Murray State - BIO 101 Final Exam
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
Which of the following statements is a proper scientific hypothesis?
A.) Bats can navigate at night because they use sonar that does not require light.
B.) If you give more green light, plants will grow faster.
C.) If you take vitamin C, you will not get a cold.
A.) Bats can navigate at night because they use sonar that does not require light.
Choose the word that correctly completes the following statement:
'A(n) ________ is a proposed explanation for an observation.'
A.) Scientific method
B.) Scientific theory
C.) Experiment
D.) Hypothesis
E.) Prediction
D.) Hypothesis
What are all the steps used for the Scientific Method?
Note: The sequence does not matter.
A.) Observation/hypothesis/prediction/conclusion
B.) Hypothesis/conclusion/experiment/prediction
C.) Observation/statistics/hypothesis/conclusion/prediction
D.) Observation/experiment/hypothesis/conclusion/prediction
E.) Hypothesis/prediction/observation/proof/experiment
D.) Observation/experiment/hypothesis/conclusion/prediction
In an experiment, you measure the effect of 3 different fertilizers on the growth of sun flowers.You measure how much 30 sun flowers have grown on each fertilizer after 1 month.
What is the independent variable of your experiment?
A.) Sun flower growth
B.) Type of fertilizer
C.) Duration of experiment (1 month)
D.) 30 sun flowers
B.) Type of fertilizer
If you would measure the size and age of all the cows on your farm and plot the collected data, which kind of graph should you use?
A.) Line graph
B.) Bar graph
C.) Scatter plot
C.) Scatter plot
You measure how fast you are driving and your fuel consumption of your car. Which one is your dependent variable?
A.) Fuel consumption
B) Speed
C.) Make of the car
A.) Fuel consumption
Which variable do you put on the x-axis (horizontal axis) of a graph?
A.) Controlled variable
B.) Dependent variable
C.) Independent variable
C.) Independent variable
You designed an experiment and collected data for one control and one experimental group to test your hypothesis. Your statistical test yields a
p-value of 0.1. What do you conclude?
A.) The data between the control and experimental group are significantly different.
B.) The data between the control and experimental group are not significantly different.
C.) You cannot say.
B.) The data between the control and experimental group are not significantly different.
If the data from an experiment support the Null hypothesis, which of the p-values below could bethe hypothetical result of your statistical test?
A.) P = 0.01
B.) P =0.0001
C.) P =1.0
D.) P =0.5
E.) C & D
E.) C & D
A statistically relevant difference between two groups is detected when the p-value is ....
A.) > 0.05
B.) < 0.50
C.) < 0.99
D.) ≤ 0.05
D.) ≤ 0.05
Which kind of source of scientific information is your text book?
A.) Primary source
B.) Secondary source
C.) Tertiary source
B.) Secondary source
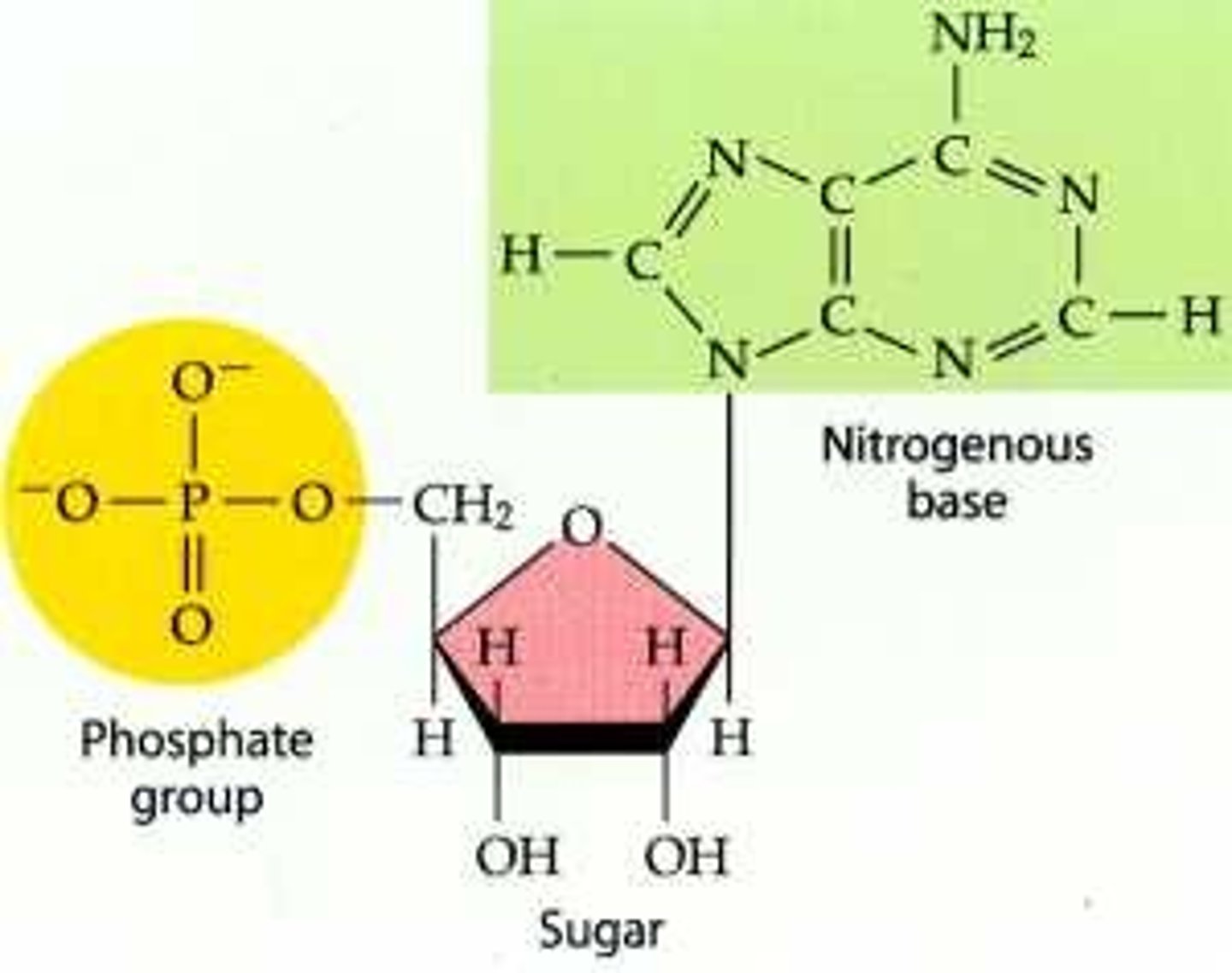
What is the molecule shown to the right?
A.) Protein
B.) Peptide
C.) Enzyme
D.) Amino acid
E.) Nucleotide
E.) Nucleotide
All scientific hypotheses need to fulfill which of the following criteria?
A.) Well-supported by several lines of research
B.) Testable & falsifiable
C.) Supported beyond reasonable doubt
B.) Testable & falsifiable
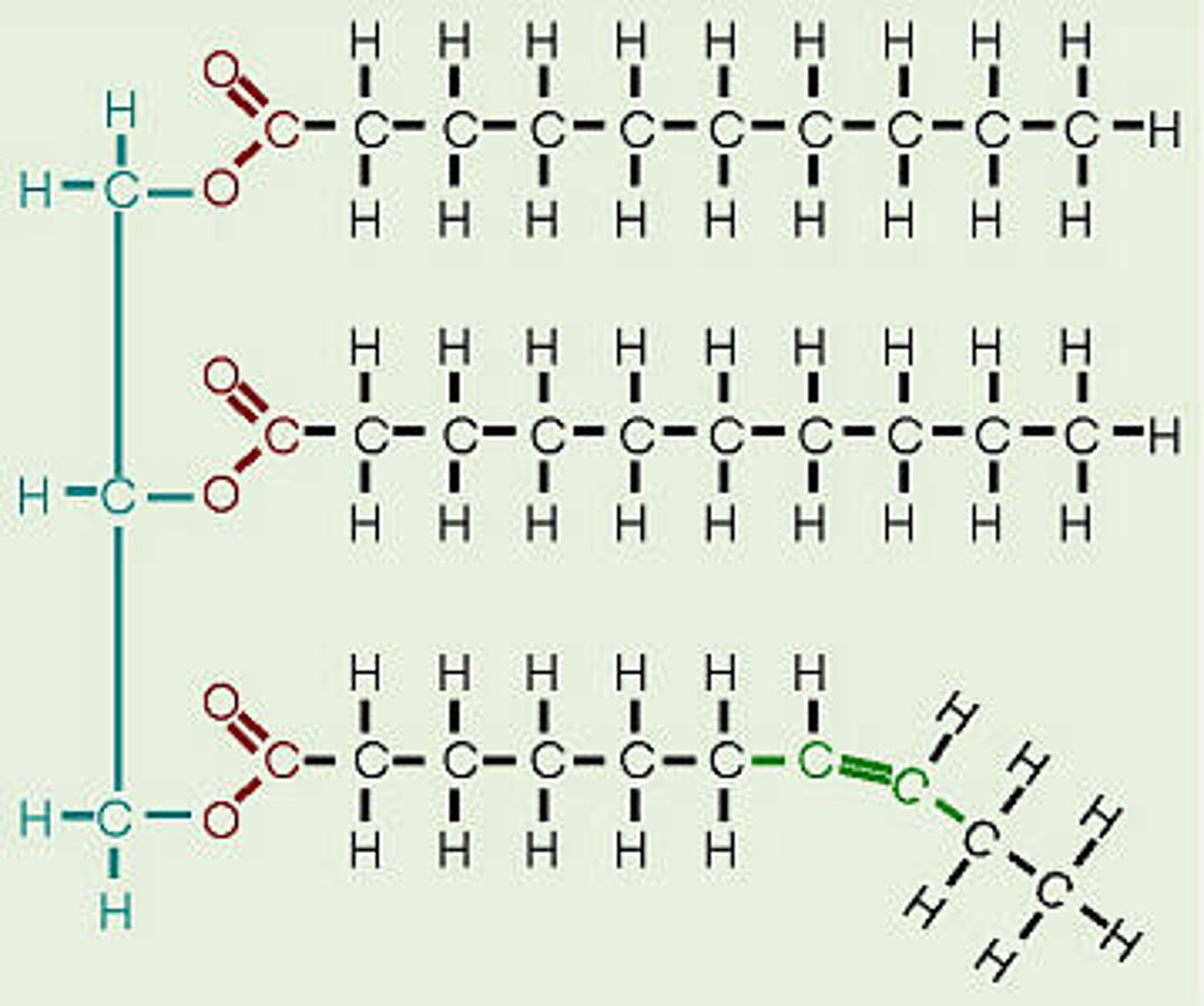
14. What is the molecule shown to the right?
A.) Glucose
B.) Nucleotide
C.) Lipid
D.) Amino acid
E.) Protein
C.) Lipid
15. Which macromolecules do amino acids assemble?
A.) Proteins
B.) Lipids
C.) Carbohydrates
D.) DNA/RNA
A.) Proteins
16. Which statement defines the cell theory?
A.) Every form of life consists of cells and cells can grow.
B.) Every form of life is a cell and cells can evolve.
C.) Every cell comes from a cell, and every form of life is a cell or consists of cells.
D.) Every cell is made up of other cells and they can move.
E.) Every cell has a metabolism and can reproduce.
C.) Every cell comes from a cell, and every form of life is a cell or consists of cells.
17. Which of the statements below states a proper Null hypothesis?
A.) The amount of light affects plant growth.
B.) The amount of light does not affect plant growth.
B.) The amount of light does not affect plant growth.
18. What is the theory called that states that mitochondria and chloroplasts were originally bacteria that were taken up by a primitive eukaryotic cell?
A.) Endoplasmic theory
B.) Endosymbiotic theory
C.) Cell theory
D.) Prokaryotic theory
B.) Endosymbiotic theory
19. Plant cells differ from animal cells in that they have.....
A.) Membrane-bound organelles
B.) A large central vacuole
C.) A Golgi complex
D.) Nucleus with membrane
B.) A large central vacuole
20. What kind of cell is shown in the picture to the right?
A.) Animal cell
B.) Plant cell
C.) Prokaryote
B.) Plant cell
21. What is the function of mitochondria?
A.) Photosynthesis
B.) DNA synthesis
C.) Energy production
D.) Detoxification
E.) Protein synthesis
C.) Energy production
22. Which of the following cell organelles cannot be found in a plant cell?
A.) Nucleus
B.) Golgi Apparatus
C.) Centrioles
D.) Large vacuole
E.) Mitochondrion
C.) Centrioles
You have an aquarium full of water that is separated by a membrane placed in the center of the aquarium. On the left side, you have a high concentration of a dissolved substance and on the right side, you have a low concentration of the same dissolved substance. The membrane does not let the substance pass through. What is going to happen?
A.) Water moves from left to right.
B.) Water moves from right to left.
B.) Water moves from right to left.
What process moves water from low concentration to high concentration?
A.) Diffusion
B.) Osmosis
C.) Equilibrium
B.) Osmosis
From where to where do dissolved substances go during diffusion?
A.) From high to low concentration
B.) From low to high concentration
A.) From high to low concentration
Choose the word from the list below that correctly completes the following statement.
'The plasma membrane is called _____________________ because it lets certain substances pass but not others.'
A.) impermeable
B.) selectively permeable
C.) phospholipid
D.) flexible
B.) selectively permeable
If an animal cell is placed in a highly concentrated solution (e.g., salt water), what is going to happen to it?
A.) The cell will gain water and burst.
B) The cell will lose water and shrivel
C.) Nothing
B) The cell will lose water and shrivel
If a cell is placed in a highly concentrated solution, what is the solution called relative to the cell?
A.) Isotonic
B.) Hypotonic
C.) Hypertonic
C.) Hypertonic
What is the process called when large molecules enter a cell and does it require energy?
A.) Exocytosis and no energy
B.) Exocytosis and energy
C.) Facilitated diffusion, no energy
D.) Endocytosis and energy
E.) Endocytosis and no energy
E.) Endocytosis and no energy
What is it called when small, charged molecules cross a membrane through channels according to their concentration gradient?
A.) Diffusion
B.) Active transport
C.) Facilitate diffusion
C.) Facilitate diffusion
What are you?
A.) Prokaryote
B.) Eukaryote
C.) Smurf/Smurfette
B.) Eukaryote
What are essential amino acids?
A.) Amino acids that are essential for all cell processes.
B) Amino acids that your body can synthesize from other amino acids.
C.) Amino acids that the body cannot synthesize on its own.
D.) Amino acids that are essentially in any type of food.
C.) Amino acids that the body cannot synthesize on its own.
Are vitamins micronutrients or macronutrients?
A.) Micronutrients
B.) Macronutrients
A.) Micronutrients
What can bad cholesterol cause?
A.) Constipation
B.) Liver failure
C.) Heart attack
D.) Diarrhea
E.) Bad gas
C.) Heart attack
What is the following statement?
'If protein makes puppies grow faster, then increasing protein in their diet will cause a faster weight gain compared to puppies on a standard diet'.
A.) Hypothesis
B.) Prediction
C.) Scientific theory
B.) Prediction
What kind of molecule is a protease?
A.) A complex sugar
B.) A fat
C.) An enzyme
C.) An enzyme
Chose the combination of terms below that correctly completes the following sentence:
' ___________________ require input of energy and their products are ____________ in stored energy'.
A.) Exergonic reactions/low
B.) Exergonic reactions/high
C.) Endergonic reactions /low
D.) Endergonic reactions /high
D.) Endergonic reactions /high
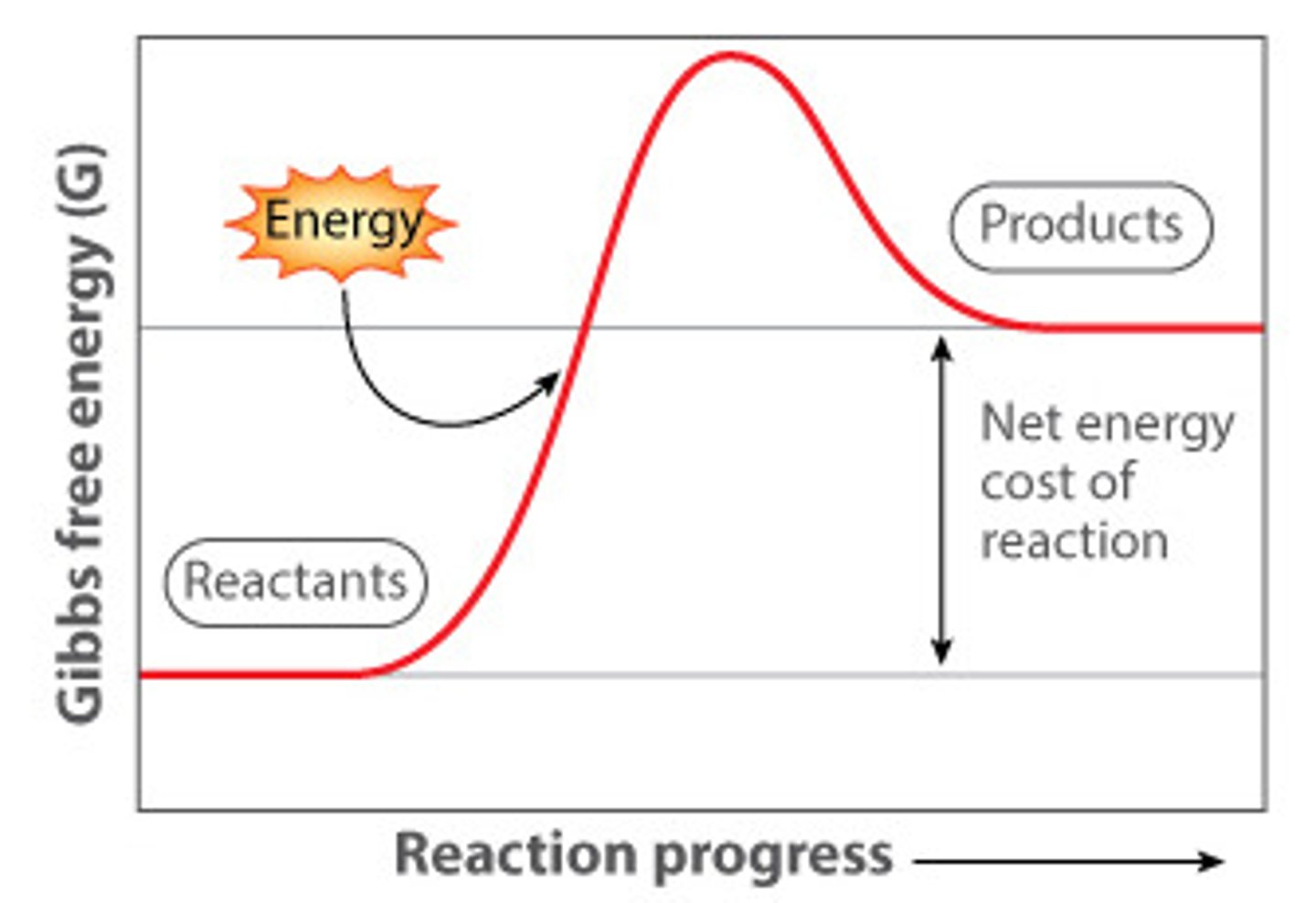
The graph to the right shows, an .....
A.) ...exergonic reaction
B.) ....endergonic reaction
C.) ...ectogonic reaction
B.) ....endergonic reaction
Choose the combination of terms that correctly completes the following sentence
'An enzyme _________the rate of a chemical reaction by_______the activation energy.'
A.) Speeds up/increasing
B.) Slows down/decreasing
C.) Speeds up/decreasing
D.) Slows down/increasing
C.) Speeds up/decreasing
When the enzyme binds the substrate, it changes its shape. What this change of shape called?
A.) Active site
B.) Induced-fit
C.) Hydrolysis
B.) Induced-fit
What are the two cyclic processes that are involved in the generation and chemical breakdown of ATP?
A.) Induced fit and Hydrolysis
B.) Metabolic rate and Hydrolysis
C.) Phosphorylation and Hydrolysis
D.) Glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation
C.) Phosphorylation and Hydrolysis
What are enzymes specific for?
A.) The product & substrate
B.) The reaction & product
C.) The substrate & reaction
C.) The substrate & reaction
'All physical and chemical reactions in your body that produce and use energy are cumulatively referred to as......'
A.) Cellular respiration
B.) Metabolism
C.) Catalysis
D.) Exergonic reactions
B.) Metabolism
Which of the following reactions correctly summarizes cellular respiration?
A.) C6H12O6 + 6CO2 -> 6O2 + 6H20 + ATP
B.) C6H12O6 + 6O2 -> 6CO2 + ATP
C.) C6H12O6 + O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H20
D.) C6H12O6 + 6O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H20 + ATP
D.) C6H12O6 + 6O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H20 + ATP
Which process(es) of cellular respiration does not require oxygen?
A.) Citric acid cycle
B.) Glycolysis & Calvin cycle
C.) Glycolysis
D.) Oxidative phosphorylation & Citric acid cycle
C.) Glycolysis
Which process of cellular respiration generates CO2?
A.) Glycolysis
B.) Oxidative phosphorylation
C.) Citric acid cycle
C.) Citric acid cycle
Which is the correct sequence of the processes taking place during cellular respiration?
A.) Citric acid cycle -> oxidative phosphorylation -> glycolysis
B.) Glycolysis -> citric acid cycle -> oxidative phosphorylation
C.) Citric acid cycle -> glycolysis -> oxidative phosphorylation
D.) Glycolysis -> oxidative phosphorylation -> citric acid cycle
B.) Glycolysis -> citric acid cycle -> oxidative phosphorylation
What is ATP used for?
A.) Transport work
B.) Mechanical work
C.) Chemical work
D.) All of the above
D.) All of the above
What is the final product of anaerobic respiration (fermentation) that takes place in your muscle?
A.) Pyruvate/Pyruvic acid + ethanol
B.) CO2
C.) Lactate/Lactic acid
D.) NADH
C.) Lactate/Lactic acid
When you cannot supply enough oxygen during your workout, fermentation in your muscles takes place. Which process of cellular respiration still works without sufficient oxygen supply?
A.) Citric acid cycle
B.) Glycolysis
C.) Oxidative phosphorylation
B.) Glycolysis
Which statement about global warming is true?
A.) Ozone needs to be regulated to reduce the heating of the planet.
B.) Methane is the greenhouse gas that is emitted most by human activities.
C.) Global warming is a cyclical event.
D.) Human-produced CO2 emissions need to be reduced to slow down global warming.
D.) Human-produced CO2 emissions need to be reduced to slow down global warming.
Which one is not a greenhouse gas?
A.) CO2
B.) Ozone
C.) Methane
D.) CFCs
B.) Ozone
Which is the correct equation for photosynthesis?
A.) 6CO2 + 6H2O --> C6H12O6 + 6O2 + light energy
B.) 6CO2 + 6O2 + light energy --> C6H12O6 + 6H2O
C.) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy --> C6H12O6 + 6O
C.) 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy --> C6H12O6 + 6O
Which step of photosynthesis assembles glucose?
A.) Light reactions
B.) Citric Acid Cycle
C.) Calvin cycle
C.) Calvin cycle
What are the two reactions that take place during photosynthesis?
A.) Light reactions and oxidative phosphorylation
B.) Light reactions and Calvin cycle
C.) Light reactions and Citric Acid Cycle
B.) Light reactions and Calvin cycle
Where does photosynthesis take place?
A.) Mitochondrion
B.) Cytoplasm
C.) Chloroplast
C.) Chloroplast
What is the correct sequence of events that correctly describes the greenhouse effect?
A.) Sunlight warms the atmosphere -> thick layer of ozone accumulates heat directly from the sun -> atmosphere and Earth warm up.
B.) Sun warms up CO2 -> the warm CO2 rises into the atmosphere -> this movement of CO2 causes the warming of Earth.
C.) Sunlight warms the Earth -> some heat from the globe radiates into the atmosphere and space -> thick layer of greenhouse gases traps some of the radiated heat and re-radiates it back to Earth warming the globe.
D.) Sun warms Earth -> warm CO2 is released from hot soil -> accumulates in the atmosphere and warms up Earth.
C.) Sunlight warms the Earth -> some heat from the globe radiates into the atmosphere and space -> thick layer of greenhouse gases traps some of the radiated heat and re-radiates it back to Earth warming the globe.
Which step of photosynthesis produces oxygen?
A.) Light reactions
B.) Calvin cycle
A.) Light reactions
True or false? Photosynthesis uses green and blue light.
A.) True
B.) False
B.) False
What is a benign tumor?
A.) A tumor that has no effect on surrounding tissue.
B.) A tumor invades surrounding tissue.
C.) A tumor that is caused if individual cells break away and start a new tumor elsewhere.
A.) A tumor that has no effect on surrounding tissue.
What are the chromosome members of a chromosome pair called?
A.) alleles
B.) homologous chromosomes
C.) sister chromatids
B.) homologous chromosomes
What are the two halves of one duplicated chromosome called?
A.) alleles
B.) homologous chromosomes
C.) sister chromatids
C.) sister chromatids
During which phase of the cell cycle does the cell plate and cell wall grow across the cell, dividing it into two new cells?
A.) Interphase
B.) Telophase
C.) Cytokinesis
D.) Prophase
C.) Cytokinesis
What is DNA replication?
A.) A process that duplicates the chromatids.
B.) A process that doubles the number of chromosomes.
C.) A process that synthesizes homologous chromosomes.
A.) A process that duplicates the chromatids.
A cell (sperm or egg cell) at the end of Meiosis shows which of the following features?
A.) Diploid with unduplicated chromosomes
B.) Haploid with duplicated chromosomes
C.) Diploid with duplicated chromosomes
D.) Haploid with unduplicated chromosomes
D.) Haploid with unduplicated chromosomes
A cell at the start of Mitosis is......?
A.) Haploid
B.) Diploid
B.) Diploid
During Meiosis, what is being separated in the second meiotic division?
A.) Homologous chromosomes
B.) Sister chromatids
C.) Homologous chromosomes and sister chromatids
D.) Nothing
B.) Sister chromatids
After the first meiotic division, the cells are...?
A.) Haploid
B.) Diploid
A.) Haploid
True or false? The second meiotic division is similar (i.e., what is being separated) to Mitosis.
A) True
B) False
A) True
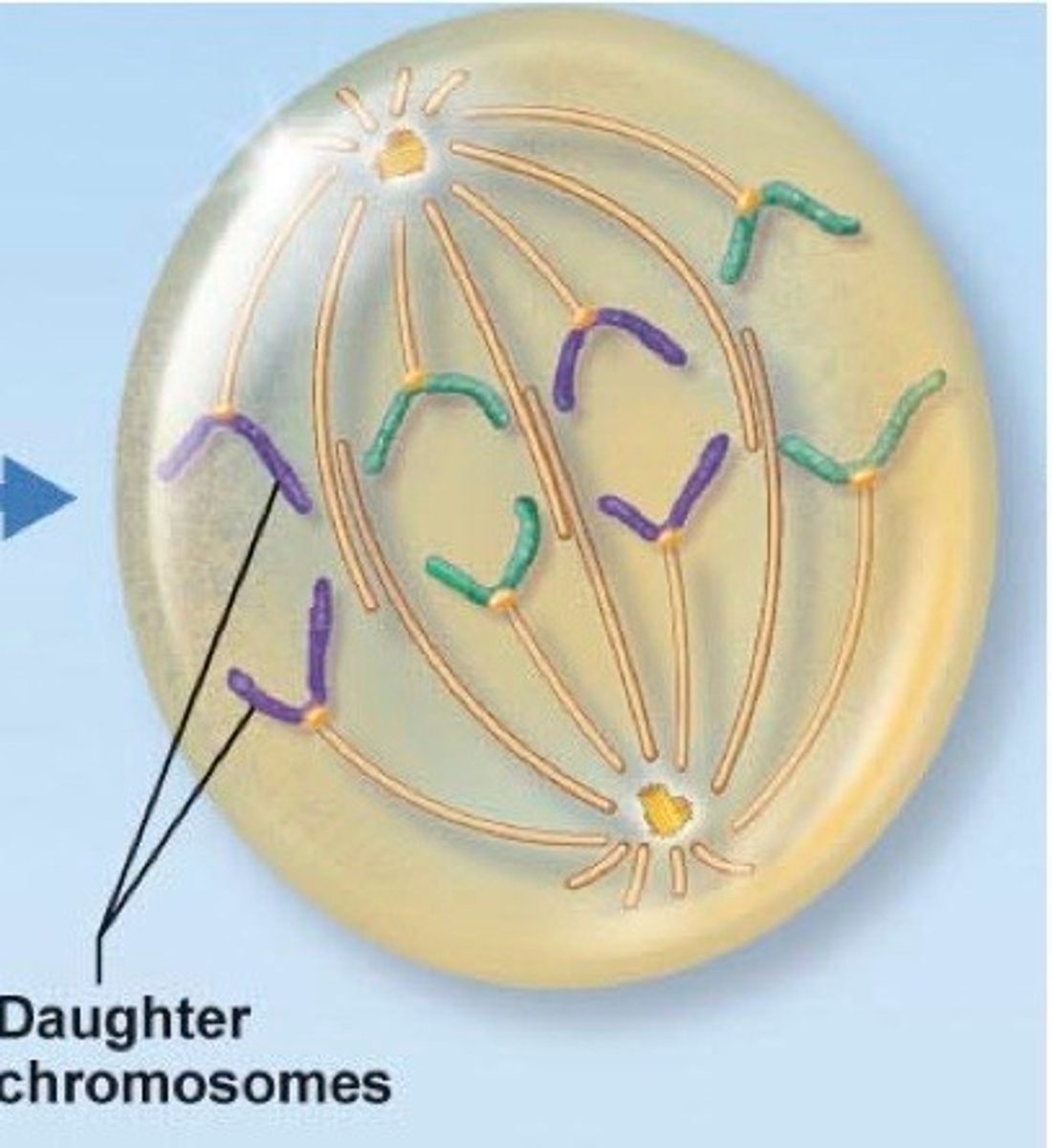
Which mitotic phase is shown in the cartoon to the right?
A.) Prophase
B.) Metaphase
C.) Telophase
D.) Anaphase
E.) Interphase
D.) Anaphase
Why is DNA replication considered semiconservative?
A.) The DNA molecule is composed of a parental strand and newly synthesized DNA strand.
B.) DNA is not just one strand, but two complementary strands.
C.) DNA is divided into a top half and a bottom half before replicating.
A.) The DNA molecule is composed of a parental strand and newly synthesized DNA strand.
What happens during a crossing-over event?
A.) Homologous chromosomes exchange genes.
B.) Homologous chromosomes are separated.
C.) Sister chromatids arrange randomly in the equatorial plane.
A.) Homologous chromosomes exchange genes.
True or false? Cells during mitosis are always haploid.
A.) True
B.) False
B.) False
1. On average, what percentage of alleles do dizygotic (fraternal) twins share? A.) 0%
B.) 50%
C.) 75%
D.) 100%
E.) 25%
B.) 50%
2. A mutation that results in an allele that functions in the same way as the original allele is called a...
A.) Non-sense mutation
B.) Dysfunctional mutation
C.) Neutral mutation
C.) Neutral mutation
3. Black hair is the result of a dominant allele ('B') and blond hair is the result of recessive alleles ('b'). The mother has blond hair (phenotype). Which genotype (i.e., Bb, BB, bb) does the mother have for her hair color?
A.) BB
B.) Bb
C.) bb
C.) bb
4. Assuming that all of the kids (without exception) of the mother from the previous question have blond hair, which genotype does the father have for hair color?
A.) BB
B.) Bb
C.) bb
C.) bb
5. There are different kinds of twins. Monozygotic twins are .....
A) The result of two separate eggs fusing with different sperm cells at the same time.
B) The result of one fertilized and one unfertilized egg cell.
C) The result of daughter cells that separate from each other early in development and each becomes one embryo.
C) The result of daughter cells that separate from each other early in development and each becomes one embryo.
6. Is your height a quantitative or qualitative trait?
A.) Quantitative trait
B.) Qualitative trait
A.) Quantitative trait
7. True or false? 'Quantitative traits are typically the result of many interacting genes'.
A.) True
B.) False
A.) True
8. A widow's peak (hairline on forehead) is the result of a dominant allele ('W'). If the father is homozygous dominant for this allele and the mother does not have a widow's peak, what is the probability (%) for each of their kids to have a widow's peak?
A.) 0%
B.) 25%
C.) 50%
D.) 75%
E.) 100%
E.) 100%
9. If both parents are heterozygous for an allele (e.g., Bb), what percentage of their offspring will be homozygous recessive for that allele?
A.) 100%
B.) 75%
C.) 50%
D.) 25%
E.) 0%
D.) 25%
10. If both parents are heterozygous for an allele (e.g., Bb), what is the genotype ratio of their offspring regarding this allele?
A) 3:1
B) 2:2
C) 1:2:1
D) 4:0
C) 1:2:1
11. Genes contain what kind of information?
A.) Instructions that are used to build fats.
B.) Instructions that are used to build amino acids.
C.) Instructions that are used to build proteins.
D.) Instructions that are used to build carbohydrates.
C.) Instructions that are used to build proteins.
12. If a black male cat and a white female cat mate and the offspring are gray what is this phenomenon (grey) called?
A.) Co-dominance of alleles
B.) Dominance of alleles
C.) Incomplete dominance of alleles
C.) Incomplete dominance of alleles
13. What is one difference between DNA and RNA?
A.) DNA is double-stranded and RNA is single-stranded.
B.) DNA has ribose as sugar and RNA has deoxyribose as sugar.
C.) DNA has Uracil as a base and RNA Thymine.
A.) DNA is double-stranded and RNA is single-stranded.
14. If someone says that he/she is 'born this way', what is this person referring to? His/her 'inherited genes' or 'upbringing'?
A.) Genes
B.) Upbringing
A.) Genes
15. Which enzyme is involved in the process of transcription?
A.) DNA promoterase
B.) RNA polymerase
C.) RNA synthetase
B.) RNA polymerase
16. What happens during translation?
A.) DNA is replicated, i.e., doubled in its amount.
B.) Proteins are assembled and mRNA is used as a template for the sequence of the amino acids.
C.) mRNA is rewritten into DNA.
B.) Proteins are assembled and mRNA is used as a template for the sequence of the amino acids.
17. What happens during transcription?
A.) Proteins are assembled and mRNA is used as a template.
B.) DNA is rewritten into mRNA.
C.) DNA is replicated, i.e., doubled in its amount.
B.) DNA is rewritten into mRNA.
18. Where is a codon located?
A.) On the t-RNA
B.) On the rRNA
C.) On the mRNA
C.) On the mRNA
19. What happens during protein synthesis when the ribosome encounters the sequence 'UAA' on the mRNA strand?
A.) It inserts the amino acid 'Tyrosine'.
B.) It inserts the amino acid 'Isoleucine'.
C.) It stops the process of adding amino acids.
C.) It stops the process of adding amino acids.
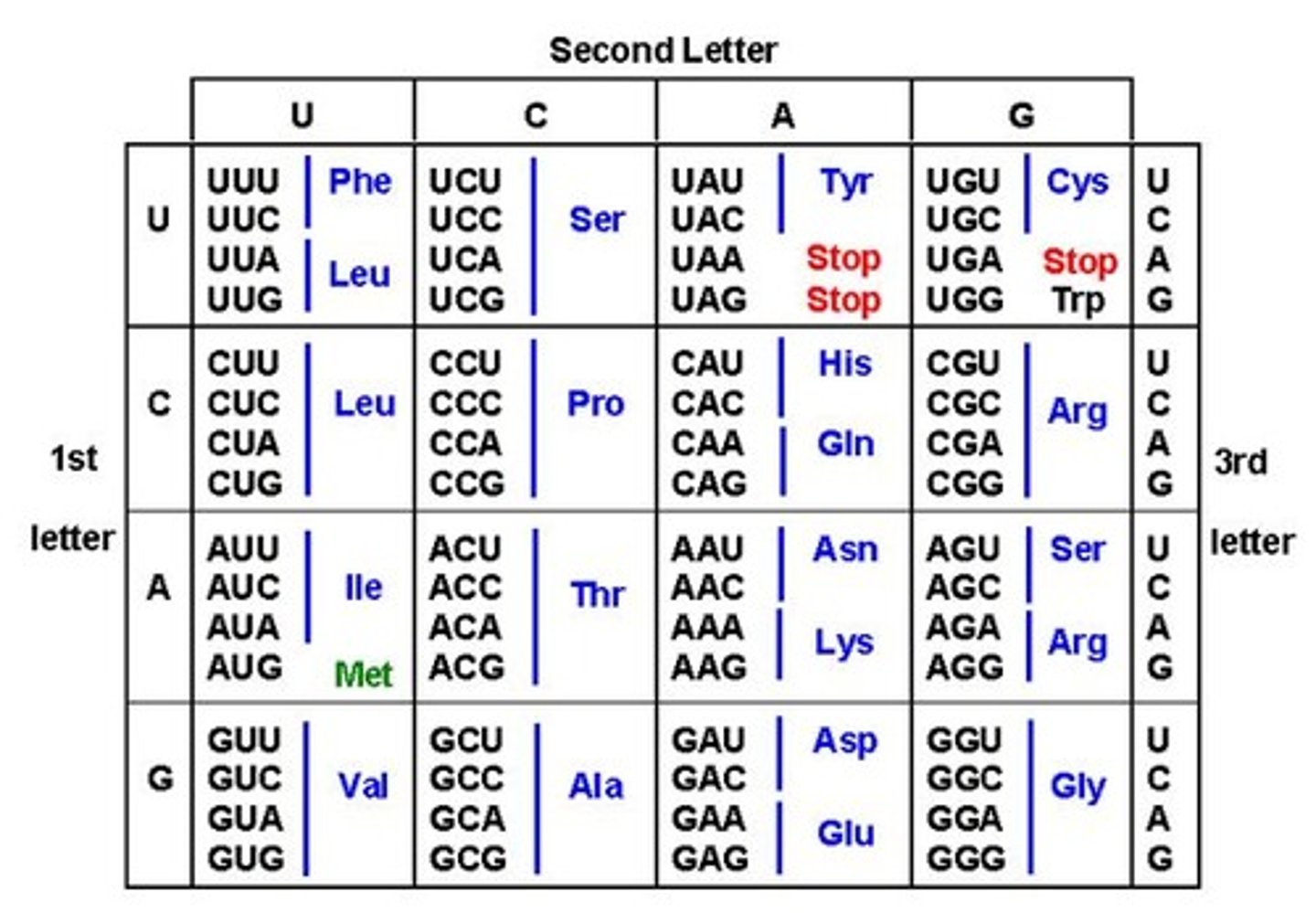
20. What is the region on the t-RNA called that interacts with the m-RNA during translation?
A.) Codon
B.) Anti-codon
C.) Stop codon
D.) Start codon
B.) Anti-codon
21. If the mRNA has the sequence UAA, what will be the sequence of the complementary/matching tRNA molecule?
A.) UAA
B.) AUU
C.) TAA
D.) ATT
B.) AUU
22. Choose the word from the list below that correctly completes the following statement. The feature that no codon codes for more than one amino acid is called the _______ of the genetic code.
A.) Universality
B.) Unambiguity
C.) Redundancy
B.) Unambiguity
23. Where in the cell does Transcription take place?
A.) Cytoplasm
B.) Nucleus
C.) Endoplasmic reticulum
B.) Nucleus
24. What causes a frameshift mutation?
A.) Mutation that converts nucleotides
B.) Insertion of a nucleotide
C.) Deletion of a nucleotide
D.) B and C
D.) B and C
25. What are stem cells?
A.) Undifferentiated precursor cells.
B.) Cells from the brain stem.
C.) Cells that contain genes that were introduced.
A.) Undifferentiated precursor cells.
26. True or false? Evolution takes place in individuals.
A.) True
B.) False
B.) False
27. True or false? You are related, to some degree, to a bird.
A.) True
B.) False
A.) True