Comprehensive Guide to Presbyopia, Multifocal Lenses, and Orthokeratology
1/563
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
564 Terms
What is presbyopia?
A condition characterized by the gradual loss of the eye's ability to focus on nearby objects, typically occurring with age.
What are multifocal lenses?
Lenses that provide multiple focal points, allowing for both distance and near vision in one lens.
What is a common symptom of early presbyopia (ages 40-45)?
Fatigue when focusing on near objects.
What is the main symptom of more advanced presbyopia?
Blurred vision.
What is the benefit of simultaneous vision designs in multifocal lenses?
They allow patients to see both distance and near simultaneously without needing to move their eyes up and down.
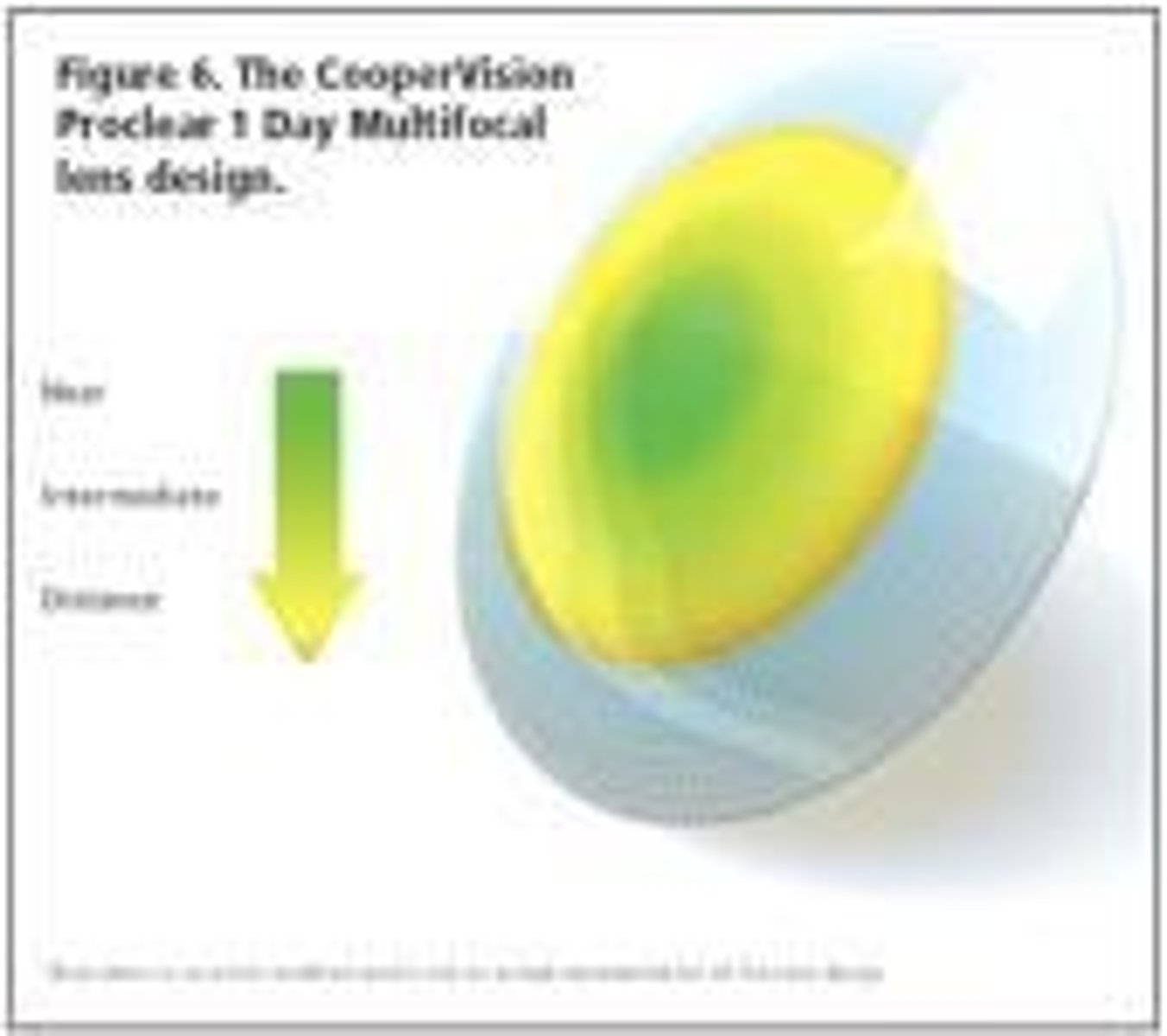
What is the underminus design in presbyopic lenses?
A design that allows patients to see both distance and near at the same time, often by reducing the distance power by 0.25-0.50.
What is the concept of depth of focus in relation to presbyopia?
It refers to the range within which objects appear in focus, allowing for functional vision at all distances.
What are the advantages of using reading glasses for presbyopia?
They are easy to obtain, readily available, and can slightly magnify reading material.
What is a disadvantage of using reading glasses for presbyopia?
Patients must wear glasses at least part of the time.
How do aspheric curves differ from toric designs?
Aspheric curves have a change in power across the pupil, while toric designs have rotational asymmetry with powers in the lens.
What is monovision in the context of presbyopia correction?
A method where one eye is corrected for distance and the other for near vision.
What is the success rate of monovision compared to multifocal lenses?
The success rate for monovision is about 80%, which compares well to multifocals.
What is a disadvantage of monovision?
It can make depth perception more difficult and may reduce overall visual acuity.
What is the recommended method for fitting presbyopic lenses?
Determine the dominant eye for distance correction and fit the non-dominant eye for near vision.
What should you never do when over-refracting a presbyope?
Never over-refract a presbyope in the phoropter.
What is the role of back surface aspherics in lens design?
They provide increased depth of field and focus, particularly in distance center designs.
What is the significance of checking eye dominance in presbyopic fitting?
It helps determine which eye should be fitted for distance vision.
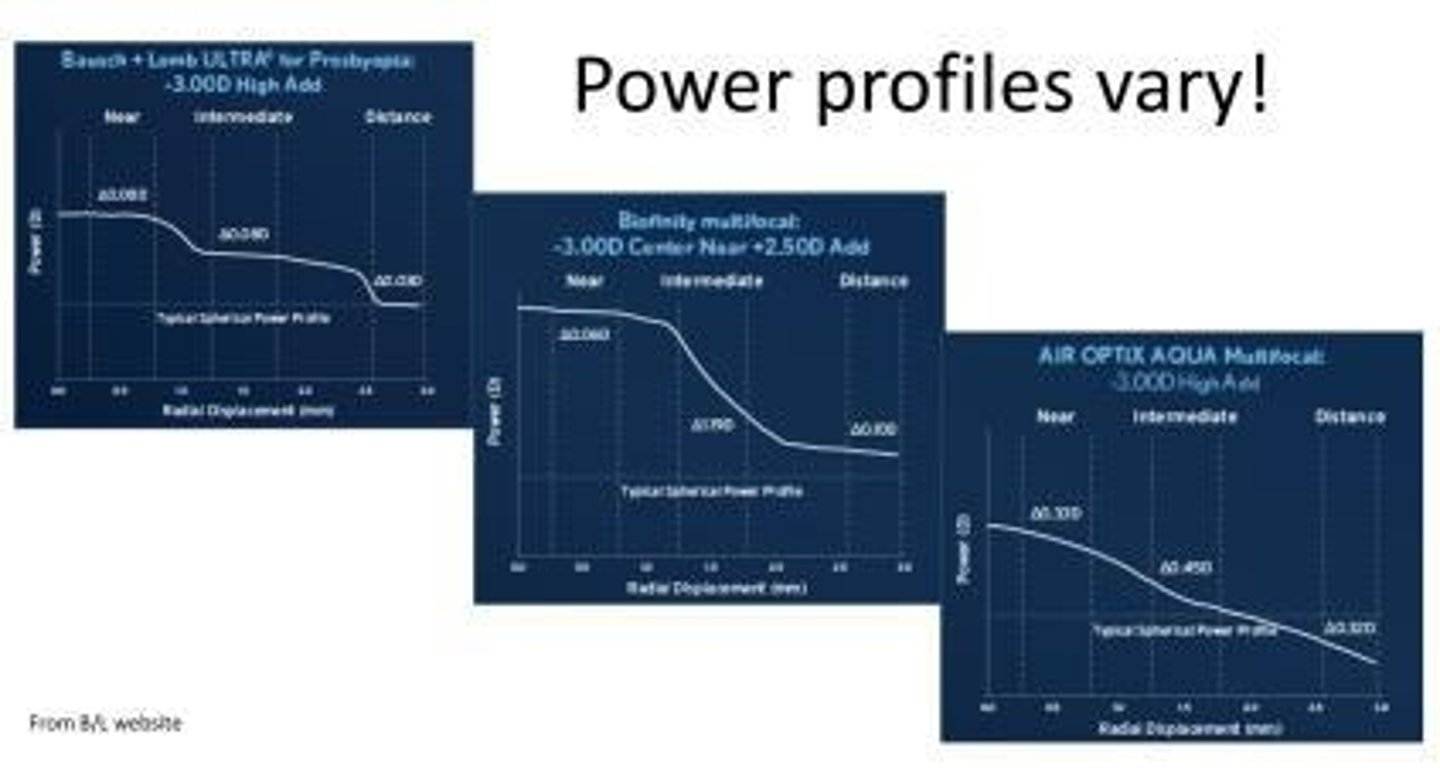
What is the effect of higher add power in multifocal lenses?
The higher the add power, the less crisp the vision will be.
What are the characteristics of functional emmetropes?
Individuals who have no prescription or do not wear correction, often low hyperopes or myopes.
What is a common challenge for patients using soft torics in presbyopia correction?
The lens can move slightly with blinks, causing blur, especially since only one eye is used for distance or near.
What is the purpose of over-refracting with loose lenses?
To fine-tune the prescription for both binocular and monocular vision.
What is the role of selective central suppression in monovision?
It helps the brain ignore the blurred image from the non-dominant eye, improving visual comfort.
What should you never do when refracting a presbyope in the phoropter?
Never over refract.
How does the phoropter environment affect a presbyope's vision?
It can cause their pupils to enlarge, worsening their vision.
Under what condition can you over refract a presbyope in the phoropter?
During a sphero-cyl overreaction (SCOR) with the JCC.
What is the design feature of front surface aspherics that aids vision?
They have front surface flattening which induces NSA (near spherical aberration) and increased depth of field.
What is more important when checking visual acuity for presbyopes, functional vision or Snellen acuity?
Functional vision is more important.
What font size should patients ideally be able to read comfortably?
6-8 point font.
What was the prescription for Abby Normal, a 47-year-old white female presbyope?
OD -3.00 sph, OS -3.00 sph, Add +1.25.
What were Abby Normal's binocular acuities for distance and near vision?
Distance: 20/20-, Near: 8 point.
What adjustments were made to Abby Normal's lenses during the over refraction?
Changed to -3.25 OD and -1.50 OS.
What is a key consideration when over refracting a patient?
Binocular acuities are more important than monocular acuities.
What should you communicate to the patient during the lens fitting process?
Clue them in to what is happening, explaining the purpose of each eye's correction.
What is the adaptation period for new presbyopic lenses?
About one week.
What are some common difficulties experienced by presbyopes when driving at night?
Decrease in depth perception and difficulty seeing.
What can be provided to a patient for driving comfort when they are presbyopic?
Spectacles with minus over the near eye.
What is the monovision power example given for a patient with a distance CL Rx of +2.00 OU and an add of +2.50?
+2.00 OD, +4.00 OS.
What were the binocular acuities for Abby Normal's distance vision?
20/20 OU.
What was Abby Normal's near vision acuity?
10 point, comfortably.
What issue was identified for Abby Normal's vision?
Near vision problems.
What is the first step in troubleshooting distance binocular over refraction?
Ensure the patient has enough plus.
What is the purpose of giving each eye as much plus as they can tolerate in distance?
To establish a 'Distance Set-Point'.
What should you do if a patient can tolerate more plus during over refraction?
Follow the fitting guide for the next step.
What is a key reminder when fitting lenses for presbyopes?
Don't be a cowboy; follow the fitting guide.
What is the advantage of GP bifocal/trifocal lenses?
They provide great optics with spherical optics in both distance and near portions.

What is a disadvantage of GP multifocal lenses?
They require correct lid anatomy, which most people do not have.
What is the primary need for crisper optics in GP multifocals?
To enhance visual clarity and performance.
What is the significance of non-rotational optics in GP multifocals?
To prevent soft torics from rotating excessively during use.
What are the two main designs of corneal GP multifocal lenses?
Translating lenses and simultaneous vision designs.
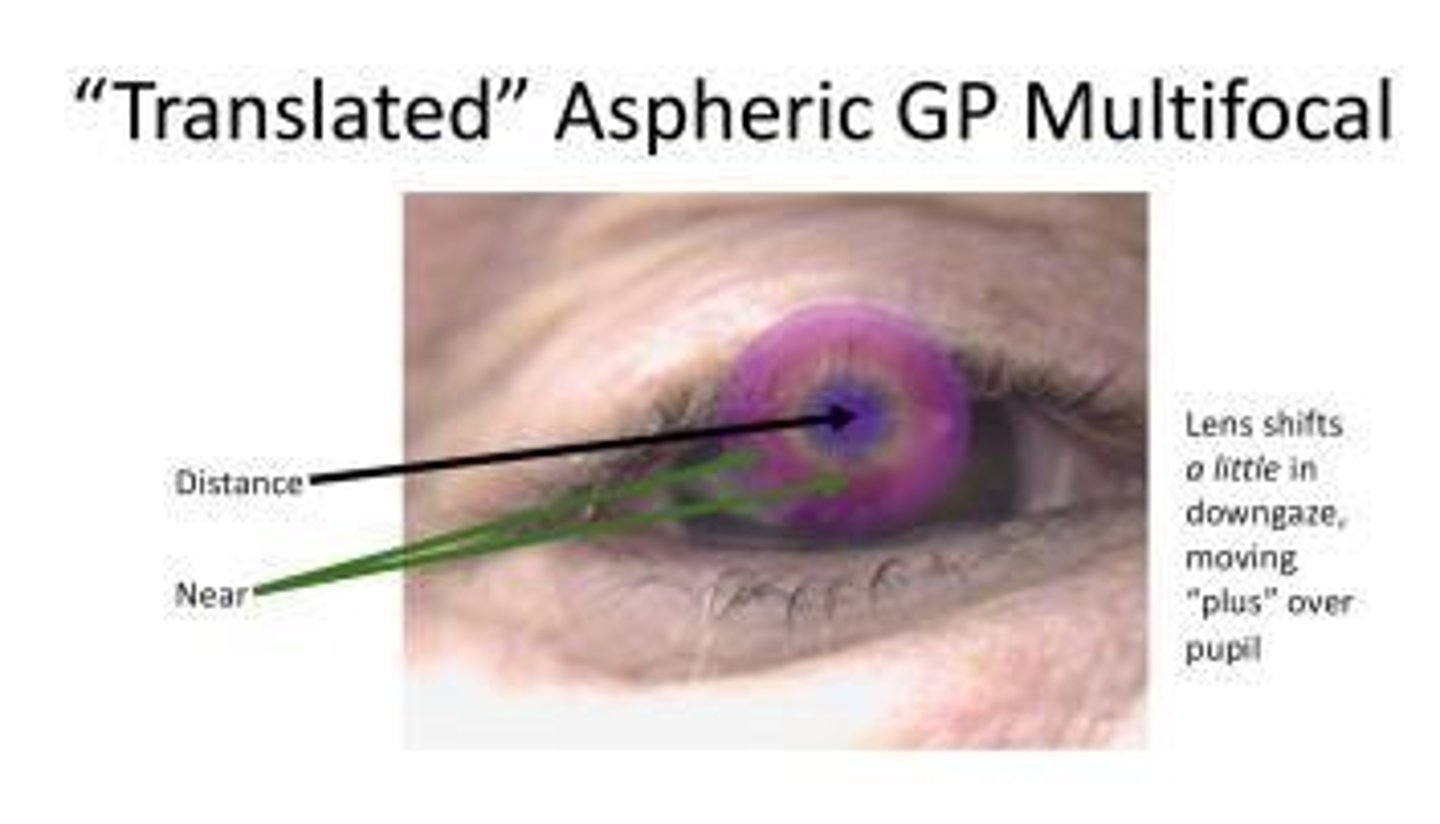
How do translating lenses function in GP multifocals?
They rest on the lower lid and require the eye to move up and down to access different powers.
What is the typical power arrangement in simultaneous vision designs?
They are usually distance center, allowing for both distance and near power simultaneously.
What happens to the lens during near vision with simultaneous vision designs?
The lens translates upward as the eye moves down, positioning the near segment over the pupil.
What is the ideal lid position for fitting GP multifocals?
The bottom lid should be at or very close to the bottom limbus.
What is prism ballasting in GP multifocals?
It helps enhance near vision by allowing the lens to decenter slightly in downgaze.
What fitting technique is recommended for back-aspheric GP multifocals?
Fit a little steeper than a spherical lens to compensate for the asphericity.
Why is a steeper fit necessary for back-aspheric GP multifocals?
To counteract the decrease in sag depth as the lens flattens in the periphery.
What is the trend in fitting GP multifocals regarding lid attachment?
The trend is towards mild lid attachment.
What is the effect of a 7.4mm aspheric BC on tear film compared to a spherical BC?
The tear film thins out quicker at the periphery with the aspheric BC.
What is the advantage of fitting front-aspheric GP multifocals?
They provide an easy transition from single vision spheres to multifocals.
What is the first step in the over-refraction process with translating bifocals?
Perform a distance over-refraction.
How does the aspheric back surface of a lens affect its positioning?
It tends to push the lens to the center of the eye due to capillary attraction.
What is the typical order of operations for fitting GP multifocals?
1. Distance OR, 2. Add power, 3. Check binocular acuity.
What is the purpose of checking binocular acuity when fitting GP multifocals?
To ensure that the patient has optimal vision with both eyes.
What does a +2.50 add power indicate in the context of GP multifocals?
It means the patient is seeing through a -0.50 distance correction.
What should be done if the distance power is under-corrected in GP multifocals?
Adjust the add power to achieve the correct near vision.
What is the role of the bottom lid in supporting GP multifocals?
The lens should be supported by the bottom lid as the patient looks down.
What fitting guide should be referred to for exact steps in fitting GP multifocals?
The specific fitting guide for GP multifocals.
What is the importance of segment line positioning in GP multifocals?
It should drop quickly to the lower lid after a blink to minimize rotation.
What is the significance of the tear film profile in relation to GP multifocals?
It helps assess the fit and comfort of the lens on the eye.
What is the significance of 'add power' in scleral multifocal options?
Add power increases from Series I to Series III, indicating the additional magnification for near vision.
What does a '0.0mm' add indicate in a lens design?
It indicates no add power because it is a distance center design.
How do scleral lenses typically position themselves on the eye?
Scleral lenses decenter temporally and downward.
What should be the same in scleral lenses compared to glasses?
The add power should be the same as in glasses.
What is a common issue when there is an apparent need to increase add power?
It may be a zone size issue where the optic zone moves slightly temporal and down from the pupil.
What is the first step in fitting a scleral lens?
Work on the fit of the lens first, optics second.
What is the purpose of hybrid multifocals?
They blend rigid and soft lens characteristics, providing the optics of GP lenses with the comfort of soft lenses.
What does EDOF stand for in lens design?
Extended Depth of Focus.
How do EDOF lenses differ from normal multifocal designs?
EDOF lenses theoretically provide a wider range of clear vision zones, transitioning from distance to near and intermediate.
What is modified monovision in the context of multifocals?
It refers to a fitting approach where both eyes are not equal, such as one eye for distance and the other for multifocal.
What should be used to assess a patient's vision during multifocal fitting?
Real text or a phone, rather than Snellen charts.
What is a realistic expectation for multifocal lenses?
Multifocals are not perfect for everything; patients should have realistic expectations.
What is a common recommendation regarding the use of phoropters in fitting?
Avoid using phoropters unless necessary.
What is the importance of curvature maps in lens fitting?
Curvature maps are used to assess the shape of the cornea and aid in fitting contact lenses.
What is the significance of fatigue and blur in multifocal lens fitting?
Fatigue is often experienced first, followed by blur, indicating the need for adjustments.
What is the general guideline for fitting multifocal lenses?
Follow the fitting guide closely to ensure optimal results.
What is the relationship between early presbyopes and late presbyopes in lens fitting?
Different approaches may be needed based on the stage of presbyopia.
What is the recommended lens power change when fitting scleral lenses?
Changing the base curve or fit may alter the vertical lens position and potentially require a lens power change.
What is the role of the fitting guide in the multifocal lens fitting process?
The fitting guide provides essential steps and recommendations for achieving the best lens fit.
What is the expected functional vision percentage for patients using multifocal lenses?
Around 80% functional vision is often considered acceptable.
What should be confirmed during the fitting process of multifocal lenses?
Confirm the fit and troubleshoot any issues as necessary.
What is the primary purpose of baseline examinations in corneal assessment?
Screening and diagnosing pathology.
What surgical procedures are mentioned in relation to corneal assessment?
Surgical work-up, follow-up, and refractive surgery including corneal transplants.
What imaging technique is used to enhance fitting of RGPs?
Topographers use Placido-disk imaging.
What does the axial map in corneal topography assume?
It assumes the center of curvature is on the optic axis and smoothes out data.
What is the advantage of using an axial map for corneal fitting?
It is best for picking base curves.
What caution should be taken when interpreting power in corneal topography?
Caution should be taken when interpreting power in the periphery.
What does a tangential map measure in corneal topography?
It measures the radius from the true center of curvature point by point.
How does the cornea reflect light in topography?
The cornea reflects like a convex (minus) mirror.
What is the significance of knowing the curvature and power of the cornea in topography?
It allows prediction of image size and helps find the radius of curvature.
What does the refractive power map provide in corneal assessment?
It is closer to true corneal power and useful for pre/post evaluation.