Unit 3-2: Language and Religion - AP Outline
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Acculturation
Process of cultural and social change that occurs when two distinct cultures come into contact. Typically, this involves a less dominant culture adopting some of the traits (language, customs, beliefs, technology, etc.) of a more dominant or host culture
Minority or adapting culture retains some aspects of its original culture while incorporating elements from the new one
Assimilation
Process where individuals or groups from one culture adopt the practices, values, and behaviors of another, more dominant culture to the extent that they lose their original cultural identity and become socially or culturally indistinguishable from the host group
Dominant culture completely absorbs a less-dominant culture (usually takes a few generations)
Key Characteristics
Voluntary - driven by social pressure or economic advantage
Involuntary - forced/coerced - government policies or colonization
Ethnic Religion
Religion closely identified with a specific ethnic group or culture and is generally not actively seeking converts outside of that group - typically in clustered geographic distribution
Key Characteristics
Tied to Ethnicity/Culture
Limited Diffusion - primarily relocation diffusion
Cultural Landscape - heavily influenced by sacred sights
Syncretism
Blending of two or more cultural traits, beliefs, or practices to form a new, unique cultural expression or system
Key Characteristics
Blending/Fusion - creation of something NEW from existing parts
Combines elements of distinct traditions
Often occurs in areas of cultural contact and exchange
Time-Space Convergence (Time-Space Compression)
Refers to the reduction in the time it takes to travel between two places due to innovations in transportation and communication technologies
Key Characteristics
Transportation - physically reduces travel time
Communication - improves access to information and connections almost immediately
Toponym
Name given to a specific place or geographic feature
Key Characteristics
Migration and Origin - names related to homeland of settlers
Historical Events/Values - important people, historical events, or values associated with the location
Physical Features - natural environment
Linguistic Heritage - names reveal dominant or previous languages spoken in the area
Universalizing Religion
Belief system that attempts to appeal to all people, regardless of their ethnicity, location, or culture. These religions actively seek converts and spread globally
Key Characteristics
Global Appeal
Missionary Work - actively seeking to convert individuals
Clear Hearth - precise, identifiable point of origin
Diffusion - Relocation (migration/missionaries) and Expansion (contagious, hierarchical, stimulus)
Multiculturalism
A set of policies that promote the active participation and inclusion of minority groups in national histories, national politics, and cultural institutions with the goal of embracing difference with society
Presence and active support of multiple, distinct cultural groups coexisting within a single society (cultural pluralism)
Examples of Multiculturalism
Ethnic Enclaves/Neighborhoods
Bilingual or Multilingual Signage
Diverse Architecture
Diverse Cuisine (restaurants and grocery stores)
Cultural Convergence
Process where different cultures become more similar as they interact and share ideas, values, and practices. Essentially, it's the blending or fusion of cultural elements across societies
Key Drivers of Cultural Convergence
Globalization - increased interconnectedness of the world through trade, travel, and global communication networks
Technology and Media - Internet, social media, global media networks - instant sharing
Migration and Travel - people bring cultural traits to new places where interaction and merging with local practices
Urbanization - Cities are hubs where diverse populations accelerate cultural mixing
Cultural Divergence
Process where distinct cultural groups become increasingly different from one another over time - divergence happens when factors cause cultures to separate, isolate, or actively resist outside influences, leading to the development of unique and distinct cultural traits
Key Factors Driving Cultural Divergence
Geographic Isolation - physical barriers (mountains/oceans/deserts)
Social/Political Separation - strong nationalist movements or political division (North/South Korea)
Cultural Resistance/Revival - efforts to preserve traditional customs and practices in the face of globalization
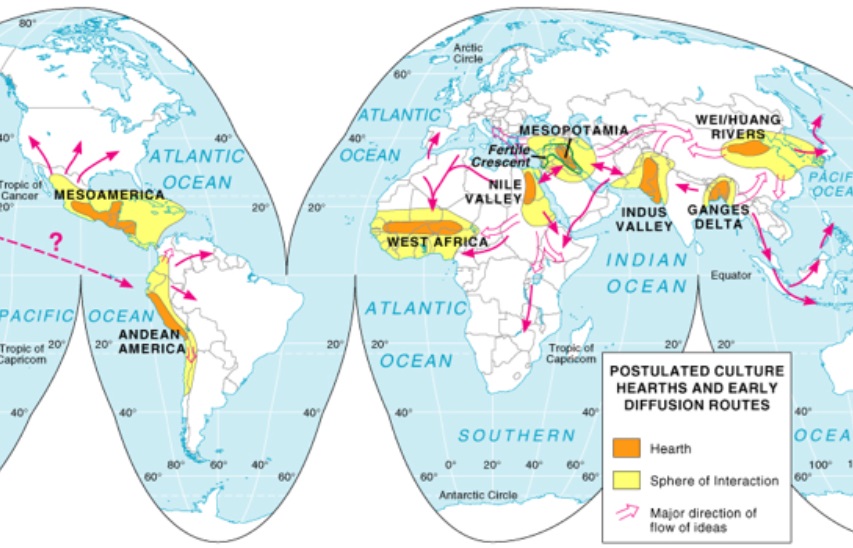
Cultural Hearth
Geographic origin or birthplace of a significant cultural trait, idea, religion, social practice, or innovation, from which it then spreads to other regions
Early Civilization Cultural Hearths - Mesopotamia, Nile River, Indus Valley, Huang He (Yellow River) Valley, Mesoamerica
Modern Cultural Hearths - New York City, London, Paris, Tokyo, Los Angeles
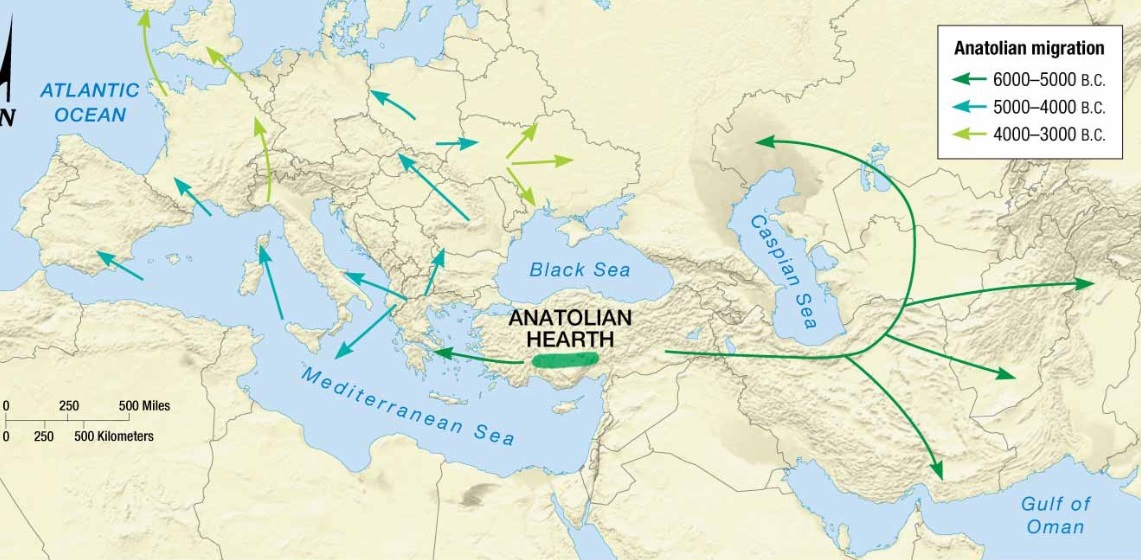
Indo European Language Diffusion - Kurgan Model
Most widely accepted hypothesis for explaining the origin and diffusion of the Indo-European language family
Hearth located north of Caspian Sea by Russia/Kazakhstan
Pastoral nomadic group called the Kurgans
Relocation diffusion driven by the conquest or military superiority of the Kurgan people (use of HORSES)
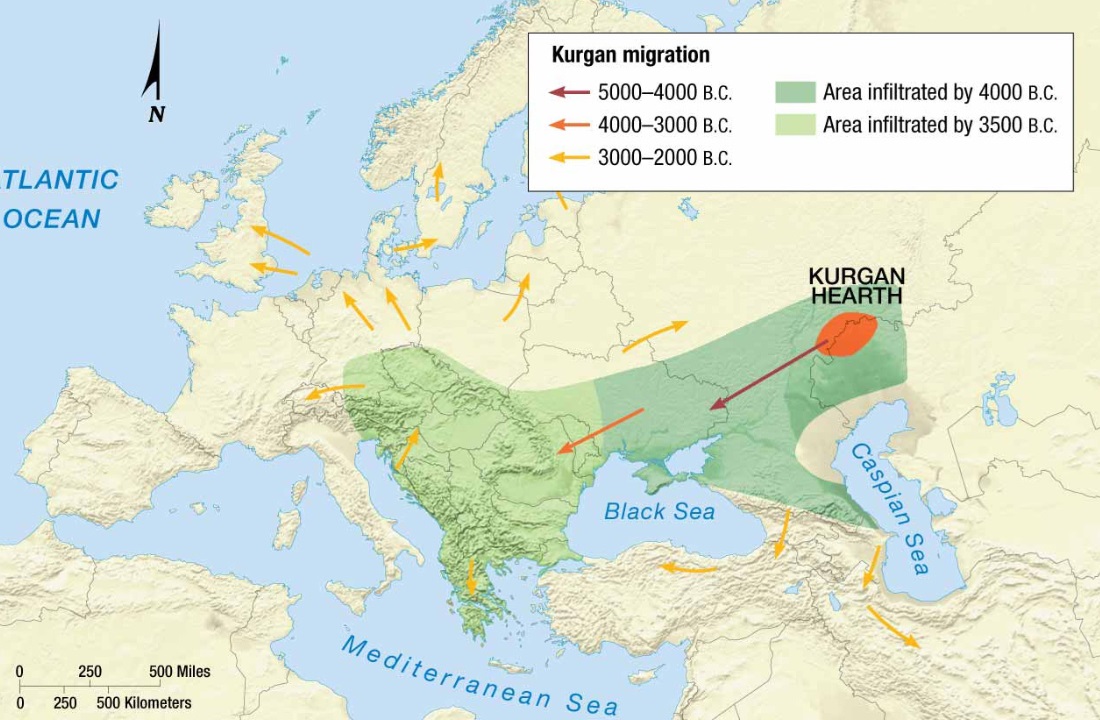
Indo European Language Diffusion - Anatolian Model
Hearth located in present day Turkey (Asia Minor)
Nomadic group called the Anatolians
Farmers who migrated/diffused language into Europe and Asia using agricultural (farming) methods