Week 4: Biomedical Sciences (Funk)
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What A1c values correspond to normal, pre-diabetes, and diabetes?
Normal: <5.7%
Pre-diabetes: 5.7-6.4%
Diabetes: ≥6.5%
Besides A1c, what fasting glucose range indicates impaired glucose tolerance consistent with pre-diabetes?
Fasting blood glucose 100-124 mg/dL
What patient factors are considered in the ADA risk test for type 2 diabetes?
Age, sex, history of gestational diabetes, family history of diabetes, blood pressure, activity level, and weight
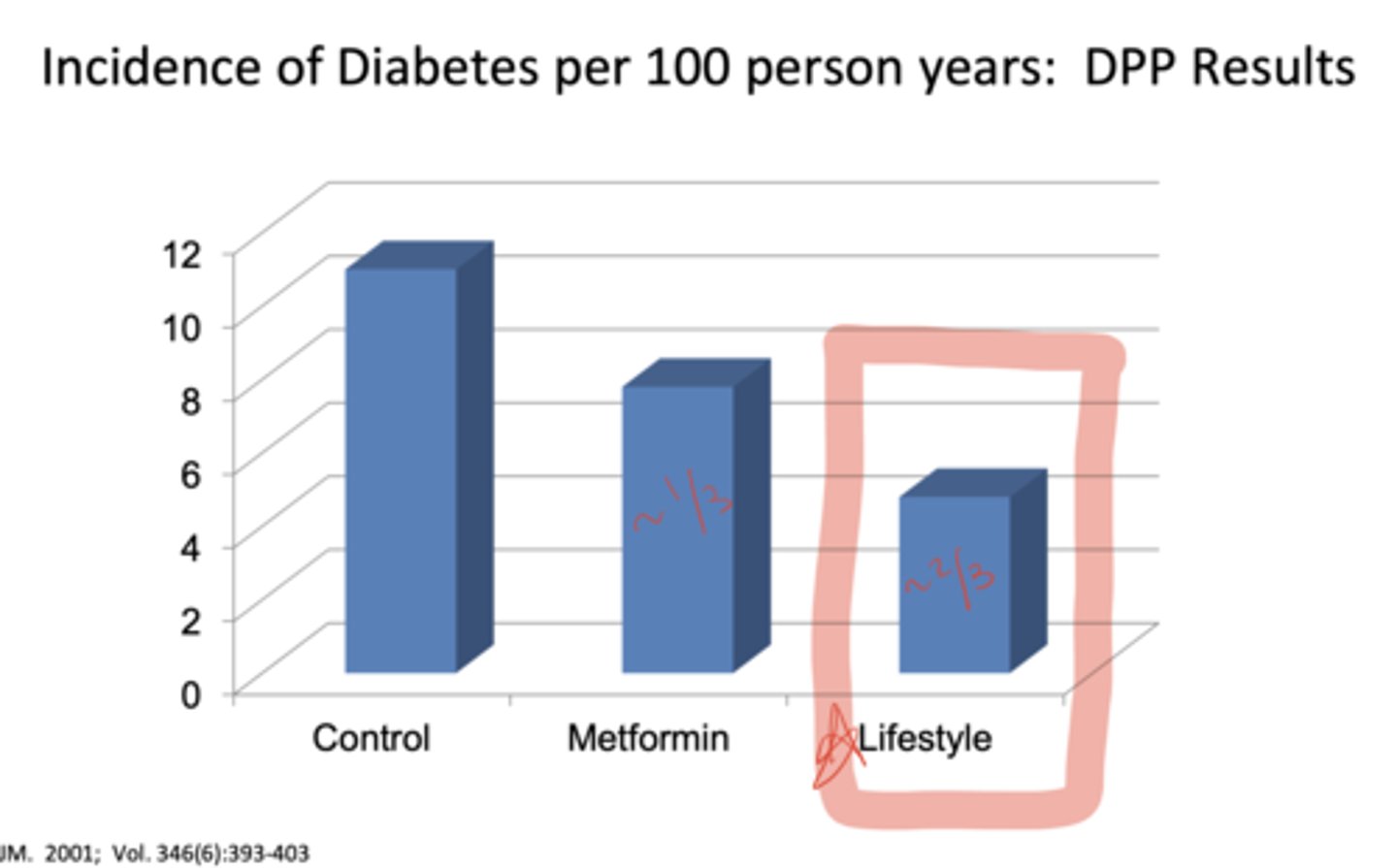
What was the purpose of the Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP) trial?
To determine whether modest weight loss through diet and exercise, or treatment with metformin, could prevent or delay type 2 diabetes in overweight patients with pre-diabetes
How were patients randomized in the DPP study?
Into three groups: (1) placebo twice daily, (2) metformin 850 mg twice daily, or (3) intensive lifestyle intervention (diet + 150 min/week exercise aiming for 7% weight loss)
What were the results of the DPP trial in terms of diabetes risk reduction?
Lifestyle: reduced risk by 58% (≈ two-thirds)
Metformin: reduced risk by 31% (≈ one-third)
Placebo: highest incidence
According to ADA 2025, what are the A-level recommendations for pre-diabetes management?A:
Achieve and maintain ≥7% weight loss with reduced calorie diet
≥150 minutes/week of moderate-intense physical activity
Consider metformin for prevention of type 2 diabetes, especially in younger patients, higher BMI, or prior gestational diabetes
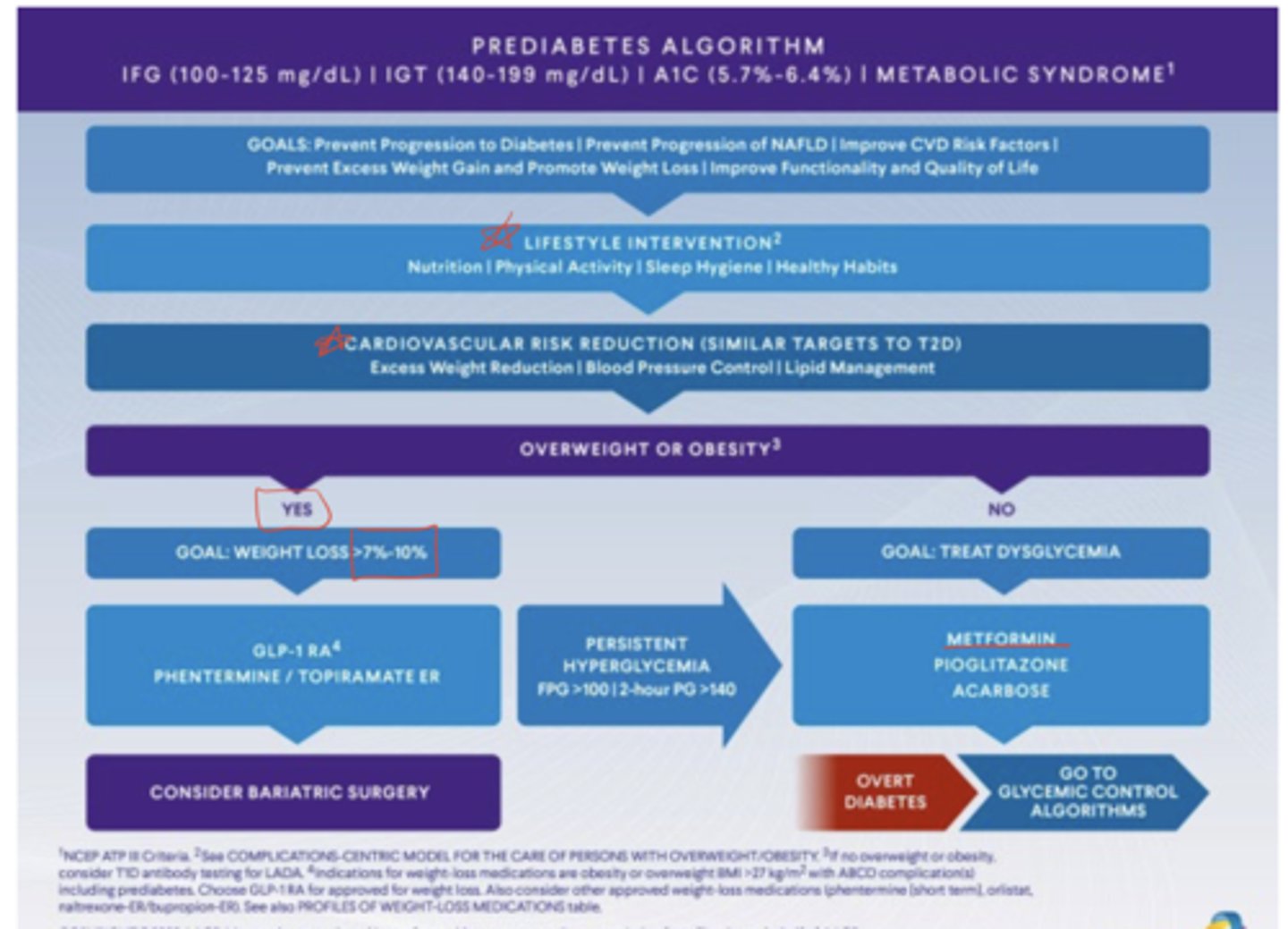
Which additional pharmacologic agents are mentioned in the AACE pre-diabetes algorithm?
GLP-1 agonists and, in some cases, phentermine/topiramate for patients who are overweight or obese
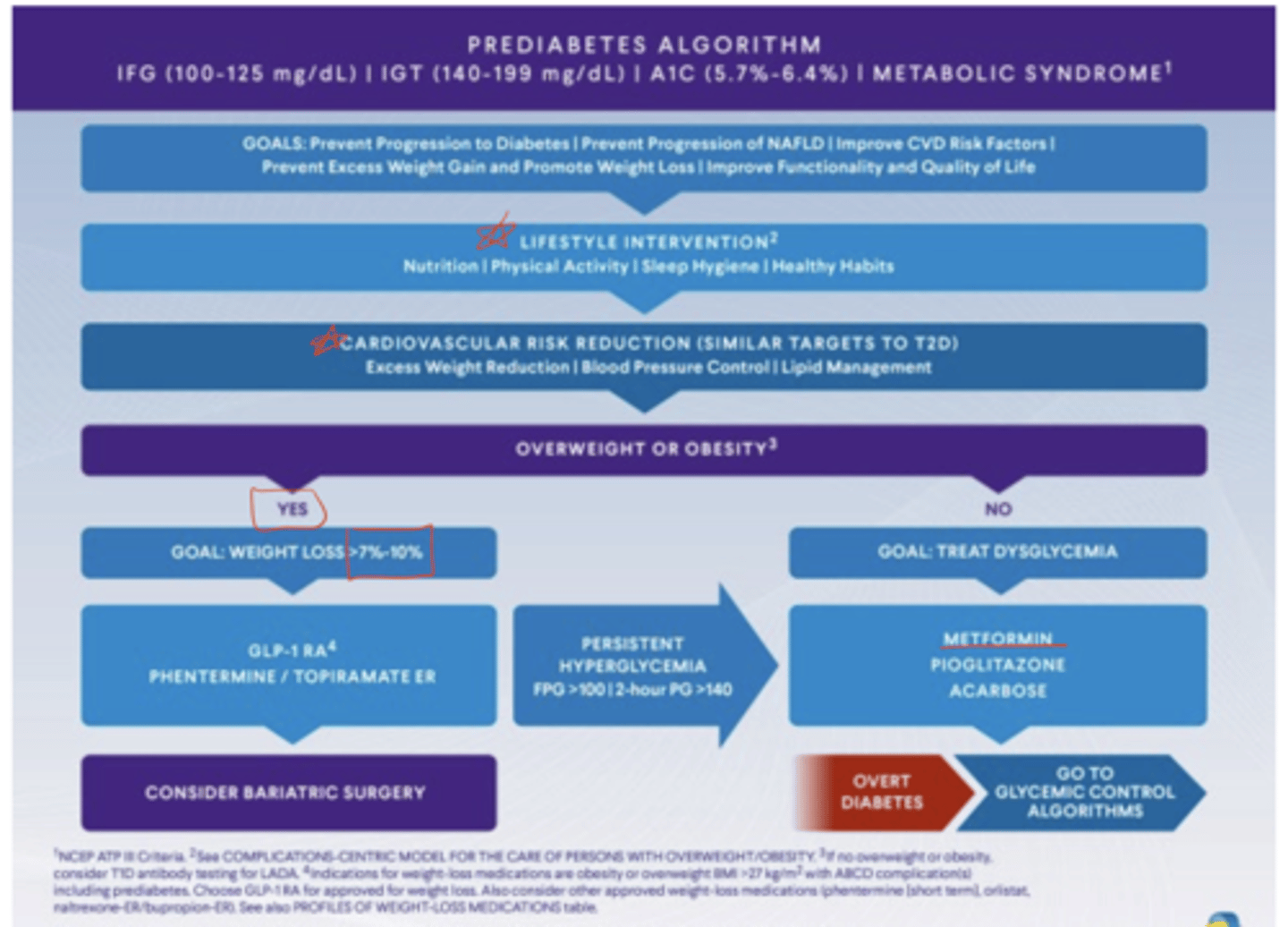
Why is cardiovascular care emphasized in patients with pre-diabetes?
Pre-diabetes is associated with increased cardiovascular disease and mortality
What CV risk reduction strategies are recommended in pre-diabetes?
Screen and treat hypertension, dyslipidemia
Encourage smoking cessation
Promote lifestyle changes
Should statins be discontinued if they increase the risk of diabetes?
No — monitor blood glucose, but do not stop statins for this reason
How is diabetes defined?
A chronic condition caused by an absolute lack of insulin or relative lack of insulin due to impaired insulin secretion and/or action
What causes type 1 diabetes?
Destruction of pancreatic beta cells, often autoimmune, possibly triggered by toxins or viruses, in genetically susceptible individuals
What causes type 2 diabetes?
Beta cell dysfunction and insulin resistance
When is gestational diabetes diagnosed?
In the 2nd or 3rd trimester of pregnancy when diabetes was not present before gestation
Besides type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes, are there other forms?
Yes, other specific types of diabetes exist, but are less common
What is the basic role of insulin?
to enable sugar (glucose) to enter cells
What happens when there is too much sugar in the blood?
Damage to blood vessels and nerves
What happens when there is not enough sugar in the cells?
Tiredness and weight loss as the body uses fat and muscle for energy
What are three classic symptoms of uncontrolled diabetes?
Frequent urination (osmotic diuresis), excessive thirst (due to high osmolarity), and weight loss (from fat and muscle breakdown)
What are the microvascular complications of uncontrolled diabetes?
Eye problems (retinopathy), kidney problems (nephropathy), and nerve damage (neuropathy)
What are the macrovascular complications of uncontrolled diabetes?
Heart disease, coronary artery disease, and stroke
What other complications can occur in diabetes?
Oral health issues, infections, and foot problems
What three steps are involved in the treatment roadmap for diabetes?
1. establish blood sugar goals
2. evaluate treatment options, 3. account for complexities and additional factors
What are the two main methods to track blood sugar?
Hemoglobin A1c and glucose monitoring (SMBG or CGM)
What does A1c measure?
The average blood sugar over 2-3 months; sometimes explained as the "amount of glucose sticking to red blood cells"
How often should A1c be checked?
Every 3 months if not at goal or therapy changes; every 6 months if at goal and stable
When are common times for SMBG (self-monitoring blood glucose)?
Fasting, pre-prandial (before meals), and 1-2 hours post-prandial
What is CGM?
Continuous glucose monitoring — sensors that provide ongoing glucose readings
How are A1c and SMBG related?
A1c correlates with expected average fasting and post-prandial glucose values
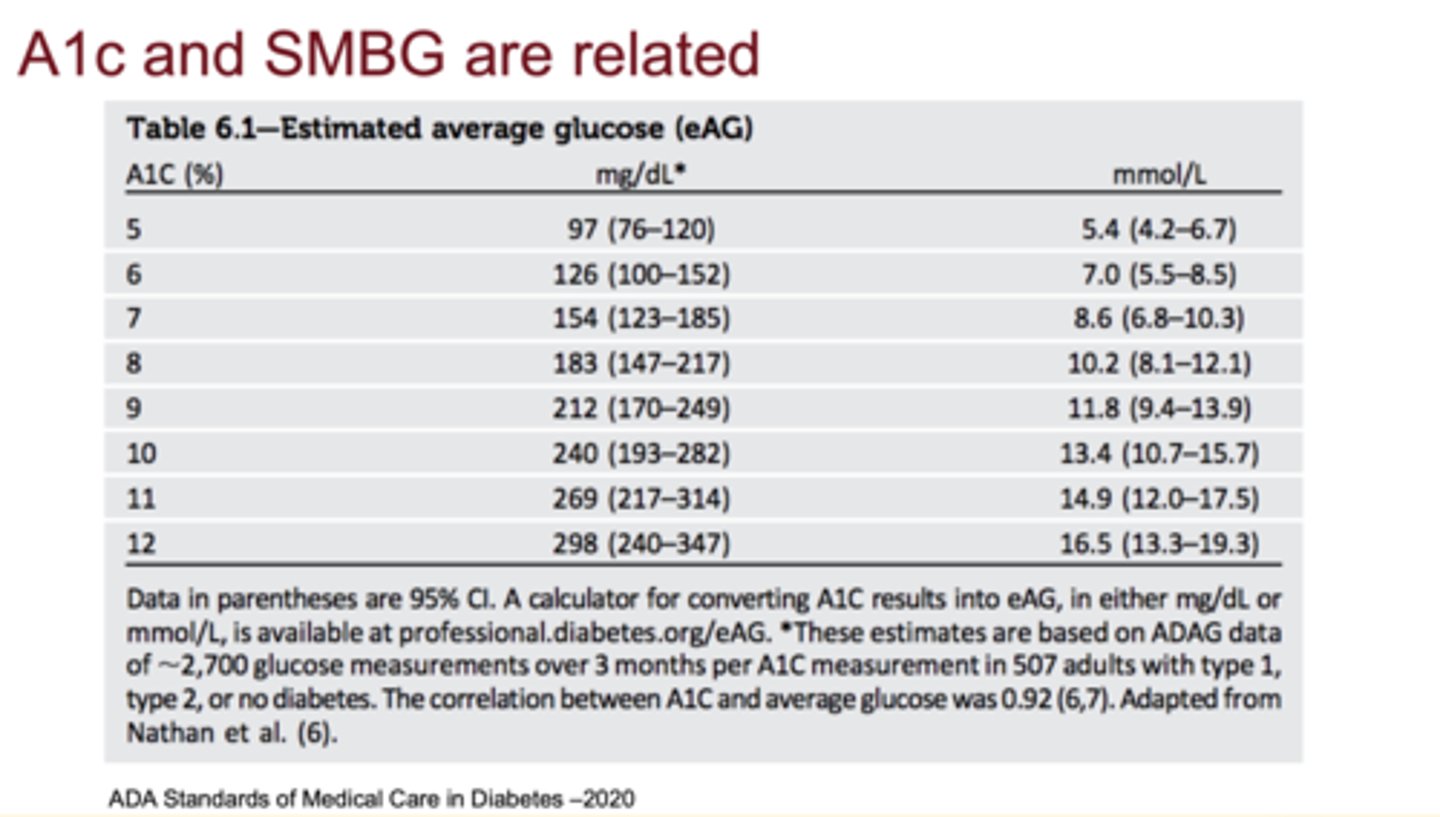
What are the A1c cutoffs for normal, prediabetes, and diabetes?
Normal: <5.7%, Prediabetes: 5.7-6.4%, Diabetes: ≥6.5%
What are the four criteria for diagnosing diabetes?
1. A1c ≥ 6.5%*
2. Fasting plasma glucose ≥ 126 mg/dL*
3. 2-hour OGTT plasma glucose ≥ 200 mg/dL*
4. Random plasma glucose ≥ 200 mg/dL with symptoms
**need unequivocal hyperglycemia or 2 abnormal results
Why is repeat testing sometimes needed?
Because diabetes is a lifelong diagnosis
**confirm with second test unless hyperglycemia is unequivocal
What is the most common A1c goal for patients with diabetes?
Less than 7%
What are the corresponding SMBG/CGM goals for an A1c <7%?
Fasting glucose: 80-130 mg/dL
Post-prandial glucose: <180 mg/dL
CGM: >70% time in range (70-180 mg/dL)
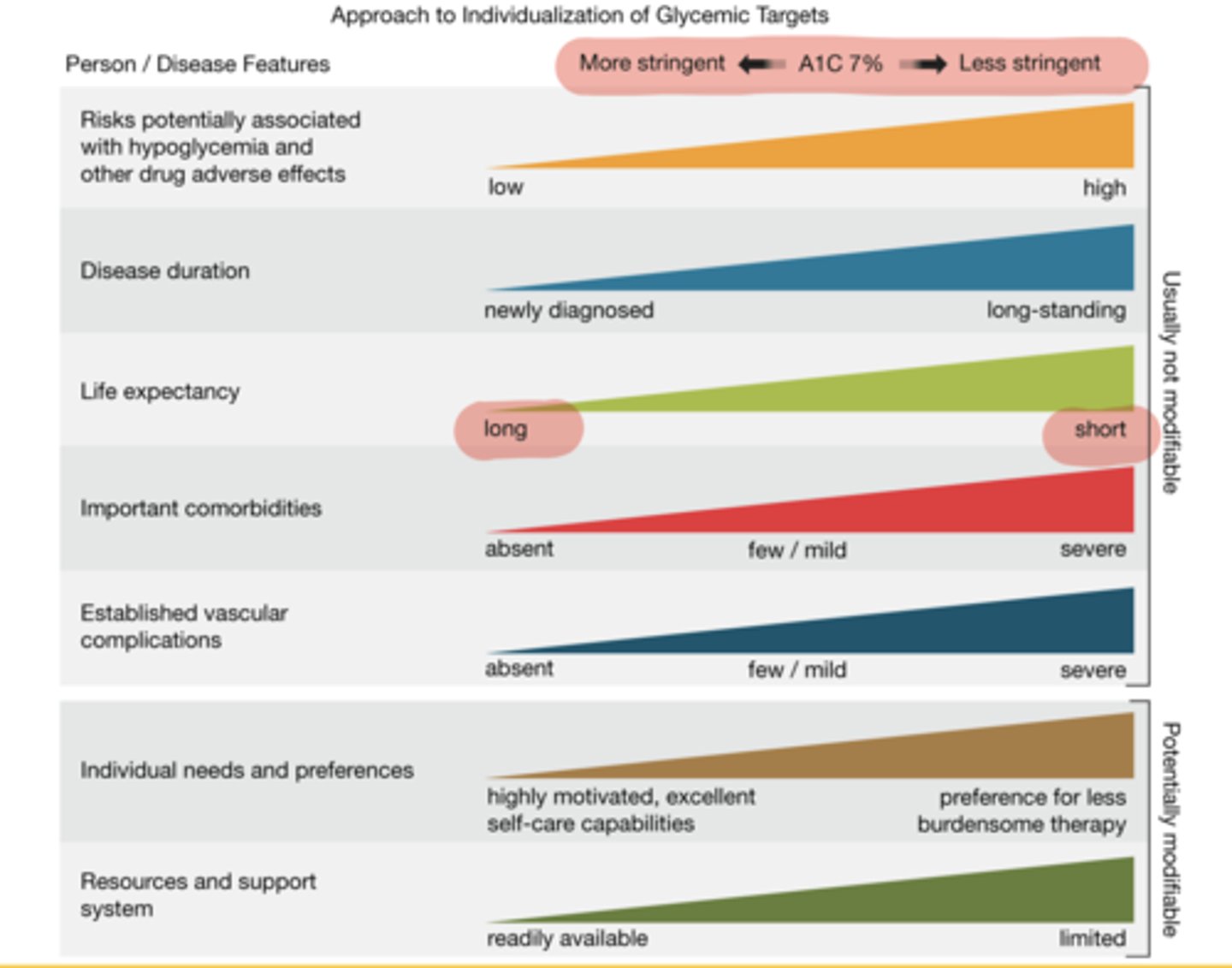
Why must A1c goals be individualized?
Factors such as disease duration, life expectancy, comorbidities, and patient preferences impact appropriate targets
What is the primary non-drug treatment for both type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
Lifestyle modifications: diet and exercise
What is the only medication for type 1 diabetes?
Insulin
What is often the first-line medication for type 2 diabetes?
Metformin
Are there many medication classes for type 2 diabetes?
Yes, multiple oral and injectable agents exist, chosen based on patient-specific factors
What annual or regular screenings are recommended for diabetes complications?
Nephropathy: annual albumin/creatinine ratio
Neuropathy: annual foot exam with monofilament
Retinopathy: dilated eye exam every 1-2 years
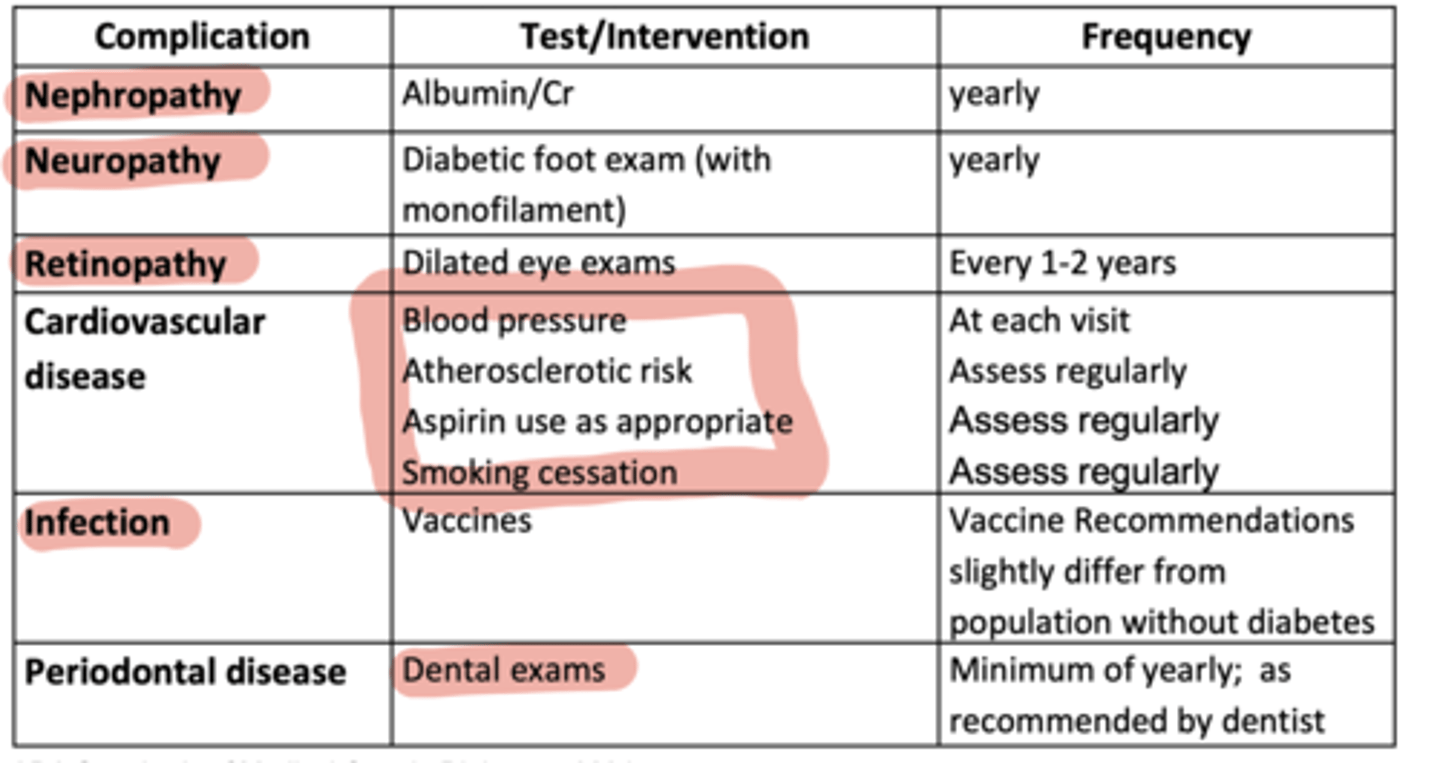
What additional CV and preventive measures are important in diabetes care?
Blood pressure checks, ASCVD risk assessment, aspirin as appropriate, smoking cessation, vaccines, and dental exams
What psychosocial issues are common in diabetes?
Increased risk of depression, diabetes distress, anxiety, eating disorders, and cognitive problems
Why are psychosocial issues important in diabetes care?
They significantly impact a patient's ability to manage their diabetes effectively
What should providers regularly assess in patients with diabetes?
Psychological and social situations, with screening for depression, distress, anxiety, and related issues
What are the two main branches of the ADA pharmacologic treatment algorithm?
Left-hand side: Focus on patients with specific comorbidities (ASCVD, high CV risk, heart failure, CKD)
Right-hand side: Focus on patients without those conditions, emphasizing weight management and glycemic goals
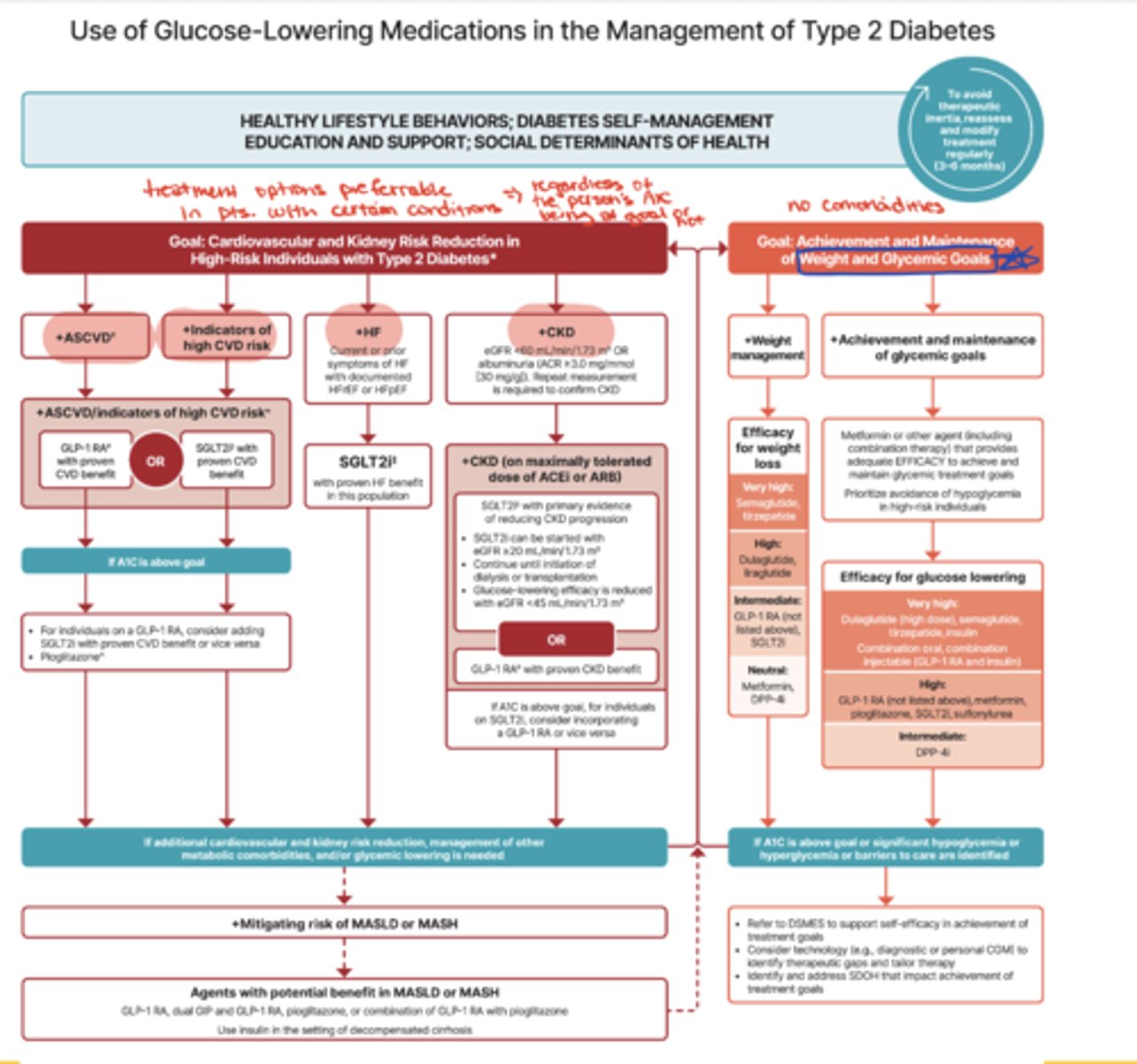
Why is the ADA algorithm important for clinical practice?
It guides treatment selection based on comorbidities and patient-specific needs, and is widely used across diabetes care
What type of medications are preferred for patients with ASCVD, heart failure, or CKD according to ADA?
Medications proven to reduce risk or progression of these conditions (e.g., GLP-1 receptor agonists, SGLT2 inhibitors) — regardless of whether A1c is at goal
How does the ADA algorithm address weight management?
It ranks medications by their efficacy for weight loss in patients where weight reduction is a priority
How does the ADA algorithm address glycemic control?
It lists medications in order of efficacy for glucose lowering, guiding choices for patients focused on A1c targets
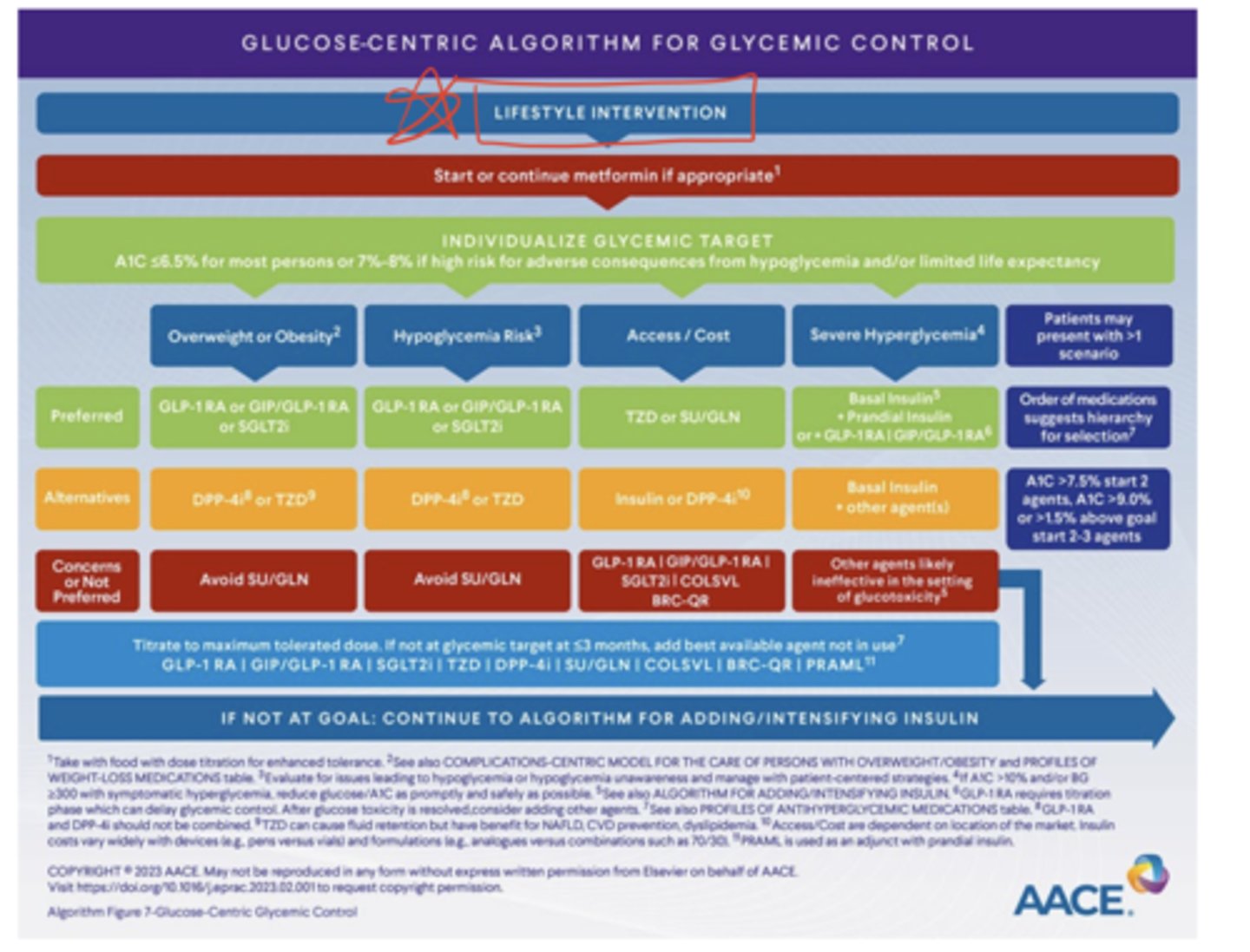
What unique patient categories does the AACE glucose-centric algorithm address?
- overweight or obese patients
- patients at high risk for hypoglycemia
- patients with access/cost concerns
- patients with severe hyperglycemia