General Anesthesia (Cram)
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
What are the four componants of anesthesia?
Preanesthetic period
Induction
Maintenance
Recovery
During which three componants of general anesthesia should the patient be monitered?
Induction
Maintenance
Recovery
True or false: Most reflexes are absent in general anesthesia, but not all
True
Fill in the blank: General anesthesia can be accomplished using ______ drugs or ______ drugs or a ______ of both
injectable, inhaled, combination
The period immediately preceding anesthesia inwhich the patient (and staff) is prepared for anesthesia
Preanesthetic period
The transition of the patient from the conscious, preanesthetic state to complete unconsciousness, usually the level of anesthesia at which the patient can be intubated
Induction
True or false: The level of anethesia achieved during induction is sufficient for fairly painful procedures
False. It is NOT sufficient to do any fairly painful procedures
The period of anesthesia during which the patient is provided with enough anesthetic to allow a painless and humane procedure to be performed
Maintenance
True or false: It is better to give too much anesthesia during maintenance than too little, a good rule is to air on the side of caution by giving more than you think you need to
False. It is essential to provide enough, BUT ONLY ENOUGH! (and not too much or too little). That's why monitering is so important during this time
This period begins when the anesthetic level is lessened or anesthetic is removed so that the patient can return to consciousness
Recovery
At which point does the recovery period stop: When anesthetic is removed, when oxygen is removed, when the patient is returned to the recovery kennel, or when the patient is fully awake (may be several hours later)?
Recovery period only stops when the patient is fully awake! You must monitor until this time
What are the five most likely (but not limited to) concerns for the patient undergoing general anesthesia?
Hypotension (↓BP)
Hypoventilation (↓ resp rate &/or volume)
Hypoxia (lack of oxygen for tissues)
Hypothermia (↓ body temp)
Bradycardia (↓ heart rate)
Fill in the blank: To ensure patient safety you should use the _______ amounts of drugs (including anesthetics) necessary to provide the effects that are required.
minimum
What are the stages of anesthetic depth? Include common names for stages in list
Stage I – Induction/analgesia stage
Stage II – Excitement stage
Stage III – Anesthesia stage
Stage IV – Terminal stage
What are the planes of stage III (anesthesia stage)? Include common names for stages in list
Plane I – Light anesthesia
Plane II – Medium/surgical anesthesia
Plane III – Deep anesthesia
Plane IV – Overdose
What stage/plane of anesthesia is this patient in? The induction agent has just been given, she is conscious but disoriented. All reflexes are present
Stage I (induction/analgesia stage)

What stage/plane of anesthesia is this patient in? The stage begins with the loss of consciousness. Patients are known to paddle or bite during this stage
Stage II (excitement stage)
What stage/plane of anesthesia is this? It is divided into four planes which represent increasing anesthetic depth
Stage III (Anesthesia stage)

What stage/plane of anesthesia is this? The patient's eyeballs start to rotate ventrally. Pupils may become partially constricted. The animal is not deep enough for surgical procedures
Stage III, plane I (light anesthesia)
In which stage/plane of anesthesia do gagging and swallowing reflexes gradually disappear so that intubation may be possible?
Stage III, plane I (light anesthsia)
What stage/plane of anesthesia is this? At this depth, most surgical procedures can occur without response from the patient (except possible increase HR or RR)
Stage III, plane II (medium/surgical anesthesia)
What stage/plane of anesthesia is this? This plane is too deep for most procedures, but may be necessary for very painful surgery like orthopedics
Stage III, plane III (deep anesthesia)
In which plane of stage III anesthesia does respiration become very slow and shallow, HR gets slower, and BP falls?
Stage III, plane III (deep anesthesia)
Other than monitering devices, what could indicate a falling blood pressure?
Increased CRT
Throughout stage III, planes I & II the eyes have been rotated ventrally and constricted. In stage III, plane III what occurs to eyeball rotation and size?
Eyeballs start moving to central, and pupils become more dilated
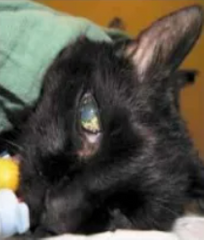
What stage/plane of anesthesia is this? It is characterized by apnea or respiratory failure followed by circulatory collapse and cardiac failure and death within a short time
Stage IV (terminal stage)
What is the rotation and pupil size asscociated with stage IV?
Central position and completely dilated
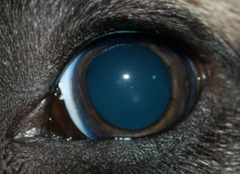

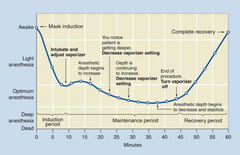
What type of induction agent does this curve represent?
IM injection
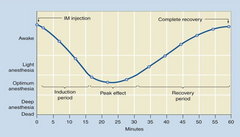
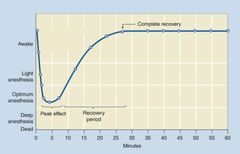
What type of induction agent does this curve represent?
IV injection
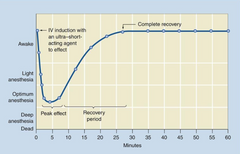
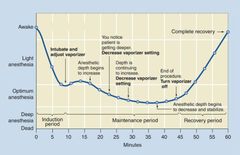
What type of induction agent/maintenance agent does this curve represent?
IV induction and inhalational maintenance
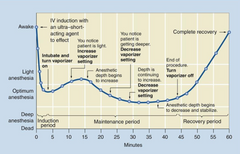
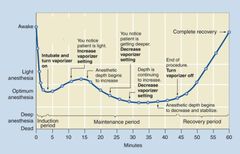
What type of induction agent/maintenance agent does this curve represent?
IV induction and maintenance

Is IV induction and maintenance more common in small animal or large animal medicine?
Large animal medicine
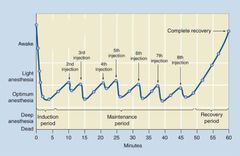
What type of induction agent/maintenance agent does this curve represent?
Inhalational induction and maintenance
What are the five vital signs that should be constantly measured during general anesthesia?
Heart rate & rhythm
Blood pressure & pulse strength
CRT & mucous membrane color
Respiratory rate & depth (and effort)
Body temperature
Fill in the blank: Vital signs should be monitored AT LEAST every ____ minutes
five
What is the lowest acceptable heart rate in a dog under anesthesia?
60 bpm
What is the lowest acceptable heart rate in a cat under anesthesia?
100 bpm
What are some options to treat a low heart rate (3 total)?
Anticholinergics
Increasing body temperature
Decreasing anesthetic level
What is a device for monitoring heart rate during general anesthesia? It makes auscultating a slow, quiet heart rate easier
Esophageal stethoscope
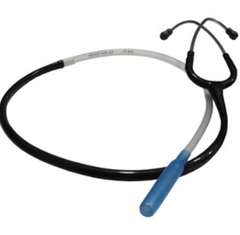
Device which amplifies sounds, either of the pulse or of the heart through the esophageal stethoscope
Doppler

Heart monitor that detects and visualizes mostly heart rate
ECG

Fill in the blank: The strength of the pulse is an estimate of _____ ______ [2 words]
blood pressure
Fill in the blank: Cuff width should be ___ – ___% of the circumference of the extremity used
30 – 50
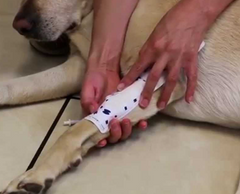

What do cyanotic (bluish) gums indicate?
Hypoxia
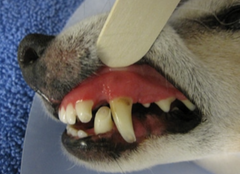
What do very red/purple gums indicate?
High blood pressure, or septicemia
Fill in the blank: Respiratory ______ and ______ is slowed by anesthesia, but ______ should not be affected unless the animal is getting too deep or something is obstructing airways or lungs
rate, depth, effort
Fill in the blank: Less than __ breaths per minute in cats and dogs is a concern
8
Measure of the amount of air inhaled during a breath
Tidal volume
What is the normal tidal volume per kg?
10 – 15mL/kg
Term for the partial collaspe or incomplete inflation of the lung
Atelectasis
How is atelectasis prevented or reversed in an intubated/oxygenated patient?
Sighing the patient once every 5–10 minutes
True or false: Hypothermic patients require more anesthesia, and are therefore more expensive to keep anesthetized
False. Hypothermic patients require less anesthetic, they are more easily overdosed
How does hypothermia affect heart rate, increase or decrease?
Decrease
How does hypothermia affect oxygen requirements?
It increases them, because shivering is so energy intensive
An anesthetic (usually inhaled) reaction, there is a genetic predilection. It mainly affects pigs as a part of Porcine Stress Syndrome
Malignant hyperthermia
What device moniters oxygen saturation of hemoglobin
Pulse oximeter

Fill in the blank: Oxygen saturation should not drop below ___, and below ___ indicates hypoxia
95%, 90%
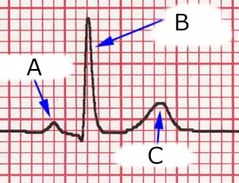
Label these waves on an ECG

You are placing electrodes for an ECG. Which colours of electrodes correspond with these locations? Right front elbow, left front elbow, right back stifle, left back stifle
Note: Patient is placed in right lateral recumbency
Remember: Snow over grass, smoke over fire
Right front – White
Left front – Black
Right back – Green
Left back – Red
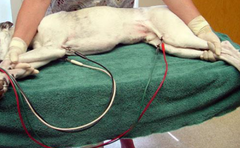
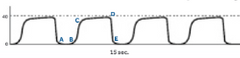
What machine visualizes carbon dioxide concentration like this?
Note: A normal waveform looks like the side profile of elephants marching
Capnograph