AP Chem Aqueous Stoichiometry/Reaction Families + Redox
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Solution
a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances (ex. saltwater, sugar water)
Homogeneous
uniform throughout
Aqueous solution
a solution involving water as the solvent
Solute
the substance present in the SMALLER molar quantity
Solvent
the substance present in the LARGER molar quantity
Electrolyte
A solute that, when dissolved in water, results in a solution that can conduct electricity.
Nonelectrolyte
Solute that does not conduct electricity when dissolved in water
What makes some solutes electrolytes and some not?
The level of hydration (amount of ions)
Hydration
The process in which an ion or molecule is surrounded by water molecules.
Dissolve
Surrounded by enough water to look like water (clear)
Dissociate
When a compound separates into its ions
Strong electrolytes
Completely dissociate; include soluble ionic salts, the 6 strong acids, and the 8 strong bases
Hydration shell
A structured group of water molecules surrounding a dissolved ion or polar solute, oriented by electrostatic interactions
Strong Acids
HCl, HBr, HI, HNO3, HClO4, H2SO4
Strong Bases
Alkali metal hydroxides, CaBaSr hydroxides
Soluble Ionic Compounds
Alkali metals, NH4+, CH3COO-, HCO3-, ClO3-, NO3-, ClO4-
Usually Soluble (*Insoluble)
[Cl-, Br-, I-]*(MLS)
[F-]*(MLS, CaBaSr, Mg)
[SO42-]*(MLSCaBaSr)
Insoluble Ionic Compounds
metal oxides*(alkali + ammonium), metal hydroxides, phosphates, chromates, dichromates, carbonates, sulfides*(CaBaSr)
Electrolysis
using electricity to drive a nonspontaneous redox reaction
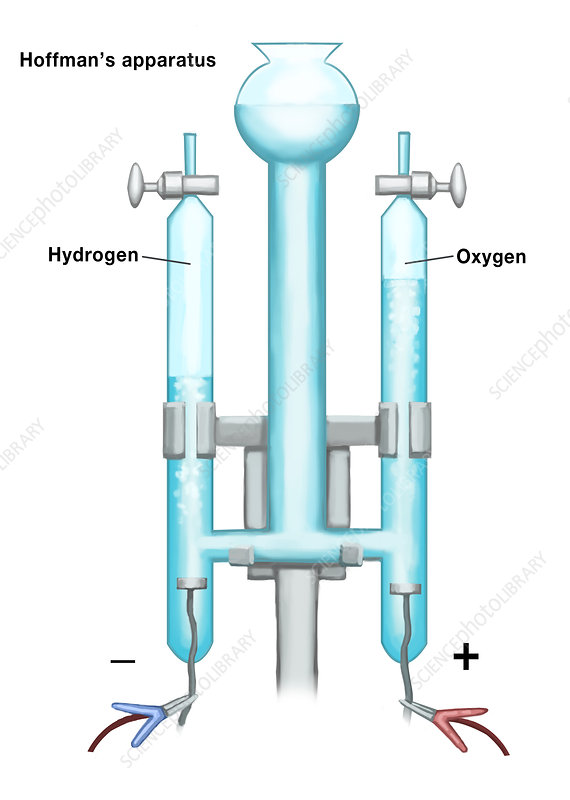
What is the left side called?
Anode
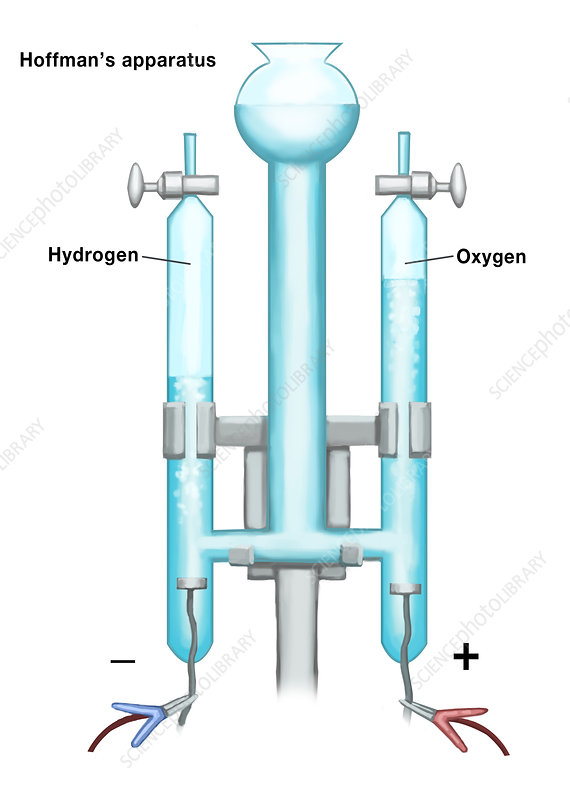
What is the right side called?
Cathode
Anode
electrons leave here in the Hoffman apparatus
Cathode
electrons enter here in the Hoffman apparatus
Bromothymol blue
pH indicator; yellow in acidic conditions <7, blue in basic conditions >7, and green in neutral conditions =7