Forensic Serology and DNA Analysis Techniques
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
162 Terms
Serology
the study of bodily fluids
Presumptive Tests
Gives an indication of the presence of the material (MAY or MAY NOT be present)
Sensitivity of Presumptive Tests
Very sensitive; does not need a lot of material
Specificity of Presumptive Tests
Not specific; may get false positives
Luminol
More difficult to interpret results due to luminol having much more false positives
Fluorescein
Produces fluorescence and must be illuminated at 450 nm with an alternate light source (ALS) to be visualized
Phenolphthalein (Phe)
Results should be observed in 15 seconds or less; any pink color change is considered a positive result and warrants further testing
Confirmatory Tests
Confirms the identity of the material
Specificity of Confirmatory Tests
Very specific; only material testing for will give a positive result
Sensitivity of Confirmatory Tests
Not sensitive; usually need a lot of material - may get a false positive if not enough
Takayama Test
Iron in the heme group in blood bonds with nitrogen in pyridine to form characteristic crystals
Species Origin Tests
Tests that determine the species from which a blood sample originated are: diffusion reactions and electrophoretic methods
Ouchterlony Test
Based on antibody-antigen reaction between human blood and human antiserum
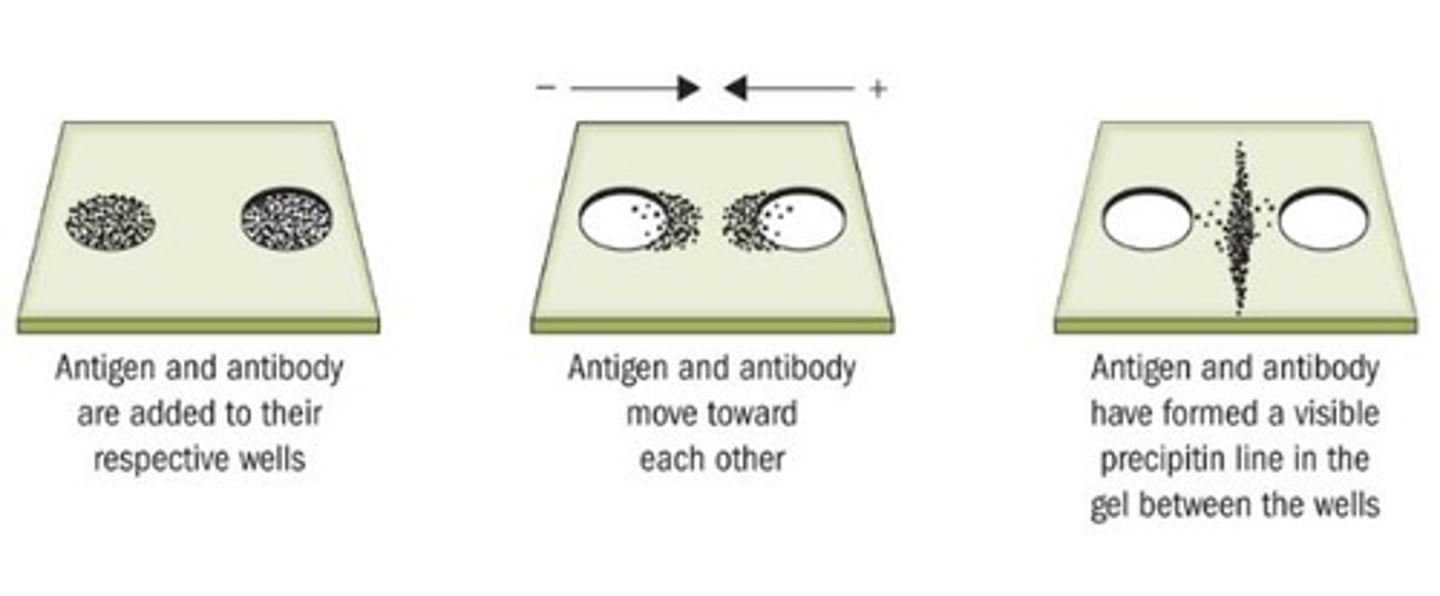
Precipitin Test
If the blood sample originated from the same origin as the antigen, bands form between the two wells
Blood Plasma
Made up of many types of cells including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets
ABO Blood Grouping
A robust biological marker for blood types
'A' Blood Group
'A' antigen on RBCs; 'Anti-B' antibody in serum; 'AA' or 'AO' genotypes; Population: 40%
'B' Blood Group
'B' antigen on RBCs; 'Anti-A' antibody in serum; 'BB' or 'BO' genotypes; Population: 10%
'AB' Blood Group
UNIVERSAL RECEIVER; 'A' & 'B' antigen on RBCs; No antibody in serum; 'AB' genotype; Population: 5%
'O' Blood Group
UNIVERSAL DONOR; No antigen on RBCs; 'Anti-A' & 'Anti-B' antibodies in serum; 'OO' genotype; Population: 45%
Rhesus (Rh) Factor
A blood group classification based on the presence or absence of the Rh antigen
Seminal Material
Spermatozoa & Seminal Plasma (contains male DNA) is used to determine sexual activity
Ejaculate Volume
2-6 ml; 100-150 million sperm cells per ml (need 100 sperm head for DNA analysis)
Intact sperm
Identification Tests for semen.
Screening
Use of UV light or alternative light source (ALS).
Presumptive test
Semen contains acid phosphatase (AP), a common enzyme that occurs at a very high level in semen.
Brentamine Fast Blue B
Detects acid phosphatase and develops a deep purple color in the presence of semen.
Confirmatory test
Presence of intact spermatozoa in a biological stain has historically been the conclusive test for semen.
Christmas Tree Stain
Traditional method used to visualize sperm cells.
Hematoxylin-eosin Stain
Based on the same premise as the Christmas Tree Stain.
Prostate specific antigen (PSA)
Water soluble protein found in semen.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
Used to detect p30, based on antibody-antigen reaction.
Time since intercourse (TSI)
Determination may be necessary.
Microscopic Sperm Search
Actual visualization of spermatozoa extracted from a sample.
Morphology of sperm cells
Specific size and shape of head, acrosomal cap, bowling-pin shaped profile, midpiece and tail when present.
Amylase
Digestive enzyme found in high levels in saliva and fecal matter.
Saliva
Can be evidenced in many situations: bite marks, lick adhesives, eating/drinking surfaces, expectoration.
Urine
Can be presumptively tested for the presence of urea or creatinine.
Human Hair Identification
Microscopic examination; DNA analysis can only be done if the hair has a root.
Passive Bloodstains
Created by force of gravity (clots, drops, flows, pooling).
Transfer Bloodstains
Wet blood surface contacts with another surface (wipes, swipes, pattern transfers, general contact).
Impact (projected) Bloodstains
Created when blood receives a blow or force resulting in random dispersion.
Skeletonization
A bloodstain that has been disturbed but still reflects its general shape and size through drying of the outer edge of the stain.
Impact Stains
Depends on angle, direction, point of origin, and/or effect of target surface.
Expirated Blood
Contains air bubbles and saliva.
Mitochondrial DNA
Inherited from mother and located in mitochondria.
Nuclear/Genomic DNA
Large molecule made by linking a series of repeating units called nucleotides, comprised of two strands wrapped around each other in the form of a double-helix.
Nucleotide
Composed of a sugar, a phosphorus-containing group, and a nitrogen-containing molecule called a base.
Bases
Four types: Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C), and Thymine (T).
Complementary-Base Pairing
A-T and C-G.
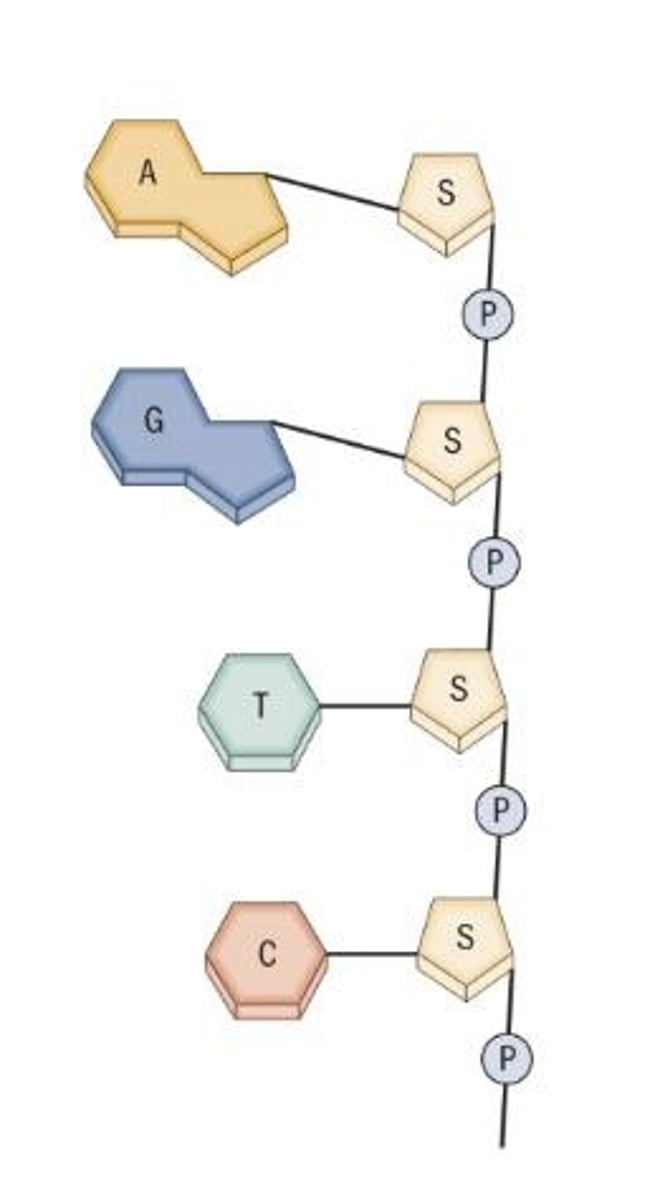
DNA
The basic unit of heredity found inside most cells of the body that codes for characteristics of a person.
Chromosomes
DNA is arranged within 23 pairs of chromosomes, totaling 46, with each chromosome coming from a parent.
Autosomes
23 chromosome pairs that are not sex chromosomes.
Sex Chromosomes
The last pair of chromosomes, which are X and Y.
Sources of DNA
Blood, semen, saliva, skin cells, hair, and bone can be used as sources of DNA.
Buccal Swab
A method of collecting standard/reference DNA specimens by swabbing the mouth and cheek.
Biological Evidence
Needs to be photographed and recorded before being packaged.
Disposable Gloves
Wearing disposable double non-latex powder-free gloves while handling evidence is required.
Safety Considerations
Wearing face masks, a lab coat, eye protection, shoe covers, and possibly coveralls is required to avoid contamination.
Packaging Biological Evidence
Must avoid plastic or airtight containers to prevent the growth of DNA-destroying bacteria and fungi.
DNA Production of Proteins
DNA directs the production of proteins, which are made by combining amino acids.
Amino Acids
The sequence of amino acids in a protein chain determines the shape and function of the protein.
Nucleotide Sequence
Each group of three nucleotides in a DNA sequence codes for a particular amino acid.
G-A-G
Codes for the amino acid glutamine.
C-G-T
Codes for the amino acid alanine.
Nucleotide Change
If a nucleotide is 'changed', for example a T is substituted for A and G-A-G becomes G-T-G, the 'wrong' amino acid is placed in the protein (in this case glutamine is replaced with valine).
Alleles
Variations of genes.
Phenotype
Observable/physical characteristics.
Genotype
The alleles that make up the phenotype (AA, Aa, aa).
Tandem Repeats
Sequences of bases that are repeated numerous times, acting as a filler/spacer between the coding regions of DNA and offering a means of distinguishing one person from another.
Sequence Polymorphisms
The two sequences of a particular gene are similar (the exact same length) but different at some base pair locations.
Length Polymorphisms
Differ in length.
RFLP
Restriction fragment length polymorphisms (sequence polymorphisms) associated with length differences from relatively long repeating DNA strands.
PCR
Polymerase chain reaction, a technique used for replicating small quantities of DNA or broken pieces found at a crime scene.
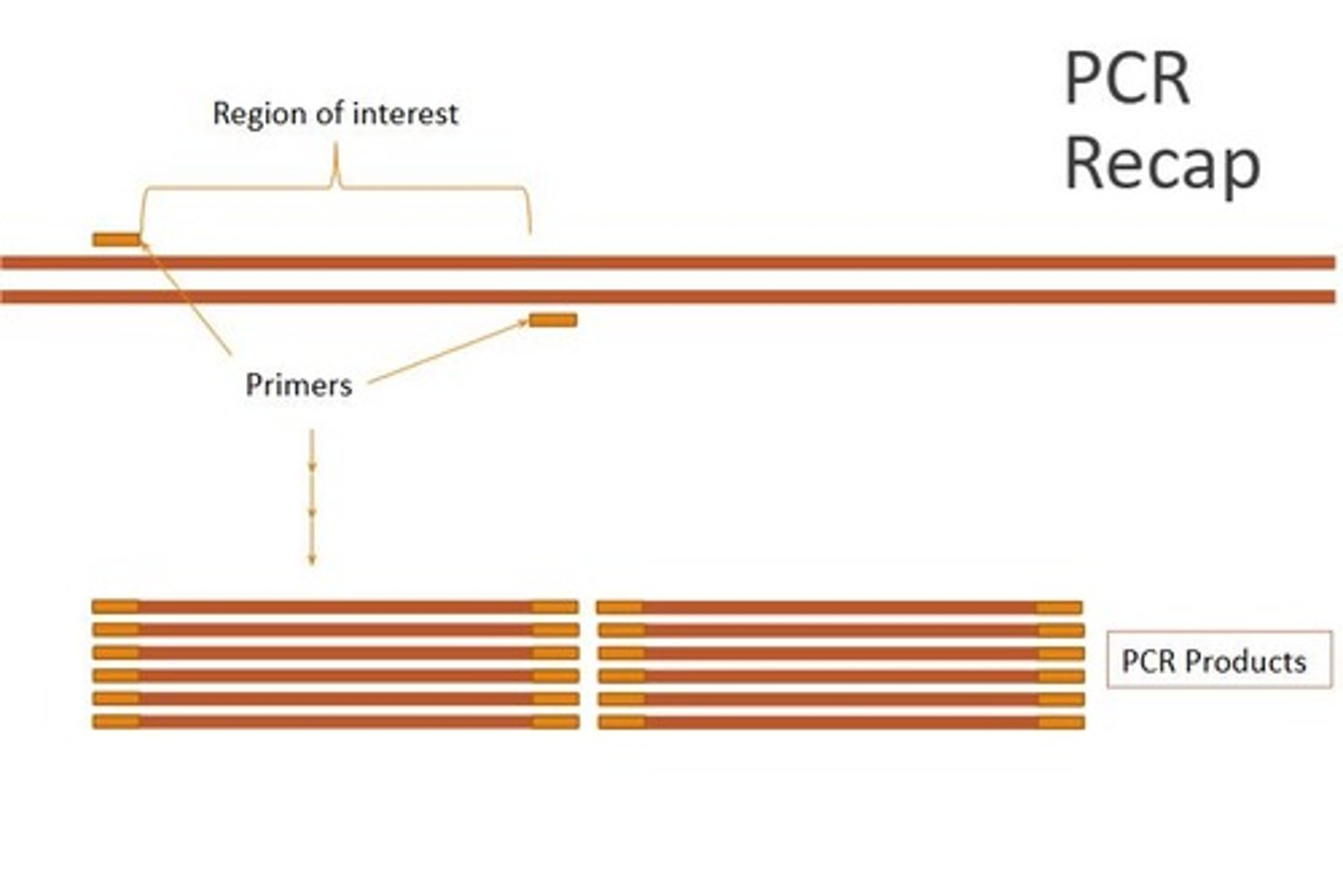
DNA Replication
DNA duplicates itself prior to cell division, beginning with the unwinding of the DNA strands of the double-helix.
Denaturation
The process where DNA is heated to separate it, breaking hydrogen bonds.
Annealing
The process where primers (short strands of DNA) are added and hybridize with the strands.
Multiplexing
One can simultaneously extract and amplify a combination of different STRs.
Homozygote
Both alleles are the same length.
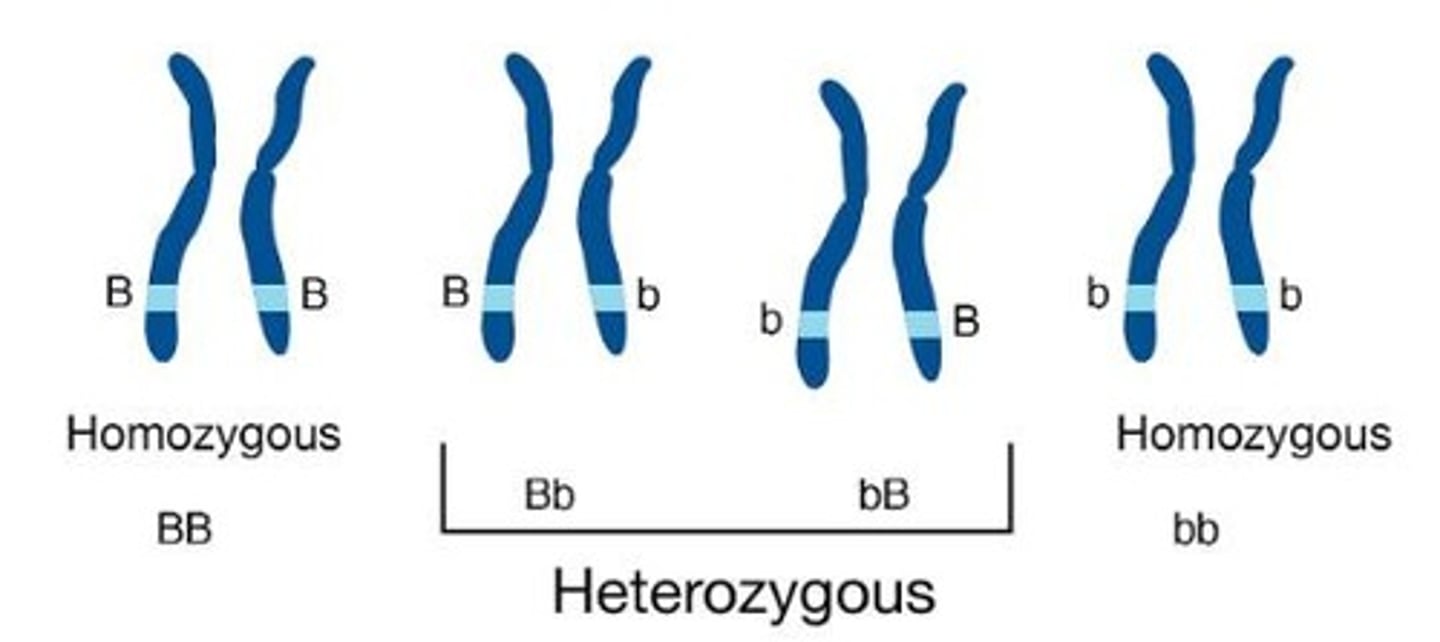
Heterozygous
Alleles differ and can be resolved from one another.
STR
Short tandem repeat analysis, locations on the chromosome that contain short tandem repeats that repeat themselves within the DNA molecule.
Amelogenin gene
Gene used for sex determination.
Contamination
The presence of unwanted substances in DNA samples.
Degradation
UV light, sunlight, and moisture degrade DNA, leading to random fragmentation.
Mixtures
Samples containing DNA from multiple sources.
Low template DNA
Samples with insufficient DNA for analysis.
CODIS
Combined DNA Index System, a computer software program developed by the FBI that maintains local, state, and national databases of DNA profiles.
NDIS
National DNA Index System, which began in 1990.
SDIS
State DNA Index System.
LDIS
Local DNA Index System.
Forensic Samples
Profiles from crime scenes.
Criminal Offender Database
Database containing profiles of convicted offenders.
Missing Persons
Database containing profiles of missing individuals.
Genes
Determine the nature and growth of every body structure and positioned on chromosomes.
Genotypes
Pair of allele genes together (genotype AO).
Homozygous
Same alleles.
Heterozygous
Different alleles.
Phenotypes
Person's outward characteristics (phenotype A, doesn't tell us AA or AO).
Chromosomes
On the nucleus of every body cell.
Nucleated cells
All nucleated cells contain 46 chromosomes mated in 23 pairs, except the sperm and egg.