Chapter 11 Flashcards
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Chromatin
the loose form of DNA decondensed- associated with histone proteins
Chromosome
consists of a long, thin DNA molecule that contains the genetic information for the organism (condensed DNA)- associated with histone proteins
Histone proteins
positively charged proteins that bind to DNA (which is negatively charged) in the nucleus of a cell to help organize and compact it
Diploid
2n (2 sets/copies) copies of each chromosome, one copy inherited from each parent (in humans, that’s 46 chromosomes total, 23 from each parent)
n= number of chromosomes
Haploid
1n (1 copy/set) of each chromosome (23 chromosomes total in humans)
Sister chromatids
identical copies of a chromosome that are joined together at the centromere
Homologous chromosomes
a pair of chromosomes similar in size/shape and carry the same genes but can have different alleles (versions of specific genes)
Centromere
where the chromatids are held together
Spindles
organelles composed of protein microtubules
they function in moving chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis
Somatic cells
all the cells of the body that are not specialized for reproduction (contain 2 sets of chromosomes, one set from each parent)
Chiasma
location on homologous chromosomes where crossing over occurs
Synapsis
process where homologous pairs align their DNA sequences at similar alleles
Independent assortment
the random alignment of homologous chromosomes at the metaphase plate during metaphase I of meiosis
How do prokaryotes divide?
Binary fission:
the cell grows in size, replicates its DNA, and then separates the cytoplasm and DNA into two new genetically identical daughter cells
Binary Fission Steps
DNA replication: When a cell divides, its chromosome (most prokaryotes have just one main chromosome) must be replicated, and each of the two new daughter cells must receive a copy
DNA segregation: When replication is complete, the two daughter DNA molecules separate and segregate from one another at opposite ends of the cell
Cytokinesis: the cytoplasm divides and a protein called FtsZ pinches the cell in half, which separates the DNA molecules into 2 genetically identical daughter cells. each daughter cell has the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell (clones)
FtsZ is in prokaryotes only!
What are the phases that a eukaryotic cell passes to produce daughter cells by cell division?
G1, S, G2, and M
The M phase includes mitosis and cytokinesis
The other three phases together make up interphase
Interphase
typical cell functions occur, including DNA/chromosome replication
G1 phase
cells grow in volume and carry out their normal functions
S phase
DNA replication (duplicating its chromosomes each into 2 sister chromatids)
G2 phase
continues growth and carrying out normal functions, spindle synthesis begins, and prepares for mitosis and cytokinesis.
G0 phase
cells do not divide again once they reach maturity
the resting phase or gap phase, is a cellular state outside of the cell cycle where cells are not dividing or preparing to divide
ex: nerve (neurons) cells and heart cells
Mitosis
the separation of chromosomes, resulting in diploid cells (2 genetically identical daughter cells)
Prophase (mitosis)
condensation of sister chromatids
centrosomes migrate to opposite poles of the cell which allows microtubules to begin to form mitotic spindles
the nuclear membrane breaks down
the nucleolus disappears from the nucleus.
Metaphase (mitosis)
mitotic spindles align chromosomes in the middle of the cell in a line
Anaphase (mitosis)
sister chromatid pairs are pulled apart by the spindle fibers.
the separated chromatids (daughter chromosomes) move toward opposite poles (to opposite ends of the cell)
Telophase (final step of mitosis)
chromosomes begin to uncoil (revert back to their lose form- chromatin)
mitotic spindle degrade
nucleolus, nuclear envelope, and nuclear membrane reassemble
forms 2 nuclei
Cytokinesis (mitosis) + in plants and animals
the cytoplasm divides and the 2 nuclei become separated into the 2 daughter cells (the actual separation process). each daughter cell is genetically identical to the parent cell (clones)
In plant cells, a membrane called the cell plate forms in the center to divide the nuclei
In animal cells, the cell membrane pinches the cytoplasm into 2 equal parts (cleavage furrow) to divide the nuclei
Image of Mitosis Process
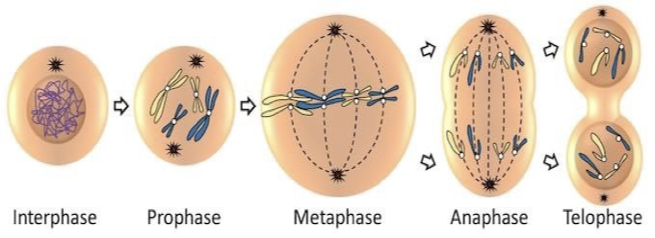
Cell division (Mitosis) is a normal part of an organism’s:
growth and development
asexual reproduction (reproduction without gametes)
repair and regeneration of damaged tissues
Meiosis
sexual reproduction that produces 4 haploid daughter cells that are not genetically identical to the diploid parent cells, with each carrying half the amount of DNA as the original parent cells
1 diploid parent (results from mitosis) → 4 haploid daughter cells
Meiosis reduces the chromosome number by half, transitioning from a diploid cell (containing two sets of chromosomes) to a haploid cell (containing one set of chromosomes).
Asexual reproduction
involves only mitosis (become clones of a single parent organism)
Sexual reproduction
involves both mitosis and meiosis. it increases genetic diversity
Gametes
the mature sexual reproductive cell: the egg or sperm, produced by meiosis (each parent contributes one gamete to their offspring- egg or sperm)
Human gametes are haploid since they have one copy of every chromosome
Fertilization
the process of merging 2 haploid gametes (egg and sperm fusion), producing a diploid cell
Zygote
the very first diploid (2n) cell of a newly developing organism
Meiosis has three main effects:
It reduces the chromosome number from diploid (2n) to haploid (n) → aka by half
It ensures that each of the haploid products has a complete set of chromosomes
It generates genetic diversity among the products
Meiosis occurs in 2 separate stages:
Meiosis 1: reduction division – diploid cells divide into 2 haploid daughter cells 2N -->1N
Meiosis 2: Separates the sister chromatids. 2 haploid cells divide, producing 4 genetically different haploid daughter cells 1N -1N that will develop into egg or sperm.
Meiosis 1 Process:
Prophase 1: recombination and crossing over: Homologous chromosomes condense and pair up closely (synapsis- adhering along their lengths), allowing for a process called "crossing over" where parts of the chromosomes exchange genetic material (DNA) between the maternal and paternal chromosome pairs, resulting in new allele combinations and genetically different chromosomes
Metaphase 1: The spindle attaches to chromosomes, lining up the pairs of homologous chromosomes in the middle. They are independently and randomly assigned. Independent assortment results in an enormous amount of possible genetic combinations
Anaphase 1: Homologous chromosomes separated to opposite ends
Telophase 1: Chromosomes arrive at opposite poles and uncoil. 2 new nuclear membranes form
Cytokinesis 1: the cytoplasm divides, forming 2 haploid daughter cells
Meiosis 2 Process:
Prophase 2: chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane breaks down, spindle forms
Metaphase 2: Sister chromatids line up at the middle of the cell
Anaphase 2: Sister chromatids are separated, chromosomes move to opposite ends
Telophase 2: 4 new nuclear membranes form, cytoplasm divides, 4 genetically unique haploid cells
Cytokinesis 2: the cytoplasm divides, resulting in 4 total haploid daughter cells
Differences between Mitosis and Meiosis
(function, which cells they occur in, how many nuclear divisons occur in each, what types of cells do they produce and how much?)
Mitosis:
Growth, repair & asexual reproduction
Occurs in somatic cells
1 nuclear division
2 genetically identical diploid daughter cells produced
Meiosis:
Gametes for sexual reproduction
Occurs only in germ cells
2 nuclear divisions
4 genetically unique haploid gametes produced
Nondisjunction
the failure of sister chromatids to separate in meiosis II or homologous chromosomes to separate in meiosis I
Aneuploidy (which type of error is it + give its definition + ex.)
A type of nondisjunction
a condition in which one or a few chromosomes are either lacking or present in excess
ex: Klinefelter syndrome: a male with an extra X chromosome- both aneuploidy and trisomy
Trisomy (which type of error is it + give its definition + ex.)
A type of nondisjunction
has 3 chromosomes instead of the usual pair of chromosomes
ex: Down Syndrome (have an extra chromosome- chromosome 21)
ex: Klinefelter syndrome: a male with an extra X chromosome- both aneuploidy and trisomy
Monosomy (which type of error is it + give its definition + ex.)
A type of nondisjunction
a cell or organism with only one chromosome instead of the usual pair
ex: Turner syndrome: a female condition where there is only one X chromosome (both monosomy and aneuploidy)
Translocation
a piece of a chromosome may break away and become attached to another chromosome
Apoptosis
programmed cell death
Cells may no longer be needed (ex: connective tissue between fingers of a fetus)
Old cells are prone to genetic damage that can lead to cancer (ex: epithelial cells may be exposed to radiation and toxins; they live only days or weeks)
What error occurs that results in abnormal chromosome structures and numbers?
no separation of chromosomes in meiosis