lipids
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Are lipids soluble and why ?
Lipids are not polar , so they they don’t attract water molecules, meaning they are insoluble in water
What are lipids classed as ?
A macromolecule, not a polymer
What are the most important lipids in living organisms?
Triglycerides
What are lipids made up of ?
A glycerol molecule with 3 fatty acids bonded to it
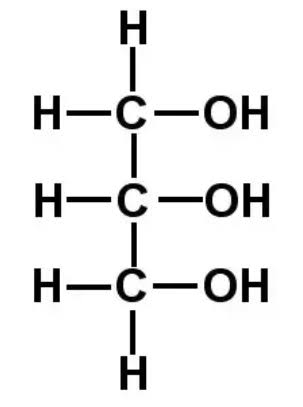
What is the structure of glycerol?
Made up of 3 carbon atoms
Each of these has a hydroxyl (OH) group attached to it
Hydrogen atoms occupy the remaining positions
What formula is in any acid group ?
COOH
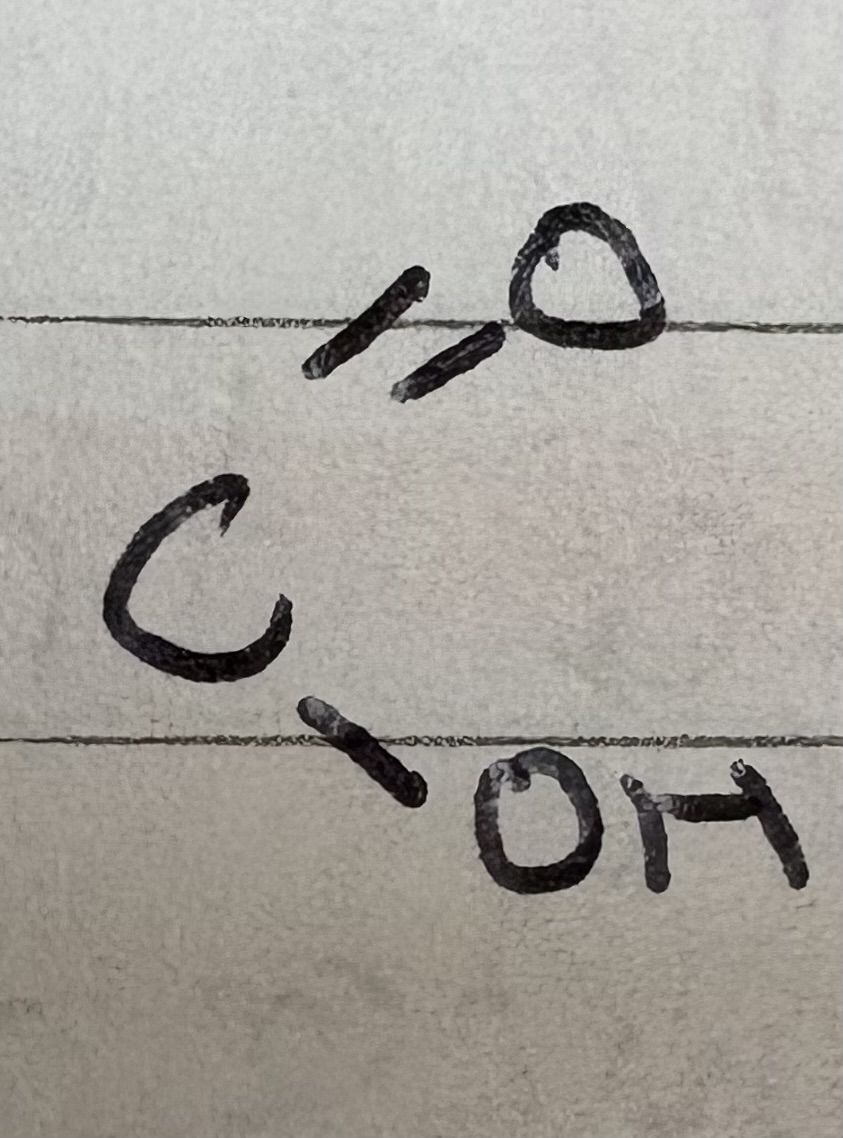
What is the structure of a fatty acid molecule?
A single fatty acid molecule contains an acid (COOH) group attached to a hydrocarbon chain (a compound with only hydrogen and carbon atoms ). The hydrocarbon chain can be from 2-20 carbons long , this is what makes the fatty acids (and therefore the triglycerides) different.
What is an ester bond ?
When glycerol and fatty acids bonded, the bond between the 2 hydroxyl groups. A water molecule is made form this and the left over oxygen atom bonds the two molecules together.
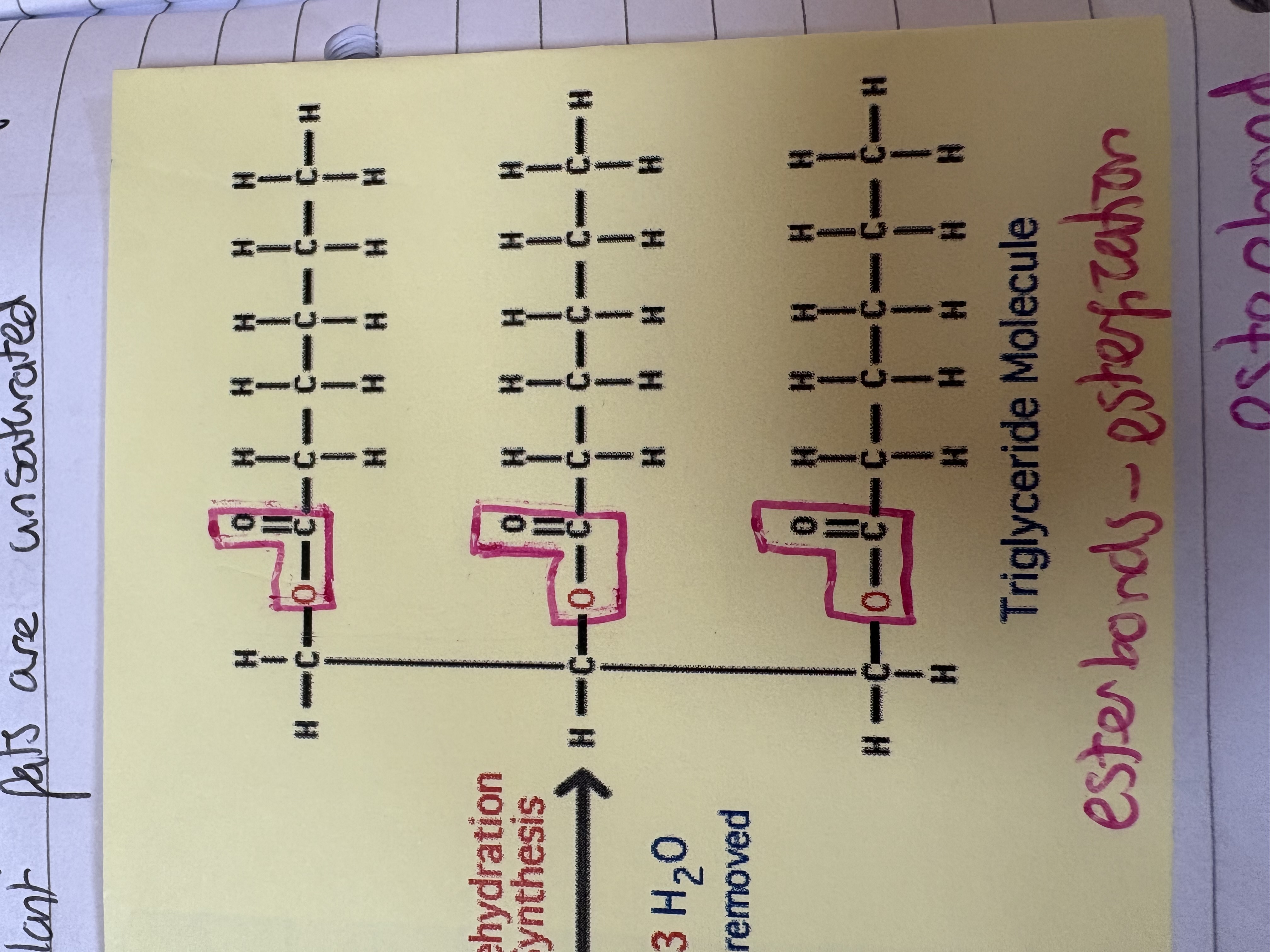
What is the process called where ester bonds are made ?
Esterfication
What are the three types of fatty acids and explain them ?
Saturated , these have single C-C bonds and form a straight chain
Unsaturated, these have at least one double C=C bond and form a mainly straight chain with a couple a kink where the double bond is
Polyunsaturated, these are mainly double bonds and form a mainly bent and kinked chain where there are many double bonds
What fats are saturated and unsaturated?
Most animal fats are saturated whereas most plant fats are unsaturated.
What are 5 functions of triglycerides and explain them ?
Energy source
They are broken down in respiration to release energy and generate ATP
Energy store
They are insoluble in water , so they can be stored without affecting the water potential of cells
Insulation
Lipids around nerve cells act as an electrical insulation
Buoyancy
Fat is less dense than water so is used by aquatic mammals to help them stay afloat
Protection
Fat around organs act as a shock absorber