Uncomplicated Labor and Delivery
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
First Stage of Labor
time between onset of labor and full cervical dilation (10 cm)
Latent phase of First Stage of Labor
effacement and early dilation (<6 cm)
Active phase of First Stage of Labor
RAPID dilation (6-10 cm)
Second Stage of Labor
time between full cervical dilation and delivery of infant
Third Stage of Labor
time between delivery of infant to delivery of placenta (~30 min)
Fourth Stage of Labor
2 hours following delivery of placenta
Average rate of dilation during labor
Roughly 1-2 cm per hour
1st stage of labor: Initial exam
Review prenatal record, determine whether new disorders have developed, eval maternal and fetal status, and confirm pt is in labor
Physical exam during 1st stage of labor
Status of membranes: intact or ruptured
Presence and amount of vaginal bleeding
Cervical dilation and effacement — DO NOT perform digital exam before placenta previa and prenatal rupture of membranes have been excluded
Fetal lie, presentation, position, station
Fetal size and pelvic capacity
Fetal wellbeing
Maternal wellbeing
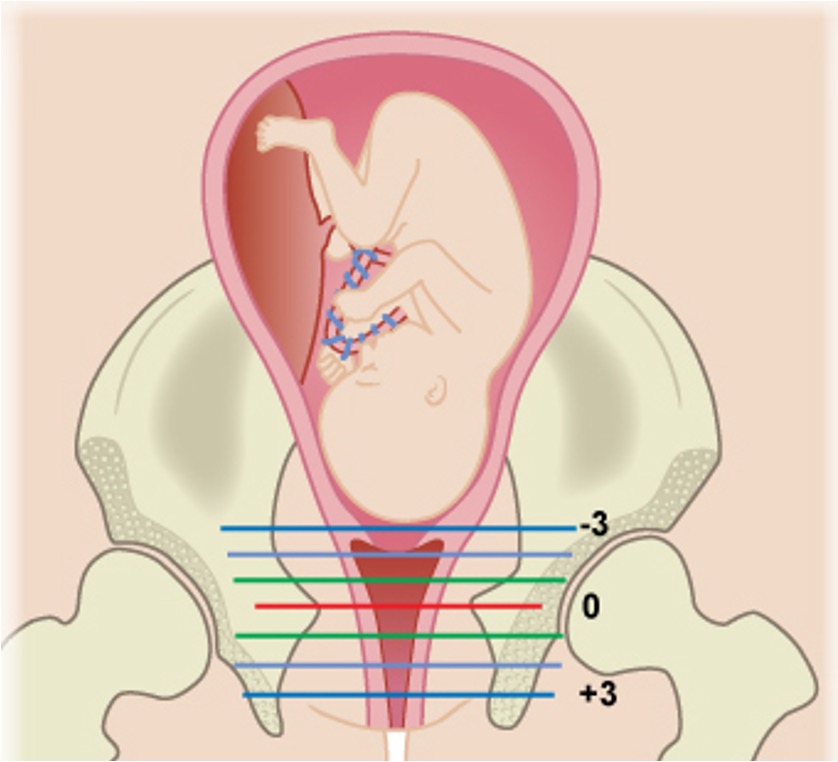
Fetal Station
The number of centimeters of the leading bondy edge of the presenting part
measurement of engagement
Measures in distance from ischial spines
Patient Prep — First stage of labor
oral intake / IV fluids if NPO (heparin lock)
Medication mgmt (routine meds, PCN G for GB strep)
Pain mgmt (pt specific)
Movement (encourage walking)
Position (pt preference)
Amniotomy (risk of cord prolapse)
Monitoring (FHR, contraction, cervical)
Managing — 2nd stage of labor
Monitoring (FHR, vaginal exams)
Pushing (once fully dilated, open glottis) — normal duration is < 3 hrs and < 2 hrs (multiparous)
Perineal protection intrapartum (warm compress, massage, ritgan)
Cardinal Movements
movement of baby through the birth canal
head floating, before engagement
engagement; descent and flexion
further descent, internal rotation
complete extension
restitution, external rotation
delivery of anterior shoulder
expulsion of baby
Most common incision for an episiotomy
Mediolateral incision — preferred because it doesn’t increase risk of anal sphincter laceration
Managing — 3rd stage of labor
Cord severance (delayed cord clamping)
Placental separation precedes expulsion
Active mgmt of expulsion (reduces risk of severe postpartum blood loss and blood transfusion; oxytocin)
Assess uterine contraction post-placental delivery to ensure uterus is contracted (hemorrhage, typical blood loss is <500 mL)
Inspection (placenta, cord, and fetal membranes; should be 3 cord vessels)
Lacerations
Degree — injury to the perineal skin and vaginal epithelium ONLY
Degree — fascia + muscles of perineum
Degree — fascia + muscles + involvement of anal sphincter
Degree — perineal fascia + muscles + external and internal anal sphincters + anal epithelium
Managing — 4th stage of labor
Immediate skin-to-skin contact with mother and initiation of breastfeeding w/in first hour
Maternal monitoring (hourly x 2 hrs, then q4 hours x 24 hours; routine vital signs, fundal checks, perineal checks)
Labor Induction
Initiate labor when benefits of delivery outweigh risks. Elective induction permitted after 39 weeks
Cervical Ripening
Labor Induction — typically started at night so pt can sleep throughout the night.
Misoprostol inserted vaginally prior to induction.
Cervical ripening balloon
Amniotomy
Labor Induction — if cervix is favorable, more effective in conjunction with oxytocin
Oxytocin
Labor Induction — IV oxytocin titrated to induce/augment contractions
Stripping or sweeping of membranes
Labor Induction — inserting finger beyond the internal cervical os and then rotating finger circumferentially along the lower uterine segment to detach the fetal membranes from the decidua
Cesarean Delivery
Operative delivery using abdominal incision to deliver fetus
May be scheduled or following trial of labor/unscheduled
Trial of Labor after Cesarean / Vaginal birth after cesarean
attempt of vaginal birth after prior c-section
Risks of vaginal birth after c-section
uterine rupture
peripartum hysterectomy
increased infection if convert VBAC to c-section
higher perinatal mortality
Benefits of vaginal birth after c-section
potentially avoid surgical risk
quicker recovery
potentially larger family size (repeat c-section increases risk placenta previa)
desire to experienc evaginal birth