superman or voldemort -- lactate
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
lactate in the anaerobic system
byproduct of the glycolytic system
steps to lactate creation
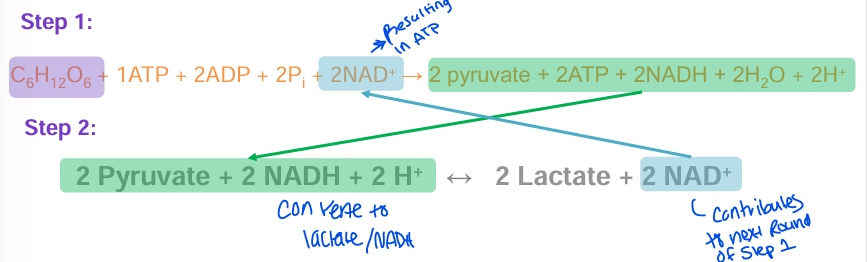
Lactate doesn’t give us energy but it
allows us to start glycolysus again
production of lactate from pyruvate recycles
NAD shuttles and prevents pyruvate from accumulating
conversion provides
recycled NAD to enable continued glycolysis
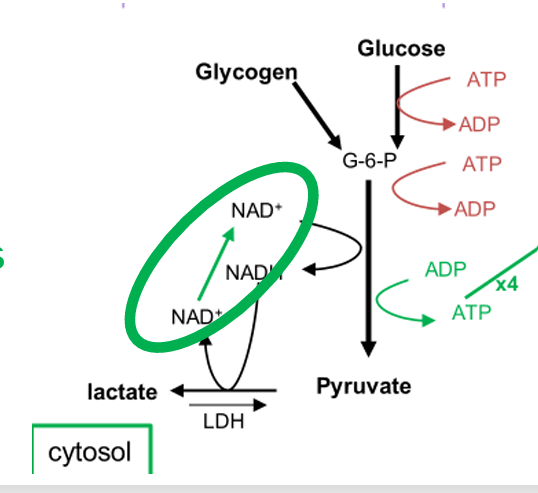
conversion of pryuvate to lactate enables
continued glycolysis
faster lactate production leads to
higher power in 30s
faster final sprint during 5KM time trial
more lactate =
more energy
lactate’s sidekick
H +
Acidosis
drop in PH due to the accumulation of H
Decrease in PH of the muscle (muscular acidosis) impairs
Ca release and re-uptake into SR
sensitivity of myofilaments to Ca+
ATPase activity
enzyme (PFK and phsophorylase) activity
acidosis gives (force)
32% lower max force
acidosis gives (length)
13% muscle shortening
Acidosis and CA
more calcium is required to activate muscle but less calcium is available
acidosis and atpase activity
slower crossbridge cycling
enzyme activity and acidosis
slower metabolism
decreased PH in the muscle and systemically can lead to
muscle soreness
vomiting
lightheadedness and fainting
headache
more hydrogen =
more fatigue
lactate production enables fast
glycolytic energy
lactate production is key mechanism for
fatigue and feelings of unwell
how does lactate become the villain
once it accumulates then it becomes bad.
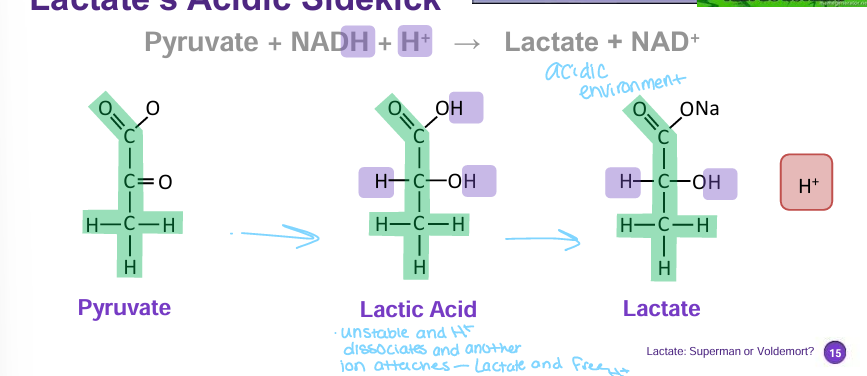
how lactate is created
pyruvate → lactic acid → lactate and H+
Acid-base regulation
buffering describes processes that reduce changes in H+ concentration
pertubation for acid-base regulation
accumulation of H+ reduces PH
Adjustment for acid base regulation
buffering = the adjustments needed to restore equilibrium
buffering
the processes that reduce changes in H+ concentration
bicarbonate buffering
bicarbonate (HCO3) combines with H+ to form water and carbon dioxide
can occur within the cytosol and or within the blood
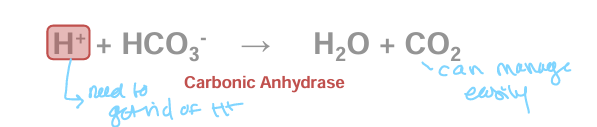
summary of lactate clearing
H⁺ and lactate are produced during metabolism.
HCO₃⁻ buffers H⁺, converting it into CO₂ and water.
CO₂ is transported by red blood cells and plasma.
CO₂ is exhaled in the lungs, helping to maintain pH balance.
The kidneys and liver also help remove excess lactate and H⁺.
lactate will be converted
back into pryuvate to be utilized again
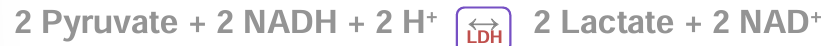
conversion of pryuvate occurs
in the muscle of origin
in the liver of different muscles
pryuvate in muscle of origin
pryuvate restarts it oxidative journey
conversion back to pryuvate
lactate is transported into the blood through monocarboxylate transporter (MCT)
transported in the blood to other muscles
transported in the blood to the liver
Cori Cycle
overall lactate
conversion of pyruvate into lactrate recyles NAD shuttle and enables continued glycolysis
H+ overall
generated during this conversion reduces muscle performance and contributes to fatigue
H+ is buffered by HCO3 to produce CO2 and H20
Lactate is oxidized and/or
converted back to pyruvate in the muscle or liver