Hint 231
1/562
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
563 Terms
pathology
study of cell/ tissue changes due to disease
pathophysiology
study of abnormalities in physiology
pathogen
any microorganism that causes disease eg bacteria, virus, fungi, parasite
lesions
the anatomic abnormalities of the disease
pathogenesis
mechanisms that cause the disease
acute onset
sudden onset of disease
insidious onset
gradual onset of disease
acute illness
sudden short term illness can be severe
chronic illness
milder, long term may have remissions exacerbation
subacute
not as severe as acute & short than chronic
Subclinical sub=lower clinical=symptoms
no symptom an early stage not delectable by patient or routine clinical exam
latent stage 1
1.) infection has taken place & pathogen has not yet replicated/amplified; latency ends when person becomes infectious; 2.) a cancer/disease had begun but symptoms are not yet present
incubation stage
the infection has taken place but no signs or symptoms yet; ends when signs and symptoms (usually overlaps with latency stage)
prodromal period
first time one is aware of signs or symptoms
local
involving or affecting only a restricted part of the organism
systemic
whole body
complications
development of further conditions
sequelae ( permeant or long term)
lesions or impairment cause by disease arising as a result of an acute/ chronic condition
convalescence rehab
period of recovery
prognosis
predicated outcome
morbidity
disease rate
mortality
death rate
how are etiology & pathogenesis used to predict clinical manifestations & response to therapy
understanding the cause & effect of a disease/ injury are used to deliver the most effective treatment
biopsy
excision and then examination tissue sample for signs of disease
diagnosis
identification of disease
Etiology
study of causes of disease
congenital defects, genetic disorder, virus, bacteria, fungus, parasite, immune dysfunction, trauma nutritional deficiencies
symptoms what they feel
subjective manifestation such as pain or weakness
signs
objective manifestation such as swelling or redness
idiopathic
cause of disease is unknown
latrogenic
treatment/drug may cause a disease or illness
predisposing factors
risk factors
age, gender, genetics, diet, occupation , location
epidemiology
tracking the pattern of disease
why is epidemiology important
prevention strategies & treatment
endemic
a specific disease is maintained in a population without an outside source
epidemic
a specific disease is occurring at a higher rate then expected with in a population
what is a communicable disease
infections
what is a notifiable disease in Canada
disease when diagnose requires health provider usually by law to report to state or public health officials
tranmission by
1 person 2 person
2 insect 2 person
3 animal 2 person
4 contaminated food
5 contaminated water
complexities in diagnosis and treatment
differing signs, symptoms, cost, availability & sensitivity of test
what may patients be not completely honest about
how much alcohol, smoking, drugs
find a cure stage 0 Combinatorial chemistry
purify natural or synthetic compound
find a cure stage 1 basic lab science (cell or animal studies)
grind up plant or synthetically produce compound
purfiy compund
dose -dependent study mortality study, effectiveness study
find a cure stage 2
small # humans
find a cure stage 3
large # humans (double - blind) study
why are most studies stopped in stage 1 or 2
there is a lack of information
why double blind
his procedure is utilized to prevent bias in research results. Double-blind studies are particularly useful for preventing bias due to demand characteristics or the placebo effect.
what is a placebo and why is is used
to learn if the new drug or treatment works better than a substance that does not have an active drug in it
what is off label
the practice of prescribing a drug for a different purpose than what the FDA approved
congenital
disease from birth
genetic / hereditary
A hereditary defect is always inherited from the genes acquired from the parent generation, and may be present at birth or develop later on in life
atrophy cells
bedrest, SCI= spinal cord injury, starvation, ischemia ,hormones
anaplasia
no cell growth
are any cell changes reversible
all of them but neoplasia
what is physiologic hyperplasia
normal cell growth
plasia
normal cell growth/ cell growth in numbers
are neoplasia bengin or malignant
they can be benign but become mligant
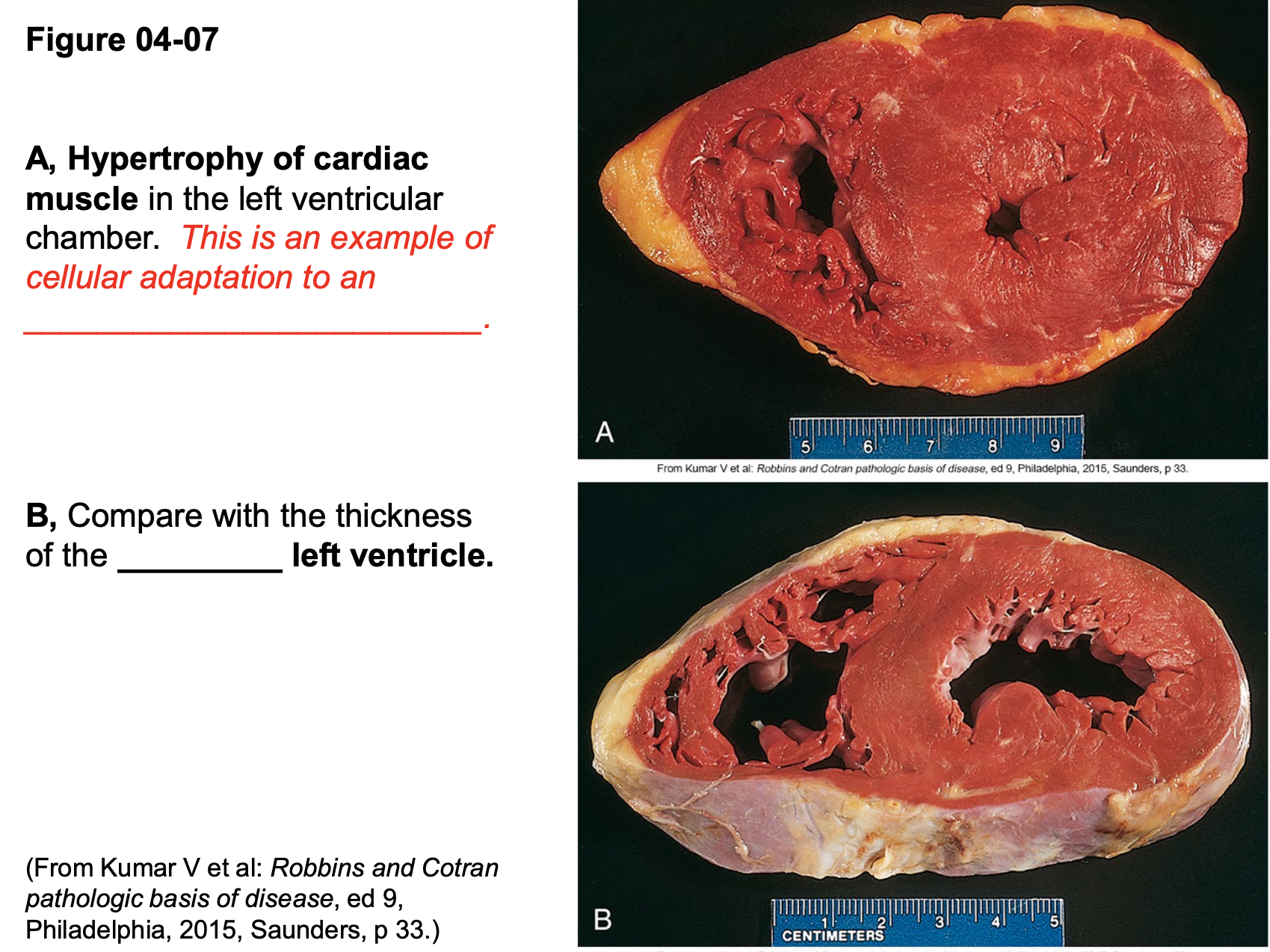
difference between physiological and pathological hypertropphy
physiologic is normal /heart structure
pathologic un-regular
true negative lab test
healthy patient with normal test result = true negative
false postive lab test
healthy patient with abnormal test = false postive
fasle negative lab test
sick patent with normal test results
ture positive lab test
sick patient with abnormal test result
pap test
annual screening for dysphasia in cells of the cervix
what test is done first sensitivity or specificity
sensitivity first then specificity after
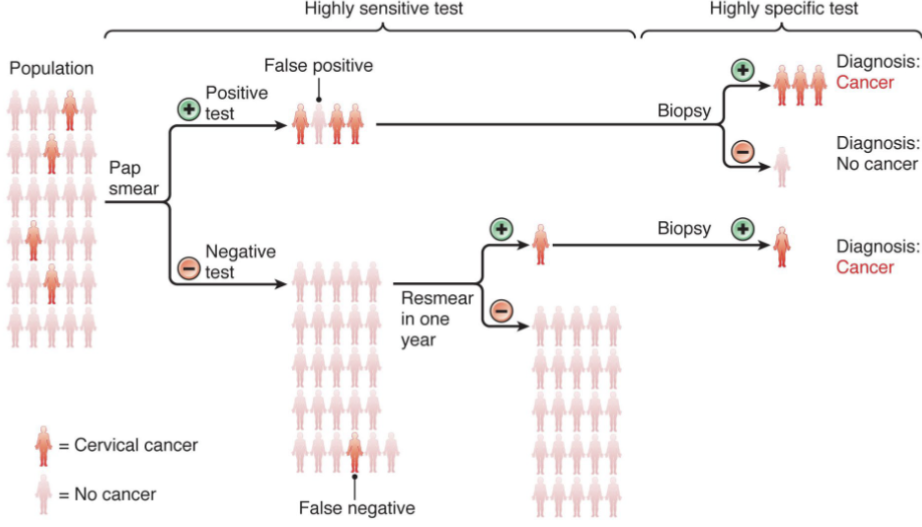
when is screening useful
1 significant # of population is at risk
2 inexpensive
3 non- invasive
4 treatment exists
sensitive test
identifies 99% postive result
specific test
identifies 99% negative results
valid measurement tool
has been proven to be the best measurement tool for the test
reliable measurement tool
repeatedly gives the same result
genetic test
changes in the genes, chromosomes or proteins in your body eg sickle cell anemia
urinalysis
a test that checks several components of a urine sample eg kidney function
blood test
Find out how well organs such as your kidneys, liver, heart, or thyroid are working bone marrow function ; liver function; immune marker ; enzyme
pulmonary functions
show how well the lungs are working spirometry , measuring lung volume
ECG - Echocardiogram
assess the structure and function of the heart and can assist with diagnosing cardiac disease and monitoring disease progression.
ECG electrocardiogram
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a simple, non-invasive test that records the electrical activity of the heart.
EMG Electromyography
Electromyography (EMG) measures muscle response or electrical activity in response to a nerve's stimulation of the muscle.
imaging test
provide a picture of the body's interior—of the whole body or part of it. x ray ultrasound ,CT , scan, MRI
endoscopy
a procedure that uses an endoscope to look inside the body to examine or treat organs or structures
histology
diagnosis and study of diseases of the tissues view biopsy under microscope
congenital and hereditary disease = developmental disturbances
1 genetic abnormality eg genetic mutation causing hemophilia
2 intrauterine injury er rubella virus infection
3 interaction of genetic and environmental factors maternal alcoholism/ drug consumption + genetic susceptibility
inflammatory disease
1 bacteria or other microbiologic agent (virus, fungi, parasite)
2 allergic reaction
3 autoimmune disease
4 unknown ethology
degenerative disease
tissue or organ degeneration as a result of disease or aging
possible contributing factor include lipid or protein or carbohydrate or pigment to toxin accumulation (endogenous or exogenous) in cells that inhibit cell funciton
metabolic disease
associated with disturbance in metabolic processes
neoplastic disease
uncontrolled cell growth
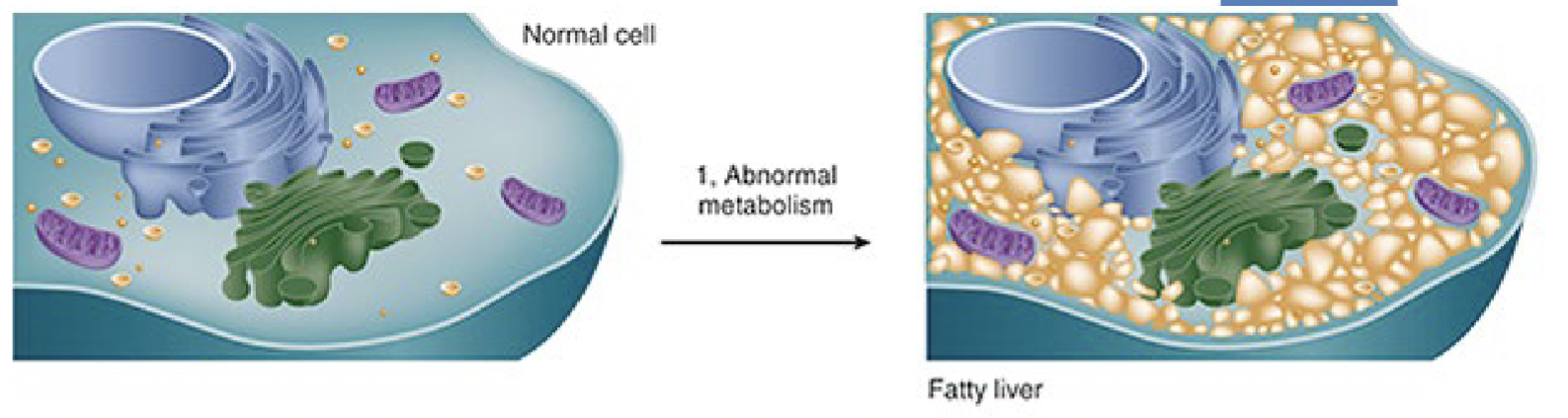
General mechanism of intercellular accumulation one
abnormal metabolism as in fatty change in the liver increased lipogenesis decreased lipolysis
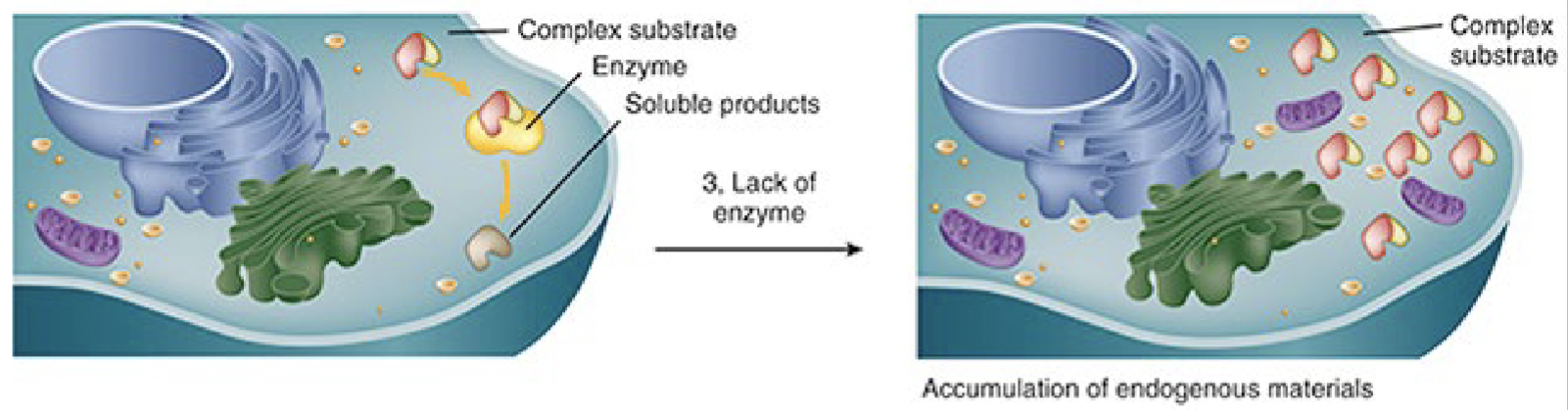
General mechanism of intercellular accumulation three
deficiency of critical enzyme responsible for lysosomal degeneration
General mechanism of intercellular accumulation two
mutation causing alteration in protein folding and transport so that defective proteins accumulate
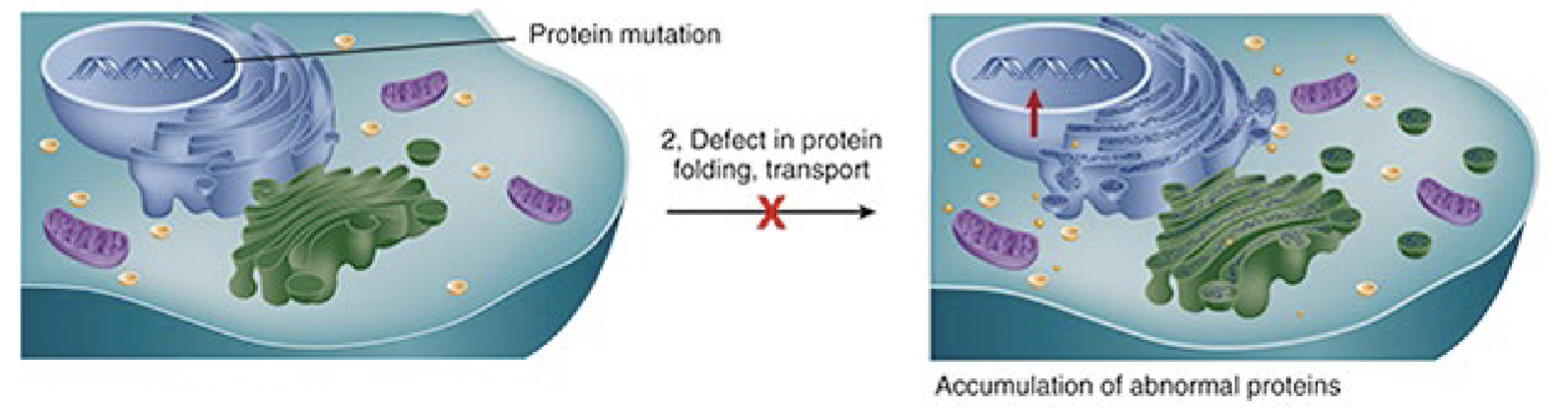
General mechanism of intercellular accumulation four
an inability to degrade phagocytosed particles such as coal dust
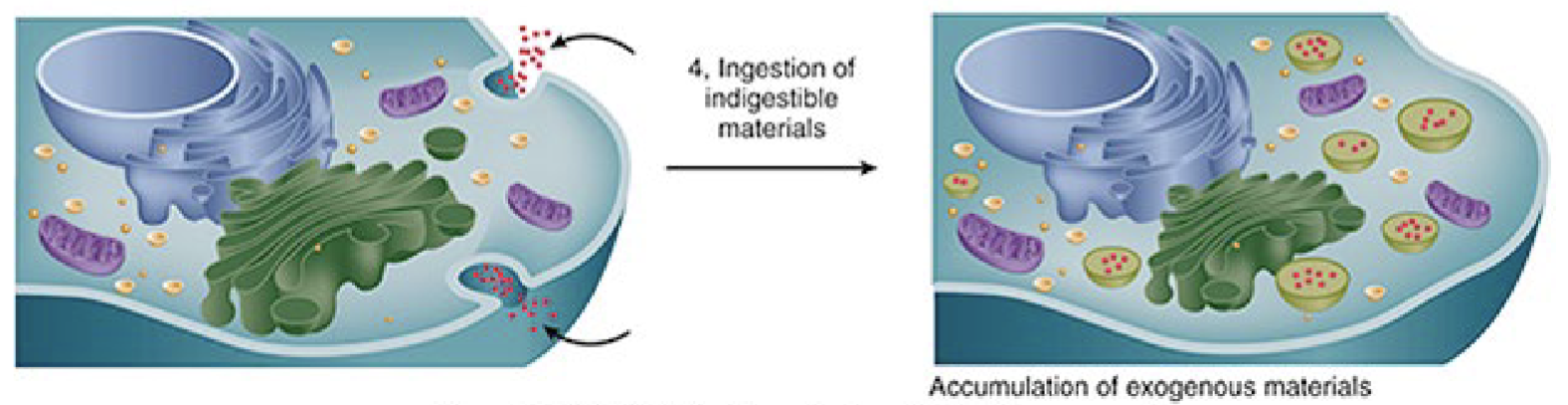
intracellular accumulation
can occur with aging or disease (endogenous) and exposure to toxin (exogenous)
disease can also cause this which can negativity affect the cell function
cell death
unplanned or planned cell suicide
apoptosis
programmed cell death - normal occurrence
digest themselves enzymatically
unplanned cell death
can occurs as a result of cell damage caused by factors ischemia, hypoxia
planned cell death
normal part of development
triggered by infection hypoxia
aging degenerative disease
ischemia
interruption of blood flow to an area resulting in O2 and nutrient deficit as well as metabolic waste accumulation causes more cell injury than hypoxia alone
hypoxia
reduced oxygen in tissues ;usually cause by ischemia can be caused by edema
which organs are most sensitive to hypoxia
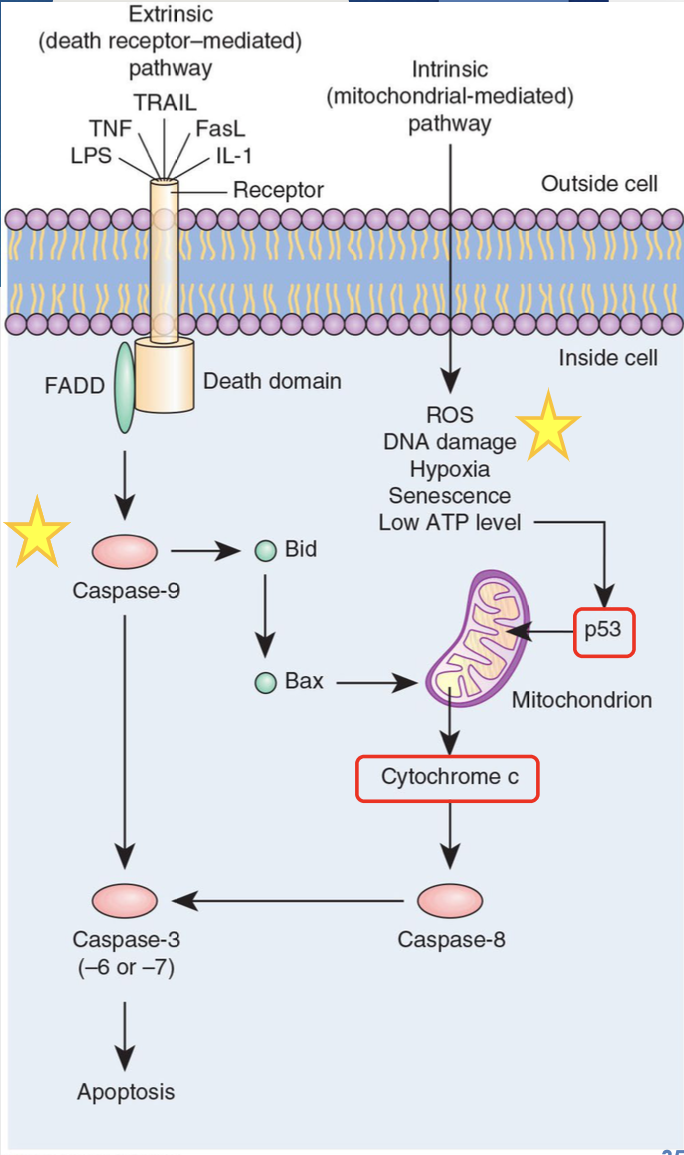
Caspase enzymatic cascade
triggered by bacterial LPS,ROS, DNA damage, senescence or low ATP level cause apoptosis
planned cell death cell shrinks
shrinks and become rounds
planned cell death chromatin condenses
and arranges into compact patches against nuclear envelope
planned cell death nuclear envelope
disintegrates & DNA fragments
planned cell death cell membrane forms
forms bleb breaking off into apoptosis bodies for phagocytosis clean up
physical damage
excessive heat or cold
radiation exposure (especially ionizing)