AP Human Geography Unit 3 Vocab
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/106
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:45 PM on 12/7/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
1
New cards
Acculturation
when two cultures come into contact and the less dominant culture adopts some of the traits of the more influential one
2
New cards
Animism
the belief that inanimate objects (rocks, mountain, rivers, plants) have spirits and a conscious life
3
New cards
Artifacts
Concrete human creations that reflect values, beliefs, and behaviors
4
New cards
Assimilation
When the dominant culture completely absorbs the less dominant; Usually 2nd, 3rd, and 4th generations
5
New cards
Baha'i
universalizing religion, relatively new, founded in Iran (most followers there), believe that Husayn 'Ali Nuri was a prophet (not Muhammad)
6
New cards
Behaviors
actions that people take
7
New cards
Beliefs
specific statements that people believe to be true
8
New cards
Bilingualism
the ability to communicate in two languages
9
New cards
Branch
large basic divisions within a religion
10
New cards
Buddhism
World's 3rd major universalizing religion; began in India and diffused along the Silk Road
11
New cards
"Cape Code" house style
a New England-style house that originated in the late 17th century; for small families; originally built for soldiers and their families after WWII; curb appeal
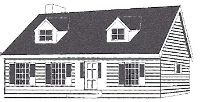
12
New cards
Christianity
a universalizing religion that has the most followers and the most widespread distribution; predominant in North America, South America, Europe, and Australia
13
New cards
composite culture
both material and non-material
14
New cards
Confucianism
often viewed as philosophy (not religion), provides code of moral conduct based on humaneness and family loyalty, Chinese
15
New cards
Contagious diffusion
form of expansion diffusion, when almost all individuals and areas outward from source region are affected
16
New cards
Creole
when a pidgin becomes the first language of a group of speakers
17
New cards
Cultural determinism
Emphasizes human culture as ultimately more important than physical environment in shaping human activities
18
New cards
Cultural diffusion
the spread of material and non-material culture to areas around them
19
New cards
Cultural ecology
the field that studies the relationship between the natural environment and culture
20
New cards
Cultural geography
important component of human geography, The study of the relationship between culture and place.
21
New cards
Cultural hearths
the areas where civilizations first began that radiated the customs, innovations, and ideologies that culturally transformed the world
22
New cards
Cultural landscape
the modification of the natural landscape by human activities
23
New cards
Cultural Possibilism
the school of thought holds that cultural heitage is as important as the physical environment in terms of shaping human behavior; PEOPLE ARE THE PRIMARY ARCHITECTS OF CULTURE
24
New cards
Cultural relativism
the practice of evaluating a culture by its own standards; the idea that a person's beliefs, values, and practices should be understood based on that person's own culture, rather than be judged against the criteria of another.
25
New cards
Cultural transmission
the process by which one generation passes culture to the next
26
New cards
culture
the complex mix of values, beliefs, behaviors, and material objects that together form a people's way of life; non-material and material
27
New cards
Culture complex
when culture traits combine in a distinctive way, consists of common values, beliefs, behaviors, and artifacts that make a group in an area distinct from others
28
New cards
Culture region
an area marked by culture that distinguishes it from other regions
29
New cards
Culture system
a group of interconnected culture complexes
30
New cards
Culture trait
single attribute of a culture (ex. wearing a turban)
31
New cards
Daoism
holds that human happiness lies in maintaining proper harmony with nature, Chinese
32
New cards
Denomination
divisions of branches that unite local groups in a single administrative body
33
New cards
Dialect
a regional variant of a standard language
34
New cards
Diasporas
forced exodus from their lands of origin (ex. Jews)
35
New cards
Durkheim's sacred and profane
French sociologist's theory that as humans we define most objects, events, and experiences as profane (ordinary), but we define some things as sacred (extraordinary)
36
New cards
Eastern Orthodox
about 12% of all Christians, officially split from Roman Catholicism in 11th century, strong in Eastern Europe and Russia
37
New cards
Environmental determinism
belief that the physical environment, especially the climate and terrain, actively shapes cultures, so that human responses are almost completely molded by the environment
38
New cards
Environmental perception
the school of thought emphasizes the importance of human perception of the environment, rather than the actual character of the land
39
New cards
Ethnic religion
appeal primarily to one group of people living in one place
40
New cards
Ethnocentrism
the practice of judging another culture by the standards of one's own culture
41
New cards
Expansion diffusion
occurs when an innovation or idea develops in a source area and remains strong there while spreading outward
42
New cards
Extinct language
a language that was once in use, but is no longer spoken or read in daily activities by anyone in the world
43
New cards
Folk culture
Culture practiced by small, homogeneous groups living in isolated areas
44
New cards
Folk culture region
When many people who live in a land space share some of the same folk customs
45
New cards
Folk life
Composite culture (material and nonmaterial) that shape the lives of folk societies
46
New cards
Food taboos
rules that forbid certain food from being consumed; can be for religious or government purposes
47
New cards
Geographic region
a culture region representing an entire culture system that intertwines with its locational and environmental circumstances
48
New cards
Globalization
the expansion of economic, political, and cultural activities to the point that they reach and have impact on many areas of the world
49
New cards
Hagerstrand, Torste
wrote about cultural diffusion at about the same time as Sauer, since then geographers have classified diffusion processes into expansion and relocation diffusion
50
New cards
Heterogeneity
the quality or state of being diverse in character or content
51
New cards
Hierarchal diffusion
type of expansion diffusion, where ideas and artifacts spread first between larger places or more prominent people and only later to smaller places and less prominent people
52
New cards
Hinduism
world's 3rd largest religion, most adherents live in India, ethnic religion, world's oldest organized religion, no central god and a single holy book (each individual decides best way to worship)
53
New cards
Homogeneity
the quality or state of being all the same or all of the same kind
54
New cards
Humanism
emphasizes the ability of human beings to guide their own lives
55
New cards
Independent inventions
developments that can be traced to a specific civilization
56
New cards
Indo-European language family
most commonly cited language family, since languages from this family are spoken by about half the world's people (with English as most widely used)
57
New cards
Islam
Universalizing religion; youngest and 2nd largest religion; mostly in the Middle East; diffused from Mecca to Central Asia, North Africa, and Spain
58
New cards
Isogloss
physical boundaries within which particular words are used
59
New cards
Judaism
Ethnic religion; one of the oldest religions; members spread due to diaspora; 1st recorded monotheistic religion
60
New cards
Language
a systematic means of communicating ideas and feelings through the use of signs, gestures, marks, or vocal sounds
61
New cards
Language families
language groups each with a shared, but fairly distant origin
62
New cards
Language sub-families
smaller, more recent groups of languages (ex. Romance languages: sub-family of Indo-European, origins in Latin, including Spanish, French and Italian)
63
New cards
Lingua franca
an established language that comes to be spoken and understood over a large area
64
New cards
Linguist
those who study languages
65
New cards
Linguist fragmentation
a condition in which many languages are spoken, each by a relatively small number of people
66
New cards
Linguistic geography
the study of speech areas and their local variations by mapping word choices, pronunciation, or grammatical constructions
67
New cards
Mahayana
branch of Buddhism, 56% of Buddhists, incorporation of ideas and gods from other religions as it spread into East Asia (China, Korea)
68
New cards
Marxism
ideology that transformed communism into a central ideology in many areas during the 20th century
69
New cards
Material culture
things that are created by humans. Examples include cars, buildings, clothing, and tools.
70
New cards
Migrant diffusion
type of relocation diffusion, where the spread of cultural traits is slow enough that they weaken in the area of origin by the time they reach other areas
71
New cards
Monotheistic religion
centered on the belief in one God
72
New cards
Multilingualism
the ability to communicate in more than two languages
73
New cards
Non-material culture
the abstract ideas and ways of thinking that make up a culture. Examples of nonmaterial culture include traffic laws, words, and dress codes.
74
New cards
Norms
Rules/ expectations by which society guides behavior of its members
75
New cards
Official language
the language endorsed and recognized by the government as the one that everyone should know and use
76
New cards
Pidgin
a grammatically simplified form of a language, used for communication between people not sharing a common language.
77
New cards
Popular culture
a set of the practices, beliefs, and objects that are dominant in a heterogeneous society at a given point in time.
78
New cards
Protestants
about 18% on the world's Christians, first split from Catholic Church in 16th century, strong in North America, Northern Europe, Britain, South Africa, and Australia
79
New cards
Regional identity
Awareness of being part of a group living in a culture region
80
New cards
Religion
a particular belief system (explains the relationship of the individual ot the world and the meaning of life nad death)
81
New cards
Religion: branches, denominations, sects
divisions of universalizing religions, branches: large and basic divisions within a religion, denominations: divisions of branches that unite local groups in a single administrative body, sects: relatively small groups that do not affiliate with the more mainstream denominations
82
New cards
Relocation diffusion
People migrating from source areas physically carry the innovation/idea to new areas
83
New cards
Roman Catholics
about 50% of the world's Christians, concentrated in Latin America, French Canada, Central Africa, and Southern and Eastern Europe
84
New cards
Saltbox house style
A colonial style of architecture originating in New England around 1650 and commonly built by the 18th century; has a roof with unequal sides (the roof in the back is longer than the front) which helps during snow falls so snow is more at the back of the house instead of the front
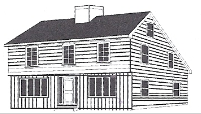
85
New cards
Sauer, Carl
A critic of environmental determinism, he sought to demonstrate that nature does not create culture, but instead, culture working with and on nature, creates ways-of-life.
86
New cards
Sect
relatively small groups that do not affiliate with the more mainstream denominations
87
New cards
Shamanism
ethnic religion in which people follow their shaman (religious leader and teacher believed to be in contact with the supernatural), followers isolated from one another, traditional religion
88
New cards
Shiite
16% of all Muslims, most located in a few countries of the Middle East (Iran, Pakistan, Iraq, Turkey, Azerbaijan, Afghanistan, and Yemen.)
89
New cards
Shintoism
a native ethnic religion of Japan; focuses on nature and reverence of ancestor; no longer the state religon of Japan, it still thrives in Japan; prayers are offered to ancestors and shrines mark reverence for house dieties
90
New cards
Sikhism
universalizing religion, 21 million live in Punjab region of India, stress continual improvement and movement toward perfection by taking individual responsibility for their actions, combines beliefs from Hinduism and Islam, Guru Nanak
91
New cards
Standard language
a language recognized by the government and the intellectual elite as the norm for use in schools, government, media, and other aspects of public life
92
New cards
Stimulus diffusion
type of expansion diffusion, a basic idea, though not the specific trait itself, stimulates imitative behavior within a population.
Expansion occurs, but the idea / product is adapted.
Expansion occurs, but the idea / product is adapted.
93
New cards
Sunni
83% of all Muslims, largest branch in Middle East and Asia, largest concentration in Indonesia, believe religious leaders should choose Muhammad's successor
94
New cards
Symbolic landscape
Land that has accumulated meaning over time. ex. The Temple mount
95
New cards
Symbols
Express personal and cultural identity
96
New cards
Syncretism
the process of the fusion of the old and new; the combining or attempted amalgamation of different religions, cultures, or schools of thought.
97
New cards
Tantrayana
branch of Buddhism, 6% of Buddhists, emphasis on magic and different meditation techniques, mainly in Tibet and Mongolia
98
New cards
Theraveda
38% of Buddhists; stricter adherence to Buddha's teachings; strong in Southeast Asia
99
New cards
Time-distance decay
the influence of the cultural traits weakens as time and distance increase
100
New cards
Toponymy
the study of place names