CompTIA Security+ SY0-601 Study Guide
1/907
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
908 Terms
Information Security
The act of protecting data and information from unauthorized access, unlawful modification and disruption, disclosure, corruption, and destruction.
Information System Security
The act of protecting the systems that hold and process our critical data.
Confidentiality
Information has not been disclosed to unauthorized people.
Ex. Data Encryption, Digital Keys
Integrity
Information has not been modified or altered without proper authorization
Ex. Hashes
Availability
Information is able to be stored, accessed, or protected at all times.
Authentication
When a person's identity is established with proof confirmed by a system.
Examples:
- Something you know
- Something you are
- Something you have
- Something you do
- Somewhere you are
Authorization
Occurs when a user is given access to a certain piece of data or certain areas of a building.
Accounting
Tracking of data, computer usage, and network resources is maintained.
Ex. Log.txt Files
Malware
Short-Hand Term for Malicious Software
Unauthorized Access
Occurs when access to computer resources and data happens without the consent of the owner.
System Failure
Occurs when a computer crashes or an individual application fails.
Social Engineering
Act of manipulating a user into revealing confidential information or performing detrimental actions.
Physical Controls
Any security measures that are designed to deter or prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information or the systems that contain it.
Alarm systems, locks, surveillance cameras, identification cards, and security guards
Technical Controls
Safeguards and countermeasures used to avoid, detect, counteract, or minimize security risks to our systems and information.
Smart cards, encryption, access control lists (ACLs), intrusion detection systems, and network authentication.
Administrative Controls/Managerial Controls
Focused on changing the behavior of people instead of removing the actual risk involved.
Policies, procedures, security awareness training, contingency planning, and disaster recovery plans.
White Hat Hacker
Non-malicious hackers who attempt to break into a company's system at their requests. (Ethical Hacker, PenTester)
Black Hat Hacker
Malicious hackers who break into computer systems and networks without authorization or permission.
Gray Hat Hacker
Malicious hackers who break into computer systems and networks without authorization or permission.
Blue Hat Hacker
Hackers who attempt to hack into a network without permission of the company but are not employed by company.
Elite Hacker
Hackers who find and exploit vulnerability before anyone else does.
- 1 in 10,000 Hackers are this role
Script Kiddies
Hackers with little to no skill who only use tools and exploits written by others.
Hacktivists
Hackers who are driven by a cause like social change, political agendas, or terrorism.
Organized Crime
Hackers who are part of a crime group that is well-funded and highly sophisticated.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
Highly trained and funded groups of hackers (often by nation states) with covert and open-source intelligence at their disposal.
Timeliness
Property of an intelligence source that ensures it is up-to-date
Relevancy
Property of an intelligence source that ensures it matches the use case intended for it.
Accuracy
Property of an intelligence source that ensures it produces effective results.
Confidence Level
Property of an intelligence source that ensures it produces qualified statements about reliability.
Proprietary (Info Source)
Threat intelligence is very widely provided as a commercial service offering, where access to updates and research is subject to a subscription fee.
Closed-Source (Info Source)
Data that is derived from the provider's own research and analysis efforts, such as data from honeynets that they operate, plus information mined from its customers' systems, suitably anonymized.
Open-Source (Info Source)
Data that is available to use without subscription, which may include threat feeds similar to commercial providers, and may contain reputation lists and malware signature databases.
Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT)
Methods of obtaining information about a person or organization through public records, websites, and social media.
Threat Hunting
A cybersecurity technique designed to detect presence of threats that have not been discovered by normal security monitoring and is potentially less disruptive than penetration testing.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
A combination of different data sources into one tool that provides real-time analysis of security alerts generated by applications and network hardware.
Lockheed Martin Kill Chain
A model developed by Lockheed Martin that describes the seven stages by which a threat actor progresses a network intrusion.
Reconnaissance
The attacker determines payload code that will enable access with exploit code that will use a vulnerability to execute on the target system(s).
Weaponization
The attacker couples payload code that will enable access with exploit code that will use a vulnerability to execute on the target system.
Delivery
The attacker identifies a vector by which to transmit weaponized code to the target environment.
Exploitation
The weaponized code is executed on the target system by this mechanism.
Installation
This mechanism enables the weaponized code to run a remote access tool and achieve persistence on the target system.
Command & Control (C2)
The weaponized code establishes an outbound channel to a remote server that can then be used to control the remote access tool and possibly download additional tools to progress the attack.
Actions and Objectives
The attacker typically uses the access he has achieved to covertly collect information from target systems and transfer it to a remote system (data exfiltration) or achieve other goals and motives.
MITRE ATT&CK Framework
A knowledge base maintained for listing and explaining specific adversary tactics, techniques, and common knowledge or procedures.
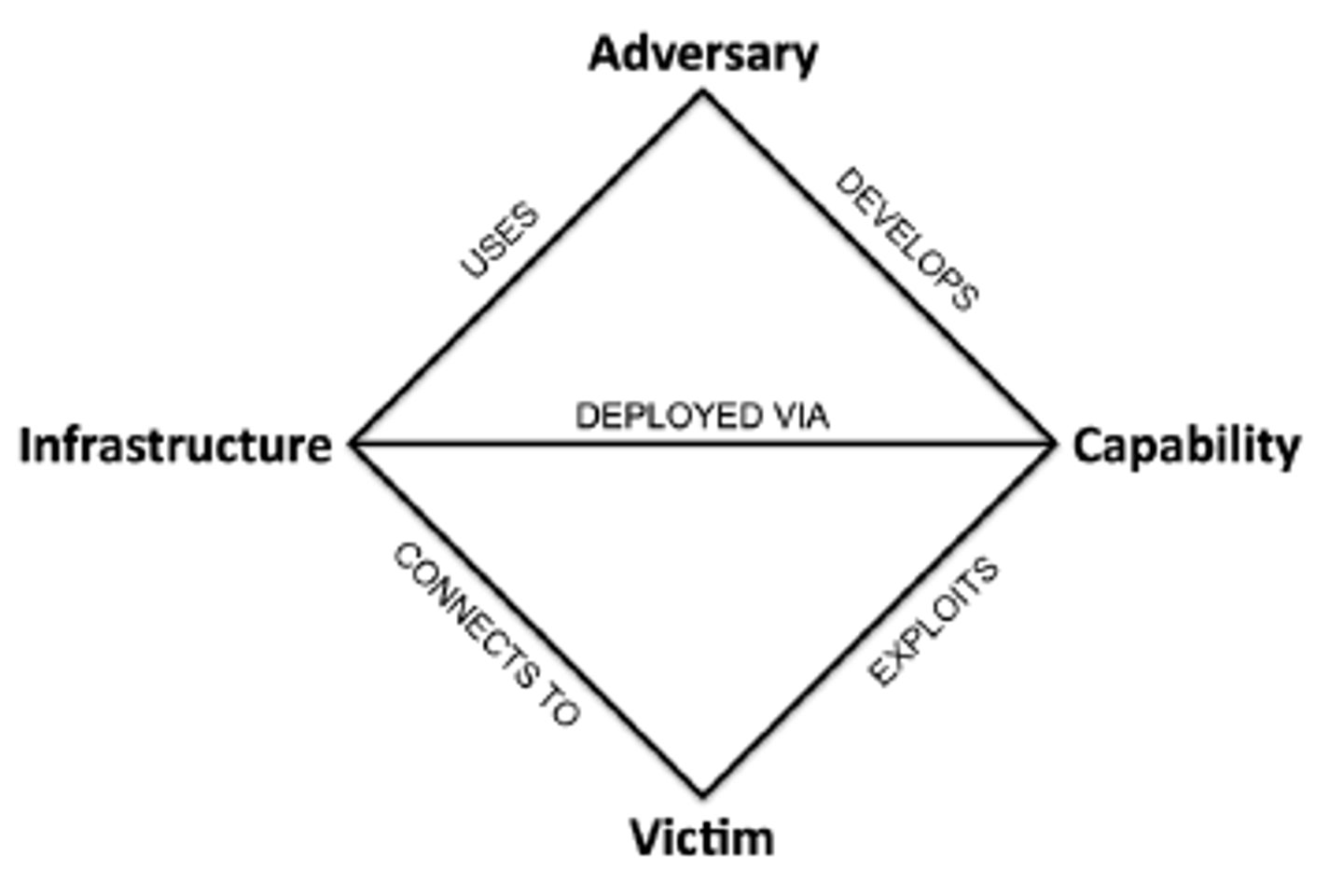
Diamond Model of Intrusion Analysis
A framework for analyzing cybersecurity incidents and intrusions by exploring the relationships between four core features: Adversary, Capability, Infrastructure, and Victim.
Metafeatures include: Timestamps, Phases, Result, Direction, Methodology, Resources
Virus
Malicious code that runs on a machine without the user's knowledge and infects the computer when executed. Requires user action in order to reproduce and spread.
Boot Sector (Virus)
Virus that is stored within the first sector of a hard drive and are loaded into memory upon boot.
Macro (Virus)
Virus embedded into a document and is executed when the document is opened by the user.
Program (Virus)
Virus that infects an executable or application.
Multipartite (Virus)
Virus that combines boot and program viruses to first attach itself to the boot sector and system files before attacking other files on the computer.
Encrypted (Virus)
Virus that Cyphers itself in order to avoid detection by any antivirus software.
Polymorphic (Virus)
Advanced version of an encrypted virus that changes itself every time it is executed by altering the decryption model to avoid detection.
Metamorphic (Virus)
Virus that is able to rewrite itself entirely before it attempts to infect a file.
Stealth (Virus)
Virus category that uses various techniques to avoid detection by antivirus software.
Armored
Viruses with a layer of protection to confuse a program or person analyzing it.
Hoax
An attempt to deceive a user into believing that something is legitimate (or vice versa).
Worm
Malicious software, like a virus, but is able to replicate itself without user interaction. This virus has the ability to disrupt normal network traffic and computing activites.
Trojan Horse
Malicious software that is disguised as a piece of harmless or desirable software. May perform desired function on top of malicious function. (Ex. McAfee Antivirus)
Ransomware
Malware that restricts access to a victim's computer system until a ransom is received. Uses a vulnerability in pre-existing software to gain access and then encrypts files.
Spyware
Malware that secretly gathers information about the user without their consent.
Keylogger
Type of spyware that gathers a users keystrokes and takes screenshots that get sent to the attacker.
Adware
Spyware that detects user behaviors and interests in order to display related advertisements.
Grayware / Jokeware
Software that isn't benign nor malicious and tends to behave improperly without serious consequences.
Rootkit
Software designed to gain administrative level control over a system without detection.
DLL Injection
Malicious code inserted into a running process on a Windows machine by taking advantage of Dynamic Link Libraries that are loaded at runtime.
Driver Manipulation
An attack that relies on compromising the kernel-mode device drivers that operate at a privileged or system level.
Spam
Activity that abuses electronic messaging systems, most commonly through email. Used often to exploit a company's open mail relays to send their messages.
Watering Hole
Occurs when malware is placed on a website that the attacker knows his potential victims will access.
Botnet
A collection of compromised computers under the control of a master node.
Zombie
A computer that has been taken over by a botnet.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS)
A group of compromised systems attack a single target simultaneously to create a Denial of Service (DoS).
Active Interception
When a computer is placed between the sender and receiver and is able to capture or modify the traffic between them.
Privilege Escalation
When an attacker exploits a design flaw or bug in a system to gain access to resources that a normal user isn't able to access.
Backdoor
A security and authentication bypass usually used for maintenance purposes. Can also be used for malicious purposes.
Easter Egg
Non-malicious code that when invoked, displays an insider joke, hidden message, or secret feature.
Logic Bomb
Malicious code that has been inserted inside a program and will execute only when certain conditions have been met.
Symptoms of Infection
Performance Degradation, BSOD, Inaccessible Files, Strange Noise, Error Messages, Icons Appearing and Disappearing, Double File Extensions, or Antivirus Software is refusing to run.
Malware Removal Steps
1. Identify Symptoms of Infection
2. Quarantine
3. Disable System Restore
4. Remediate the System
5. Schedule Auto-Update and Scans
6. Enable System Restore
7. Provide end user security awareness training
Virus Prevention
Use of Antivirus Software, Service Packs, and Updates
Worm, Trojan, and Ransomware Prevention
Antimalware Solutions
Spyware Prevention
Antispyware Solutions, Windows Defender, and Browser Configuration
Rootkit Prevention
Scanners are able to detect a file containing a this once its installed, but it is difficult to remove once installed and is best to reimage the machine.
Spam Prevention
Verify your email server configuration doesn't allow open relays, Remove email addresses from websites, use whitelists and blacklists, and train and educate end users.
Malware Prevention
1. Update your antimalware and scan
2. Update and patch your OS and apps
3. Educate and train end users over safe searching practices
Dropper
Malware designed to install or run other types of malware embedded in a payload on an infected host.
Downloader
A piece of code that connects to the internet to retrieve additional tools after the initial infection by a dropper.
Shellcode
Any lightweight code designed to run an exploit on the target, which may include any type of code format from scripting languages to binary.
Code Injection
An exploit technique that runs malicious code with the identification number of a legitimate process.
Masquerading
Replacement of a genuine executable with a malicious one.
DLL Sideloading
Dropper exposes vulnerability in a legitimate program's manifest to load a malicious DLL runtime.
Process Hollowing
Dropper starts a process in a suspended state and requires the memory locations containing the process code with the malware code.
Living Off the Land
Exploit techniques that use standard system tools and packages to perform intrusions.
Personal Firewalls
Software applications that protects a single computer from unwanted internet traffic.
Windows Firewall with Advanced Security
Firewall that comes with every version of Windows, meant mainly for business usage and those who want in-depth firewall configuration.
Packet Filter
Firewall that comes with every MacOS X version after 10.10, allows for firewall configuration within MacOS.
iptables
Linux tool that configures Firewalls through the command line using Accept and Reject tools.
Intrusion Detection System (IDS)
Device or software application that monitors a system or network and analyzes the data passing through it in order to identify an incident or attack.
Host-Based Intrusion Detection System (HIDS)
Software based IDS installed on a Computer or server that logs anything that seems suspicious.
Network-Based Intrusion Detection System (NIDS)
Piece of Hardware connected to a network switch that logs anything that seems suspicious.
Signature-Based IDS Methodology
IDS Methodology that detects a specific string of bytes and triggers an alert if it is a known bad string.
Policy-Based IDS Methodology
IDS Methodology that relies on specific declaration of the security policy in order for an alarm to go off.
Ex. "No Telnet Authorized"