourism, banking, telecommunications
Quaternary Sector
Service sector industries concerned with the collection, processing, and manipulation of information and capital. Examples include finance, administration, insurance, and legal services.
sectoral change advantages
GDP and standard of living increase, less imports and more outputs, more jobs, more taxes to government
sectoral change disadvantages
mass migration causing housing and social issues, factory pollution increase, walmart effect
enterpreneurship
individuals with the RISER abilities (risk taker, innovative, strategic, enthusiastic and resilient)
sourcing capital/finance for a business
-friends and family -banks, bank loans or liabilities -venture capitalists -government grants -personal loans
Issues when starting a business
-lack of finance -lack of research -location -poor cash flow -not developing a customer base or brand loyalty -lack of experience
business plan (bp)
an offical document detailing organization, its proposals for reaching its objectives and goals. Can be used to secure external finances
private sector
organizations owned by individuals and not the government. usually aims to make a profit
public sector
businesses run or directed by the government, that have no outside shareholders and do not publish their financial info. STILLS STRIVE FOR MONEY TO KEEP RUNNING. ex) infrastructure, healthcare, education and emergency services
sole trader/proprietor
A business owned by one person who provides all capital, other than loan capital; they have complete control over decisions and unlimited liability.
Sole trader advantages
-Owner keeps all the profit -Owner can make decisions quickly -complete control, financially, creatively and get to choose their work hours -easy setup with not a lot of legal formality -easier to establish personal relations with clients -can be based on interests and skills
Sole trader disadvantages
-Unlimited liability (held solely responsible, without excuse of the business) -Difficult to take holidays, longer hours -High risk so hard to borrow from banks -competition with multinational companies -if owners dies, business dies with them
Partnership
A business in which two or more persons combine their assets and skills. Caps at 20 unless specialized. A silent partner is one who only provides finance
Partnership Advantages
-partners may specialize, shared decision making -More capital available, losses are shared -Relatively easy to start -Income taxed once as personal income
Parternship disadvantages
-unlimited liability unless an LLP (means one of the partners is held responsible alone) -profits are shared -bound by each others decisions -if one owner dies, it ends
limited company
A business organisation which has a separate legal identity from that of its owners. Ownership is divded into units called shares, thus granting limited liability. Required to post finance info publicly
private limited company
A small to medium sized business that is owned by a few shareholders. Shares must be sold privately and other shareholders must agree. Cannot be sold on stock market
private limited company advantages
-limited liability -more capital raised -cannot be lost to public -continues after death
private limited company disadvantages
-profit is shared -big legal procedure to setup -firms not allowed shares to raise capital -finance info public, so it can be inspected by the government and rivals. thus giving an advantage
public limited company
-STILL A PRIVATE COMPANY despite the name -can sell shares, if transitioned it must go through and IPO (initial public offer)
public limited company advantages
-lots of money can be raised -lower production costs -can dominate markets due to size -banks and other external financers are more willing to invest usually
public limited company disadvantages
-setting up is expensive and formal -possible for an outsider to take complete control -inability to deal with customers personally -inflexible due to size -guided by acts to protect shareholders, rather than consumer or employee rights
Non-profit social enterprises (NPO)
Social enterprises that do not aim to make a profit at all, instead they generate surpluses. ex) charities and pressure groups
non-governmental organization (NGO)
Private organizations that pursue activities to relieve suffering or other humanitarian issues
for profit social enterprises
Have a social mission but still aim to make a profit, and compete with rival businesses.
cooperatives (co-ops)
Organizations composed of individuals or small businesses that have banded together, through a membership program. includes financial, housing, worker, producer and consumer coops
microfinancers
Businesses in low income economies that provide small amounts of finance to those in need. Loans with restrictions and scheduled repayments
private-public partnership
A business venture created between private and public sectors in order to produce something. Usually, the public provides finance while private provides experient and expertise.
mission statement
outlines the day-to-day practices a business achieves in order to inspire employees and stand out from competition. More practical and leads to creation of goals, aims and objectives
vision statement
expresses what the organization should become, where it wants to go strategically. A dreamier, broader statement
aims
Long-term plans of the business from which its corporate objectives are derived. are general but can be measureable with results and success
objectives
Specific, short-term statements detailing how to achieve the organization's goals. Follows the SMART guidelines
Corporate objectives
More specific then aims, but act as a guide for management and strategy. Can be measured with numbers and usally involve growth, survival, profit, etc
strategies
Are the actions a business uses to reach its long-term organizational aims and corporate objectives. Decided by executives
tactics
Short term approaches to achieving tacial and operational objectives
the objective hierarchy
aims > objectives > strategies > tactics
STEEPLE
social, technological, economic, environmental, political, legal, ethical
ethics
the moral principles that guide decision making and strategy, whether used or not
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
a business's concern for society's welfare and its actions to help with it.
CSR advantages
-can improve reputation -may attract dedicated employees -no target from pressure groups -increased goodwill of stakeholders -can factor into long term profit
CSR disadvantages
-short term cost increase, may make shareholders reluctant -if not properly executed, can have backlash -competitive disadvantage as spending money -ethical dilemmas internally and externally about whatever the CSR is demonstrating
social audits
Reports on ethical and social stance of a business. Essentially how its behaviours match with ethical objectives
Strength examples (SWOT)
INTERNALLY, things they do, well known for, make the most money, reputation, lead confidence in the market
Weaknesses examples (SWOT)
INTERNALLY, things they do poorly, poor reputation, losses, complaints, hardships, etc
Opportunity examples (SWOT)
EXTERNAL, directions created by their strengths, changing customer preferences, new tech, new laws, etc
Threat examples (SWOT)
EXTERNAL, activites of competitors, falling profits, change of customer preference, lack of rigour, lack of adapation
SWOT analysis advantages
-quick, simple and easy to create and understand -wide application range -encourages foresight and proactive thinking
SWOT analysis disadvantages
-simplistic, less detailed -short 'shelf life' -cannot be used, should be used in conjunction with other analysises to be effective -only works with pure honesty (esp weaknesses and threats)
Ansoff's Matrix
A graph demonstrating 4 generic growth strategies for business growth
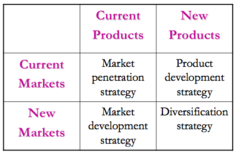
Ansoff's Matrix - market penetration
Growth focusing on developing existing products in existing markets, and is the least risky growth strategy. ex) loyalty reward cards, ad campaigns, sales
Ansoff's Matrix - market development
Growth focusing on selling existing products to new markets, and is around medium risk. ex) Nestle expanding into pet foods in India
Ansoff's Matrix - product development
Growth focusing on selling new markets to the same markets, and is medium risk as it relies on the differentiation between products to be worth it. ex) Apple releasing iPhones each year
Ansoff's Matrix - Diversification
Growth by selling new products in new markets, making it the riskiest form of growth. There are 2 types, related and unrelated. Related = in the same industry but new product, like Coke moving to energy drinks. Unrelated is a new industry, like HK McDonald weddings.
stakeholders
people or groups who can be affected by an organizations actions, and therefore have an interest in them. there are two types.
internal stakeholders
-employees (dependent on business and pay) -managers, directors -owners, shareholders, execs
external shareholders
-customers -suppliers -banks -pressure groups -competitors -government
stakeholder conflict
When different stakeholder groups have different aims and objectives, which conflicts will arise as decisions cannot satify all stakeholders.
stakeholder conflict - compromise
stakeholders making considerations for others. ex) workers improve productivity for higher wages ^ this is also called profit related pay
stakeholder conflict - conciliation
a service that aligns the needs of stakeholders
stakeholder conflict - arbitration
a 3rd party that listens to conflicts, and forms a decisions. all parties agree to listen to the party
stakeholder conflict - worker participation
involves employees having a direct voice in how things are operated. similar to share ownership schemes
stakeholder conflict - public relations
communicates news about the organization through the media, keeping them informed and faster as well
stakeholder mapping
provides a systematic way to identify the expectations, needs, importance, and relative power of various stakeholders
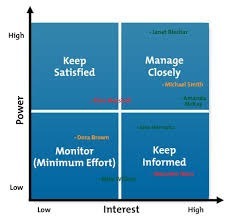
stakeholder mapping - monitor (Group A)
Neither powerful or with a high level of interest it is therefore only necessary to make a minimum amount of effort with this group
Low power/Low interest
stakeholder mapping - inform (Group B)
Make this group feel included, which is vital. Newsletters, events, ads and more are useful
low pwr/ high interest
stakeholder mapping - satisfy (Group C)
Must keep satifised, as they have power to influence all other groups. Flatter them!
high pwr/ low interest
stakeholder mapping - key players (Group D)
Most important, so communicating and consulting is critical before major decisions. Focus on their needs and priorities the most
high pwr / high interest
fiscal policy tax increases
an economic factor in which higher taxes are placed on consumers buying luxury based products. also includes possibility of increased corporate tax
interest rates
an economic factor that may increase or lessen the chance of a customer buying a product, as interest rates influence a customers money
economies of scale
when is a business benefits from lower average costs (costs per unit) from increasing in size. think of MORE BANG FOR YOUR BUCK! ex) if a business orders a lot from a supplier, they may get a bulk purchase discount. works better if the business knows they can sell all of it with the bonus included!
optimal output level
When average cost is at its lowest value, because profit is maximised
average cost = total cost/quantity produced (AC=TC/Q)
total cost of production
the sum of fixed and variable costs TC= TFC + TVC
internal economies of scale
Occurs in specific organizations as it grows, not the entire industry ex) banks giving low interests to big businesses as they are lower risk
External economies of scale
The cost benefits that all firms in the industry can enjoy when the industry expands as a whole. ex) locations w/ specialist labours, like NYC Wall Street for bankers, financers and investors.
diseconomies of scale
the situation in which a firm's long-run average costs rise as the firm increases output.
internal diseconomies of scale examples
-communication becoming non-personal and harder to speak to all stakeholders -workforce alienation, meaning employees feel less connected and valued, lowering morale and productivity -coordination difficulties
external diseconomies of scale examples
-overcrowding, causing traffic congestion and delays -rent increasing as land is in high demand, and with much more land than average -labour having higher costs due to shortages in urban areas
Internal (organic) growth
When a business grows internally, using its own resources to increase the scale of its operations and sales revenue
External growth
Business expansion achieved by means of merging with or taking over another business, from either the same or a different industry. Faster than organic growth, but riskier and more expensive
Acquistion
Involves one business buying controlling interest (majority shares) in another company.
Takeover
Is an acquisition but is often hostile, or a publicly traded company gets swept lol
Merger
Combination of two or more companies into a single, larger firm. Benefits from economies of scale
horizonal integration (M&A)
When a merger, acquisition or takeover occurs between companies within the same industry ex) Facebook buying Instagram in 2012