DNA typing
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
SNPs vs STR vs VNTR
SNPs
SNPs is a — nucleotide difference between DNA sequences
used as a marker for — genes, human ID and — analysis
detected by: sequencing, — and melt curve analysis
STRs
aka: —satelites
— sequence repeated all over the chromosome
each individual will have a different — (number of repeats, not the repeat itself)
short array: — - — bp
detected by: — with an — ladder, — PCR to detect — loci
VNTRs
aka —satelites
— repeats compared to STRs
— - — bp
detected by: — blot with single or multi loci probe
results in — bands which can make DNA fingerprinting
can use either — electrophoresis (—) or gel electrophoresis (—)
single, mapping, chimerism, microarrays, micro, short, length, 1-7, PCR, allelic, multiplex, multiple, mini, longer, 8-100, southern, 2, capillary, peaks, bands
All three polymorphisms (—, —, —) can cause — (= restriction fragment altered by changes in or between enzyme recognition site)
SNPs causing RFLP
determined by the change in — and —
affected by an insertion or deletion of a — enzyme
VNTRs causing RFLP
restriction site will be the —, the number of units — the site changes
change in —
SNPs, STRs, VNTRs, RFLP, size, number, restriction, same, within, length
amelogenin locus
the different loci polymorphism (— sequence variation) differentiate between — and —
used for — identification
amelogenin is the most common — - determining marker used in forensic DNA analysis
this is — an —
natural, male, female, gender, sex, not, STR
DNA based identity tests
to ID for their — loci (DNA regions) that are — to create a profile (DNA —)
there is a — chance that another person has the — loci/profile
types of tests
— blot with — probe loci
— blot with — locus
—
— - PCR
two samples are considered different (—) if there is — locus that does not match
positive identification is — and requires testing of — loci plus statistical calculations
— match probability
the power of discrimination— with the number of loci profiled
specific, unique, fingerprinting, small, same, southern, multi, southern, single, RFLP, STR, exclusion, one, harder, multiple, random, increases
DNA based paternity test
to find out if two or more people are — related
in this test, people will have — profiles but not the — profile
used for chain of —
useful polymorphic loci to analyze for DNA based parentage testing:
have a high degree of —
low rates of — or instability
confer no — advantage
be inherited co- —
testing:
southern blot with — probes
— or — amplified by —
biologically, similar, same, custody, heterozygosity, recombination, selective, dominant, specific, STR, VNTR, PCR
— — —: the allele that the child has that does not match the mothers
child will have — bands, one from — and the other from —
—: when alleged father does not have the obligate paternal allele with the child at — or more loci
—: alleged father shares all obligate paternal allele with child and probability value of at least 99.99%
obligate paternal allele, 2, mom, dad, exclusion, 3, inclusion
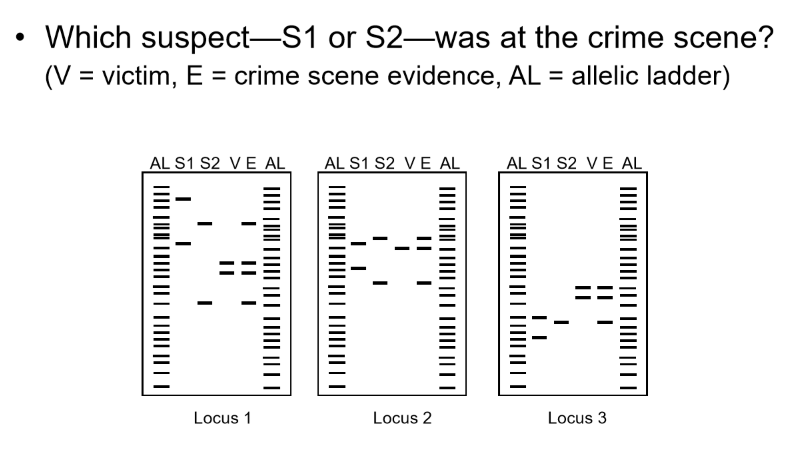
Locus 1: suspect — is the perpetrator
Locus 2: suspect — is the perpetrator
Locus 3: suspect — — be identified because — mismatch allele is enough to exclude the suspect out
2, 2, can not, 1
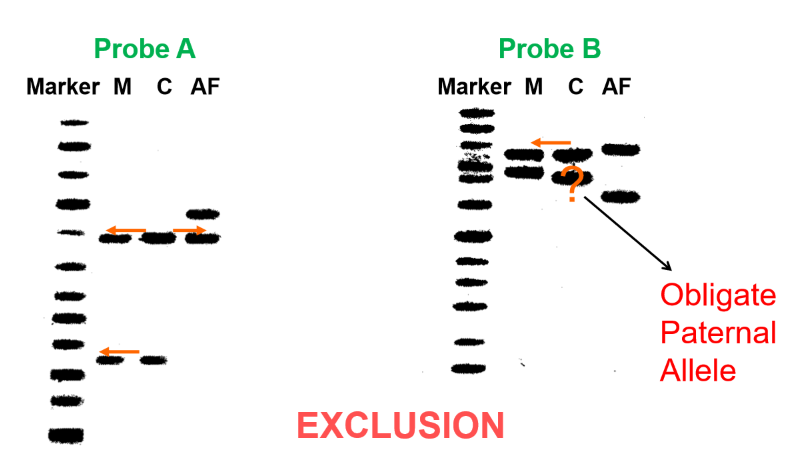
southern blot with single probe locus
Probe A: mother matches with the — band, father matches with the — band = alleged father — the father
Probe B: the mother matches the — band, alleged father — — match any of the childs bands = alleged father in — the father (—)
bottom, top, is, top, does not, not, exclusion
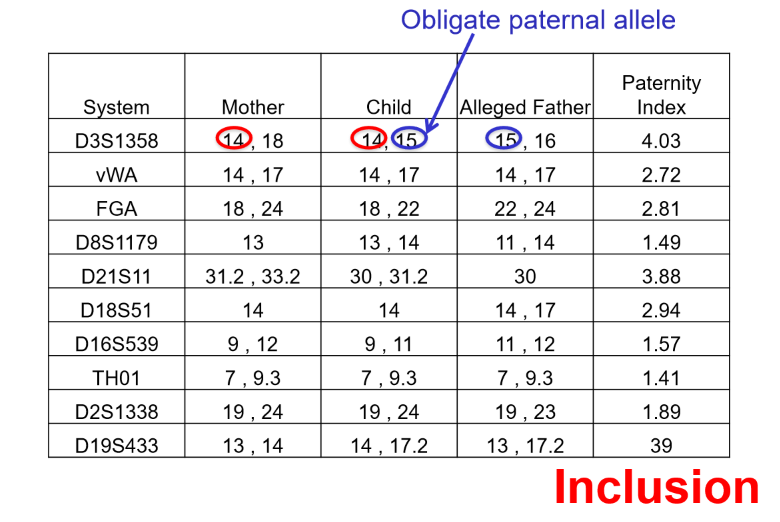
if all obligate paternal alleles are shared between the child and alleged father = the father — the child’s father
this is an example of —
is, inclusion
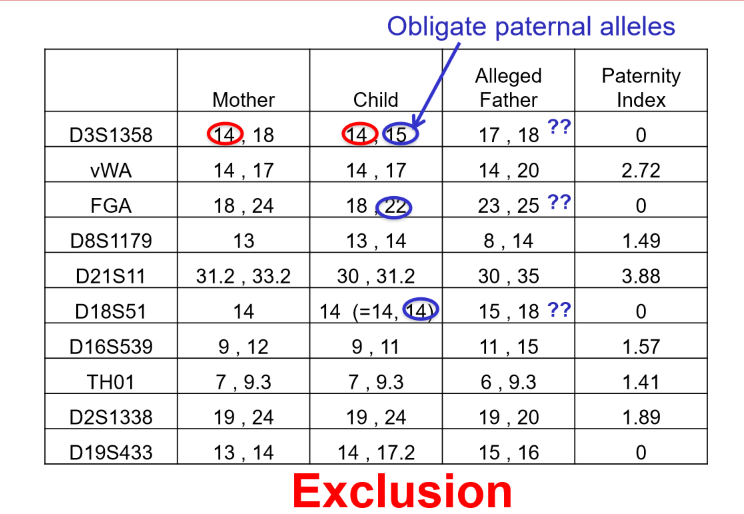
this is an example if — because there are — or more — that do not match the alleged father
exclusion, 3, loci