chapter 37 management of pts with musculoskeletal trauma
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Injuries of the musculoskeletal system ***
contusion: soft tissue injury produced by blunt force
pain swelling and discoloration: ecchymosis
strain: pulled muscle injury to the musculotendinous unit
pain, edema, muscle spasm, ecchymosis, and loss of function are on a continuum graded first, second and third degree
Sprain: injury to ligaments and supporting muscle fiber around a joint
pain (may increase with motion) edema, tenderness, severity graded according to ligament damage and joint stability
dislocation: articular surfaces of the joint are not in contact
a traumatic dislocation is an emergency with pain change in contour, axis, and length of the lib of mobility
subluxation: partial or incomplete dislocation
does not cause as much deformity as a complete dislocation
management of soft tissue injuries ***
RICE
rest
ice
compression
elevation
immobilize
types of fractures 1
closed or simple
no break in the skin
wound extends to the bone
grade I: 1 cm long clen wound
Grade II: larger wound without extensive damage
Grade III: highly contaminated, extensive soft tissue injury, may have amputation
intra- articular
extends into the joint surface of a bone
manifestations of fracture
acute pain
loss of function
deformity
shortening of the extremity
crepitus
local swelling and discoloration
diagnosis by symptoms and radiography
patients usually reports an injury to the area
emergency management
immobilize the body part
splinting: joints distal and proximal to the suspected fracture site must be supported and immobilized
assess neurovascular status before and after splinting
open fracture: cover with sterile dressing to prevent contamination
do not attempt to reduce the fracture
surgeons or paramedics reduce the fracture
medical management of fracture
fracture reduction: restoration of the fracture fragments to anatomic alignment and positioning
closed
uses manipulation and manual traction
traction may be used (skin or skeletal)
open
internal fixation devices hold bone fragment in position (metallic pins, wires, screws, plates)
immobilization
external (cast, splints) or internal fixations
factors that affect fracture healing
inadequate fracture immobilization
inadequate blood supply to the fracture site or adjacent tissue
multiple trauma
extensive bone loss
infection
poor adherence to prescribed restrictions
malignancy - cancer that metastasized to bone
certain medications (corticosteroids)
age >40 yrs
comorbidities ( diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis)
lack of care someone not going to the ER in high poverty areas
complications of fractures
early complications
shock severe fracture
fat embolism
compartment syndrome
VTE, PE
delayed complications
delayed union, malunion, nonunion
avascular necrosis of bone
complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS)
heterotrophic ossification
rehabilitation related to specific fractures ** ( CLAVICLE)
clavicle
use of clavicular strap or sling
exercises for elbow, wrist fingers asap
do not elevate arm above for 6 weeks
humeral neck and shaft fractures
slings and bracing
activity limitations until adequate period of immobilization
rehabilitation related to specific fractures #2 ** (ELBOW)
elbow fractures
monitor regularly for neurovascular compromise and signs of compartment syndrome
potential for Volkmann contracture
active exercises and ROM are encouraged to prevent limitation of joint movement after immobilization and healing (4-6 weeks for nondisplaced casted) or after internal fixation (about 1 week)
radial, ulnar, wrist and hand fractures
early functional rehabilitation exercises
active motion exercises of fingers and shoulders
rehabilitation related to specific fractures #3 (PELVIC)
pelvic fractures
management depends on type and extent of fracture and associated injuries
stable fractures are treated with a few days of bed rest and symptom management
early mobilization reduces problems related to immobility
hip fractures
surgery is usually done to reduce and fixate the fracture
care is similar to that of a patient undergoing other orthopedic surgery or hip replacement surgery
rehabilitation r/t specific fractures #4 (femoral shaft)
femoral shaft fractures
lower leg, foot, and hip exercises to preserve muscle function and improve circulation
early ambulation stimulates healing
physical therapy, ambulation and weight bearing are prescribed
active and passive knee exercises are begun as soon as possible to prevent restriction of knee movement
assessment of the pt with a brace, splint or cast #1 **
Before application
general health assessment
emotional status
presenting signs and symptoms and condition of the area
monitoring of neurovascular status and for potential complications
treat lacerations and abrasions before cast, brace, splint
provide information about the purpose of treatment
prepare patient for application by explaining procedure
know when to use a brace v splint
assessment with brace, splint or cast #2
assessing for neurovascular changes using 5 Ps
pain
pallor
pulselessness
paresthesia
paralysis
monitoring and treating pain
describe exact site, character and intensity of pain
treat with elevation, ice packs, and analgesics
once they have one of the devices put on know pts at risk for using a brace splint or cast
potential complications of the patient with a brace splint or cast #1
acute compartment syndrome
serious complication occurs from increased pressure in a confined space
compromised blood flow
ischemia and irreversible damage can occur within hours
clinical assessment of 5 Ps is the early indicator
treatment: notify physician cast may be removed and emergent surgical fasciotomy may be necessary
potential complications of the pts with a brace, splint or cast #2
pressure injuries: caused by inappropriately applied cast
lower extremity sites most susceptible
patient reports painful “hotspot” and tightness
Dx: may cut window in the cast for inspection and access
treatment: dressing applied over exposed skin
disuse syndrome: muscle atrophy and loss of strength (frozen shoulder)
treatment: isometric exercises, muscle setting exercises
education needs of the pt with a cast, brace or splint #1
what they need to do to care for themselves
impact of injury to physiologic functioning (ADL, IADL)
activity exercise rest
medications
techniques for cast drying
controlling of swelling and pain
care of minor skin irritation
pad rough edges with tape or moleskin
blow with the hair dryer to relieve itching
do not stick foreign objects into the cast
education needs of the pt with a cast, brace, or splint #2
s&s
signs and symptoms to report:
persistent pain or swelling
changes in sensation, movement, skin color, or temperature
signs of infection or pressure areas
required follow up care
required follow up care
cast removal and after care
external fixator device
if someone has pins or rods understand pin care and how to clean it
used to manage open fractures with soft tissue damage
provide support for complicated or comminuted fractures
patient requires reassurance because of appearance of device
discomfort is usually minimal, and early mobility may be anticipated with these devices
elevate to reduce edema
monitor for signs and symptoms of complications, including infection
pin care
patient education
traction 1
the application of pulling force to a part of the body
purposes
reduce muscle spasms
reduce align and immobilize fractures
reduce deformity
increase space between opposing forces
used as a short term intervention until other modalities are possible
application of weights that cause a pulling force on certain part of the body
use it for a pt having severe muscle spasms, if someone is paraplegic,
types of traction
skin traction
bucks extension traction
skeletal traction
thomas leg splint
traction #2
all traction to be applied in two directions
the lines of pull are “vectors of force” the result of the pulling force is between the two lines of the vectors of force
applied in 2 directions
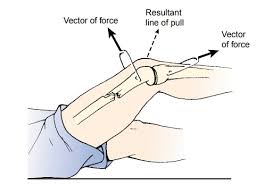
principles of effective traction
whenever traction is applied, a counterforce must be applied. frequently the patients body weight and positioning in bed supply the counterforce
traction must be continuous to reduce and immobilize fractures
skeletal traction is never interrupted
weights are not removed unless intermittent traction is prescribed
any factor that reduces pull must be eliminated
ropes must be unobstructed and weights must hang freely
knots or the footplate must not touch the foot of the bed
suspension skeletal traction with Thomas leg splint
combination of bucks traction and skeletal
bucks most common one point of pulling
complicated leg up moving verything at same time
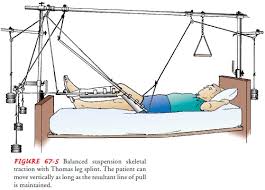
nursing interventions for the patient in skin traction #1
proper application and maintenance of traction
monitor for complications of breakdown, nerve damage and circulatory impairment
inspect skin at least three times a day
palpate traction tapes to assess for tenderness
assess sensation and movement
assess pulses, color, capillary refill, and temperature of finger or toes
assess for indicators of DVT
assess for indicators of infection
nursing interventions for the pt in skeletal traction #2
evaluate traction apparatus and patient position
maintain alignment of body
report pain promptly
trapeze to help with movement
assess pressure points in skin at least every 8 hours
regular shifting of position
special mattresses or other pressure reduction devices
perform active foot exercises and leg exercises every hour
nursing interventions for the patient in skeletal traction #2
anti-embolism sticking’s, compression devices or anticoagulant therapy may be prescribed
pin care
exercises to maintain muscle tone and strength
nursing management of patients in traction
assessing anxiety
assisting with selfcare
monitor and manage complications
atelectasis and pneumonia
constipation
anorexia
urinary stasis
infection
VTE
assessment of the patient with fracture of the hip *
health hx and presence of concomitant problems
pain
vs, respiratory status, LOC, and signs and symptoms of shock
affected extremity including frequent neurovascular assessment
bowel and bladder elimination, bowel sounds I&O
skin condition
anxiety and coping
collaborative problems and potential complications for the pt with a hip fracture *
hemorrhage
peripheral neurovascular dysfunction
skin breakdown
loss of bladder control
delayed: infection, nonunion (fracture that fails to heal), AVN (avascular necrosis, bone tissue dies)
planning and goals for the patient with fractured hip *
relief of pain
achievement of pain free functional and stable hip
healed wound
maintenance of normal urinary elimination pattern
use of effective coping mechanisms
remains oriented and participates indecision making
absence of complications
common sports related injuries
fracture: clavicle, wrist, ankle, metatarsal stress
dislocations: shoulder and elbow
sprains: wrist ankle
knee: sprain, strain and meniscal tears
prevention of sports related injuries
use of proper equipment, running shoes for runners, wrist guards for skaters and so on
effective training and conditioning specific for the person and the sport
stretching
hydration
proper nutrition
occupation related injuries
nursing ranked top 10 occupations most involved
common injuries include
strains, sprains, tears
cuts, lacerations, contusions, bruises
prevention measures may include
safe patient handling training and proper use of equipment
correct use of body mechanics
amputation
may be congenital or traumatic or caused by conditions such as progressive peripheral vascular disease, infection, malignant tumor, trauma
performed to control pain or disease process, improve function, and improve quality of life
health care team needs to communicate a positive attitude to facilitate patient acceptance and participation in rehabilitation
assessment of the patient with an amputation
neurovascular and functional status of affected extremity or residual limb and of unaffected extremity
signs and symptoms of infection
nutritional status - foods to promote healing
concurrent health problems psychological status, grief and coping
collaborative problems and potential complications of the patient with an amputation
postoperative hemorrhage
infection
skin breakdown
phantom limb pain
joint contracture
planning and goals for the patient with an amputation
major goals:
relief of pain
wound healing
acceptance of altered body image
resolution of grieving process
independence in self care
restoration of physical mobility
absence of complications
nursing interventions for the patient with an amputation #1 (pain)
relieving pain
administer analgesic or other medications as prescribed
changing position
putting a light sandbag on residual limb
alternative methods of pain relief: distraction, TENS unit
Promoting wound healing
handle limb gently
residual limb shaping
nursing intervention for the patient with an amputation #2 (resolving grief)
resolving grief and enhancing body image
encourage expression of feelings
create an accepting supportive atmosphere
provide support and listen
encourage patient to look at feel and care for the residual limb
help patient resume self care and independence
referral to counselors and support groups
nursing interventions for the patient with an amputation #3 ( self care)
promoting self care
encourage active participation in care
continue support in rehabilitation facility or at home
focus on safety and mobility
nursing intervention for the pt with amputation #4 ( physical mobility)
assisting the patient to achieve physical mobility
proper positioning of limb, avoid abduction, external rotation and flexion
turn frequently, prone positioning if possible
use of assistive device
ROM exercises
muscle strengthening exercises
prepprosthetic care - proper bandaging massage and toughening of the residual limb