Oligopoly
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Define oligopoly
is an imperfectly competitive industry with high level of market concentration
What are the features of an oligopoly
Few dominant firms, high barriers to entry and exit, interdependence, non price competition
Give examples of oligopoly markets
Airlines, high street banks, broadbands
What are sunk costs
Costs that can’t be recovered eg advertising costs
What’s interdependence
The decisions of one firm will directly impact the decisions of other firms in the market
Give an example of a firms interdependence
If one firm changes their price other firms may be forced to change their price to maintain market share
What does interdependence lead to
Creates a competitive environment making it volatile and uncertain
what’s non price competition
it’s the use of other competitive strategies to gain an advantage over rivals
What are some non price competition strategies
Advertising, product innovation, branding/loyalty
Why is price competition not effective
It isn’t effective as there’s only a few dominant firms
Give an example of non price competition
Tesco loyalty card. Also if two firms sell similar products they can compete in advertising instead of price
What are the barriers to entry in an oligopoly
Economies of scale such as purchasing or marketing
Brand loyalty
Patent protection this means competitors cannot replicate
Expertise and reputation
Control of important platforms
Vertical intergration
Expertise and reputation
What’s concentration ratio
The combined market share of leading business in a clearly defined market
How do you calculate the concentration ratio
We sum the market share of leading 3 or 5 firms an oligopoly exits when the five firm concentration ratio is 60% ( can be around that figure)
What’s a price war
Firms will keep trying to undercut eachother till the price is driven down super low and very little profit can be made by either firm
What’s in the pay off matrix graph
Two firms and their two strategy
Eg two firms- Pepsi and cola and two strategies low price and high price
And there pay off in the split boxes
Left box is the left firm and right box is right firm
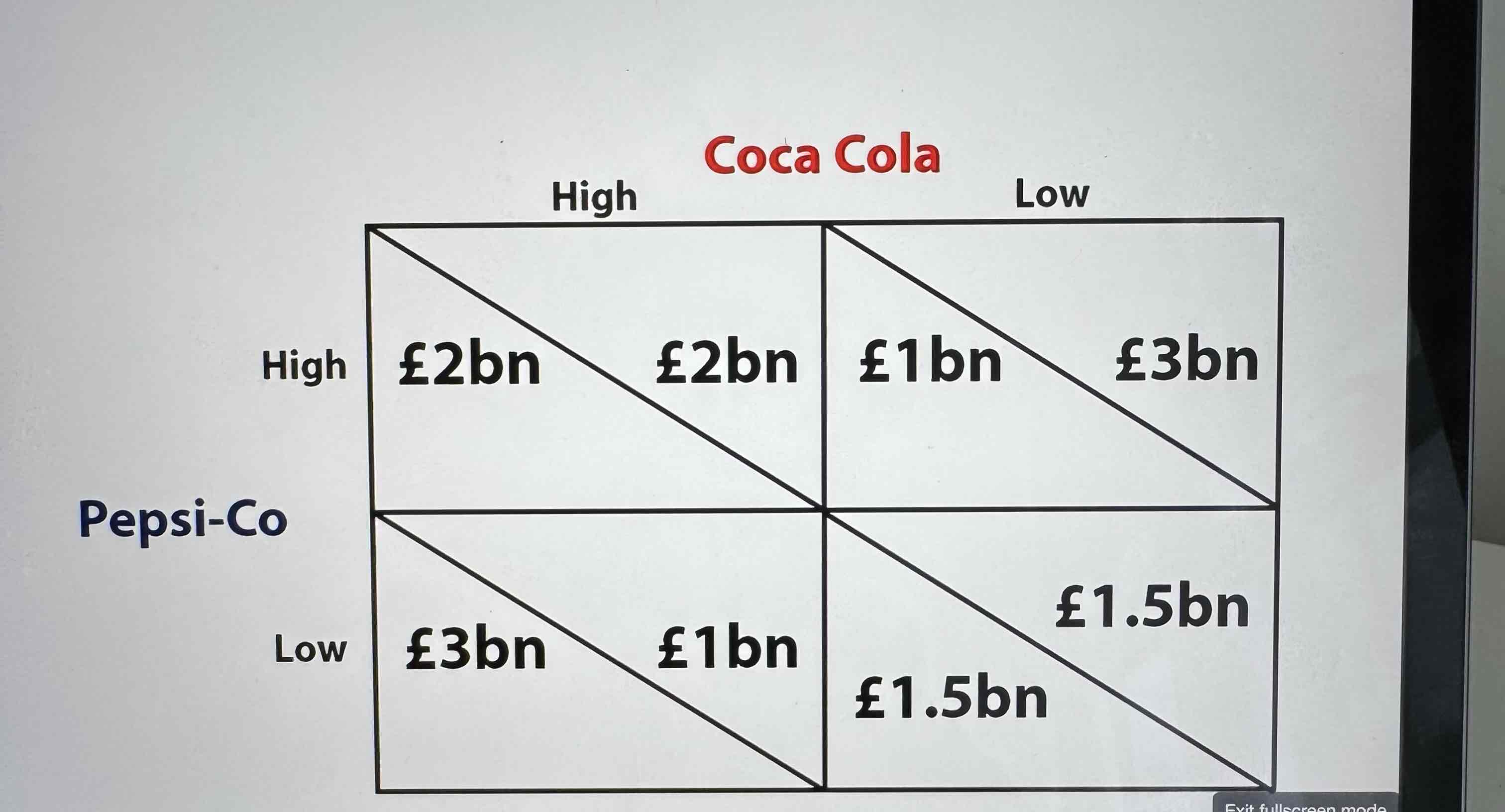
From the example above why do Pepsi and cola have an incentive to cut their prices
Pepsi has an incentive to set a low price because undercutting cocla can increase its pay off from 2bn-3bn
Equally cola has an incentive to set a low price because undercutting Pepsi it can increase its payoff
Why is game theory important and used
firms face a number of strategic choices which govern their ability to achieve a desired pay off
What can game theory be useful for
it can be used for two different options wether it’s price or non pricing like advertising
Define collusion
When rival companies agree to work together for their mutual benefit: high profits and revenues
Give a reason for collusive behavior
firms may chose to act together to influence price levels or production which minimises competitive pressure they face
What does collusion lead to
Lower consumer surplus but higher prices and greater profits for firms colluding
What are the two types of collusion
Overt collusion and tacit collusion
Overt collusion is a formal agreement between firms to collude
Tacit collusion is an unspoken agreement between firms
Why’s overt collusion illegal
As it’s a formal agreements amongst competing firms they can avoid competition and raise prices which is bad for consumers
Why is whistle blowing good
When someone reports illegal practises the firm will get immunity from fines and the competitor firms you were colluding with end up with huge fine reducing their profits
Why is the formal agreement in overt collusion secret
To avoid fines or penalties from cma
Give an example of overt collusion
OPEC which is a oil cartel of countries, they collude together to keep prices high
What’s tacit collusion
Unspoken agreement between firms, firms act independently and don’t communicate but collusion is implied
Give an example of tacit collusion firms
The Uk supermarket industry they compete in terms of prices even if there’s no contact between eachother
Eg Tesco and Sainsbury’s
What are the types of price competition
Price wars , predatory pricing , limit pricing
Give an example of price war
Supermarkets in the 1990 started a price war over baked beans they kept lowering their prices
What’s predatory pricing
It involves firms setting prices very low to drive out firms already in the industry (illegal)
What’s the effect of predatory pricing in the short run
In the short run it leads to firm making a loss Ar is lower then ac but as firms leave in the long run the remaining firms raise their prices to regain revenue and profits take over market
What’s limit pricing
When Incumbent firms lower prices to discourage the entry of other firms so there are low profits, potential firms are unable to complete
What’s price wars
Firms will keep trying to undercut eachother till the price is driven down super low and very little profit can be made by either firm
What are the types of non price competition
Advertising
Loyalty cards
Branding
Quality
Why may advertising be beneficial
Helps make the brand more known and influence consumer preferences, attracting more customers to the brand
Why may advertising be bad
It’s difficult to know what the effect is of increased advertising spending and for some firms it may be ineffective which would make them incur large sunk costs which are unrecoverable
Why may loyalty cards be good
Helps Intise customers and increase demand for that firm as there can be good deals and offers which attract more customers
Give an example of a company that already offers loyalty card
Tesco loyalty card - gives money off shopping and tickets to leisure activities, this helps Tesco compete with other supermarkets
Why’s branding good
It can increase brand loyalty and demand becomes more price inelastic, it can attract more customers as its well known brand and keep customers, increasing market share
Why’s quality good
Firms can invest into r&d increasing dynamic efficiency and higher quality eg Samsung making screen bigger but firms need supernormal profits to do this, to re invest
Firms might have better customer service such as more available delivery times or keep shops open to increase convenience