Oceans
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
When dissolving ionic compounds in water, what bonds are broken
ionic bonds in the solid
Hydrogen bonds between water molecules
When dissolving ionic compounds, what bonds are made
Ion- dipole bonds between the ions and water molecules
How do you know if a substance is soluble
If the bonds made are similar in strength or stronger than the bonds broken
What are some insoluble ionic compounds
AgCl, Agbr
BaSO4
Cu(OH)2
Fe(OH)2
CaCO3
Definition of lattice enthalpy and symbol
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of a solid ionic compounds is formed from separate, gaseous ions

Example equation of lattice enthalpy for sodium chloride

In lattice enthalpy endothermic or exothermic and why
ALWAYS EXOTHERMIC because ionic bonds are being made
Is it endothermic or exothermic to dissolve an ionic compounds in water and how do you do it
We need to break up the lattice to get separate ions, so we need to do the reverse of lattice enthalpy.
This will always be endothermic as bonds are being broken
How does a lattice enthalpy become more negative
The stronger ionic bonding, the more negative the lattice enthalpy
Which factors affect the size of lattice enthalpy for different compounds
The charge on the ions- Ions with higher charges attract together more strongly. This means more energy is needed to break the lattice so lattice enthalpy is more exothermic
Size of ions- ions with small ionic radius can get closer to the opposite ions in the lattice, giving stronger attractions so more exothermic lattice energy (not as big of a factor as charge)
Enthalpy of hydration definition
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous ions are added to water to give 1 mole of aqueous ions to give an infinitely dilute so.lution

Example equation of enthalpy of hydration
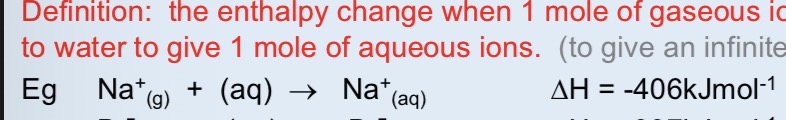
Why is enthalpy of hydration always negative
Always negative for positive and negative ions as ion dipole bonds are being made between the polar water molecules and the fully charged ions. The ions are hydrated- they have water molecules bound to them
Draw a diagram of a hydrated sodium ion with charges and partial charges
What factors affect the size of thee hydration enthalpy
Hydration enthalpy is more exothermic for ions which have a higher charge and a smaller ionic radius so have a higher charge density. Smaller ions get closer to the water molecules so there’s stronger ion dipole bonds and more water molecule bind to them
For example mg2+ and Na+ Mg2+ has higher charge density as higher charge and smaller size
Enthalpy change of solution
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of ionic solid dissolves in enough water to make an infinitely dilute solution

Is enthalpy change of solution endothermic or exothermic
Depends on relative size of lattice enthalpy breaking step (endothermic) and hydration of ions step (exothermic)
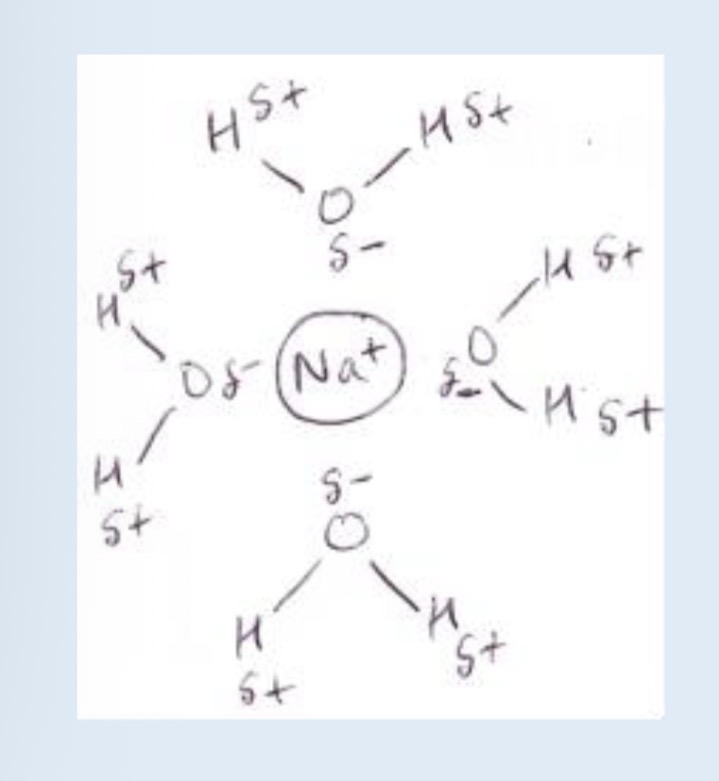
How to draw enthalpy level diagram

How to calculate enthalpy of solution
What are the 3 possibilities for enthalpy of solution and solubility
Enthalpy of solution is exothermic overall. These substances are almost all soluble and when they dissolve the solution warms up
Enthalpy of solution is endothermic and large. These solids are insoluble
Enthalpy of solution is endothermic but small, these solids are usually soluble but they have to take in heat to dissolve so the solution will feel cold
Non-polar solvents
Ionic substances do not dissolve. The ions cannot form strong attractions with non-polar solvent molecules so the down step (enthalpy of solvation) is very small making enthalpy of hydration large and positive
Radiation in and out relating to the greenhouse effect
Hot objects send out electromagnetic radiation. The hotter the object, the higher the energy of this radiation. The sun (surface temperature of 6000K) gives out mainly UV and visible radiation. When this radiation reaches earth, part is absorbed by the earths surface and atmosphere, and part is reflected back into space. The part that gets absorbed warms up the earth and the earth send electromagnetic radiation back into space, but the earth is a lot cooler than the sun so it gives out lower energy radiation (infra red)
A steady state is reached where the earth is radiating energy into space as fast as it is absorbing it, so the earths average temperature stays constant
What is the role of greenhouse gasses
greenhouse gas molecules in the atmosphere absorb some of the infrared red radiation emitted from the earths surface and stop it being re-radiated into space.
This warms the earth because:
some of the IR is then re emitted by the molecules , but in all directions so some of the IR that was going out into space now gets radiated back towards earth.
When molecules absorb certain frequencies of IR radiation, their vibrational energy increases: the bonds vibrate more vigorously. When they collide with other molecules in the atmosphere this extra energy is transferred increasing the kinetic energy of air molecules, raising the temperature of the atmosphere
They do not absorb UV or visible from the sun but let it in but do absorb IR and stop IR radiation from earth getting out- without this life would be too cold to support life but human actions is changing this balance by adding additional greenhouse gasses in atmosphere
What are the very abundant greenhouse gasses
CO2
H2O
What are the less abundant greenhouse gasses
CH4
N2O
CFC
O3
What is the Infra red window
Water vapour is the most abundant greenhouse gas in the atmosphere but water only absorbs certain frequencies of IR and the rest of the IR spectrum is the IR window where infra red can escape without being absorbed. If human activity puts gasses into the troposphere which absorb IR in this window there will have big greenhouse impact with CO2 and CH4 being important examples. The higher conc of greenhouse gasses in troposphere the more IR absorbed increasing greenhouse effect
Is CO2 a problem
Increase in CO2 in atmosphere is due to more use of fossil fuels worldwide
A lot of extra CO2 is removed by oceans by dissolving and marine plants like phytoplankton
What is an acid
Proton donor
What is an alkali
A proton acceptor
When an acid has donated H+ what is given
When a base has accepted H+ what is given
Acid leaves a conjugate base
Base leaves a conjugate acid
Why can water act as an acid and a base
Acid because it can donate H+ leaving OH- and can accept H+ giving H3O+
Why is water neutral in PH
As the tiny percentage of water molecules that dissosciate into ions give equal quantities of H+ and OH- so [H+] = [OH-]
What is the name of something that acts as both an acid or a base
Amphoteric
What is a strong acid and how do you write the equation
An acid which when dissolved in water is fully dissociated into ions so a strong acid is a very good H+ donor.
Use a full arrow in equation to show complete reaction
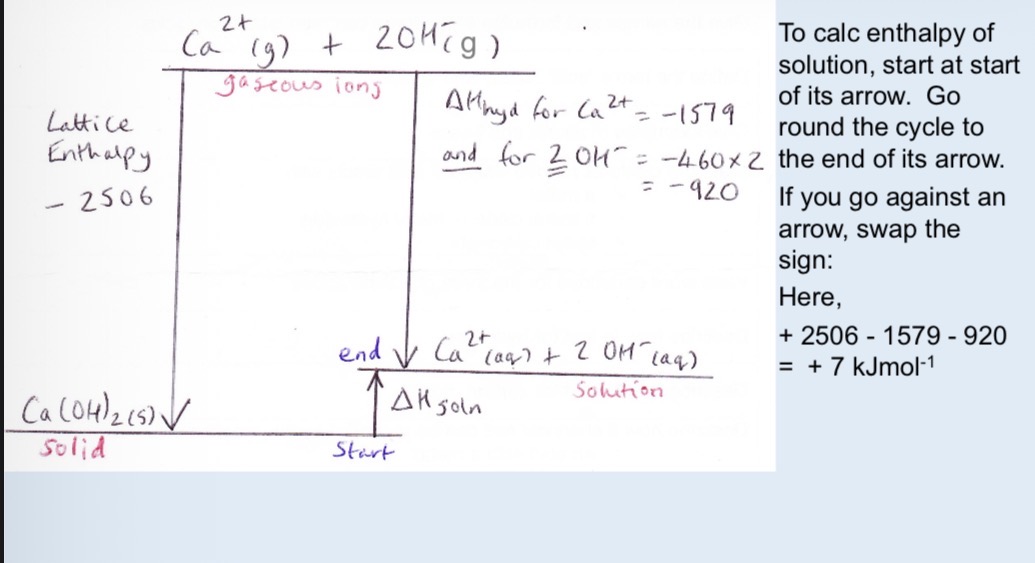
Show equation for HCL as a strong acid

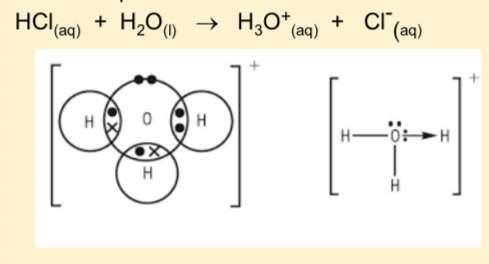
How do H+ ions usually exist and what is the dot and cross diagram and the equation forming it from HCl
As oxoniuum ion H3O+
What is a weak acid and how do you write the equation for one
An acid that when dissolved in water only very slightly dissociates into ions and once ions form they start joining back together so reaction is in equilibrium. Use equilibrium arrow
Write equation for weak acid of HF
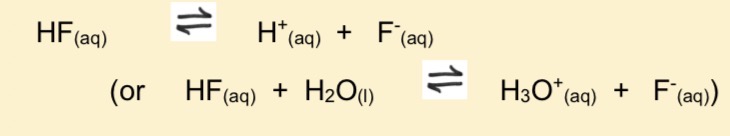
How do indicators work
Indicators are weak acids but where HA is a different colour to A-.
If acid is added, conc H+ increases so equilibrium shifts left to use up some extra H+ and most of indicator is present as HA so we see that colour. If alkali is added, it reacts with and removes H+ so equilibrium shifts right to replace H+. Most of indicator is now in the A- form so we see that colour
What is evidence that water is partially split into ions
Even when completely pure water will still conduct a current so water must be partially split into ions as ions carry current and this is autoionisation of water.
Why is conductivity of pure water low
As almost all water is unionised as position of equilibrium is far on the left
Write the Kc expression of water and state why [H2O] can be taken as a constant
As [H2O] is so much larger than [H+] or [OH-] it is taken as constant
![<p>As [H2O] is so much larger than [H+] or [OH-] it is taken as constant </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/92787c73-dc03-4b33-be2f-4d80eba5b86d.jpg)
Rewrite the water Kc expression with H2O as a constant and What is the new constant called

What is the molar concentrations of [H2O] [H+] and [OH-] at 25 degrees
Kw= 1X10-14 mol2dm-6
[H+] = 1X10-7 mol dm-3
[OH-] = 1x10-7 mol dm-3
Work out the concentration of H+, OH- ions in a o.1 mol dm-3 solution of HCl

What is pH
Measure of concentration of H+
What is the equation to work out pH

How many decimal points do we write ph to
2 decimal points e.g. 7.00
How to work out PH of strong acids vs strong alkali

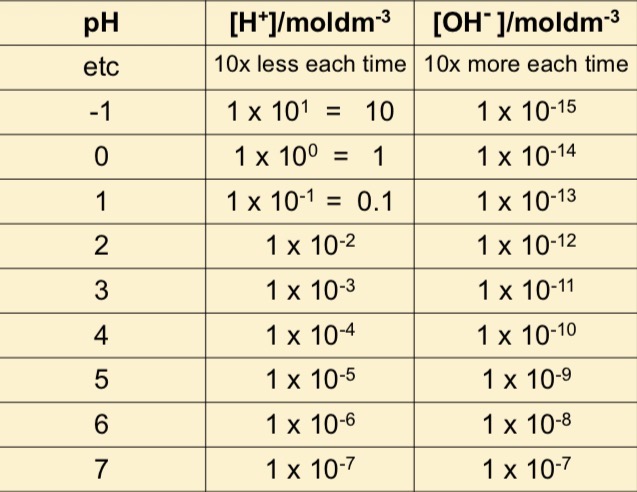
Acid PH scale
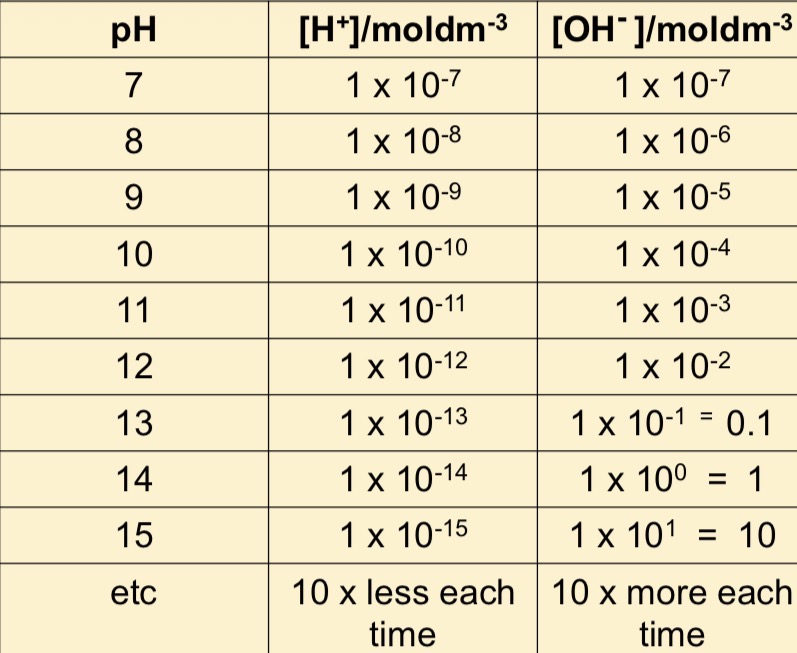
Alkali PH scale
How to calculate PH at various points in an acid-base titration

Effect of temperature on PH values
Kw is 1X10-14 only at 25 degrees so Ph 7 is only at 25 degrees
Water dissociating into its ions is endothermic as bonds are being broken so at a higher temperature equilibrium will shift right so Kw will increase
If the solution is neutral for example water what is the main rule
[H+] = [OH-] so do square root of Kw to find out there conc
How to calculate [H+] from PH

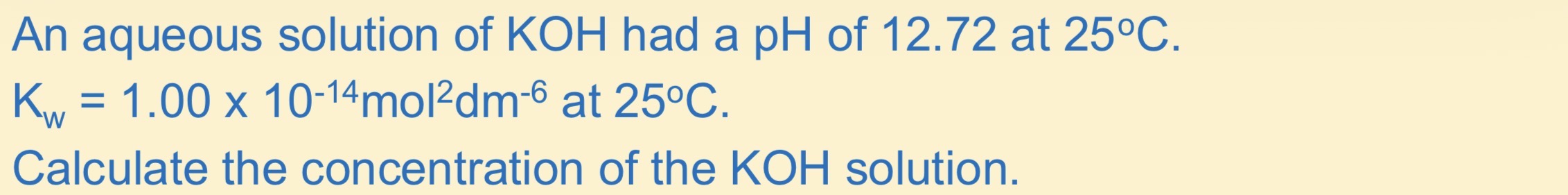
'Answer this question

Why is it harder to work out PH of weak acids then strong acids
As strong acids are fully ionised but weak acids are not fully dissociated so we need a measure of how dissociated they are
Write the Kc equation for weak acids

Rearrange Kc for weak acids to get Ka equation and units of Ka
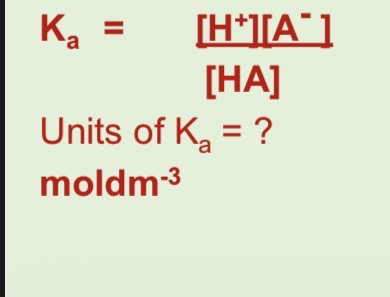
What does Ka stand for
Acid dissociation constant
What makes Ka value bigger
The stronger the acid is the bigger the Ka value
What factor changes the value of Ka
Ka only changes if temperature changes
What is pKa
Another way of showing Ka
How do you work out pKa
PKa = -logKa
What is the trend in Ka vs pKa if an acid is getting stronger
The stronger the acid the larger the Ka value but smaller the pKa value
How to work out Ka from pKa
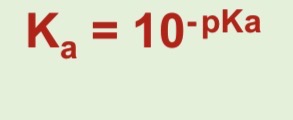
What are the 2 approximations for Ka

How to find Ka of a weak acid from its PH and concentration

How do oceans remove CO2
Marine life photosynthesise
And CO2 dissolves
What are the 3 equilibrium equations for CO2 being removed by the oceans from the atmosphere
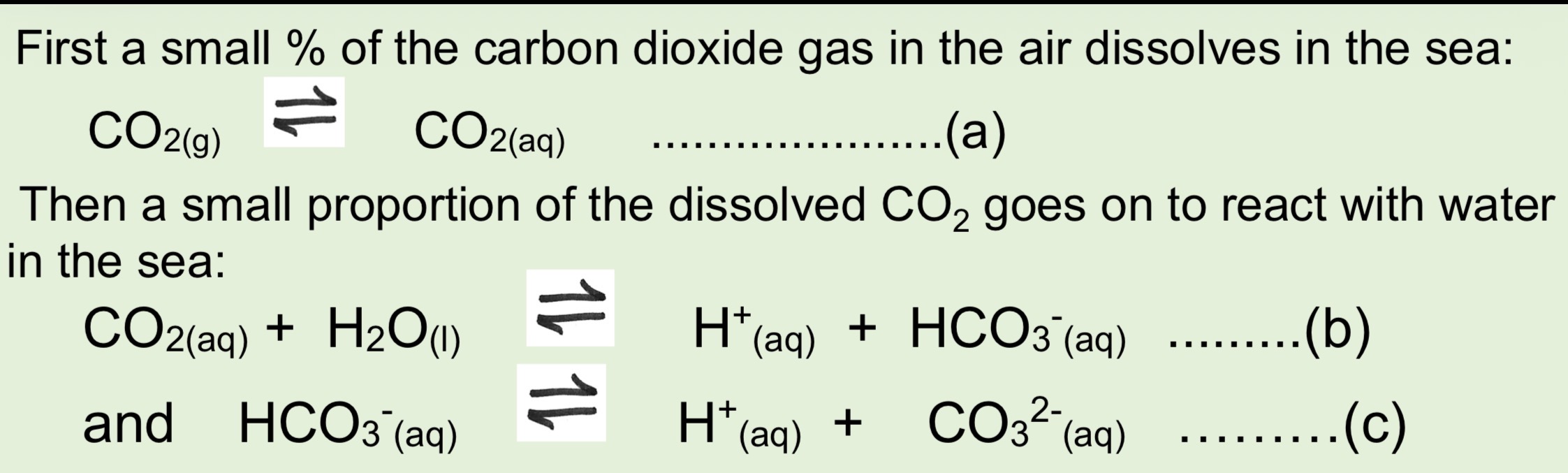
As the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere rises what will happen to concentration of H+ (aq) in the sea

Even with concentration of H+ increasing in ocean why are the oceans not becoming significantly more acidic
When the conc of a weak acid increases, PH does not change as much as it would for a strong acid which means the ocean can act as a buffer
What are the main concerns for the ocean when the concentration of H+ is increasing
Worried about the effects of ocean acidification and warming of sea water on coral reefs ecosystems
Definition of a buffer
a buffer solution is a solution which minimises changes in PH when acid or alkali is added to it in small quantities or when diluted so they maintain an almost constant PH
What are buffers made of

Make the rest of buffers flashcards
How do ionic substances dissolve in water
Many ionic substances dissolve in water, the ions completely separate from each other, each becoming surrounded by water molecules as water molecules are polar and form ion dipole bonds with the ions.
They are said to be hydrated ions and ions can react separately from each other
How do ionic solids dissolve
They dissolve only to a tiny extent as in a saturated solution a dynamic equilibrium exists between dissolved ions and the undissolved solid
Write an equation between saturated solution of silver chloride in contact with un dissolved Silver chloride
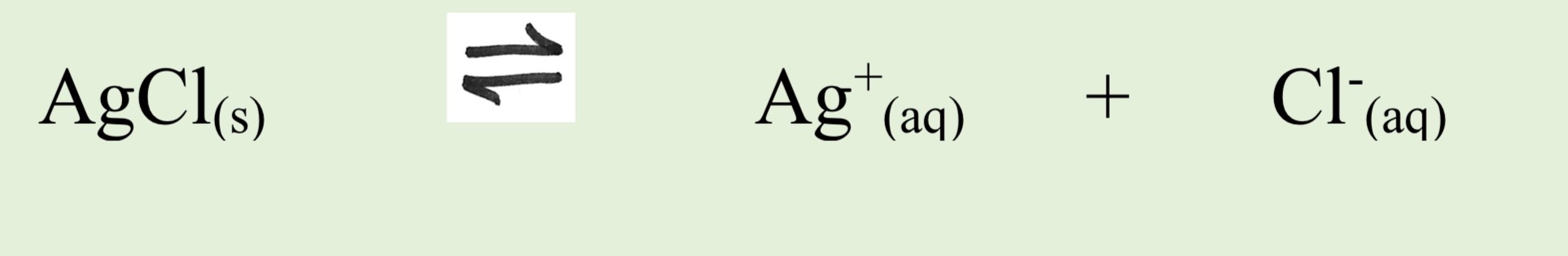
What is solubility product
Ksp =[Ag+ (aq)] [cl- (aq)]
Which always has the same value for a given solution at a given temperature and constant unless temperature changes
Need state symbols for a mark
What does Ksp give
Maximum conc of ions that be in a solution before a ppt forms
How to predict with Ksp if a pot will form

How to work out Ksp when mixing solutions
Work out concentration of each ion by working out the moles then divide by the volume
Calculating solubility product from solubility and vice versa

Common ion effect
Determining solubility products by experiment aim
To make a saturated solution of solid and do a titration to find the concentration of on of the ions it cotains. By knowing its formula the concentration of the other ion can be determined and using both concentrations Ksp can be calculated
Determining solubility products by experiment practical
to ensure solution is saturated excess solid is added to water and the mixture stirred thoroughly so no more solid will dissolve
Before titrating, the solution should be filtered to remove remaining solid- if any solid was remaining during titration when one of the ions reacts more solid would dissolve affecting the results
Accurately measure a volume of solution using a pipettes and put into a conical flask
The conc of standard solution in the titration in the burette should be adjusted so a big enough titre is given to avoid large % errors. It will need diluting using a pipettes and volumetric flask
Usual titration procedure
Why do oil and water not mix
Here ae strong attractive forces of hydrogen on ding between after molecules, holding them together and preventing molecules that cannot form hydrogen bods from mixing
Symbol for entropy
S
Entropy definition
A measure of disorder or of the number of ways of arranging the particles and their associated energy quanta
What has a higher entropy a mixture or separate susatnces
A mixture because there are more ways of arranging particles in a mixture
Which states have highest and lowest entropy and why
Solids have lower because in a solid particles are in a more ordered arrangement , in fixed positions. In a gas the particles are spread out and moving in random directions at different speeds so is much more disordered. So when a liquid boils change in entropy is positive as entropy increased.
Also when molecules get bigger their entropy increases
Do the molecules in a substance have equal entropy
No the molecules in a substance don’t all have equal energy which gives more entropy. Molecules hav electronic, vibrational, rotational and translational energy and these energies ae quantised
What effect does heating a substance have on entropy
Heating increases number of nervy quanta available and increases entropy. Substances with bigger molecules / heavier atoms in their molecules have higher entropies as energy levels are closer together so there are more energy quanta at a given temperature