materials definitions
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
metals
inorganic dense materials that conduct electricity and heat and are typically solids that are malleable and ductile with a lustrous appearance
ceramics
inorganic, non-metallic compound. Constituent atoms typically comprise metal and non-metal (oxygen, boron, carbon) which are wither covalently or ionically bonded to each other
metal properties
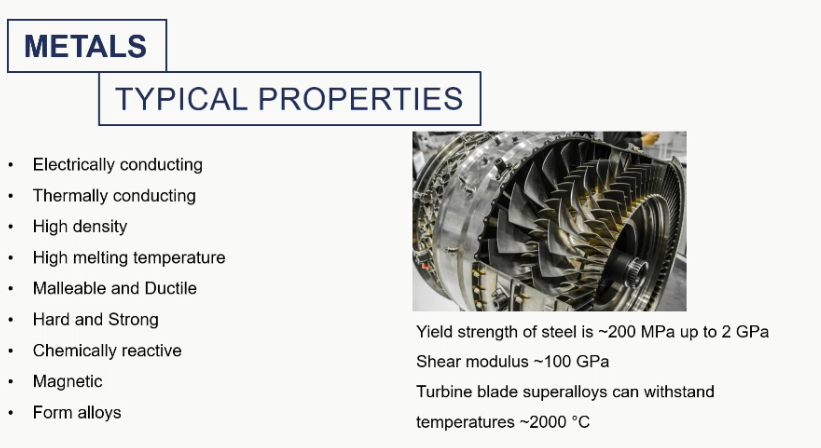

metal applications

ceramic properties

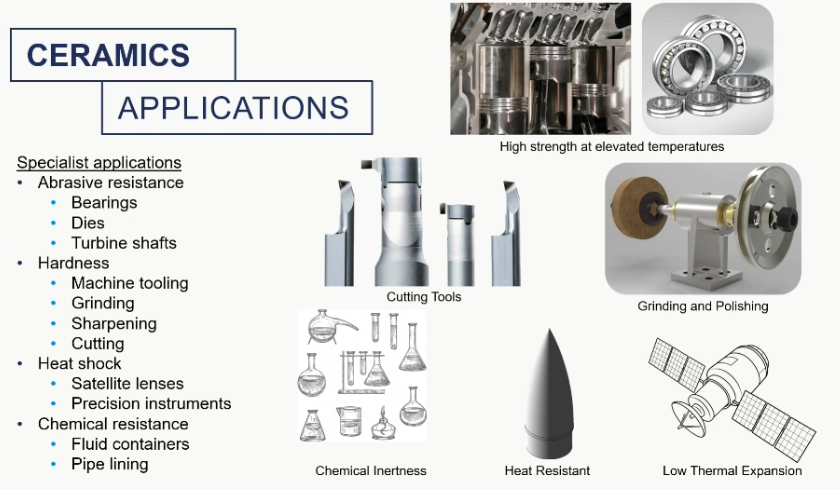
ceramic applications
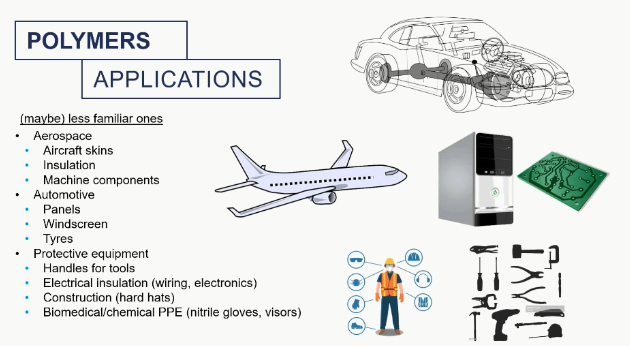
polymers
long chain (macromolecules) made up of repeat units, typically linked by covalent bonds between atoms
linear
branched
ring
stars
brush/comb
polymer properties

composites
composite material is composed of at least 2 materials, which combine to give modified, and superior properties to those of the individual constituents
composite properties

composite applications

phase diagrams
indicate the conditions at which different phases are found at thermodynamic equilibrium
phase
material with distinct chemical compositions and physical state
entropy S
measure of disorder. The number of ways to arrange the atoms in the material at a given temperature (T)
system internal energy (U)
total energy associated with all the bonds in the material
triple point
all 3 phases are in equilibrium (are are equally likely to be observed)
degrees of freedom
describes the number of independent variables that can be changed without affecting the equilibrium
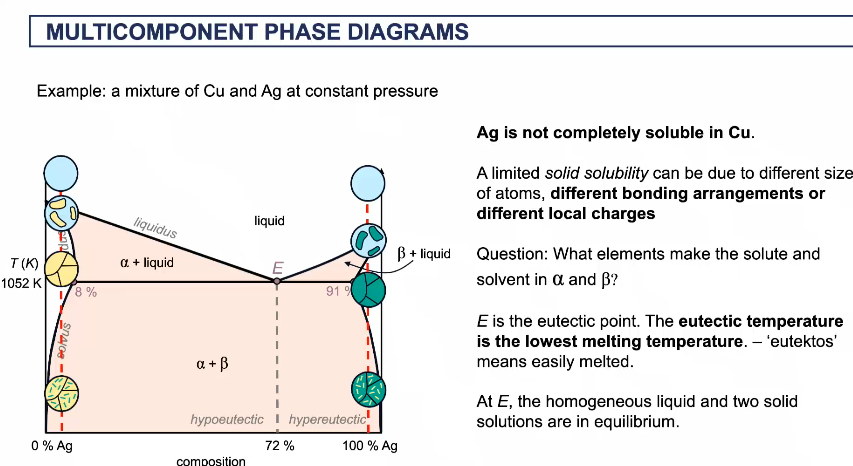
Eutectic point E
eutectic temperature is the lowest melting temperature (easily melted at that point)
seen in the phase diagrams
at E, the homogeneous liquid and 2 solid solutions are in equilibrium
precipitates
crystals of different phases can also form within crystalline solid solutions
crystals
in cooled liquids, the changes in free energy give rise to crystals
nucleation
emergence of a new phase and is rate determining
growth
the speed of which has a strong influence on microsturcture
continuous casting
is an efficient high through put process for producing large amount of metal products, by continuously pouring and solidifying molten metal into desired shapes
superior to ingot casting, as it has fewer defects and can be fed directly into the rolling mill
heat capacity
the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a material by 1 degree
quantifies how much energy can is absorbed/ released by the bonds in material
specific hear capacity
is the mass dependent heat capacity
enthalpy of fusion ( Hf)
provides the amount of heat energy required to change the state of a material from liquid to solid or solid to liquid
also known as latent heat/ heat of fusion
is negative when freezing (liquid to solid)
is positive when melting (soldi to liquid)