Chemistry final
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/113
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:50 AM on 12/13/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
1
New cards
trend of atomic radius
decreases across a period and increases down a group
2
New cards
trend of ionization energy
decreases down a group (easier to remove electrons as you go down), increases across a period from left to right (harder to remove electrons as you move right).
inverse of atomic radius
inverse of atomic radius
3
New cards
How do the size of cations compare to the atoms from which they are formed?
Smaller; the more positive the ionic charge the smaller the radius
4
New cards
How do the size of anions compare to the atoms from which they are formed?
Larger; the more negative the charge the larger the radius
5
New cards
What are exceptions to the ionization energy trend?
Based on screening and penetration
ex) Al IE smaller than Mg;S lower than P
ex) Al IE smaller than Mg;S lower than P
6
New cards
What is the trend for electron affinity?
increases across a period, decreases down a group
7
New cards
Diamagnetic
all electrons paired
weakly repelled by magnetic field
weakly repelled by magnetic field
8
New cards
paramagnetic
Atom or substance containing unpaired electrons and is consequently attracted by a magnet.
9
New cards
Polarizability
measure of the ability of a charge to distort a molecule's charge distribution (electron cloud)
10
New cards
What is the periodic trend for polarizability
Increases with atomic radius
11
New cards
Polar covalent bond
electrons not shared equally and displaced toward more nonmetallic element
12
New cards
Electrostatic potential
work done in moving a uit of positive charge at a constant speed from one reigon of a molecule to the other
13
New cards
How can an electrostatic potential map be used?
gives info about distribution of electron charge
help determine polarity/nonpolarity
help determine polarity/nonpolarity
14
New cards
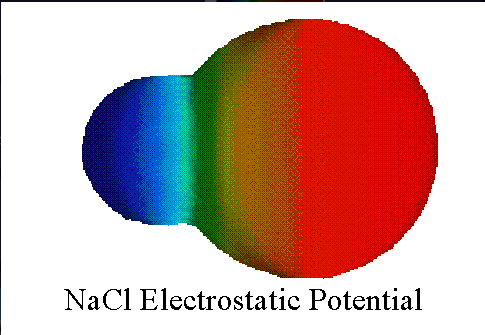
is this ionic or covalent
ionic
15
New cards
What is the trend for electronegativity?
It increases across a period and decreases down a group.
16
New cards
What kind of bond has a large EN difference
ionic
17
New cards
What kind of bond has small EN difference
covalent
18
New cards
What kind of bond has intermediate EN difference
polar covalent
19
New cards
What are exceptions to the octet rule?
Odd-electron species, incomplete octets, expanded octets
20
New cards
Concepts of Lewis Theory
valence electrons are important in bonding
each atom has octet
electrons shared between atoms in covalent
Starting point for VSEPR theory, valence bond theory, and orbital hybridization
each atom has octet
electrons shared between atoms in covalent
Starting point for VSEPR theory, valence bond theory, and orbital hybridization
21
New cards
Shortcomings of Lewis theory
does not explain delocalized charge or the need for resonance structures
22
New cards
VSEPR theory concepts
repulsion between pairs of electrons to predict of molecule
explains need for hybridization
explains need for hybridization
23
New cards
VSEPR theory shortcoming
approximate, not exact bond angles
24
New cards
valence bond theory concepts
covalent bonds form from overlap of atomic orbitals
describes combination of half-filled atomic orbitals to create molecular orbitals
describes combination of half-filled atomic orbitals to create molecular orbitals
25
New cards
Valence bond theory shortcomings
ionized picture of bonding
does not describe delocalization
predicts 90 degree bond angles from overlap of p atomic orbitals
needs to be combined with hybridization
does not describe delocalization
predicts 90 degree bond angles from overlap of p atomic orbitals
needs to be combined with hybridization
26
New cards
Hybridization main concepts
atomic orbitals can be combined into hybrid orbitals to reconcile observed molecular geometry with valence bond theory
useful for predicting molecular geometry around carbon
useful for predicting molecular geometry around carbon
27
New cards
hybridization shortcomings
not exact solutions to schrodinger equation
debate about d orbitals
debate about d orbitals
28
New cards
Molecular orbital theory concepts
atomic orbitals combine in constructive and destructive ways to create new molecular orbitals
debate about d orbital
determine bond order and predict magnetic properties
delocalized charges well
debate about d orbital
determine bond order and predict magnetic properties
delocalized charges well
29
New cards
What is the geometries, bond angle, and hybridization BeCl2
linear, 180, sp
30
New cards
What is the geometries, bond angle, and hybridization of BF3
trigonal planar, 120, sp2
31
New cards
What is the geometries, bond angle, and hybridization of SO2
bent/trigonal planar,
32
New cards
What is the geometries, bond angle, and hybridization of CH4
tetrahedral, 109.5, sp3
33
New cards
What is the geometries, bond angle, and hybridization of NH3
trigonal pyramidal/tetrahedral,
34
New cards
What is the geometries, bond angle, and hybridization of OH2
bent/tetrahedral,
35
New cards
What is the geometries, bond angle, and hybridization of PCl5
trigonal bipyramidal, 90 and 120, sp3d
36
New cards
What is the geometries, bond angle, and hybridization of SF4
seesaw, 90 adn 120, sp3d
37
New cards
What is the geometries, bond angle, and hybridization of ClF3
T-shaped, 90, sp3d
38
New cards
What is the geometries, bond angle, and hybridization of XeF2
linear, 180, sp3d
39
New cards
What is the geometries, bond angle, and hybridization of SF6
octahedral, 90, sp3d2
40
New cards
What is the geometries, bond angle, and hybridization of BrF5
square pyramidal, 90, sp3d2
41
New cards
What is the geometries, bond angle, and hybridization of XeF4
square planar, 90, sp3d2
42
New cards
order of repulsive forces
lone-pair lone-pair> lone pair-bond pair > bond pair-bond pair
43
New cards
London dispersion forces
the intermolecular attraction resulting from the uneven distribution of electrons and the creation of temporary dipoles
44
New cards
Relationship between London Dispersion forces and molar mass
HIgher molar mass higher LDF
45
New cards
Relationship between temperature and vapor pressure
Higher temp = higher vapor pressure
46
New cards
relationship between IMF and enthalpy ofvaporization
higher IMG = Higher enthalpy of vaporization
47
New cards
Relationship between IMF and vapor pressure
Higher IMG = Lower vapor pressure
48
New cards
Is vapor pressure intrinsic or extensic?
intrinsic
49
New cards
Clausius-Clapeyron equation
mathematical relationship between the temperature, vapor pressure, and enthalpy of vaporization for a substance
50
New cards
Deposition
gas to solid
51
New cards
Sublimation
solid to gas
52
New cards
Condensation
Gas to liquid
53
New cards
Evaporation
Liquid to gas
54
New cards
Melting
solid to liquid
55
New cards
Freezing
liquid to solid
56
New cards
lattice energy
the energy released when one mole of an ionic crystalline compound is formed from gaseous ions
57
New cards
standard enthalpy of formation
enthalpy change if 1 mole of compound in standard state were formed directly from its elements
58
New cards
Relationship between molecule branching and London Dispersion force strenght
Increase in branching (aka surface area,) increase in LDF
59
New cards
What is a critical point?
the temperature and pressure at which liquids and gases become indistinguishable
60
New cards
What is a triple point
the temperature and pressure at which all three phases of matter coexist in an equilibrium
61
New cards
solid water is ______ dense than liquid water
less
62
New cards
Why is solid water less dense than liquid water?
negative phase change slope between solid and liquid
63
New cards
Equation for entropy Isothermal (only pressure change)
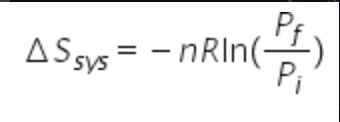
64
New cards
Equation for entropy Isobaric (only change in Temperature)
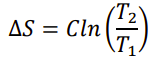
65
New cards
3rd law of thermodynamics
entropy at 0 K = 0
66
New cards
Relationship between entropy and temperature
increased temp = increased entropy
67
New cards
Molecule complexity and entropy
molecule complexity higher = higher entropy
68
New cards
2nd law of thermodynamics
Every energy transfer or transformation increases the entropy of the universe.
69
New cards
A reaction where bonds are broken is ___
endothermic because more energy goes into system
70
New cards
A reaction where more bonds are formed is __
Exothermic because forming bonds releases energy
71
New cards
Gibbs free energy equation

72
New cards
How do we determine spontaneity based on properties of the system alone?
Gibbs Free Energy
73
New cards
Spontaneity and entropy of the universe

74
New cards
Gibbs Free Energy and Spontaneity

75
New cards
Spontaneity with negative enthalpy and positive entropy
Spontaneous all temperatures
76
New cards
Spontaneity with negative enthalpy and negative entropy
Spontaneous at low temperatures
77
New cards
Spontaneity with positive enthalpy and positive entropy
spontaneous high temperatures
78
New cards
Spontaneity with positive enthalpy and negative entropy
nonSpontaneous at all temperatures
79
New cards
Is Gibbs free energy a state function? Can hess' law apply
yes; Hess' law can be applied
80
New cards
reactant quotient
Describe extent of reaction
81
New cards
Gibbs energy of reaction and reaction quotient
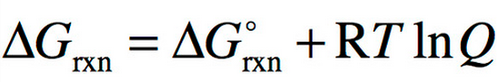
82
New cards
Relationship between Q and reaciton conditions

83
New cards
Gibbs standard free energy and K
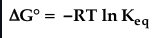
84
New cards
Activity of pure solids/liquids
1
85
New cards
Activity for gases
Numerical pressure in bar (very close to atm)
86
New cards
Activity of solutes in aqueous solution
Molarity
87
New cards
What does a large K value mean
products are more thermodynamically stable than reactions in standard states
88
New cards
What does a small K value mean
products less thermodynamically stable than reactants
89
New cards
relationship between K and Temperature
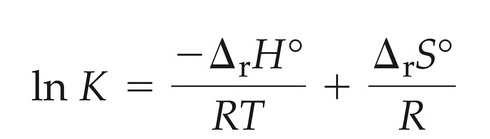
90
New cards
Chemical Potential
A substance's ability to change gibbs energy of the system
91
New cards
How is K affected when reaction multiplied by coefficient x
K^x
92
New cards
How is K affected when reaction divided by coefficient x
K^(1/x)
93
New cards
How do you combine K values for two reactants that can be added together?
mutliply K values
94
New cards
How is K affected when reaction reversed
1/K
95
New cards
Are ionic compounds soluble in polar solvents?
Most are
96
New cards
What are molecular solids?
covalently bonded molecule
97
New cards
What are nonpolar molecular solids soluble in?
Soluble in some nonpolar solvents
98
New cards
What are polar molecular solids soluble in?
Soluble in some nonpolar and polar solvents
99
New cards
What are molecular solids with hydrogen bonding soluble in?
Soluble in polar or hydrogen bonded solvents (Water)
100
New cards
How does attractive force between oppositely charged ions change with increased charge?
Attractive force increases