258 Final Review
1/169
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
170 Terms
all types of shock: manifestations
early:
↓ BP
↑ HR
↑ RR
late:
temp
loc
kidneys: low UO, bun/cr high
no bowel sounds
septic shock
circulating bacteria causes inflammation, vasodilation, and decreased bp
SIRS criteria:
only need 2/4
-temp > 38.3 (101) or < 36 (96.8)
-tachycardia > 90
-tachypnea > 20
-WBC > 12 or < 4, bands >10% or 10% immature bands
septic shock priority
find the cause
-cbc
-ua
-culture and sensitivity
1 hour sepsis bundle
1. lactate, remeasure if greater than 2
2. obtain blood culture before abx
3. broad abx
4. rapid LR for low bp + lactate greater than 4
5. vasopressors if bp is low, or after a fluid bolus to maintain map (nor epi)
hypovolemic shock
shock resulting from blood or fluid loss = low venous return, low stroke volume, low cardiac output and low tissue perfusion
-15-30% in volume (750-1000ml in a 70 kg person)
hypovolemic causes
increased fluid loss (burns, diuresis, vomiting, diarrhea)
blood loss (due to trauma, surgery, NSAIDS)
gynecologic/obstetric causes
hypovolemia shock due to diarrhea consideration
need constant ekg monitoring due to hypokalemia risk
hypovolemic shock labs
blood loss: ↓ H+H
fluid loss: ↑ H+H
hypovolemic shock tx
treat the underlying causes of fluid loss
fluids + blood replacement: isotonic crystalloids (NS, LR, D5W)
medications: after fluids (fill the tank first), vasopressors
PRIO = ABC, FLUIDS
cardiogenic shock causes
decreased ability to contract and to pump blood (low cardiac output) due to a direct cardiac cause
mi
hf
cardiomyopathy
dysrhythmias
valvular rupture/stenosis
cardiogenic shock treatment
client cannot tolerate lots of fluids to increase bp
-inotropes (dobutamine + dopamine + epi + milrinone) to increase hr and contractility
-pressors to increase bp
-nitro
-oxygen and morphine
distributive shock
leaky blood vessels
decreased blood return to the heart = decreased perfusion
distributive shock types
neurogenic, anaphylactic, septic
anaphylactic shock meds
antihistamines: diphenhydramine(urticaria)
Epi before fluids
- Bronchoconstriction
- Angioedema
- Urticaria
- Hypotension
**assess vitals & client
Priority medications is IM epinephrine (vasoconstricts and bronchodilates)
Oxygen
Adjunct therapies:
- Antihistamines
- Corticosteroids
- Bronchodilators
- IV fluids
airway: swelling
breathing: wheezing
circulation: decreased bp, increased hr
skin: urticaria
gi: nv
Obstructive Shock
Blood flow to heart is blocked
Causes:
- PE (blocks pulmonary artery)
- cardiac tamponade, fluid in pericardium compresses heart (ssx: becks triad ↓ bp, jvd, muffled heart sounds. Tx: pericardiocentesis, monitor ecg, O2, bowel sounds, color)
- tension pneumothorax (Tx: needle decompression + chest tube)
stages of shock
-initial: no visible changes, map drops 5-10, mild vasoconstriction, a slight increase in hr
-compensatory (non-progressive): increase co to increase perfusion + oxygenation
-progressive
-refractory (irreversible)
shock priority and management
ABC's
priority: oxygen status (high flow 15L nonrebreather), be prepared to intubate
-then: vs, continuous ecg, hourly uo
-loc
-skin color, temp, moisture, turgor, cap refill
first intervention with low bp
elevate legs 45 degrees (modified trendelenburg): if bp increases fluids will help, if there is no change fluids wont help and you need to do pressors
inotropic agents
increase contraction and cardiac output
decrease afterload
-dobutamine, dopamine, epi, milrinone
vasoactive agents
increase resistance + bp
keeps blood on the arterial side
-dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine
dobutamine + dopamine + epi + milrinone AE
arrhythmias and increased hr
-if extravasates into tissues the reversal is phentolamine
dopamine + norepinephrine + epinephrine considerations
low dose: increases kidney perfusion
high dose: decreases kidney perfusion
-phentolamine is the reversal agent
-prolonged use: necrosis
MODS patho
release of toxic metabolites + destructive enzymes in response to low oxygenation
-original organ + 2 additional organs
MODS risk factors
shock/sepsis
severe trauma
burns
acute pancreatitis
major surgery
ards
*any severe illness that decreases BP + organ perfusion
MODS manifestation
lungs are often first to be affected
resp: hypoxia, tachy, low o2 sat
CNS: changes in loc, confusion, psychosis
hepatic: jaundice, increase liver enzymes, low albumin
cardiac: tachy, low bp, increased lactate, changes in ecg
renal: oliguria, increased bun/creatinine
hematological: low plts + protein c, increased d-dimer, petechia, dic
MODS management
early detection + control of initiating event
supportive measures
nutritional support
patient comfort
measures that compensate: dialysis, mechanical vent
Open (wide) angle glaucoma
- most common
- usually bilateral
- decreased outflow of aqueous humor, blockage in drainage, ↑ IOP
- loss of peripheral visions
- "silent thief"
- lifelong treatment to reduce IOP and prevent vision loss
- Timolol ( 5 mins apart)
Open (wide) angle glaucoma manifestations
initially asymptomatic
- mild eye pain
- blurry vision
- halos around lights
- headaches
Angle-closure (narrow-angle) glaucoma
ocular emergency
- sudden closure of angle (often pupil dilation), IOP rapidly ↑ ( ≥ 30 mm Hg)
- loss of central visual acuity & pain
- an ocular emergency, immediate surgery required to lower IOP
- nursing management: nausea and pain
glaucoma surgery and post-op care
- wear glasses in bright areas
- avoid activities that ↑ IOP (bending down, sneezing, lifting >15 lb, straining w/ bowel movement)
- do not lie on operative side
- REPORT: severe pain and nausea (hemorrhage)
glaucoma goal, meds, and management
goal: prevent vision loss and optic damage, maintain IOP <21 mm Hg
medications:
- timolol reduced IOP (used in both)
- pilocarpine causes miosis of the pupil (closed angle)
- analgesics & antiemetics: pain and nausea (closed angle)
nursing management:
- monitor IOP
- med adherence
- monitor vision
cataracts manifestations/management
- painless progressive blurred vision
- reduced night vision
- sensitivity to glare
- reduced visual acuity
- decreased color perception
- color shifts, lens become more brown
- myopic shift
- prescription changes
- diplopia in single eye
- opacity of lens
- check visual acuity with Snellen chart
- determine functional capacity
- ↑ light in room
- adaptive devices: magnifying glass, large print, talking devices
cataracts surgical management and post-op
- surgery needed if vision alters ADL
- outpatient basis, local anesthesia, 1 hr surgery, small incision, lens removed, replacement lens inserted
post-op:
- avoid heavy lifting
- wrap around glasses to protect against UV & glare
- padded, metal eye protector during bedtime to prevent accidental rubbing or pressure
retinal detachment manifestations
Ocular emergency
- "shade" or "curtain" across vision of one eye
- bright flashing lights
- sudden onset of floaters
- NO pain
- "cob web" eye
retinal detachment surgical management
scleral buckle - band compresses
vitrectomy - dissection with substitute
pneumatic retinopexy Post op: Prone positioning - gas bubble w/ pressure
acute otitis media Ssx/tx
common in children,<6 weeks
- causes: viral, bacterial
- s/s: pain when lying down, tugging/pulling ear, irritable, drainage if eardrum ruptures but no pain, muffled hearing (pearly gray healthy color, red bad)
- Tx: analgesics, abx, myringotomy (incision to drain fluid), tympanostomy tubes (to ventilate preventing buildup)
chronic otitis media
- causes: recurrent infection, mastoid air cells w/ TMP
- s/s: hearing loss, "fullness", otalgia, otorrhea, vertigo
- tx: topical antibiotics
**can cause irreversible damage/scarring
Meniere disease
overproduction of inner ear fluid balance in vestibular system
- s/s: vertigo, tinnitus, "fullness", N/V, progressive hearing loss
- tx: low sodium diet (1000-1500 mg/day), NO surgical procedures for vertigo, avoid sudden movements
- meds: antihistamines (meclizine), tranquillizers (diazepam), antiemetics, diuretics
-Fall risk
No sudden manuevors =
No sodium menUVieres
hearing impairment
Face client when speaking
no loud voice
occupations: construction/military
ototoxic meds: lasix/furosemide, NSAIDS, Myocins
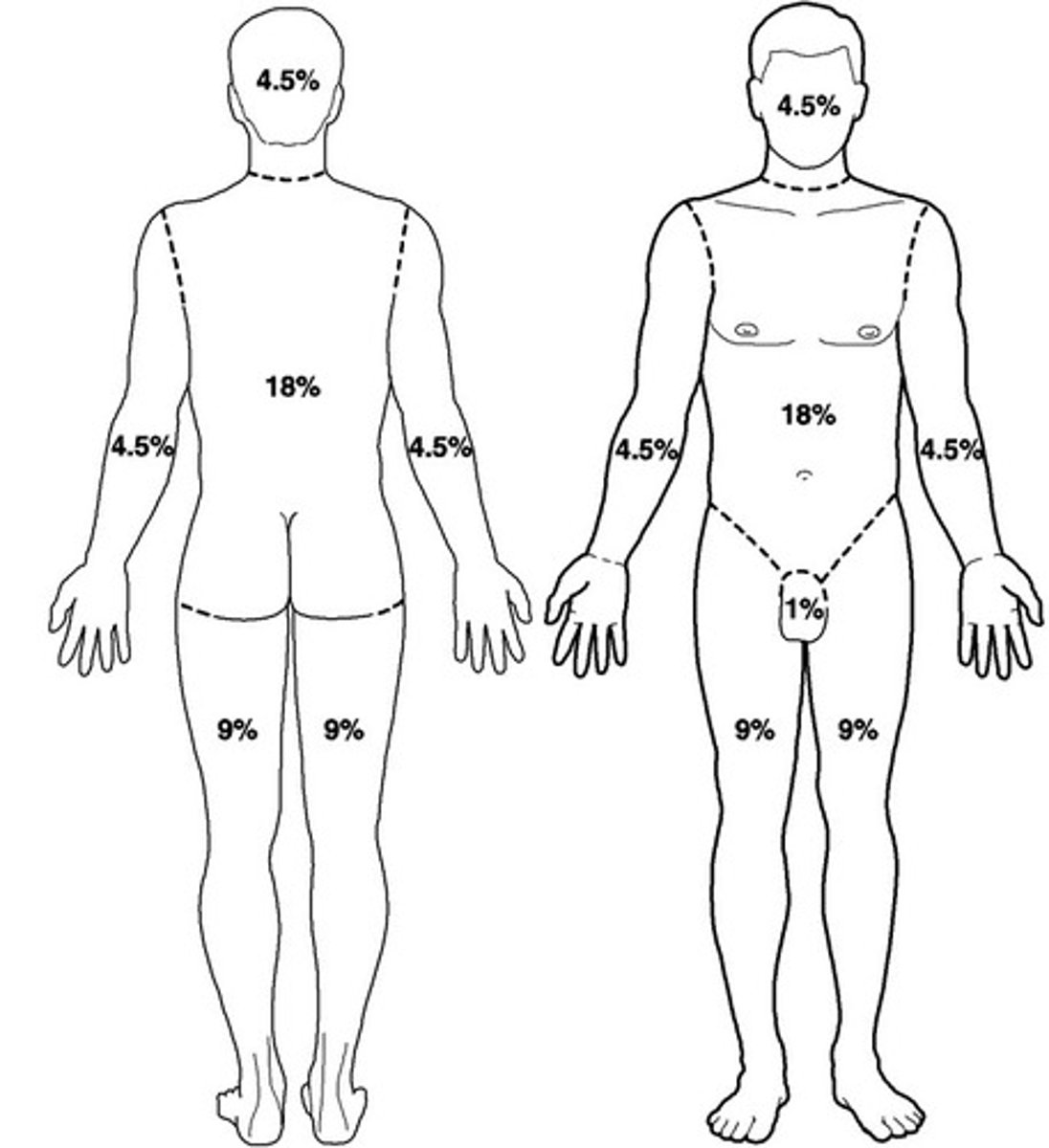
Rule of nines
determines TBSA% burned
- anatomic regions of the body
- add all affected burn areas
parkland formula
remember PARKLAND FOURMULA
4 mL x % burn (TBSA) x pt weight in kg = total fluids (mL) for 24 hours
- ½ of the total volume is given over the first 8 hrs
- remaining fluid given over next 16 hrs
Burns labs
Hyperkalemia
Hyponatremia
High H&H
Burns: Emergent/Resuscitative Phase: In-hospital care
•Airway/breathing
•Fluid resuscitation
•Indwelling urinary catheter insertion
•NG tube insertion
•Client is stabilized and condition is continually monitored
•Continuous telemetry monitoring
•Pain control
•Psychosocial and emotional support
neutropenic precautions
□ Monitor WBC count, neutrophil levels
□ Assess for signs and symptoms of infection, such as fever, chills, or sore throat
□ Strict hygiene
□ Limit visitors
□ Avoid flowers or plants to avoid pathogens
□ Ensure proper ventilation and air filtration
□ Educate on early signs of infection
□ Educate on avoiding raw or uncooked foods
HIV
- chronic infection
- cannot be cured, lifelong therapy
- acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) is the disease caused by HIV infection
Transmission: blood, semen, vaginal fluid, breast milk, sharing needles
HIV post-exposure prophylaxis
1. CDC: begin antiretroviral meds ASAP (<72 hours after possible HIV exposure
2. drugs prescribed for 28 days
3. follow-up blood testing
**not 100% effective
AIDS: Stage 3
**All people with AIDS have HIV, but not all people with HIV have AIDS.
○ Defined as a CD4 count <200 CD4 or the occurrence of an AIDS defining illness
○ Not enough CD4 T-lymphocytes present to fight off infection
○ Immune system is severely impaired
○ Characterized by life-threatening opportunistic infections
○ End stage of HIV
○ Without treatment, death often occurs within 5 years
AIDS defining conditions
these typically occur in individuals with significantly weakened immune systems due to advanced HIV infection
- pneumocytes pneumonia
- Kaposi's sarcoma
- candidiasis
- cytomegalovirus
- TB
- HIV wasting syndrome
- malnutrition
- infection in general
etc.
HIV testing
screening: ELISA
confirmation: western blot
viral load: effectiveness of ART
CD4 Count: if western blot positive, checks pt's immune system
HIV medications
- ART (antiretroviral therapy): combination drug therapy
- PrEP (pre-exposure prophylaxis): do not have HIV but at risk
- PEP (post-exposure prophylaxis): exposed to HIV, <72 hours
At least 2-3 medications are used in combination every day to suppress HIV replication
HIV education
Avoid large gatherings
clean toothbrush through dishwasher
avoid digging in garden
hand hygiene regularly
airborne precautions
PPE: gown, gloves, N95
- private negative air pressure/airflow room
- keep door closed
- Measles, TB, Varicella (MTV=airborne)
droplet precautions
PPE: mask, face shield/goggles
- face mask within 3-6 ft to pt
- private room, but door can remain open
- pneumonia, influenza, meningitis, mumps, pertussis (PIMMP = droplet)
flu vaccine - egg allergy, and Guillian barre
flu tx: viral, supportive care, FLUIDS, bedrest
contact precautions
PPE: gown, gloves (mask not needed)
- private room or pt with same infection
- MRSA, VRE, CDIFF
Clostridium difficile
○ causes: antibiotic therapy or immunosuppression, toxins from bacteria are released into the bowel and cause excessive diarrhea, spreads easily
risk: dehydration and fluid and electrolyte imbalance
○ tx: oral vancomycin or metronidazole, fluids
○ management: contact precautions, gowns and gloves, handwashing, clean equipment with a bleach product, dedicated equipment, leave equipment in room, gloves off first(dirtiest piece)
Central line associated blood stream infections (CLABSI) nursing interventions
□ Hand hygiene
□ Sterile technique
□ Skin preparation with antiseptic solution (chlorhexidine)
□ Daily assessment
□ Securement of catheter
□ Cap and line care
□ Change dressing every 7 days
Catheter associated UTI (CAUTI) nursing interventions
- assess need, avoid indwelling catheter whenever possible
- monitor urinary output
- sterile technique with insertion
- securement device
- adequate hydration to promote urine flow and flush bacteria
- timely removal
rheumatoid arthritis & manifestations
○ Chronic systemic inflammatory disease (autoimmune)
○ Destruction of connective tissue and synovial membrane within the joint
○ bilateral and symmetric
Shows up in Small joints of hands and feet. Knees would be more like osteoarthritis.
bilateral/symmetrical, typically begins in hands and feet, morning stiffness, ↓ ROM, tenderness, joint deformities, muscle atrophy, joint spongy on palpation
systemic: fever, fatigue, weakness
rheumatoid arthritis management
○ non-pharm management: education, physiotherapy, rest, exercise
○ NSAIDS
○ DMARDS: Methotrexate (bone marrow suppression, monitor BP and s/s of infections (Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs))
○ Corticosteroids (long-term risk for immunosuppression)
○ Reconstructive surgery
○ Joint arthroplasty
systemic lupus erythematosus
Chronic, progressive, systemic inflammatory disease (no cure)
○ Exaggerated production of autoantibodies that attack many sites in the body
○ Can cause failure of major organs
Extreme fatigue
Photosensitivity (sensitivity to sun exposure)
Hair loss
Skin rashes
Joint pain or swelling
Chest pain when breathing deeply
Headaches
Lupus nursing management
Pharm: NSAIDS
Corticosteroids (immunosuppression)
-biologic DMARDS
-non-biologic DMARDS
-Antimalarials (hydroxychloroquine)
○ Monitor for medication effectiveness
○ Monitor adverse effects of medications
○ Adequate nutrition
○ Pain relief
○ Routine health screenings
○ Report manifestations that can indicate SLE exacerbation or complications
○ Teach to avoid cold hands/toes, raynauds
○ Protect from sun exposure
○ Treatments for impaired skin integrity
○ psychosocial support
○ monitor body temperature
What can exacerbate this?
sunlight, warm to cold, illness/infection, pregnancy, emotional stress, sleep deprivation, rigorous exercise
gout & ssx
- inflammatory arthritis
- hyperuricemia: uric acid crystals to deposit in joints and body tissues, can lead to breakdown of purines in cells
- s/s: pain with movement or touch, redness, warmth, edema,
- most common in big toe joint
- attacks: 3-10 days with tx
gout tx
- allopurinol: prevention, take every day even w/ feeling well, drink plenty of fluids (renal failure side effects= ↑ fluids)
- tx: NSAIDs, Colchicine(Diarrhea), Corticosteroids
- diet: low in purines, avoid meats, shellfish, alcohol
take allopurinol as prescribed
exercise
limit intake of foods high in purine
increase fluids 2+L a day
avoid citrus juices
Addison's disease
↓ cortisol and aldosterone from adrenal glands
cortisol: metabolism, BP, glucose
aldosterone: fluid balance, reabsorbs NA and secretes potassium
- fatigue, irritability, depression
- skin hyperpigmentation, vitiligo
- weight loss
- N/V/D, constipation, abdominal pain
Sodium ↓
Potassium ↑
Sugar ↓
BP ↓
Remember Opposite of cushings
Addison Disease nursing management
○ ACTH stimulation test (addisons doesnt respond to acth stim)
- IV hydrocortisone 3-4L NS or dextrose
- 0.9 NS bolus
- Hyperkalemia = calcium gluconate/insulin & glucose
- daily weights
- monitor infection/hypoglycemia
Addisonian Crisis manifestations
○ Triggering factors: most common cause is abrupt withdrawal of glucocorticoid therapy
○ Stress on the body
- Dehydration
- ↓ BP Severe
○ ↓ NA
○ ↑ Potassium
○ ↑ BUN/Creatinine
- Profound fatigue
- Confusion and restlessness
Addisonian Crisis nursing management
○ Administer IV fluids (1st, secondary is meds)
○ Position: recumbent, legs elevated
○ IV hydrocortisone
○ Vasopressors to ↑ BP
○ Treat underlying cause (did we stop steroids abruptly? Tumor?)
Cushing disease/syndrome & ssx
Syndrome: ↑ cortisol usually from steroids
Disease: ↑ cortisol, inside harm from pituitary/adrenal/tumor
manifestations:
○ Personality changes
○ Weight gain
○ Fluid retention
○ Paper thin skin
○ Buffalo hump
○ Striae
○ Moon face
○ Sick more often
○ Osteoporosis
Sodium ↑
Potassium ↓
Sugar ↑
BP ↑
Think fat + fluids
Cushing disease/syndrome medical management
Dexamethasone Suppression test - before sleep, PO at 11 pm and cortisol lvl taken at 8 am.
○ Corticosteroids (syndrome): taper off
○ Tumor removal
○ Diuretics
○ No salt
hypothyroidism & ssx
Hashimoto's
T3/T4 ↓ TSH ↑
- ↓ metabolism = ↑ weight
- fatigue and lethargic
- cold intolerant
- dry skin, brittle hair
- large tongue (monitor airway)
- ↓ HR
- ↓ BP
hypothyroidism tx
Levothyroxine
- monitor for hyperthyroidism
- take in morning on empty stomach
- lifelong
fluids for ↓ bp
hyperthyroidism & ssx
Graves disease
T3 T4 ↑ TSH ↓
- anxiety, restless, irritable
- heat intolerant
- HTN
- bulging eyes
- diarrhea
- ↓ weight
- ↑ HR
- ↑ BP
hyperthyroidism tx
- thyroidectomy (monitor for hypocalcemia, trach kit nearby)
- Propylthiouracil (PTU) (monitor for infection, thrombocytopenia)
- Methimazole
- Betablockers LOL's
- Radioactive iodine therapy (radioactive precautions)
thyroid storm & ssx
Surge of thyroid hormones by stressful event
↑ temp
↑ HR
↑ BP
chest pain, delirium, psychosis
thyroid storm tx
- O2
- cool patient (blanket, antipyretics, acetaminophen)
- ↓ HR = digoxin
- Dextrose IV fluids
- calm environment
- PTU
- BB
diabetes insipidus & ssx
Dry inside
↓ ADH
- ↑ Urine output > 250 mL/hr
- ↓ gravity = diluted
- polydipsia (thirsty)
- polyuria
- ↓ BP
- ↑ HR
- ↑ NA
- dehydration
- weight loss
- seizures
diabetes insipidus tx
fluid deprivation test: fluids held for 8-12 hrs or until 3-5% body weight lost, stop if dehydration ssx occur.
Desmopressin (at night, prevent nocturia)
- lifelong
- fluids first
Remove tumor
Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion (SIADH) & ssx
Soaked Inside
↑ ADH
- ↓ Urine output
- ↑ gravity = concentrated
- ↓ osmolality
- seizures
- ↑ BP
- ↓ HR
- ↓ NA
- fluid overload ssx
Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion (SIADH) tx
S -Sodium tabs, 3% saline, NS
I -I&O's strict
A -abx
D -diuretics, daily weights, diet
H -head check
type 1 diabetes mellitus
Autoimmune, insulin dependent
- Insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas are destroyed
- Result: absence of pancreatic insulin production, unchecked glucose release by the liver, and fasting hyperglycemia, fat breakdown, producing ketoacidosis and a profound reduction in blood pH
- Tx: Insulin
fasting glucose = 126+
2-hour, post meal glucose = 200+
A1C = 6.5+
type 1 diabetes manifestations
Hyperglycemia
3 P's = Polydipsia, Polyuria, Polyphagia
Weight loss (ketones)
Fatigue, weakness
N/V
Abdominal Pain
Kussmaul resp. with acidosis
type 2 diabetes mellitus
Insulin resistance, impaired insulin secretion
- Risks: obesity, >30, slow progressive, hyperosmolar coma
- Tx: diet, exercise, oral hypoglycemic drugs, lifestyle changes, +/- insulin
type 2 diabetes manifestations
slow onset, polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia, may go undetected for years, obesity, usually after age 35, wounds heal slow, lots of itching, blurred vision, recurring infections, fatigue.
diabetes diet
carbs- 45%
- whole grains, non-starchy veggies
fats- 20-35%
- reduce saturated and trans fats
protein- 15-20%
increase fiber, lowers cholesterol
diabetes and exercise
↓ BG
↓ weight
↓ cardiovascular risk
exercise when BG 80-250
DONT exercise if ketones present
high-intensity workout= snack prior, 15-g carb
HAVE comfortable shoes
sick day rules
○ Monitor BS every 2-4 hrs.
○ Continue taking insulin/oral meds during illness (can lead to hyperglycemia)
○ Consume liquids every hour to prevent dehydration
○ Meet carbohydrate needs through soft food 6-8 times per day
○ Test urine for ketones every 3-4 hrs of if BS is >240 mg/dL
meal coverage insulin
rapid acting, lispro = 10-15 mins before meal
short acting, regular = 30 mins before meal
Hypoglycemia ssx
- cold & clammy needs some candy
- hunger
- lightheaded
- tachycardia
- decreased LOC
- headache
diabetic ketoacidosis ssx
hyperglycemia emergency
T1D
S/S:
- 3 P's
- fruity breath
- Kussmaul breathing
diabetic ketoacidosis tx
Analyze:
- hyperglycemia >330
- glycosuria, positive ketones (acidotic)
- hyperkalemia
Tx:
1. 0.9% NS
2. IV regular insulin
3. Add dextrose to IV fluids once BG decreases to 200-250
- hourly BG monitoring
- monitor potassium, add once BG decreases
- cardiac monitor for arrhythmias
Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Syndrome (HHS) & ssx
Lack of insulin
T2D
>600 glucose
↓ BP
↑ HR
dehydration
neuro ssx
HHS management
1. Rehydration with IV fluid (usually 0.9% N/S bolus then 0.45% N/S infusion since hyperosmolar blood needs diluting), 6 liters of fluid replacement in initial 12 hours
2. IV regular insulin infusion
Monitor:
- I&Os, glucose, electrolytes
- educate about not stopping insulin
Neuro diagnostics
Glasgow Coma Scale
15 = Awake and Alert
8 = 8 or Less than 8 Intubate
6 = Coma
3 = Brain dead
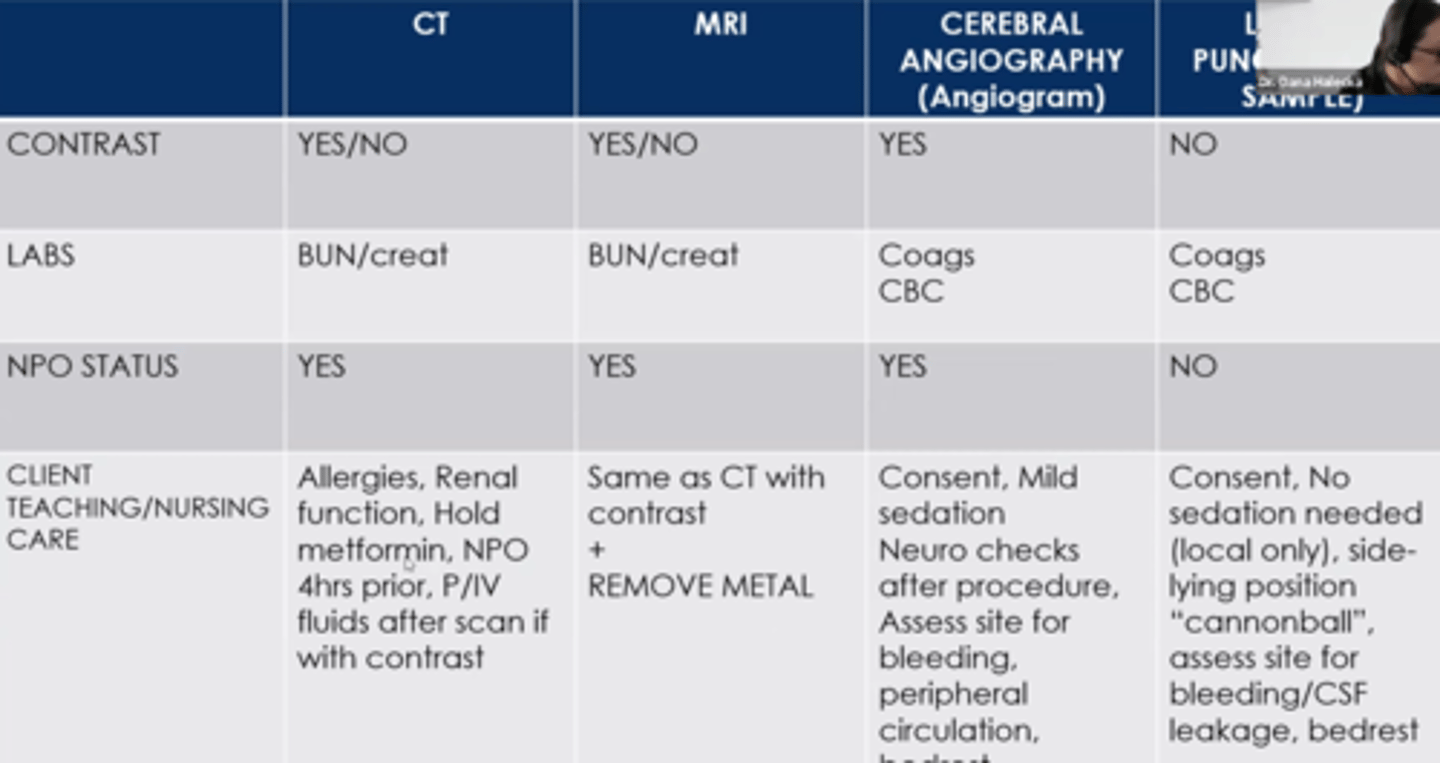
ICP Tx & Education
Tx:
- mannitol (working if they have ↑ UO), corticosteroid
- phenytoin (stop or prevent seizures)
- 3% NS
- semi-fowlers, elevate HOB(#1 intervention)
- Quiet environment
Educate:
- avoid: coughing, sneezing, vomiting, rapid IV bolus, suctioning
- constipation: stool softeners
ICP Cause & Early/Late ssx
Cause: increased CSF, blood entering CSF, head trauma/infection, tumors
Early
- Changes in LOC
- Confusion
- Headache
- Vision changes
Late
- ↑ Temp and BP (widened pulse pressure)
- ↓ HR and RR (two rates go down) Cushing's Triad
- vomiting
- dilated pupils
- seizures, coma, posturing
head injury priority
Stabilize/immobilize cervical spine until injury is ruled out
if have to do CPR: modified jaw thrust
Nursing Management of Spinal and Neurogenic Shock
- Vitals (bradycardia)
- MAP >= 85 mm hg
- Isotonic fluids
- Meds to ↑ BP or HR (norepi, dobutamine, atropine)
- I + O's
- VTE (scd's)
- Monitor GI fx
- NG tube gastric decompression
- prevent skin breakdown
Autonomic Dysreflexia
OVERREACTION of a stimulus below SCI.
-Distended bladder = most common cause
-Constipation or bowel impaction
-Stimulation of the skin (pressure injury, pain from ingrown toenail, restrictive clothing)
-Place client in sitting position immediately - this is priority!
-Notify the healthcare provider
-Determine and treat the cause
-Check patency of urinary catheter or insert catheter for distended bladder
-Remove fecal impaction
-Assess for injury (skin, fractures, infection)
-Remove tight clothing
-Adjust room temperature and block drafts
-Vitals
-Antihypertensives (nitrates or hydralazine)
Above injury: ↑ BP, Bradycardia, red, sweaty, ha
Below injury: Cool, clammy, pale
Left and Right brain functions/stroke manifestations
Left hemi manifestations: language, math, analytical thinking, more airway prior
Right hemi manifestations: visual, spatial awareness, proprioception, hemianopsia, more safety prio
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)
Temporary blockage of blood flow
-Warning of impending stroke
BE FAST
B=loss of Balance
E=Eyesight changes
F=Facial droop
A=Arm weakness
S=Speech difficulty
T=Terrible headache
911