KINE 3050 Angular Kinetics
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Torque is the tendency to produce a change in
rotational motion
Torque is determined by
Magnitude of applied force
Direction of applied force
Location of applied force
Force is a
action that creates changes in linear motion
What is required to rotate an object
torque
Torque is created by
force and depends on
where the force is applied
the point which the object rotates
Torque is a vector or scalar?
Vector
What are the signs of torque
Counterclockwise → positive
Clockwise → negative
Classic example of torque force is
how you open a door
hinges of door is axis of rotation
open door closer or further from the hinges
What are the units of torque and the equation
Torque (τ) created by a force = to the lever arm (d) x the magnitude of the force (F)
units : N/m
What is the center of rotation?
point or line about which an object turns
ex) doors center of rotation is the hinges
A force applied far from the center of rotation produces a
greater torque than a force applied close to the center of rotation
Torque is created when the line of action of a force
DOES NOT pass through the center of rotation
Line of action is an
imaginary line of indefinite length drawn along the direction of the force
The brachialis muscle is
a large muscle, but it has the smallest moment arm
(poorest mechanical advantage)
The biceps brachii
large cross section and has a longer moment arm
The brachioradialis has
a smaller cross section and the longest moment arm
( best mechanical advantage )
If the force due to the biceps shown is 100N and the moment arm is 1.5cm. What is the torque produced by the biceps
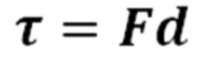
T = 100N (1.5cm)
Step 1 : Convert
100N (0.015m)
Step 2: Solve
Answer: 1.5N/m
The application is: During a concentric bicep curl, where the bicep brachii is producing 100N of force, there is 1.5N/m of torque force (rotational force) at the elbow joint
A muscle with a small moment arm needs to produce
more force to generate the same torque as a muscle with a larger moment arm
Although human motion is general (translation and rotation), it is generated by
a series of torques and rotations
Lines of action of muscle forces
DO NOT pass through the joints’ axes of rotation
The moment arm is the
shortest distance from a forces line of action to the axis of rotation
always perpendicular to the line of action and passes through the axis of rotation
The magnitude of the moment arm of the biceps muscle changes
throughout the range of motion
Computing the moment arm is determined by
distance from axis of rotation to point at which force is applied
and
angle at which the force is applied
An 80N force acts at the end of a 12cm wrench as shown. What is the torque ?
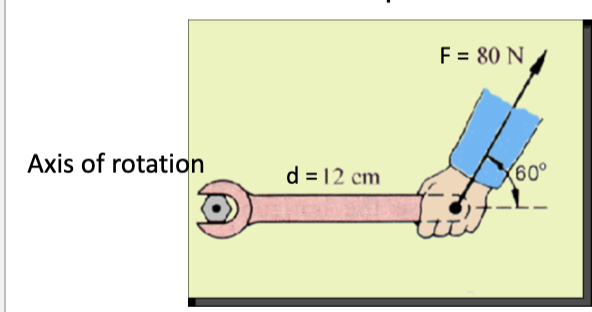
Torque = f(d) = N/m (Answer will be +)
F=80N
MA= ?
Theta Angle = 60 degrees
Step 1: Find moment arm = 0.104m
Step 2: Solve = 80N x 0.104m
Answer: 8.32N/m
The center of mass is the point in a body or system
where the entire mass may be assumed to be concentrated
imaginary point in space
not a physical activity
not a fixed point (changes when parts of an object change position)
The force of gravity acts
downward through the center of mass
Which of the following can be determined by taking the absolute value of the ratio of the velocity of separation to the velocity of approach?
Coefficient of Restitution
Stability is directly
proportional to the area of the best on which the body rest
in a given direction is directly proportional to the horizontal distance of the center of gravity from that edge of the base
directly proportional to the weight of the body
indirectly proportional to the distance of the body above the base
What does stability depend on?
State of equilibrium : balanced and forces are =
Gravity: attraction between earth and object
Gravitational Force: Directed vertically downward
Center of Gravity: Balance point of object with torque equal on all sides
Base of Support: Part of body in contact with support surface
Line of Gravity: imaginary vertical line passing through center of gravity towards earth
The outcome of torque is to produce
a rotation about an axis
Lever is a rigid
rod that is rotated about a fixed point or axis
What are the components of levers?
Resistance/Load Arm
Effort force
Effort/Load Arm
Fulcrum Arm
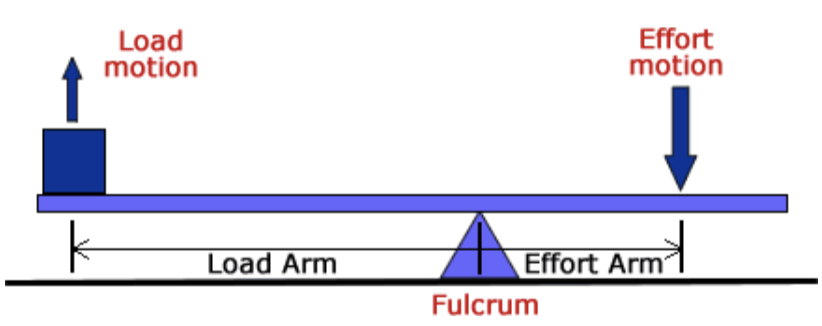
Levers are a simple
machine consisting of a relatively rigid bar-like body that can be made to rotate about an axis or fulcrum
Classification depends on
relative position of the force, applied force, and fulcrum
1st class
2nd class
3rd class
The interaction between internal and external forces in levers ultimately controls
movement
These forces interact through a system of bony levers, with the pivot point located at the axis of rotation of our joints
Through these systems of levers, the internal and external forces are converted to internal and external torques, which ultimately cause movement (or rotation) of our joints
Mechanical Advantage is the
ratio of effort arm to resistance arm

Levers will either favor
power OR distance but never both
any advantage gained in power is lost in distance and vice versa
The arrangement of axis in relation to force and the resistance determines?
the type of lever
Longer the FA, easier to move : With a longer FA, the part will be easier to move, but the FA will have to move a greater distance
Longer the RA, harder to move: With a longer RA, won’t have to move as far, but it will be harder to move
First class levers have the fulcrum located
between the load and the effort
very useful for lifting large loads with little effort
A teeter-totter, car jack, and crowbar are examples of what class lever
First Class
Second class levers load is located
between the effort and the fulcrum
easy to move objects over distance
Wheelbarrow, bottle opener, and a oar are examples of what class lever?
Second Class
In a third class lever, the effort is located between the
load and the fulcrum
good for making precise movements
Pair of tweezers, swinging a baseball bat, and using your arm to lift something are examples of what class lever?
Third Class
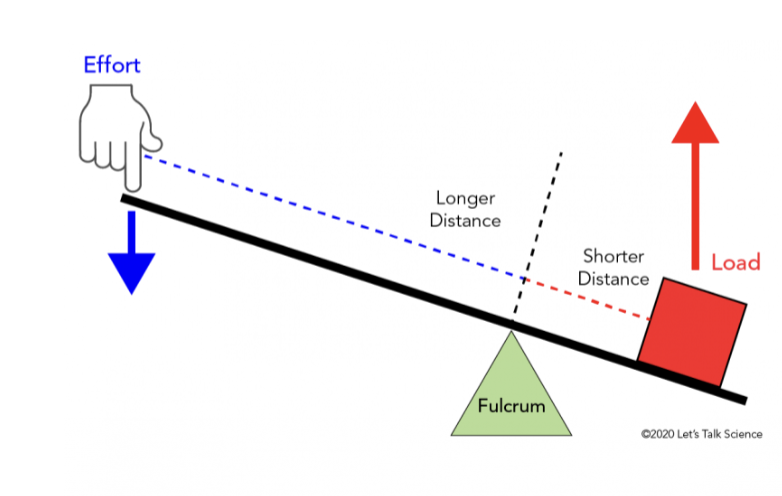
What lever class
1st class
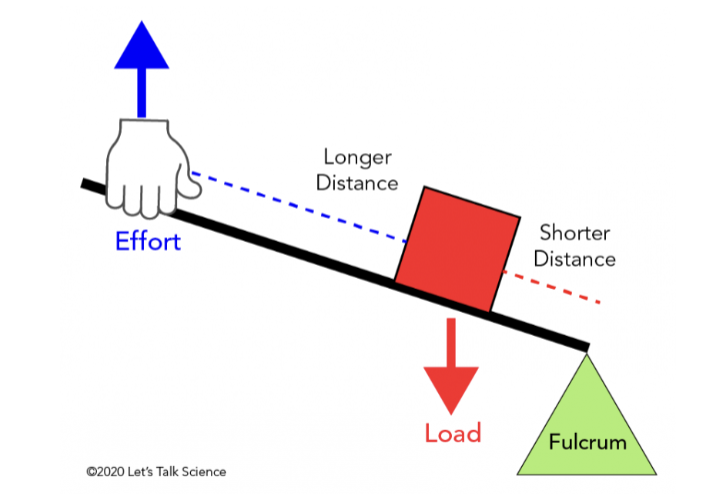
What class lever?
2nd class
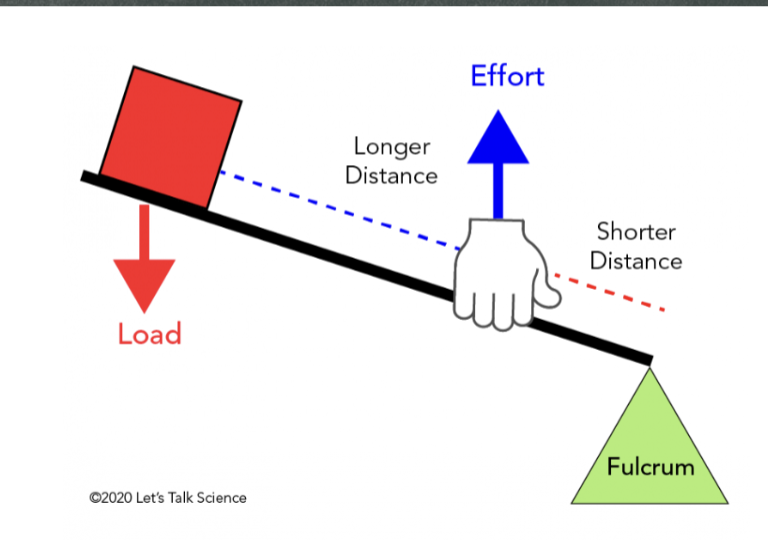
What class lever?
3rd class