biomolecules 1
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
DNA vs RNA
DNA - deoxyribonucleic acid
RNA - Ribonucleic acid
composed of chains of nucleotides
a sugar phosphate backbone
nucleotide
3 parts:
phosphate (PO4-) group that is negatively charged
5 carbon sugar (deoxyribose in DNA or ribose in RNA)
nitrogen containing base
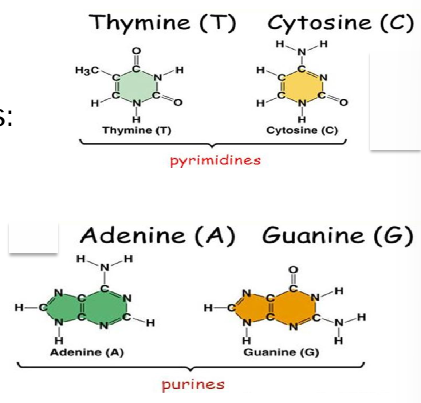
DNA bases
pyrimidines: single ring base
purines: double ring base
complimentary binding patterns: cytosine and guanine (3 hydrogen bonds), adenine and thymine (2 hydrogen bonds)
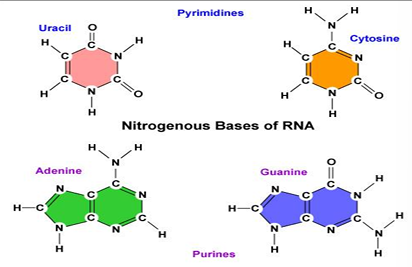
RNA bases
bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil instead of thymine
transcription (DNA to mRNA)
initiation: RNA polymerase binds to DNA and unwinds a 17-18bp (base pair) segment of the promoter region (open complex)
elongation: RNA polymerase moves along the DNA template synthesizing message mRNA until it reaches the terminator region
termination: transcribed terminator sequence causes RNA polymerase to pause and dissociate
translation (mRNA to protein)
in the cytoplasm, a ribosome attaches to the mRNA and translates its message into a polypeptide
the process is aided by transfer RNAs (tRNAs)
each tRNA molecule has a triplet anticodon on one end and amino acid attachment site on the other
triplet anticodon: 3 bases = 1 codon = 1 amino acid
amino acid
building unit of a protein
carboxyl group (COOH) + R group + amino group (NH2)
characteristics of amino acid R group
non-polar hydrophobic
aliphatic (hydrocarbon chain) → glycine, alanine, valine, leucine
aromatic (ring structure) → phenylalanine, tryptophan
polar hydrophilic
neutral → serine, threonine, tyrosine, glutamine, cysteine
basic (positive charge) → lysine, arginine, histidine
acidic (negative charge) → aspartic acid (aspartate), glutamic acid (glutamate)
groups of amino acid R groups
small amino acids: glycine and alanine
branched amino acid: valine, leucine, isoleucine
Sulphur containing amino acid: cysteine and methionine
amino acid found at a bend in a protein: proline
amino acids that can by phosphorylated: serine, threonine and tyrosine
amino acids that can be glycosylated: asparagine, serine and threonine
amino acid that can be nitrosylated: cysteine
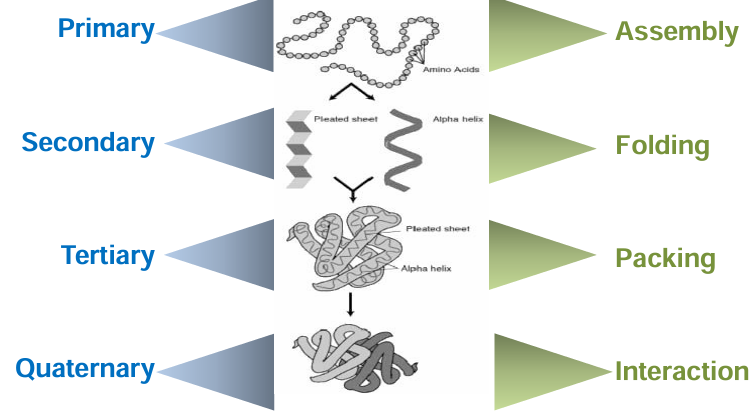
primary structure of proteins
amino acids formed in a polypeptide chain
amino acids linked together with peptide bonds
this bond is formed between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of next amino acid
the peptide bond is C(O)NH
chain has direction
start = amino terminus = N terminus
end = carboxyl terminus = C terminus
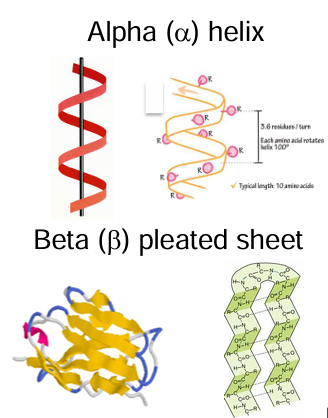
secondary structure of proteins
this is the spatial arrangement of the primary structure
it is determining by hydrogen bonding
the amino acid sequence controls folding
these structures have a regular repetitive folding pattern
most important are the alpha helix and beta pleated sheet
tertiary structure of proteins
this is further folding of the polypeptide chain
folding into a globular form
compact folded structure (hydrophobic AAs on the inside, hydrophilic AAs on the outside)
it stabilized by a wide range of bonds and interactions between the side chains of amino acids: disulphide bonds, hydrophobic interactions, ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds
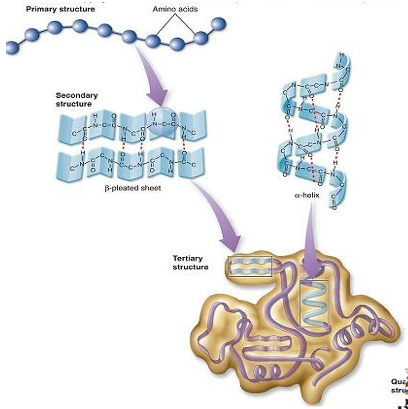
quaternary structure of proteins
it is the arrangement of protein subunits in a multimeric protein
the 3D arrangement of more than one tertiary polypeptide
consist of 2 or more polypeptide chains
polypeptide may be the same or different
held together by non covalent interactions and inter-chain disulphide bonds
process of protein strucure
typical bonds in a protein
covalent bonds
peptide bonds
disulphide bonds
non covalent bonds
hydrogen bonds
hydrophobic interactions
ionic bonds
native conformation of proteins
it is the functional fully folded protein structure
it is a unique 3 dimensional structure that determines the biological function of the protein
enzymatic
protection
regulation
signal transduction
storage
transport
post translational modifications (PTM)
chemical modification of a protein after translation
a functional group is attached to an amino acid
results in a change in protein function
increases the diversity of the proteome
some common PTMs
phosphorylation: + phosphate = phosphoprotein
glycosylation: + sugar group = glycoprotein
ubiquitination: + ubiquitin = death signal
nitrosylation: + NO (nitric oxide)