Essential Projections - Humerus and Shoulder-complete
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What are 2 humerus projections?
AP
Lateral
How is the patient positioned for AP Humerus?
-Slightly abduct humerus from bodu and supinate hand
What should be perpendicular to IR when positioning patient in AP Humerus projection?
Epicondyles of humerus
What is the CR perpendicular to in AP Humerus?
midpoint of humerus
Image criteria - AP Humerus
- what two joints are seen?
- what is without rotation
- what 2 things are in profile?
- what is seen between the humeral head and greater tubercle
- elboe anf shoulder
- epicondyles
- humeral head and greater tubercle
- lesser tubercle
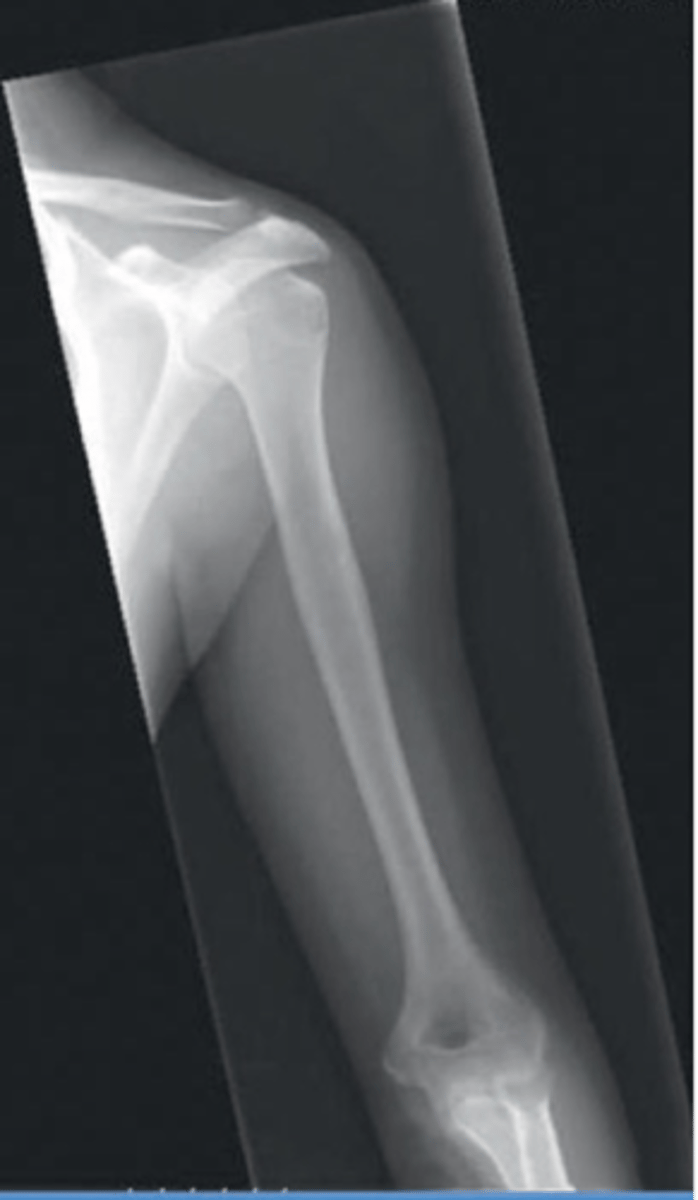
Patient position for Lateral Humerus
flex elbow 90 degrees and rest palm of hand on hip
If possible, internally rotate the humerus (PA)
What is the CR perpendicular to for AP Humerus?
midpoint of humerus
Image criteira - Lateral Humerus
- what joints are seen
- what is superimposed?
- greater tubercle is superimposed over?
- elbow and shoulder
- epicondyles
- humeral head
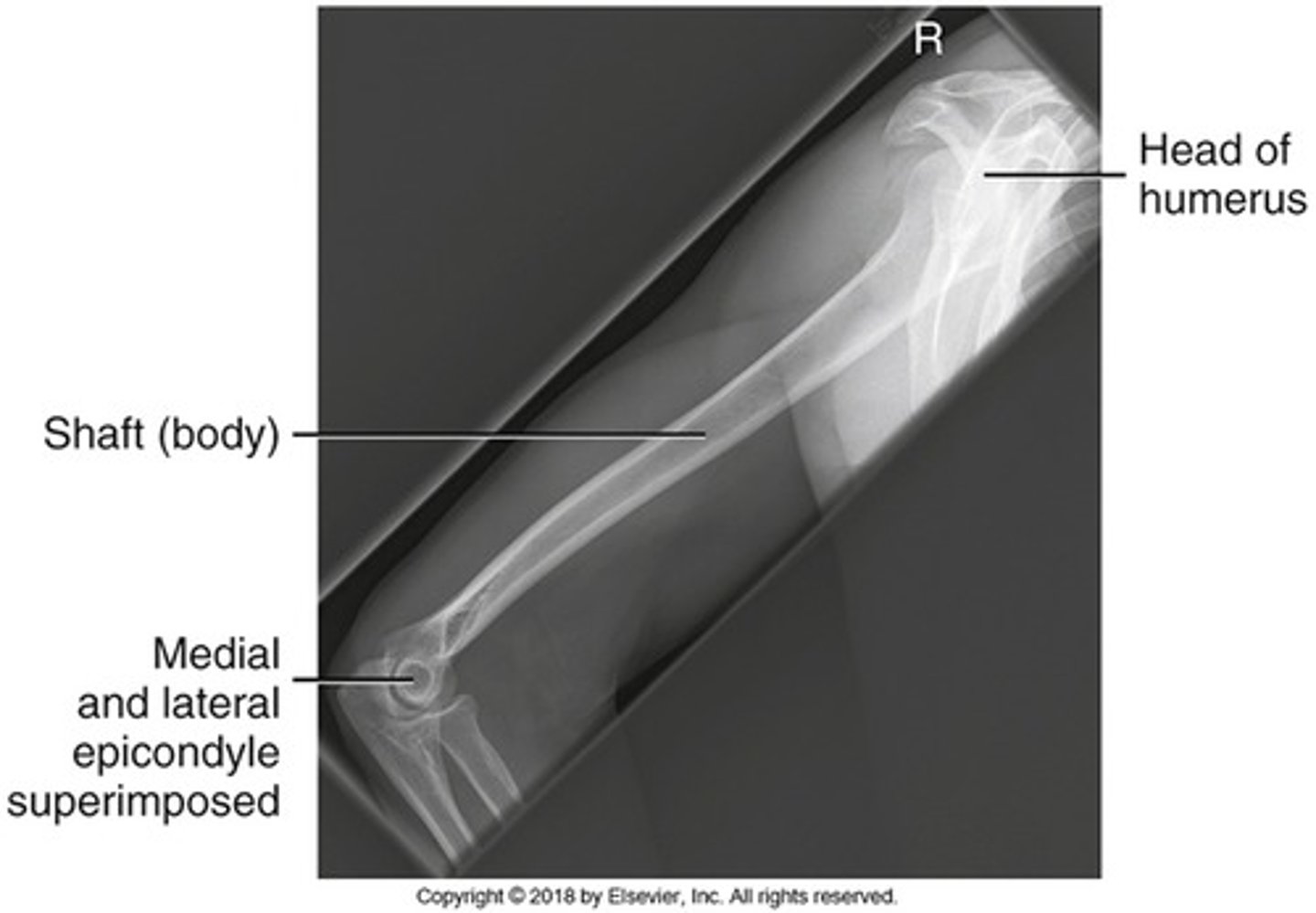
Whata re the 7 shoulder projections?
AP Neutral
AP External rotstion
AP Internal rotation
AP Oblique (Grashey Method)
Transthoracic Lateral
Inferosuperior Acial (Lawrence Method)
PA/AP Oblique (Scapular Y)
How is the patient positioned for AP Internal Rotation ?
- rotate the patient slightly toward affected shoulder
- body of scapula parallel with IR
-rotate the arm internally and rest back of hand on hip
- humeral epicondyles perpendicular to IR
What is the CR perpendicular to in AP Internal roatation ?
1" (2.5cm) inferior to coracoid prcoess
Image criteria - AP internal roation
- what is included in image?
- whats in profile?
- what is superimposing the humerla head?
- collimation includes superior scapula, lateral half of clavicle, and proximal humerus
- lesser tubercle
- greater tubercle
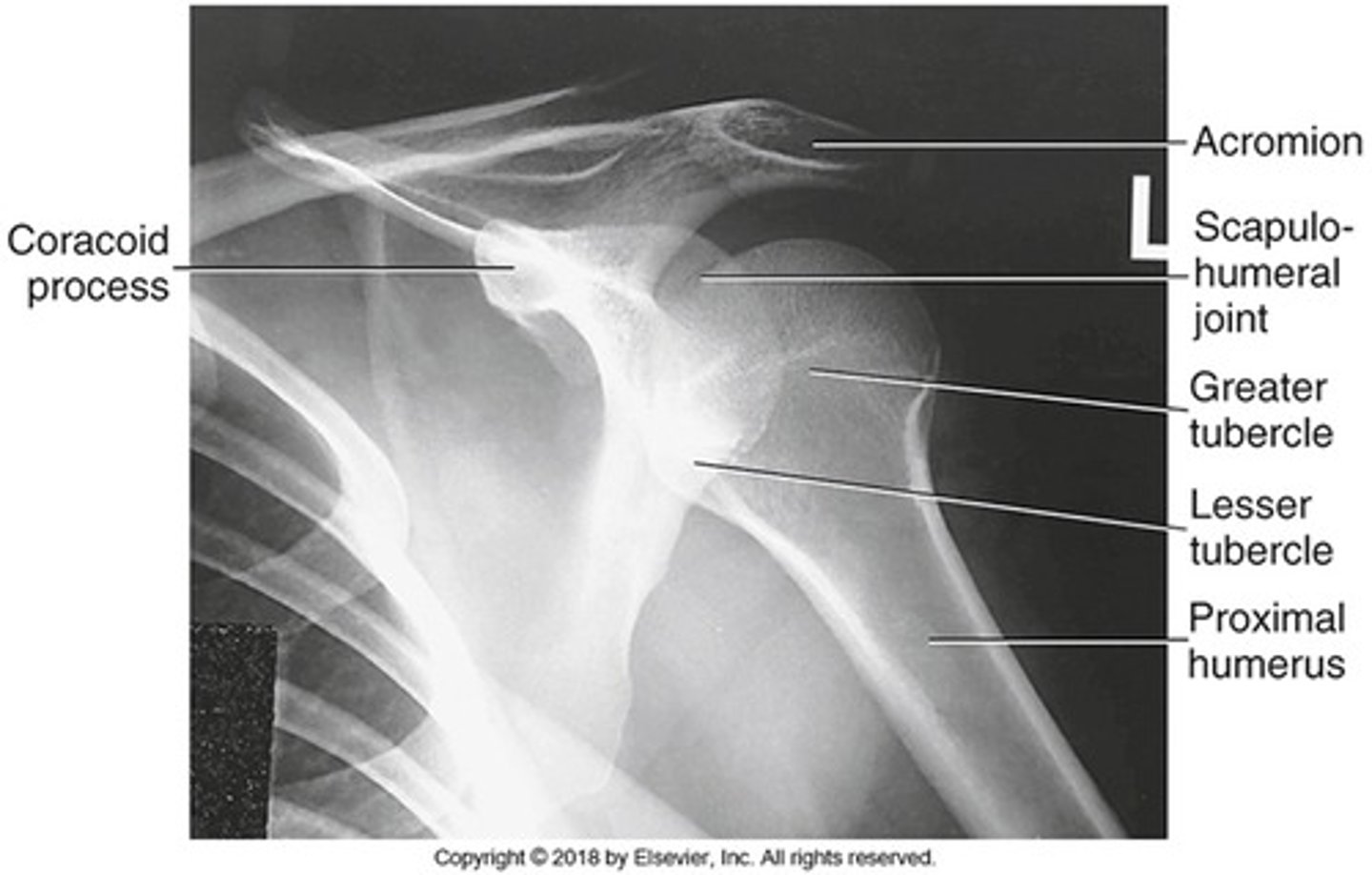
How is the patient positioned for AP External Rotation ?
- rotate the patient slightly toward affected shoulder
- body of scapula parallel with IR
-rotate the arm internally and supinate hand
- humeral epicondyles perpendicular to IR
What is the CR perpendicular to in AP external rotation?
1" (2.5cm) inferior to coracoid prcoess
Image criteria - AP external rotation
- what is included in image?
- what is in profile?
- what is outlined between the humeral head and greater tubercle?
- collimation includes superior scapula, lateral half of clavicle, and proximal humerus
- humeral head and greater tubercle
- lesser tubercule
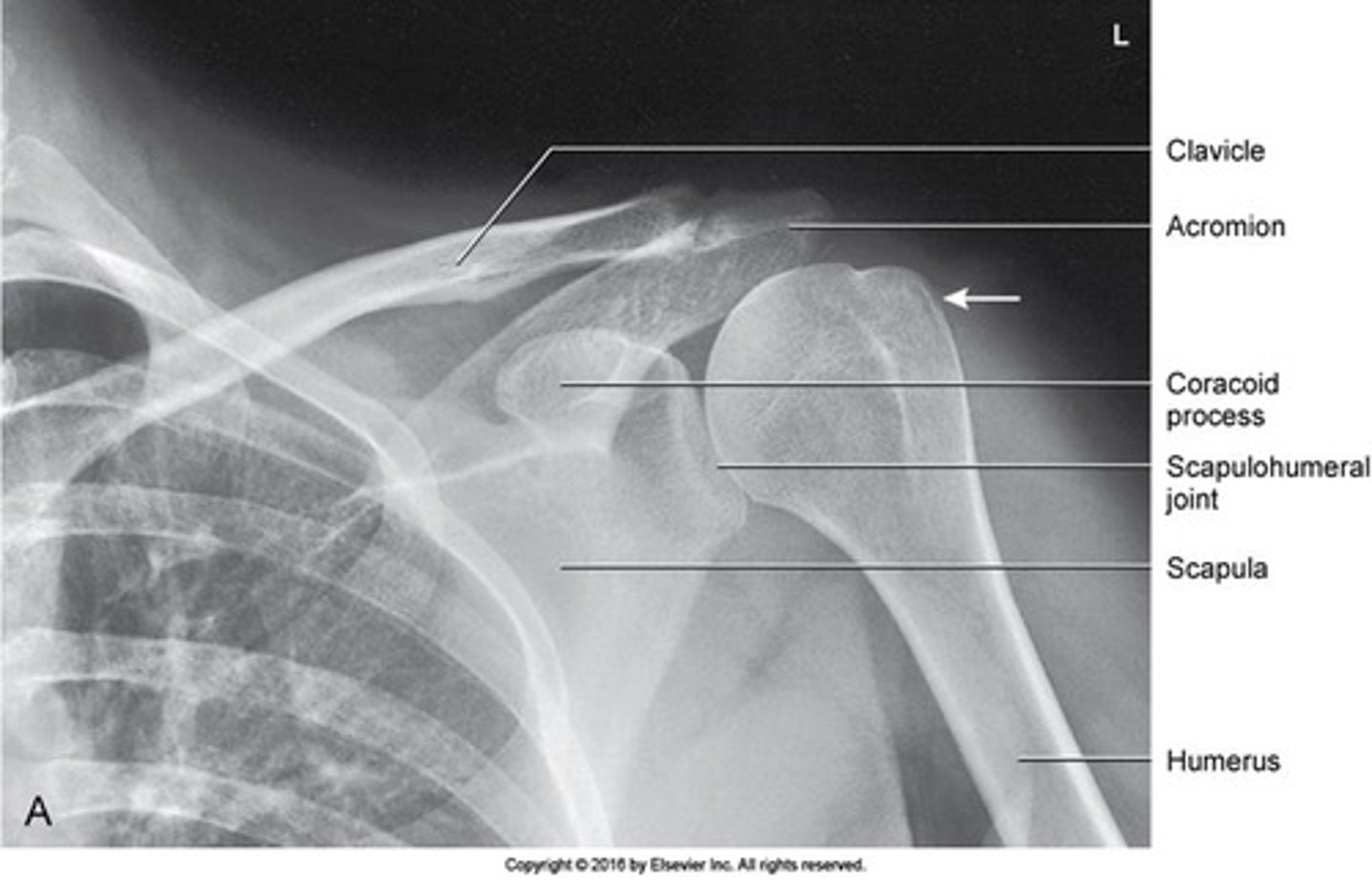
How is the patient positoned for AP Neutral shoulder?
- leave arm in neutral position
- place epicondyles at 45 degree angle to IR
Where is the CR directed for AP Neutral shoulder?
perpencidular 1" inferior to coracoid process
Image criteria - AP Neutral Shoulder
- what is partially superimposed by humeral head?
- whats in partial profile?
- what is included in image?
- greater tubercle
- humeral head
- superior scapula, lateral half of clavicle,a nd proximal humerus
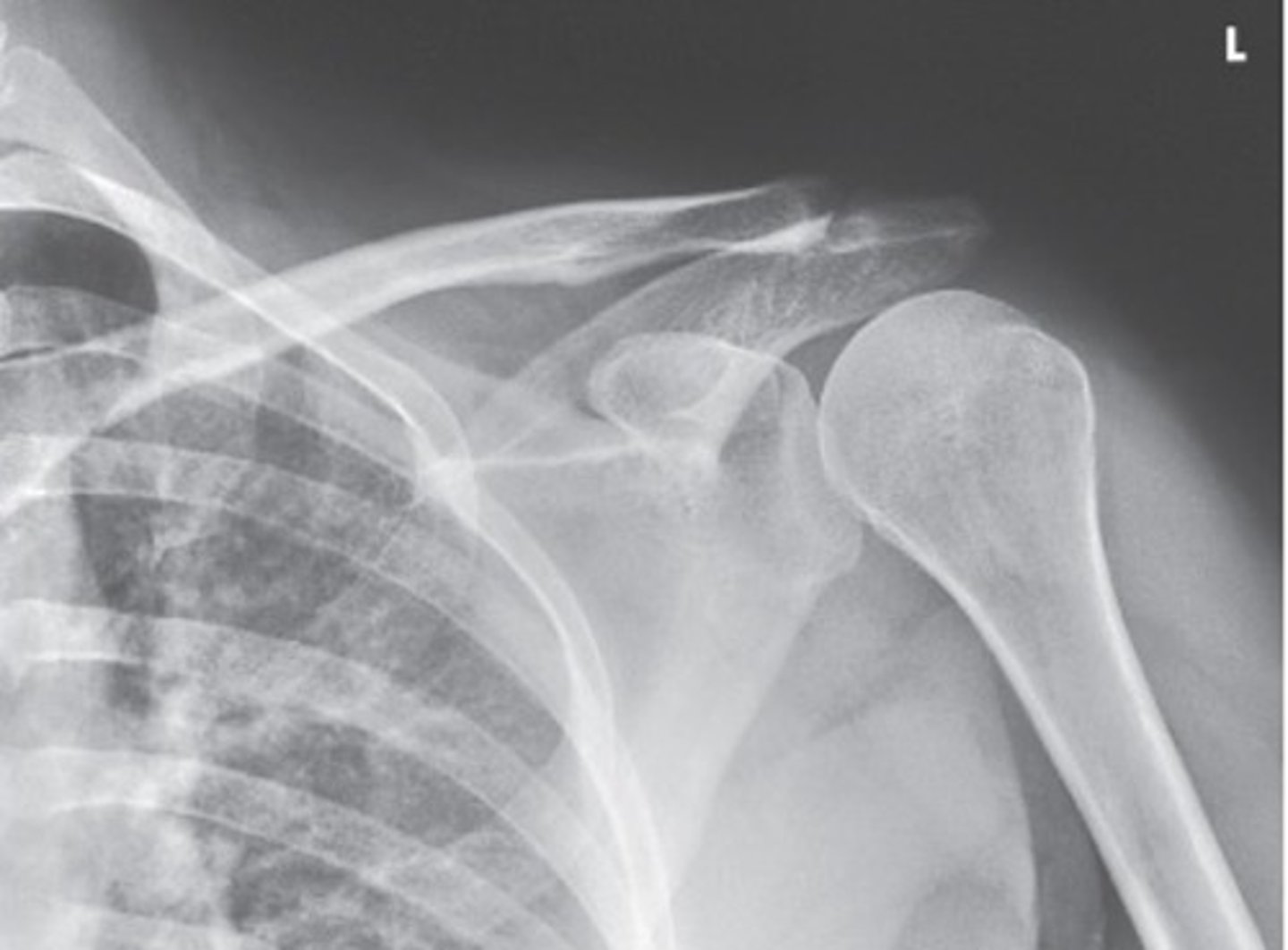
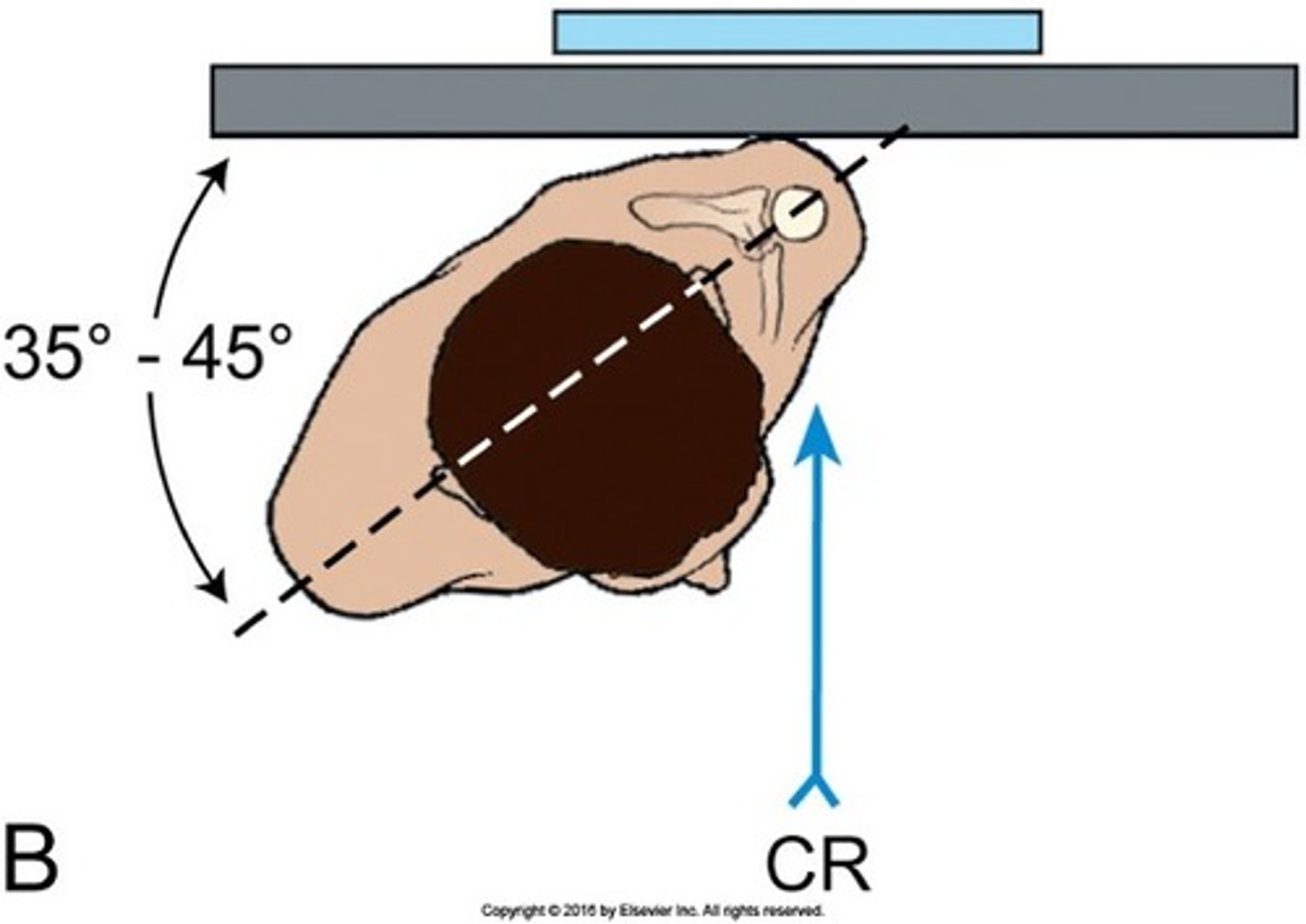
How is the patient positioned for AP Oblique (Grashey)?
- what degree is the patient rotated?
- what shoulder is closes to IR?
- When is more rotation necessary?
- rotation should place what parallel to IR?
- 35-45 degress posterior oblique position
- affected
- patient is recumbent
- scapula
What is the CR perpendicular to in AP Grashey?
glenoid cavity
enters 2" (5cm) medial and inferior to superolateral border of shoulder
Image criteria - AP Grashey
- what joint space is open?
-whats in profile?
- humeral head and glenoid cavity
- glenoid cavity
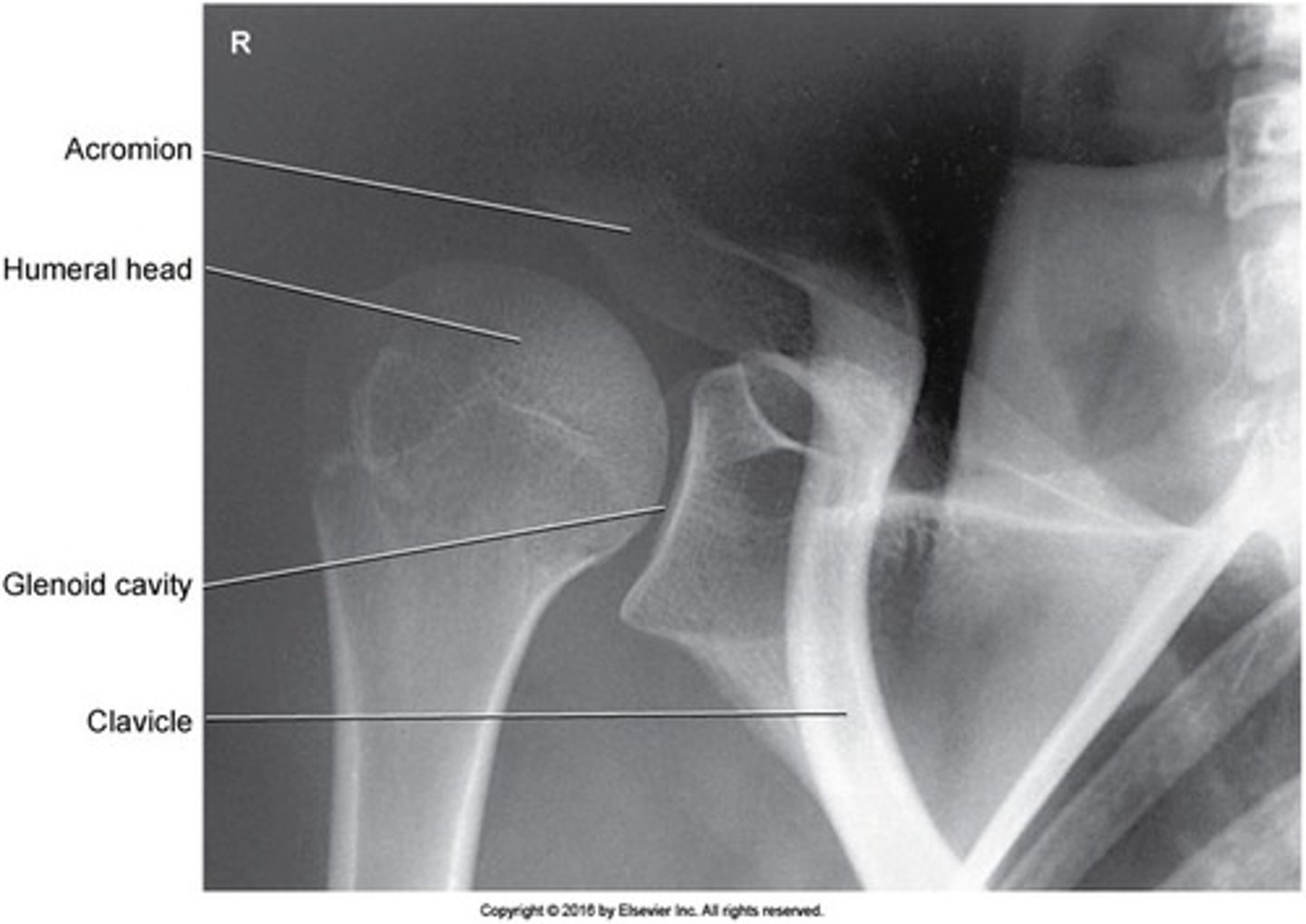
When is a trabsthoracic projection used?
for trauma patients who cannot rotate or abduct the arm
How is the patient positioned for Transthoracic Lateral (Lawrence)
- supine or upright lateral
- affected limb closes to IR
- Unaffected limb elevated over head
WHat is the CR perpendicular to for Transthoracic Lateral?
enters the midcoronal plane at the surgical neck.
If the shoulders are in the same plane for Transthoracic Lateral, where is the CR angled?
10-15 degrees, cephalad
Image Criteria- Transthoracic Lateral (Lawrence)
- what is seen throufh the lung field?
- scapula is superimposed over ?
- unaffected clavicle and humerus is projected above the?
- scapula, clavicle, and humerus
- thoracic spine
- the shoudler closest to the IR
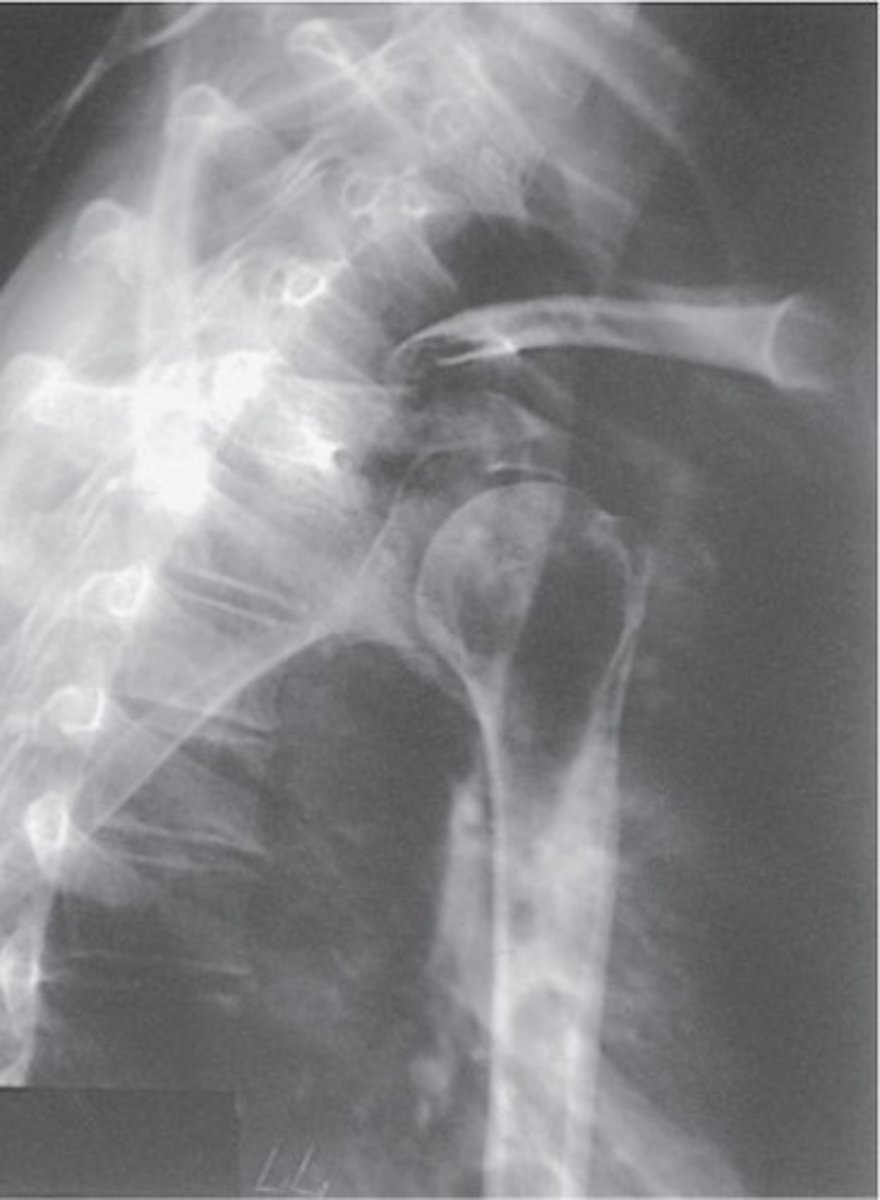
How is the patient positoned for Inferiorsuperior Axial projection (Lawrence Method)
- supine
- head and shoulders elevated on a 3" radiolucent sponge
- head turned away from CR
-abduct arm to right angle and place arm in a lateral rotation
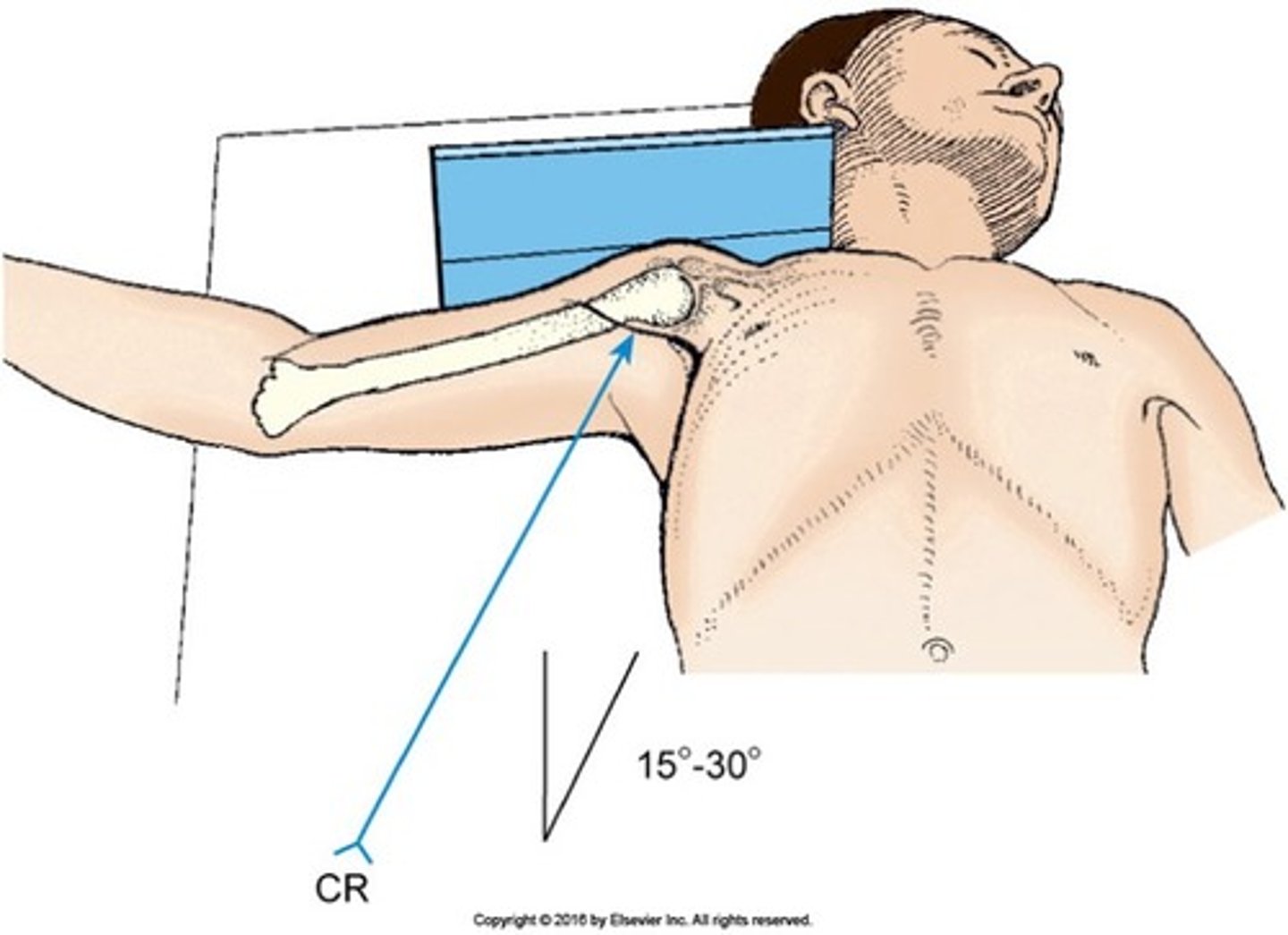
How is the CR directed for Inferosuperior Axial Shoulder?
- beam is perpendicular or horizontal?
- medial angulation of?
- entera and passes though?
- angle will depend on?
- more abduction = ?
- Horizontal
- 15-30 degrees towards shoulder
- axilla, AC joint
- abduction of humerus
- greater angle
Image criteria - Inferosuperior Axial Projection shoulder?
- what joint is slight overlap?
- whats pointing anteriorly?
- whats in profile and what direction?
- what is projected through the humeral head?
- scapulohumeral joint
- coracoid process
- lesser tubercle, anteriorly
- AC joint, acromion and acromial end of clavicle
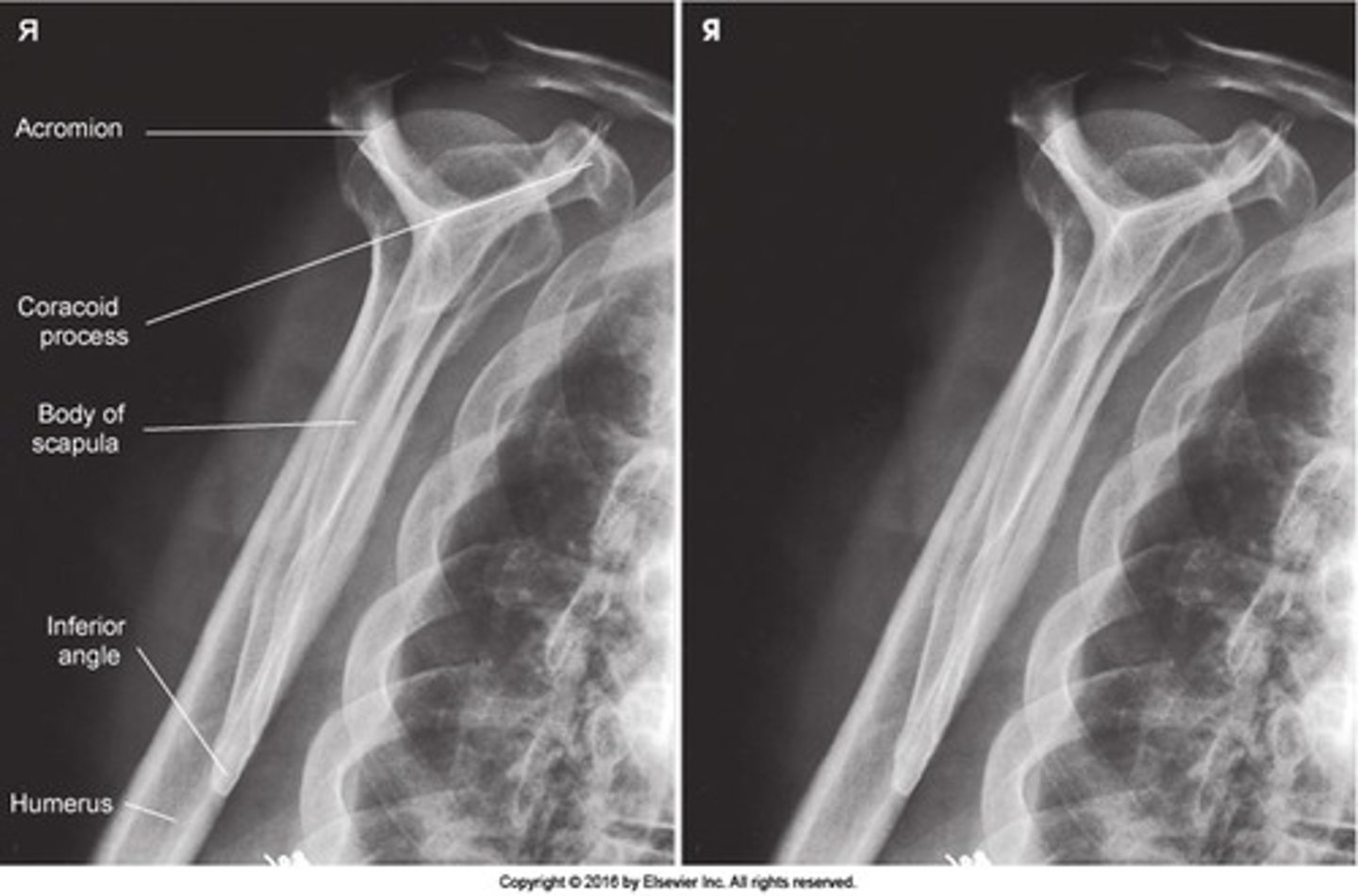
If the patient is properly position for PA Scapular Y what forms the Y?
acromion and coracoid over humerla head
What is the scapular Y used to diagnose?
dislocation
What degree is the patient positoned for PA Scapular y ?
45-60 degree
How is the CR directed for PA scapular y?
perpendicular to scapular humeral joint
Image criteria- Scapular Y
- what is projected laterally and free of superimposition
- what is possibly superimposed or projected below the clavicle?
- what part of the scapula are superimosed?
- acromion
- coracoid
- lateral and verterbral borders