Clinical Oncology - Gastrointestinal: Esophageal Cancer
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
What sex is esophageal cancer more common in?
Men are 3 to 4 times more likely to be affected than women
What is the common age of diagnosis of esophageal cancer?
55 to 85 years old
Where is esophageal cancer most common in? Why?
Northern China, northern Iran, south Africa. May be due to environmental and nutritional factors.
What are risk factors for squamous cell carcinoma of esophagus?
Excessive alcohol and smoking
*Smoking can increase risk of adenocarcinoma, as well
What are etiological risk factors of adenocarcinoma?
Barrett esophagus, GERD, being overweight, obesity, smoking
What is Barrett esophagus?
Distal esophagus is lined with columnar epithelium than stratified squamous epithelium. This may be due to gastroesophageal reflux. Chronic chemical trauma can result in mucosa to undergo metaplasia.
What conditions predispose people to esophageal cancer?
Plummer-Vinson syndrome, achalasia, tylosis
What is an etiological factor for esophageal cancer in people from Iran, China, and South Africa?
Diet low in fresh fruits and vegetables and high in nitrates (cured meats and fish, pickled vegetables)
What are poor prognostic indicators for esophageal cancer?
Tumour size (>5 cm), weight loss of 10%, older than 65 years old, overexpression of HER2 in adenocarcinoma
Where does the esophagus begin and end?
C6 to termination in abdomen at T10 to T11
What is the esophagus lined with?
Stratified squamous epithelium
Where is the cervical esophagus located?
Cricoid cartilage (C6) to SSN (T2 to T3), measuring 18 cm from upper incisors
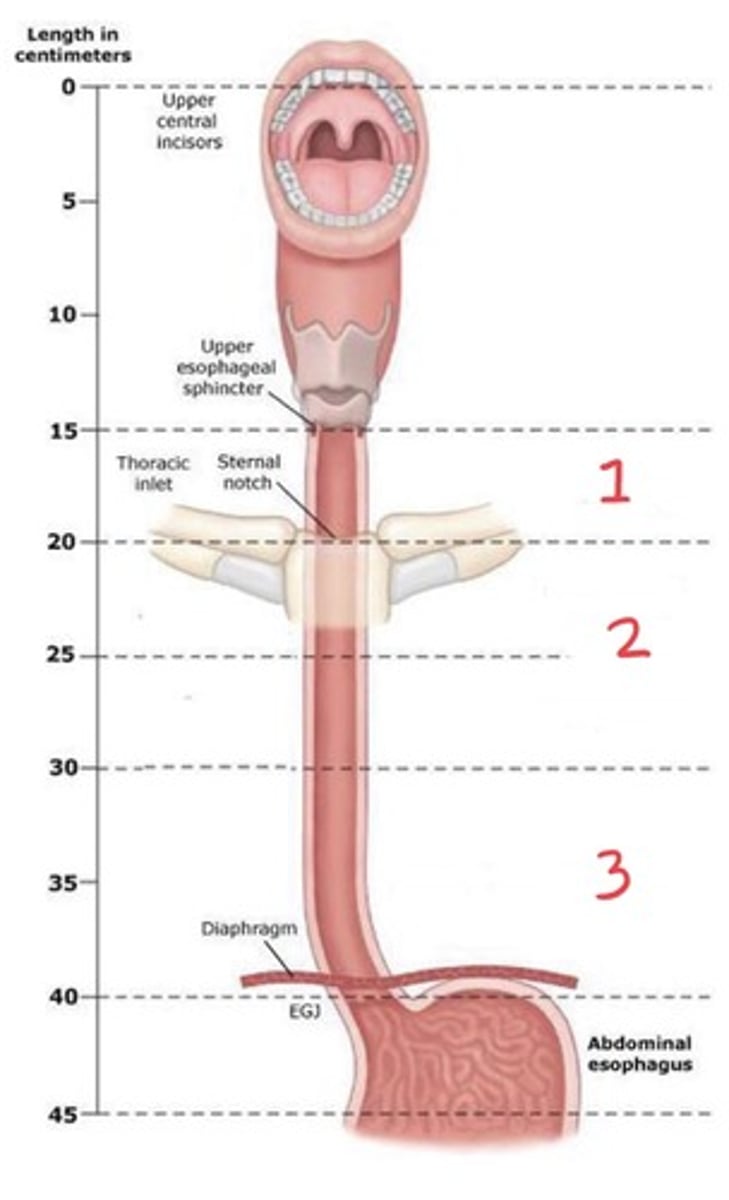
Where is the upper thoracic portion of the esophagus?
SSN (T2/3) to carina (T5); 24 cm from upper incisors
Where is the middle thoracic esophagus?
Carina (T5) to T7/8; 32 cm from incisors
Where is the lower thoracic esophagus?
T7/8 to T10/11 (GE junction). Includes abdominal esophagus; 8 cm long and 40 cm from incisors
Describe the relationship of the esophagus to nearby structures
Posterior to trachea and anterior to vertebral column
Medial and anterior to descending aorta
What are the layers of the esophagus?
Mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria. Lacks serosa, but outermost layer is adventitia, which is a thin, loose connective tissue.
What lymphatics does the cervical esophagus drain into?
Internal jugular, cervical, paraesophageal, supraclavicular nodes
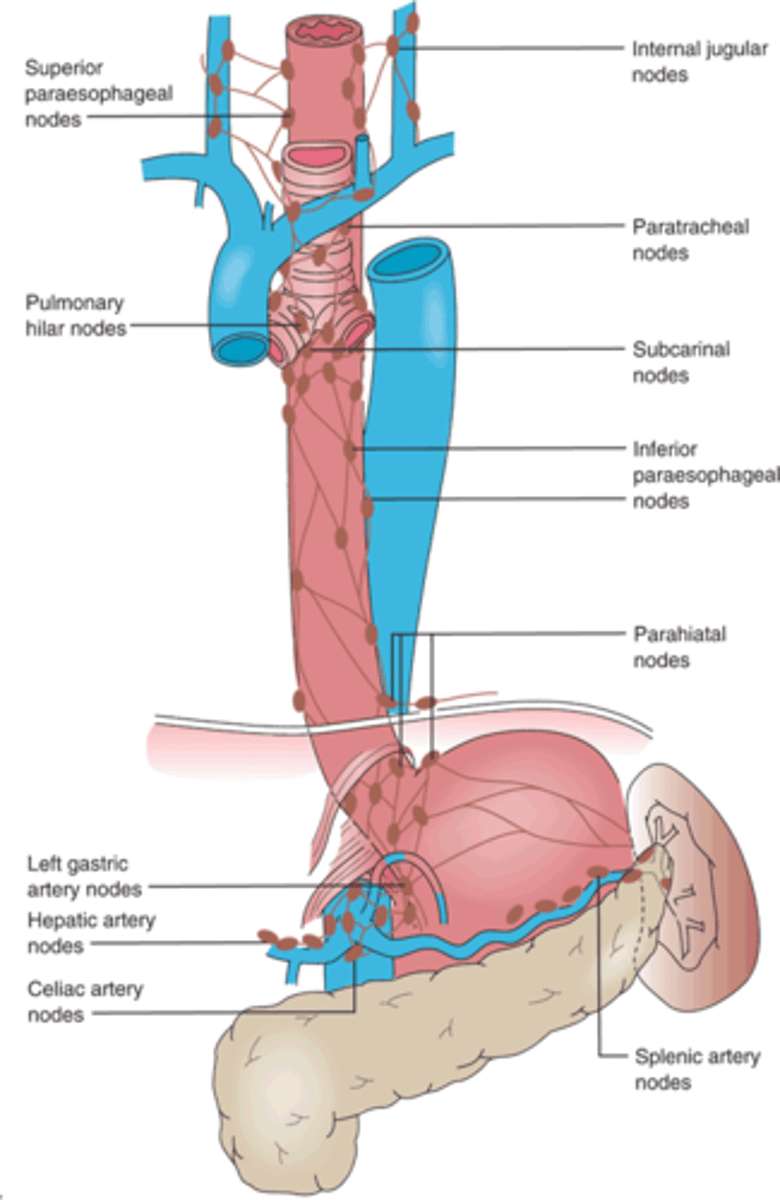
What lymphatics does the upper and middle esophagus drain into?
Paratracheal, hilar, subcarinal, paraesophageal, paracardial nodes
What are the primary draining lymphatics for the distal esophagus (lower third)?
Celiac axis, left gastric, nodes of lesser curvature of stomach
Why is there a high risk for skip metastasis and nodal involvement in esophageal cancer?
Extensive interconnected lymphatic system, in which lymph fluid can travel entire length of esophagus and drain into any nodal bed
What are signs and symptoms of esophageal cancer?
Dysphagia and weight loss (90%), odynophagia (50%), food stuck in throat/chest, regurgitation of undigested food, aspiration pneumonia, heartburn sensation
What are signs and symptoms of locally advanced esophageal cancer?
Hematemesis, coughing, hemoptysis, Horner syndrome, hoarseness
What is the most common site of occurence for esophageal cancer?
Lower one third and GE junction
What is the most common pathology of esophageal carcinoma?
Squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma
Where is squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus found most frequently?
Upper and middle thoracic esophagus
Where is adenocarcinoma of the esophagus found most frequently?
Distal esophagus and GE junction
What does staging of squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus involve?
Location relative to pulmonary vein and histologic grade
*For adenocarcinoma, staging includes grade but not location
Why are lesions of the esophagus usually large before causing symptoms?
Because the esophagus is a distensible structure
How do esophageal lesions spread?
Longitudinally
What can occur due to a lack of serosa layer in the esophagus?
Early spread to adjacent structures; tracheoesophageal or bronchoesophageal fistulas
What are common sites of distant metastasis in esophageal cancer?
Liver and lung
Approximately 30% of esophageal cancers are associated with ____.
GERD
What is the primary goal of treatment for esophageal cancer?
Relief of dysphagia and chance of a cure
What are the most commonly used treatment modalities in esophageal carcinoma?
Chemoradiation is the current nonsurgical standard for treatment of esophageal cancer, or neo-adjuvant chemoradiation followed by surgery, if feasible
What areas of the esophagus can surgery be performed?
Middle and lower esophagus, cervical esophagus is not considered surgically accessible
What surgical procedures are available for esophageal carcinoma?
Subtotal or total esophagectomy
What complications can occur with surgery for esophageal carcinoma?
Anastomotic leaks, respiratory failure, pulmonary embolus, myocardial infarctions, GE reflux, strictures, difficulty in gastric emptying
What has the addition of chemotherapy with radiotherapy improved?
Decrease in local and distant failures, and increase in overall survival rate
What chemotherapy drug combination is used in esophageal cancer?
Carboplatin and paclitaxel
Describe the field borders for radiation treatment for esophageal cancer
Long and narrow as it spreads longitudinally and skip lesions can be up to 5 cm from primary tumour
What does the clinical target volume (CTV) encompass?
Regional lymph nodes and primary tumour with 3 to 4 cm margin above and below tumour volume, with 1 cm radial margin
What does the radiation field include for lesions of the upper third of the esophagus?
Thyroid cartilage (C4/5) to carina (T5) to include supraclavicular, low anterior cervical, and mediastinal nodes
What does the radiation field include for lesions of the middle of the esophagus?
Periesophageal and mediastinal nodes, but not supraclavicular or esophagogastric junction
What does the radiation field include for lesions of the distal third of the esophagus?
Superior: paraesophageal and mediastinal nodes, and may not include supraclavicular nodes as they have a low risk of involvement
Inferior: celiac axis nodes (T12/L1)
What are the OARs in radiotherapy for esophageal carcinoma?
Spinal cord, lung, heart, kidneys, liver
For IMRT for esophageal cancer, what beam arrangements can be used?
Two posterior oblique fields and AP field (spinal cord only receives exit dose) to spare anterior structures, such as heart and lung
For treatment of the esophagus with radiation only, what dose is used?
60 Gy to 65 Gy
For neoadjuvant chemoradiation for esophageal carcinoma, what dose is used?
41.4 Gy to 50.4 Gy
What side effects are expected from radiotherapy for esophageal cancer?
Esophagitis, dysphagia, sensation of food stuck
What can be recommended to patients with difficulty or pain with eating?
Eat diet of bland, soft, or pureed foods
Eat small, but frequent meals high in calories and protein (cottage cheese, yogurt)
Liquid analgesics or viscous lidocaine before meals to provide local and systemic relief
What can occur if a large volume of lung and/or heart is included in the radiation field?
Radiation pneumonitis or pericarditis