Cranium, Ventricles, and Meninges
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Neurocranium function
Protects brain
Neurocranium bones
Formed by 8 bones
4 singular bones - centered on the midline
Frontal
Ethmoid
Sphenoid
Occipital
2 sets of bones - bilateral pairs
Temporal
Parietal
Viscerocranium function
facial skeleton
Viscerocranium bones
Formed by 15 irregular bones
3 singular bones - in the midline
Mandible
Ethmoid
Vomer
6 paired bones
Maxilla
Inferior nasal conchae
Zygomatic
Palatine
Nasal
Lacrimal bones
Cranial Sutures
• Coronal
• Sagittal
• Lambdoid
• Squamous
Anterior Cranial Fossae lobes
◦frontal lobes
Middle Cranial Fossae lobes
◦temporal lobes
Posterior Cranial Fossae lobes
◦cerebellum & brainstem
Anterior Cranial Fossa bones
◦ Frontal bone
◦ Ethmoid bone
◦ Lesser wings of sphenoid
Foramina of the Anterior Cranial Fossa
Foramen Cecum
Cribriform Foramina
Anterior & Posterior Ethmoidal Foramina
Middle Cranial Fossa bones
Sphenoid bone
Temporal bone
Foramina of the Middle Cranial Fossa
Optic Canal
Superior Orbital Fissure
Foramen Rotundum
Foramen Ovale
Foramen Spinosum
Posterior Cranial Fossa bones
◦ Occipital bone
◦ Temporal bone
◦ Sphenoid bone
Foramina of the Posterior Cranial Fossa
Foramen Magnum
Internal Acoustic (Auditory) Meatus
Jugular Foramen
Hypoglossal Canal
Cervicomedullary Junction
transition between the medulla oblongata and upper cervical spinal cord at the level of the foramen magnum
decussation
Epidural Hematoma
Arterial bleeding
Usually due to middle meningeal artery
Subdural hematoma
venous bleeding
Usually due to rupture of bridging veins
SCALP
Superficial Protection
1. Skin
2. Subcutaneous connective tissue
3. Galea aponeurotica
4. Loose areolar connective tissue
5. Pericranium
Meninges
◦Dura mater
◦Arachnoid mater
◦Pia mater
Dura Mater
Outermost meningeal layer, dense, pain-sensitive
Two layers periosteal layer (outer), meningeal layer (inner)
Dural reflections
◦ Falx cerebri
◦ Tentorium cerebelli
Falx Cerebri
Lies in the midline between the right and left cerebral hemispheres
Tentorium Cerebelli
Horizontal fold of meningeal dura mater, separates the cerebellum from the occipital
lobes
Dural Venous Sinuses
Drain venous blood and CSF from
the brain
◦ Superior sagittal sinus
◦ Inferior sagittal sinus
◦ Transverse and sigmoid sinuses
Arachnoid Mater
• Middle meningeal layer between dura mater and pia mater
Subarachnoid Space
• Filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Arachnoid Granulations
protrude into venous sinuses, CSF reabsorption into venous system
Pia Mater
• Innermost meningeal layer covering the brain
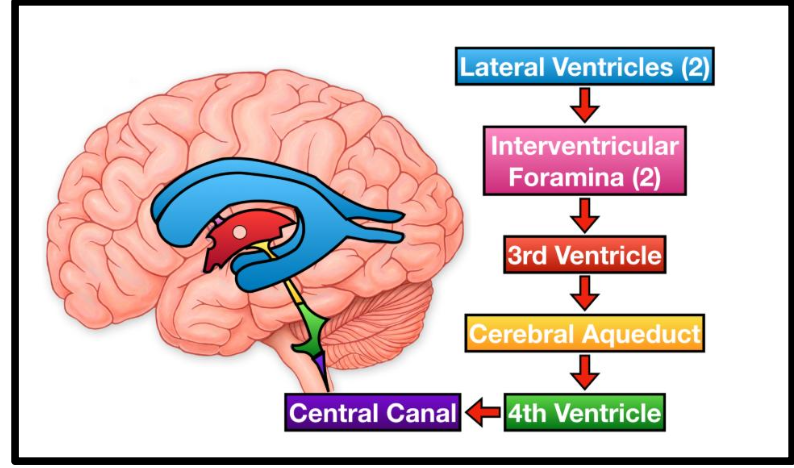
Ventricles of the Brain filled with?
CSF
Lateral Ventricles
Contain choroid plexus for CSF production
Third Ventricle
Located between the thalami
Cerebral Aqueduct
• Connects third and fourth ventricles
• Located in the midbrain
Fourth Ventricle
Located between cerebellum and brainstem
Functions of CSF
protects, delivers nutrients and removes metabolic waste
CSF Production
• Produced by choroid plexus in ventricles, 500mL produced daily, 150mL at any given time
Cisterna magna (cerebellomedullary cistern)
◦ Between cerebellum and medulla
Interpeduncular cistern
◦ base of midbrain
Suprasellar (chiasmatic) cistern
◦ surrounds optic chiasm
Quadrigeminal cistern
◦ posterior to midbrain
Pontine cistern
◦ anterior to pons
Blood–Brain Barrier
Regulates what substances enter the brain and spinal cord via tight junctions
Astrocyte end-feet surrounding capillaries
Primarily located in brain capillary endothelium
What Can and Cannot Cross the BBB
Can cross easily:
◦ Oxygen and carbon dioxide
◦ Lipid-soluble substances
Transported via carriers:
◦ Glucose (GLUT1)
◦ Amino acids
Restricted:
◦ Toxins, pathogens, most immune cells
Blood-CSF Barrier
Maintains stable chemical environment for the CNS
Primarily located at the choroid plexus
Developmental and Aging Considerations for Barriers
immature in neonates
aging may reduce barrier efficiency
Elevated Intracranial Pressure (ICP)
Normal ICP:
◦ ~5–15 mmHg in adults
Brain herniation
displacement of brain tissue due to elevated intracranial pressure
Subfalcine (cingulate) herniation
◦ Medial frontal lobe shifts under falx cerebri
Transtentorial (uncal) herniation
◦ Temporal lobe herniates through tentorial notch
Tonsillar herniation
◦ Cerebellar tonsils descend through foramen magnum
Central herniation
◦ Downward displacement of brainstem
Hydrocephalus
Excess CSF causing ventricular enlargement
Communicating:
◦ Impaired CSF absorption
Non-communicating
(Obstructive):
◦ Blockage within ventricular system
Craniotomy
bone flap replaced
Craniectomy
bone flap not replaced
Lumbar Puncture
Used to obtain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) or measure opening pressure
L3–L4 or L4–L5, below termination of the spinal cord
Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH)
Communicating hydrocephalus with enlarged ventricles and normal ICP
Compression of frontal and periventricular white matter