Electricity and Magnetism topic 5 (Physics)
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What are the electrical charge rules
Like charges repel; opposite charges attract
Electrons are the ones moving/jumping
When moving don’t go very far in the present case
Electrical force: Force of attraction or force of repulsion
What is the imbalance in an object/body due to
excess or deficiency in e- . Innermost e- are held firmly. But superficial ones are easy to remove or shiS (valence electrons). To remove an e- depends on the nature of the material. e- are held firmly in rubber or plasIc than in wool.
What is static electricity
Corresponds to electrical phenomena related to charges at rest (not dynamic electricity). So associated to insulating objects (Isulators)
How do electrons distribute with conductors
Electrons in an ecess distribute at the surface of the object
What are the 3 ways to charge an object
Friction
Conduction
Induction
How does charging with friction work
The electrostatic series (Increasing tendency to gain electrons)
What is a friction example
Between wool and a Plastic rule. Plastic becomes negatively charged
What is charging by induction
Charging without any contact (electroscope) (NO TRANSFER OF e- from one object to another)
What is Coulombs law
Two charged particles nearby at a distance d. Electrical force between them:Fq(N)
What creates and electric field, E
Any fixed charged object
What does the electric field do?
The electric field stores energy. Electric energy is stored around a fixed charged object and depends on that fixed charge Q expressed in coulombs (C). A fixed charge is called a point charge, Q. Q can be posiIve or negaIve.
Any other charge (q) placed in the electric field (E) will be subjected to
an electrical force (Fq) due to the electric field E
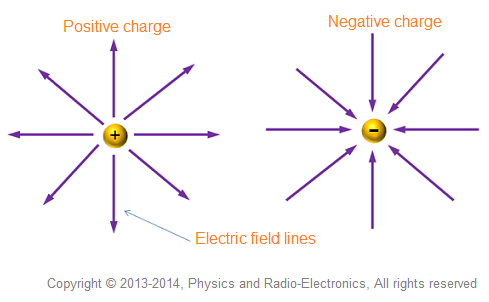
What is this? what does it create
Lines of force from a fixed charged particle:creates an electric field (E)
What does the worldwide convention says about the point charge?
Directopn of the electric field vector= as for a positive “test” charge when in presence of the electric field.
What are field line, or lines of force used to represent
Pictorially the electric field E
More than one particle and their field means what?
E is changing with/ d2
In a particle with and external field what will happen?
In an electric field E, a charged particle q will react.
The charged particle q is subjected to an electrical force