Lab 11: Nervous Tissue & Spinal Cord (Vocab)
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Homeostasis
ability of the body to maintain a controlled and stable environment by responding to internal & external stimuli
What are the 2 major division of the nervous system?
Central Nervous System
Peripheral Nervous System
List the components and functions of the CNS
brain
spinal cord
processes info received by PNS
controls actions of all parts of body
site for thoughts emotions & memory
List the components of the PNS
cranial & spinal nerves
ganglia
sensory receptors
The nervous system consists of 2 categories of cells:
Neurons
Neuroglia
What is the function of neurons
impulse conduction
responsible for all special attributes associated w/ the nervous system (e.g. thinking, controlling muscle activity, regulating glands)
Neurons can be divided into 3 classes. What is each one’s function?
Sensory (afferent) neurons → conducts impulse from sensory receptor to CNS
Interneuron (association neuron) → integrated info from the sensory neurons & passes the stimulus to motor neurons
Motor (efferent) neurons → the neuron that conducts the impulse from the CNS to an effector, usually a muscle or a gland
Describe the structure & function of: dendrites
structure → short, tapering, branched; found on soma (cell body) of axon
function → carreis electrical signals, usually graded potentials, toward the cell body
Describe the structure & function of: cell body
structure → contains nucleus surrounded by cytoplasm
function → inegrates signals from dendrites, decides whether to send action potential
Describe the structure & function of: axon
structure → long, slender projection of a neuron
function → conducts action potentials away from the soma
Describe the structure & function of: axon hillock
structure → cone-shaped elevation where the axon joins to the cell body
function → nerve impulses arise at this junction
Describe the structure & function of: axon collateral
structure → side branches along an axon
function → (of muscle spindle sensory neurons) synapses w/ inhibitory interneuron in the integrating center; relay nerve impulses to the brain over ascending pathways
Describe the structure of: axon terminals
structure → the many fine processes that an axon & its collaterals divide into
Describe the structure & function of: synaptic end bulbs/varicosities
structure → bulb-shaped tips of axon terminals
function → secretes neurotransmitters; converts electrical impulses into chemical signsls to communicate
Describe the structure & function of: Schwann cells
structure → neuroglial cell of the PNS that encircles PNS axons
function → forms myelin sheath & neurolemma; participates in axon regeneration
Describe the structure & function of: myelin sheath
structure → multilayered lipid & protein covering around axons of many PNS & CNS neurons
function → insulates & increases speed of nerve impulse conduction
Describe the structure & function of: neurolemma
structure → outer, peripheral, nucleated cytoplasmic layer of the Schwann Cell
function → aids axon regenreation by forming a regeneration tube
Describe the structure & function of: myelin sheath gaps/nodes of ranvier
structure → space along myelinated axons between the individual Schwann cells that form the myelin sheath
function → enable rapid signal transmission via saltatory conduction
Neurons can be classified into 3 categories according to their structure:
Multipolar → several dendrties & one axon; dominates the CNS
Bipolar → one dendrite & one axon; found in retina of eye, inner ear, nasal epithelium
Pseudounipolar → fused axon & dendrite that emerge from the cell body as one unit; form sensory receptors in PNS

List the general functions of neuroglia
provide structural support for neurons
form myelin sheath
englfing microorganisms & cell debris
forming CSF
prevent substances from entering CNS
List the 4 CNS neuroglia and describe each
Astrocytes → support neurons, maintain chemical environment & BBB
Oligodendrocytes → forms mylein sheath around CNS axons
Microglial Cells → phagocytosis; remove cellular debris, phagocytize microbes & damaged tissue
Ependymal Cells → cuboidal to columnar cells that possess microvilli and cilia; produce CSF, form blood-CSF barrier
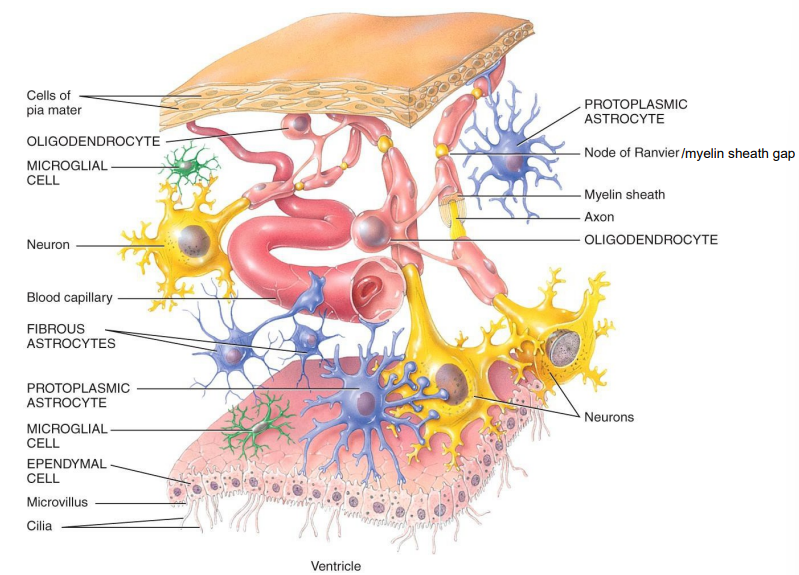
List the 2 PNS neuroglia and their functons
Schwann cells → forms myelin sheath and neurolemma around PNS axons
Satellite cells → flat cells → surround cell bodies of PNS ganglia; provides structural support
Distinguish between the functions of neurons & neuroglia
neurons → generate/propogate nerve impulses; thinking, controling muscle activity, regulating glands
neuroglia → multiply/divide in mature nervous system; structural support, form myelin sheath, engulfing microorganisms/cell debris, form CSF
Describe the functions of white matter vs. gray matter of the spinal cord
white matter → carry sensory info to the brain & motor info back to PNS; myelinated; EPSPs & IPSPs
gray matter → contains cell bodies & axons of interneurons; unmyelinated; contains many sensory/motor tracts
Describe the 3 spinal meninges
Dura mater → superficial; thick, strong — composed of dense irregular connective tissue
Arachnoid mater → midde; thin, avascular — composed of collagen & elastic fibers
Pia mater → innermost; thin, transparent connective tissue that adheres to spinal cord; filled w/ blood vessels
Describe the 3 “spaces” of the spinal cord
Epidural space → space betwen spinal dura mater & vertebral canal; contains areolar CT & plexus of veins to protect spinal cord
Subdural space → space between dura mater & arachnoid mater that contains interstitial fluid
Subarachnoid space → space betwn arachnoid mater & pia mater; contains shock-absorbing CSF
List the meninges and spaces from deep to superficial
Pia mater
Subarachnoid space
Arachnoid mater
Subdural space
Dura mater
Epidural space
Describe the structure & function of: anterior horn
contains somatic motor nuclei — clusters of cell bodies of somatic motor neurons
provides skeletal muscle contraction
Describe the structure & function of: posterior horn
contains axons of incoming sensory neurons + cell bodies & axons of interneurons
Describe the structure & function of: central canal
center of spinal cord → filled w/ CSF; extends entire length of spinal cord
Describe the structure & function of: anterior and posterior roots
anterior root → contain axons of motor neurons
posterior root → contain sensory axons; has spinal ganglion
Describe the structure & function of: ganglia
contains cell bodies of neurons; relay & process sensory info between CNS & PNS
Describe the structure & function of: anterior median fissure
wide groove; separates anterior portion of spinal cord into symmetrical halves
Describe the structure & function of: posterior median sulcus
narrow; separates posterior portion into halves
Describe the structure & function of: filum terminale
thin fibrous tissue that extends from conus medullaris to coccyx; anchors
What is a nerve?
bundle of axons; PNS
The anterior & posterior roots join outside the spinal cord to form ___ that have ______ functions
mixed nerves; both sensory & motor functions
After leaving the spinal column, the anterior spinal nerves divide into several branches called ___
ramiplexus
The anterior rami, except for those on the thoracic spinal nerves, often form a complex network of motor nerves called a ___ which ___ areas of the body
plexus; innervate
What are reflexes?
rapid-automatic sequences that occur in resp. to a stimulus; maintains homeostasis
List the 5 components of a reflex arc
Sensory receptor
Sensory neuron
Integrating center
Motor neuron
Effector
Contrast autonomic/visceral and somatic reflexes
autonomic/visceral → results in secretion by a gland/contraction of smooth or cardiac muscle; regulating functions like digestion, elimination, blood pressure, etc.
somatic → results from contraction fo skeletal muscles
Describe stretch reflexes
spimplest form of somatic reflexes
effector muscle is the same muscle as the one that is stimulated
What is a sensory receptor
distal end of sensory neuron (dendrite) serves as a receptor; responds to a stimulus
Where are sensory neurons located
located in gray matter
What is an integrating center
one or more regions of gray matter within CNS
can have monosynaptic or polysynaptic reflex arc
List 4 examples of receptors that can be involved in a reflex arc
baroreceptors → monitors blood pressure
mechanoreceptors → e.g. muscle spindles
thermoreceptors → temperature changes
tendon organs → detect changes in muscle tension caused by passive stretch or muscular contraction
List 4 examples of effectors that can be involved in a reflex arc
skeletal muscle
smooth muscle
cardiac muscle
glands
List the 4 types of somatic reflexes tested in lab
Achilles Tendon
Patellar
Biceps
Triceps
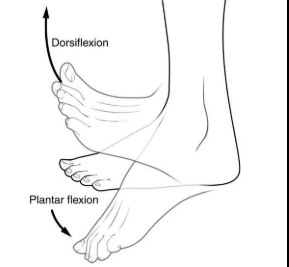
Describe the procedure, effector, & normal response of the Achilles Tendon reflex
procedure:
subject stands resting one knee on stool, foot hands relaxed
tester locates achilles tendon and uses rubber mallet to strike
effector → gastrocnemius muscle (calf)
normal response → slight plantar flexion of the foot
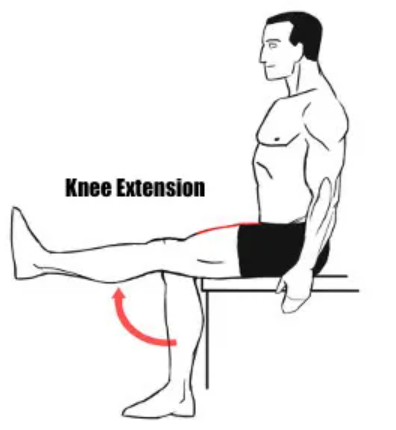
Describe the procedure, effector, & normal response of the Patellar Reflex
procedure:
subject sits on lab bench w/ both legs legs hanging freely
tester locates patellar tendon (inferior to patella) & softly strikes it with wide end of rubber mallet
effector → quadriceps femoris (anterior muscle of thigh)
normal response → slight extension of lower leg at the knee
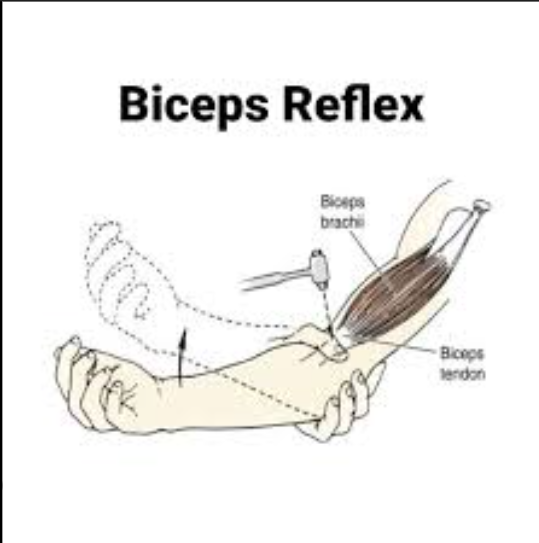
Describe the procedure, effector, & normal response of the Biceps reflex
procedure:
facing each other, tester holds subject’s left elbow in right hand. subject’s forearm should rest on tester’s forarm — bent and relaxed
tester places thumb on biceps tendon in the antecubital region
tester strikes tip of their thumb w/ mallet
watch for movement of subject’s brachium, antebrachium, hand or fingers
effector → biceps brachii muscle
normal response → slight flexion of the forearm at the albow
Describe the procedure, effector, & normal response of the Triceps Reflex
procedure:
subject flexes their arm at the elbow
tester hold subjects wrist & subject relaxes arm completely, resting qweight of arm in the tester’s fingers
tester strikes triceps tendon, above the olecranon of the ulna
effector → triceps brachii muscle
normal response → slight extension of the forearm at the elbow
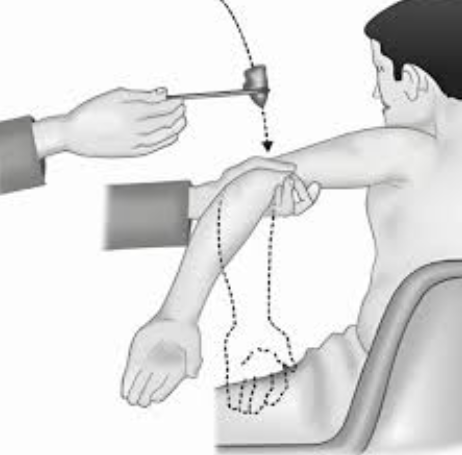
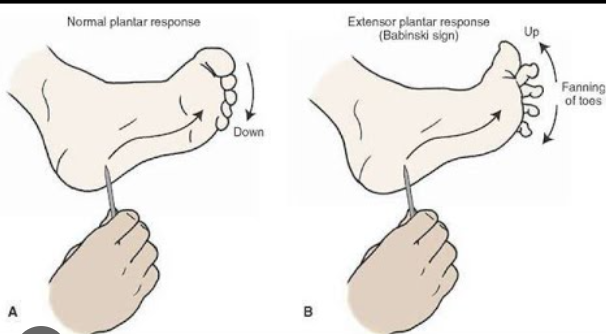
What is the one superfical/cutaneous reflex that we tested? Describe the procedure & normal and abnormal response of it.
plantar flexion
procedure:
subject remove right shoe/sock
tester takes metal handle of mallet and runs it firmly towards the big toe
normal response → in adults: toes flex
abnormal response → in adults: babinski sign — toes spread (normal in children under 18 months)
List the 3 autonomic/visceral reflexes we tested
Salivary
Pupillary
Diving
Describe the procedure, effector, & normal response of the Salivary reflex
procedure:
subject rinses mouth with water
tester dips cotton swab in water & places it under subject’s tongue for a few seconds.
subject collects all saliva produced for 3 mins in a clean graduated cylinder & measures the volume produced (not including the bubbles)
Subject rinses their mouth with water
The tester dips a new cotton swab in a glucose solution and places it under subjects tongue
subject collects all saliva produced for 3 mins & measures again
rinse mouth with water
Repeat with lemon juice
effector → salivary glands
normal response → immediate, involuntary increase of saliva production
Describe the procedure, effector, & normal response of the Pupillary Light reflex
procedure:
siubject stands facing the tester. tester notes relative size of subject’s pupils
tester quickly flashes panlight into subject’s eye & notes change in pupil diameter
effector → iris
normal response → both pupils get smaller with light
Describe the procedure, effector, & normal response of the Diving reflex
procedure:
Obtain pulse oximeter. Take resting pulse of subject
subject takes 3 deep breaths before bending at waist to submerge their face in the cold water
tester times for 30 seconds once the subect has submerged
recirder will monitor heart rate of the subject
effector → heart; vascular smooth muscle
normal response → heart rate drops to preserve body temperature
Why are stretch reflexes considered to be simpler than other reflexes?
monosynaptic reflex arc — only involves sensory and motor neuron connected by a single synapse
What is the diff. between a monosynaptic & polysynaptic reflex?
monosynapotic → NO interneurons, faster ; involves only 1 synapse between sensory & motor neuron (e.g. stretch reflex)
polysynaptic → 1+ interneuron betwn sensory & motor neuron; 2+ synapses, more complex & slower (e.g. withdrawal or pain reflex)
How can the reflexes tested be used for diagnostic purposes?
Assess the integrity of the nervous system & locate lesions
All reflexes are designed to maintain homeostasis in the body — how so? Give a few examples of somatic & autonomic reflexes that help maintain homeostasis
Involuntary, rapid, & predictable responses to sensory stimuli allow body to detect disruptions & immediately correct internal conditions
Somatic → stretch reflex: causes contraction to prevent overextension, maintaining posture & joint stability
Autonomic → pupillary reflex: constriction of pupil in bright light and dilation in dim light protects the retina & ensures optimal vision