Metathesis Reactions
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
3 Basic Types
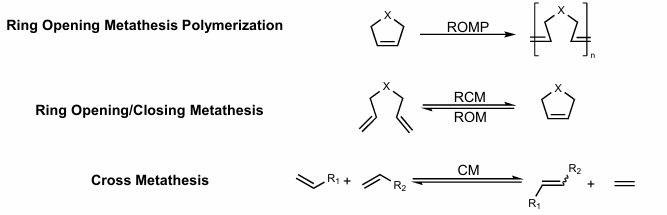
Ring opening metathesis polymerization
Ring Opening/Closing metathesis
Cross metathesis
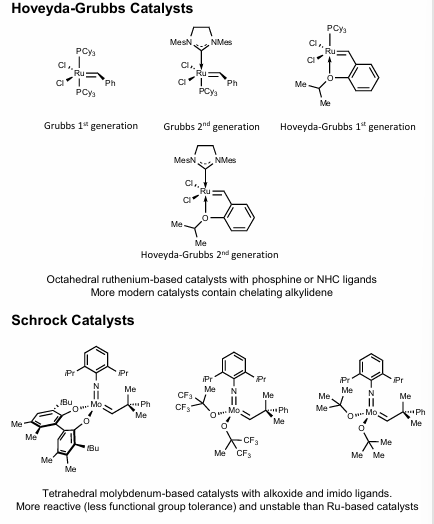
Catalysts
Hoyveda-Grubbs (Ru-based). Octahedral, w/ phosphine/NHC ligands
Schrock (Mo based). Tetrahedral, w/ alkoxide/imido ligands, more reactive (less FG tolerance), more unstable than Ru Hoyveda-Grubbs catalysts
Cross metathesis
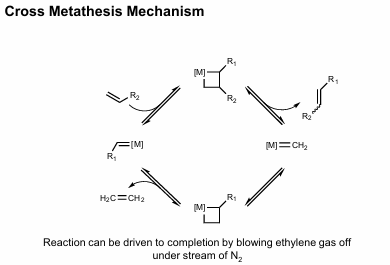
Metathesis of two alkenes. Proceeds via consecuitive [2+2] additions and retro [2+2] additions. Shortcomings: Product distribution is hard to control (scrambling possible of cross-pdts, homodimers). Can mitigate w/excess of one olefin. Statistical distribution (=R1 + =R2):
25% homodimer R1=R1
50% R1=R2
25% R2=R2.
Homodimerization reduces with excess of R1:
=R1:=R2 (10:1)
![<p>Metathesis of two alkenes. Proceeds via consecuitive [2+2] additions and retro [2+2] additions. Shortcomings: Product distribution is hard to control (scrambling possible of cross-pdts, homodimers). Can mitigate w/excess of one olefin. Statistical distribution (=R1 + =R2):</p><p>25% homodimer R1=R1</p><p>50% R1=R2</p><p>25% R2=R2.</p><p>Homodimerization reduces with excess of R1: </p><p>=R1:=R2 (10:1) </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8f7e7860-defa-43e5-aa49-6510c27a4dcd.png)
4 Olefin types
Type 1: Rapid homodimerization, very reactive (terminal olefins)
Type 2: Slow homodimerization, homodimers react slowly with catalyst, moderately reactive (unhindered conjugated olefins, enones, allylic alcohols, epoxides)
Type 3: No homodimerization, somewhat reactive (1,1 disubstituted terminal olefins, 1,2,3-trisub olefins, hindered allyl groups, allyl phosphonates)
Type 4: Inert to metathesis, unreactive (but do not deactivate catalyst) (tetrasubstituted olefins, Nitro olefins, allyl ether 1,2 disubstituted allyl ethers)
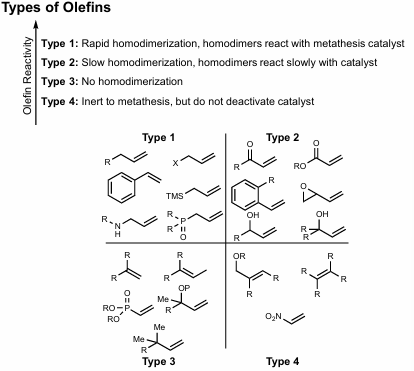
Cross metathesis between Types of Olefins
Type 4 will not react with any other type
Remember:
Most reactive to Least Reactive
Type 1 > Type 2 > Type 3 > Type 4
Type 1 + Type 2, Type 3 = most efficient cross product.
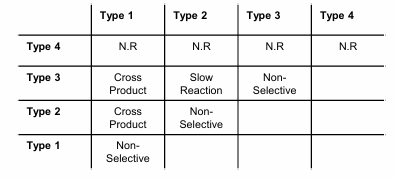
Ring-Closing metathesis
Most often terminal alkenes, ring size varies
Allylation is a good strategy for making these precursors
Good for macrocyclization, bad for strained rings
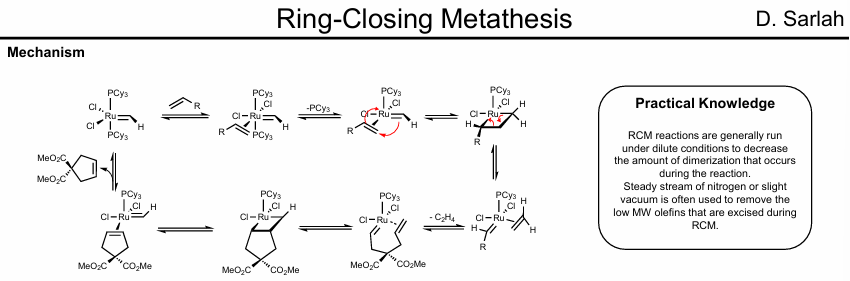
Asymmetric Ring closing metathesis
Can run Asymmetrically with Schrock chiral catalysts
Only one terminal olefin reacts
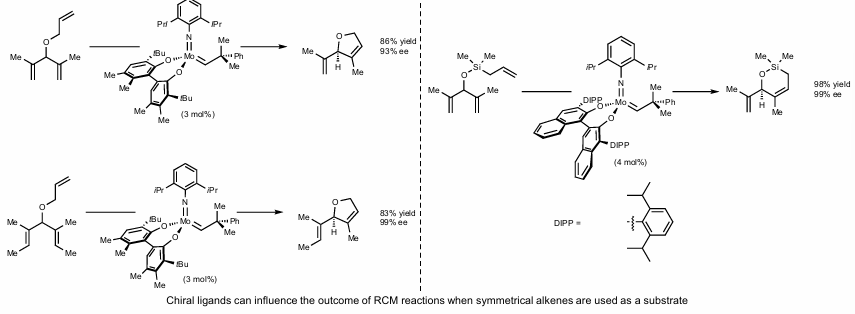
Z-selective Ring closing metathesis (macrocycles)
For Z-selective metathesis, run at reduced pressure to induce volatile olefins to prevent scrambling
Large alkoxy ligands are best for Z-selectivity, as R groups of metallocyclobutane intermediate point away from bulky ligand
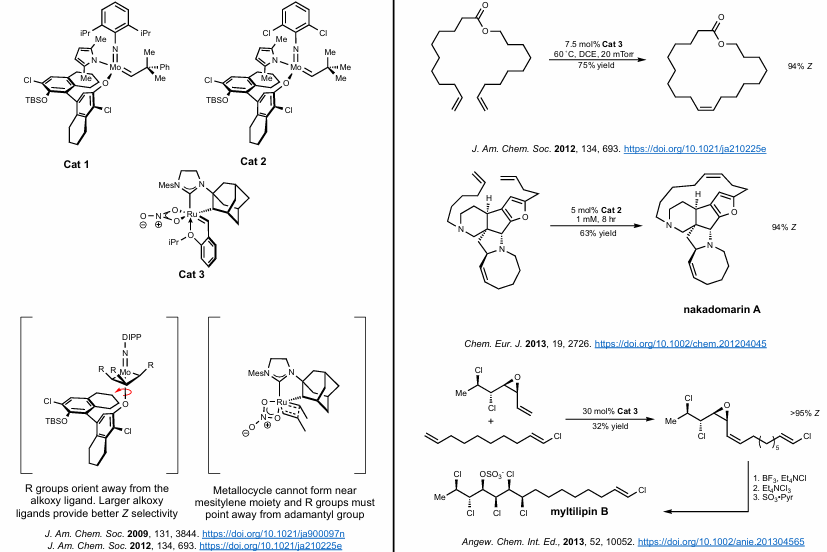
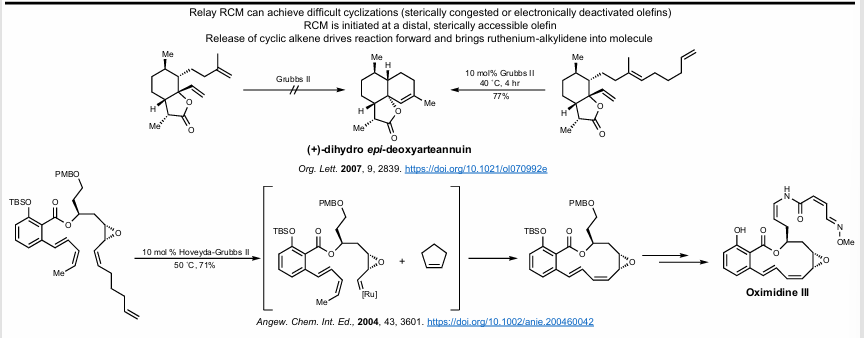
Relay Ring closing metathesis
Let’s say you can’t cyclize a particular substrate due to sterics. You can increase the allyl chain by a particular number of carbons selective with an unhindered terminal alkene. Then, ring-closing metathesis occurs, spitting out a cyclic molecule of a particular size (i.e cyclopentene). Then, the real RCM occurs because the desired intermediate is already formed! Pretty clever.
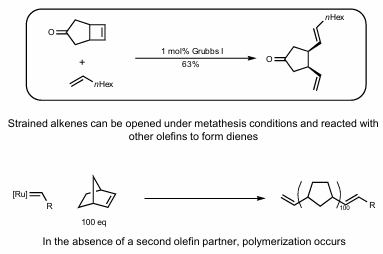
Ring Opening Metathesis (Polymerization)
Usually need strained alkenes.
Without a second olefin partner, polymerization occurs
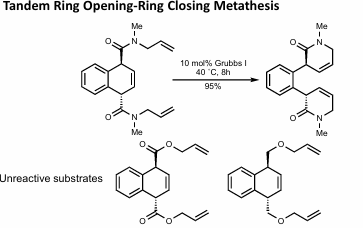
Tandem Ring Opening-Ring closing metathesis
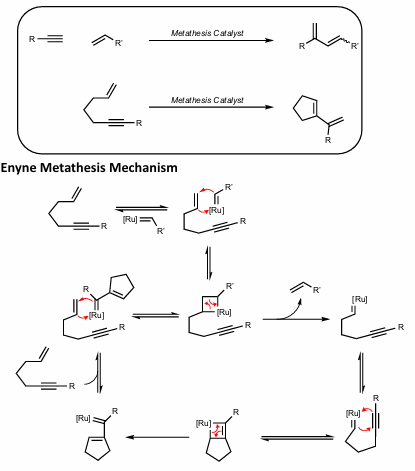
Enyne metathesis
Metathesis of an alkyne and alkene.
Olefin reacts first to form metallocyclobutane intermediate
Conj. Diene formed
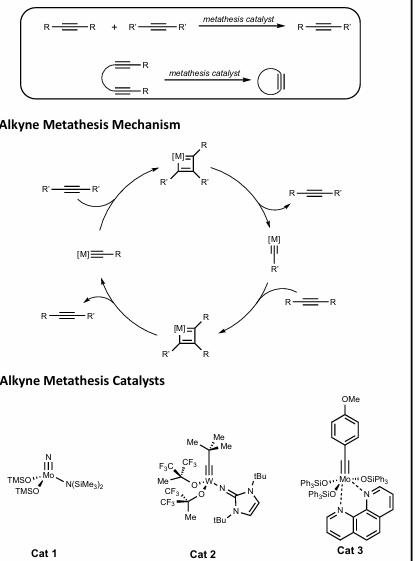
Alkyne metathesis
Orthogonal to alkene metathesis! Totally chemoselective
Reaction of two alkynes to produce scrambled alkyne product
Same mechanism as OM
Tungsten, Molybdenum catalysts
Cross metathesis mechanism