theme 1 - chapter 3 - market failure
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Market Failure
A misallocation of resources caused by the Market Mechanism.
Reasons for Market Failure:
- Missing Markets (Merit and Public Goods)
- Lack of Competition in the Market
- Externalities
- Imperfect Market Information
- Factor Immobility
- Inequality
Demerit Goods
A good which is overprovided by the market mechanism and tends to yield more costs to individuals than they realise
EXAMPLES: Tobacco, Drugs, Alcohol
Externalities
The costs or benefits that are external to an exchange. They are 3rd party effects ignored by the market mechanism
Consumption Externality
An external cost or benefit arising from a consumption activity
Production Externality
An external effect of production, which neither harms nor benefits the person or firm controlling the production
External Costs
Negative 3rd parts effects that are excluded from the market mechanism
Private Costs
Costs internal to a market transaction, which are therefore taken into account by the market mechanism
Social Costs
External costs + Private costs
External Benefits
Positive 3rd part effects that are excluded from the market mechanism
Private Benefits
Benefits internal to a market transaction, which are therefore taken into account by the market mechanism
Social benefits
External benefits + Private benefits
Market Equilibrium level
Maginal private costs = Marginal private benefits
Social optimum level
Marginal social costs = Marginal social benefits
This is where society should be
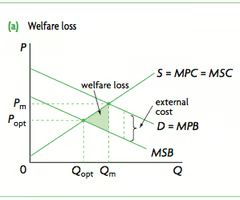
Welfare loss
The excess of social costs over social benefits for a given output. A situation where MSB ≠ to MSC and society does not achieve maximum utility
Welfare Gain
The excess of social benefits over social costs
Negative Consumption Externality
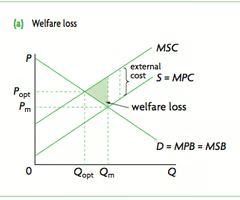
Negative Production Externality
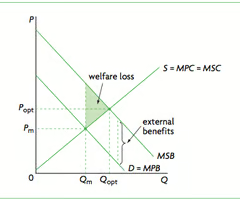
Positive Consumption Externality
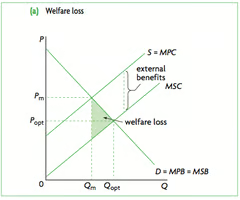
Positive Production Externality
Initialising the Externality
Eliminating the externality by bringing it back into the framework of the market mechanism = Creating a market for the externality
EXAMPLES: Tradable pollution permits, Extending Property Rights, Taxes, Regulation
Public Goods
Those goods that have non-rivalry and non-excludability in consumption.
EXAMPLES: Defence, Police Service, Street Lighting, Judiciary and Prison Service
Non-Rivalry
Consumption of goods by one person does not reduce the amount available for consumption by another
Non-Excludability
Once provided, no person can be excluded from benefitting from the good/service
Private Goods
Those goods that have rivalry and excludability in their consumption
The Free Rider Problem
If left to the free market, public goods would not be adequately provided for. The market fails because firms cannot withhold the goods and services from people who refuse to pay.
Information Gaps
Where consumers, producers or the government have insufficient knowledge to make rational economic decisions
Symmetric Information
Where consumers and producers have access to the same information about a good or service in a market
Asymmetric Information
Where consumers and producers have unequal access to information about a good or service in the market.