Introduction to COBOL
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
COBOL
stands for Common Business-Oriented Language
one of the oldest high-level programming languages
primarily used for business, finance, and administrative systems
designed to be easily understood and used by non-technical people
Key COBOL Features
global business language
easy readability
seamless integration with modern systems
portable language
evolving language
COBOL Program Structure
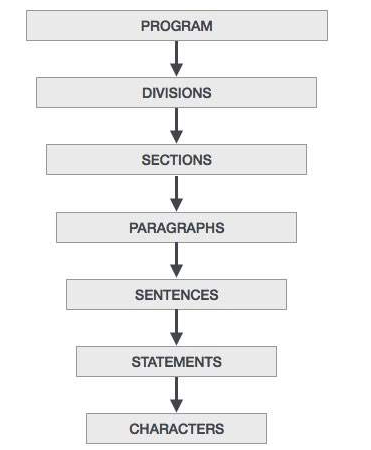
Sections (Program Structure)
logical subdivision of program logic
a collection of paragraphs
Paragraphs (Program Structure)
subdivision of a section or division
either a user defined or a predefined name followed by a period, and consists of zero or more sentences/entries
Sentences (Program Structure)
combination of one or more statements
appear only in the Procedure division
must end with a period
Statements (Program Structure)
performs some processing
Characters (Program Structure)
lowest in the hierarchy and cannot be divisible
Identification Division
mandatory division
this division is used to identify the program
PROGRAM-ID is mandatory in this division
program name
consist of 1 to 30 characters
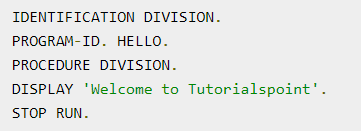
Environment Division
specify input and output files to the program
consist of two sections:
Configuration section
Input-Output Section
Configuration Section (Environment Division)
provides information about the system on which the program is written and executed
Consist of two paragraphs:
Source Computer - system used to compile the program
Object Computer - system used to execute the program
Input-Output Section (Environment Division)
provides information about the files to be used in the program
Consist of two paragraphs:
File Control - provides information of external data sets used in the program
I-O control - provides information of files used in the program
Data Division
used to define the variables used in the program
File Section (Data Division)
used to define the record structure of the file
Working-Storage Section (Data Division)
used to declare temporary variables and file structure which are used in the program
Local-Storage Section (Data Division)
similar to Working-Storage section
variables will be allocated and initialized every time a program starts execution
Linkage Section (Data Division)
used to describe the data names that are received from an external program
Procedure Division
used to include the logic of the program
consists of executable statements using variables defined in the data division
last statement to end the execution should be STOP RUN or EXIT PROGRAM
Position 1-6
column numbers
reserved for line numbers
Position 7
indicator
can have an asterisk * indicating comments
can have hyphen - indicating continuation
can have slash / indicating from feed
Position 8-11
area A
COBOL divisions, sections, paragraphs and special entries begins in this area
Positions 12-72
area B
COBOL statements must begin in this area
Positions 78-80
identification area
can be used as needed by the programmer
Symbol 9
used for declaring numeric data type
Symbol A
used for declaring alphabet
Symbol X
used for declaring alphanumeric
Symbol V
used for declaring Implicit Decimal
Symbol S
used for declaring sign
Symbol P
used for declaring assumed decimal