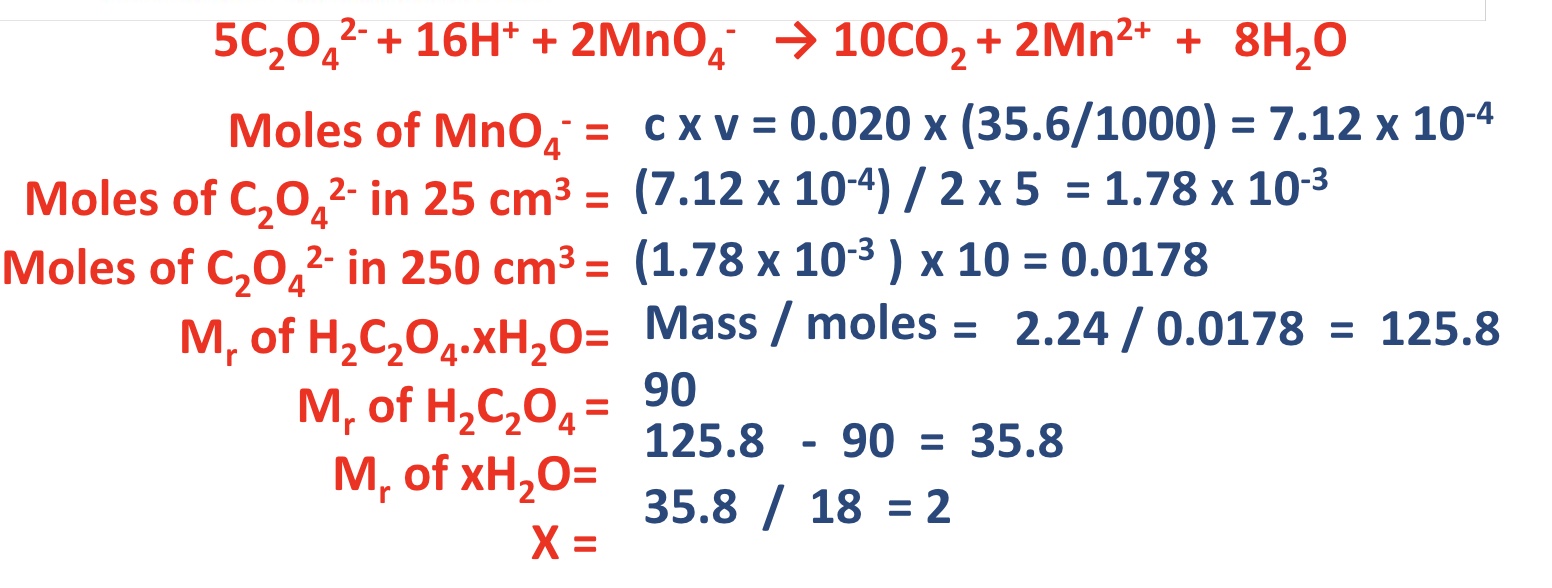3.2.5.5 variable oxidation states
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
what do all transition metals have?
a variable oxidation state
give 2 examples of tests where we have seen a variable oxidation state
testing for aldehydes
testing for primary + secondary alcohols
describe the two tests that are done to distinguish between aldehydes + ketones

describe the test used to identify primary + secondary alcohols
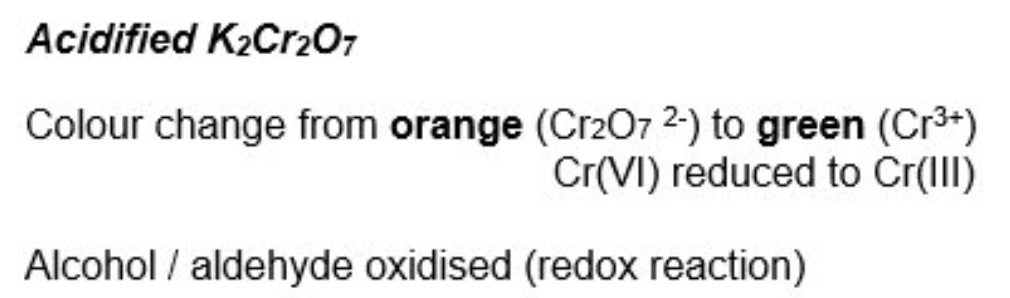
what is used to reduce vanadium(V) in stages to vanadium(II)?
zinc in acidic solution
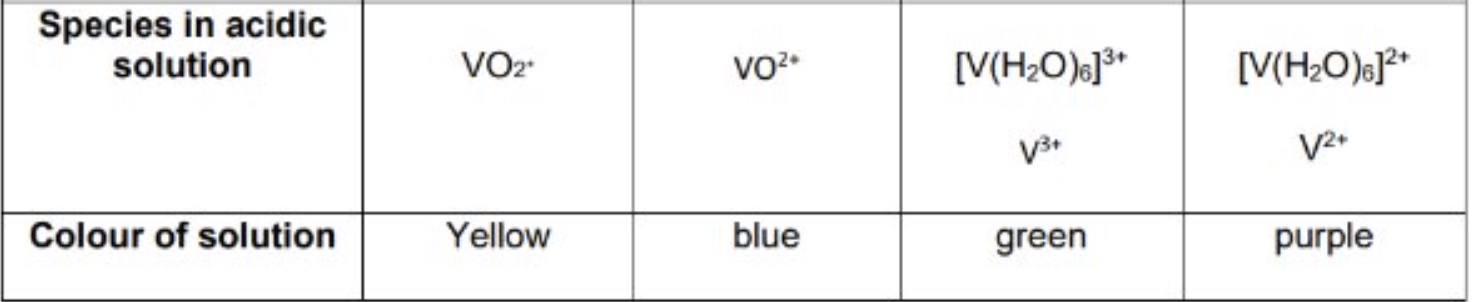
what are the 4 oxidation states vanadium has in its compounds?
+5, +4, +3 and +2
describe the method + results of reducing vanadium(V) in stages to vanadium(II)


for the four oxidation states of vanadium, give the species in acidic solution + the colour of solution
describe the method of the re-oxidation of vanadium(II)

how are redox titrations the same + how do they differ with acid base titrations?
they follow the same theory
but instead of neutralisation, a redox reaction takes place
give the 3 types of reactions studies regarding redox titrations

what is the oxidising agent in each of these 3 examples?
MnO₄⁻, provided by the reagent acidified potassium manganate KMnO₄

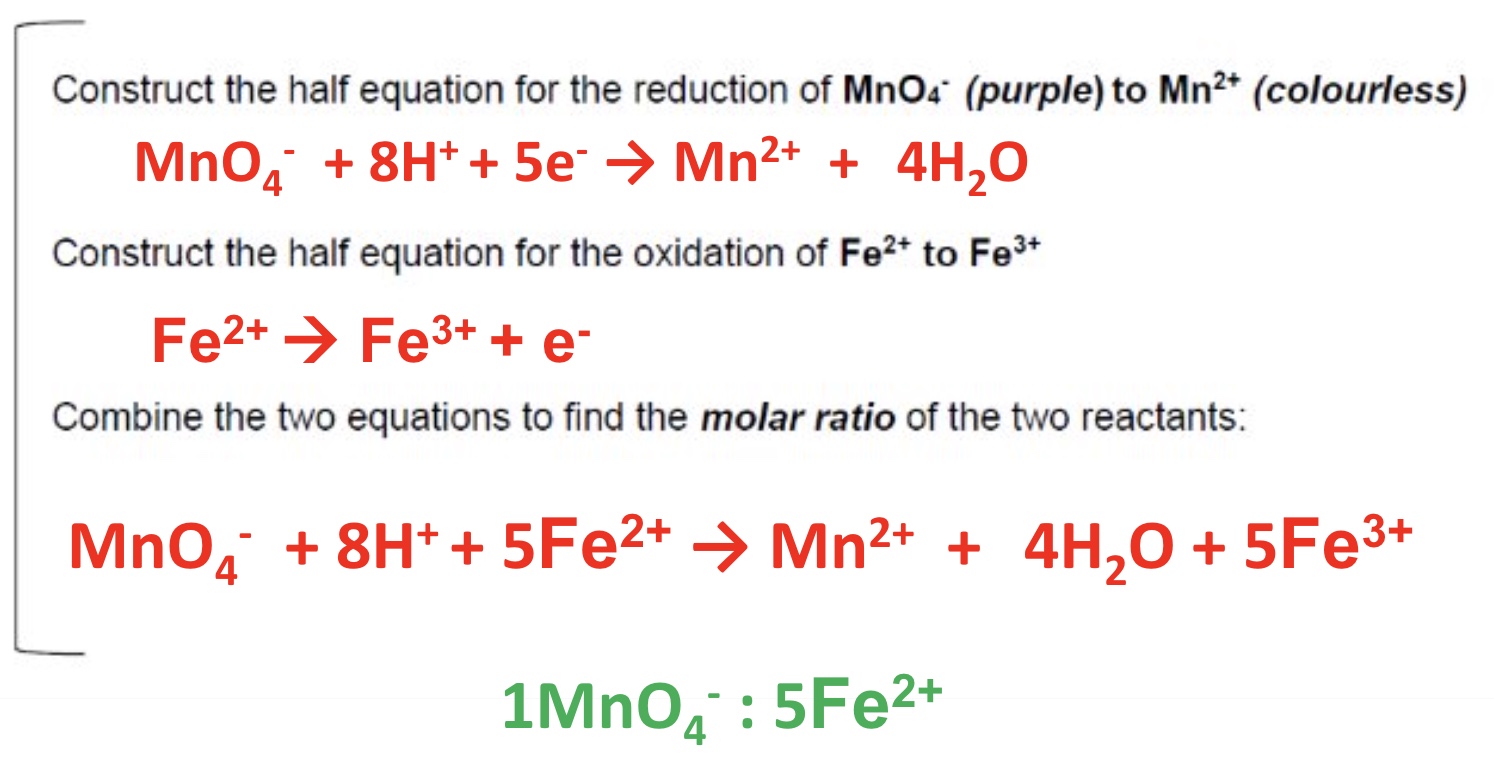



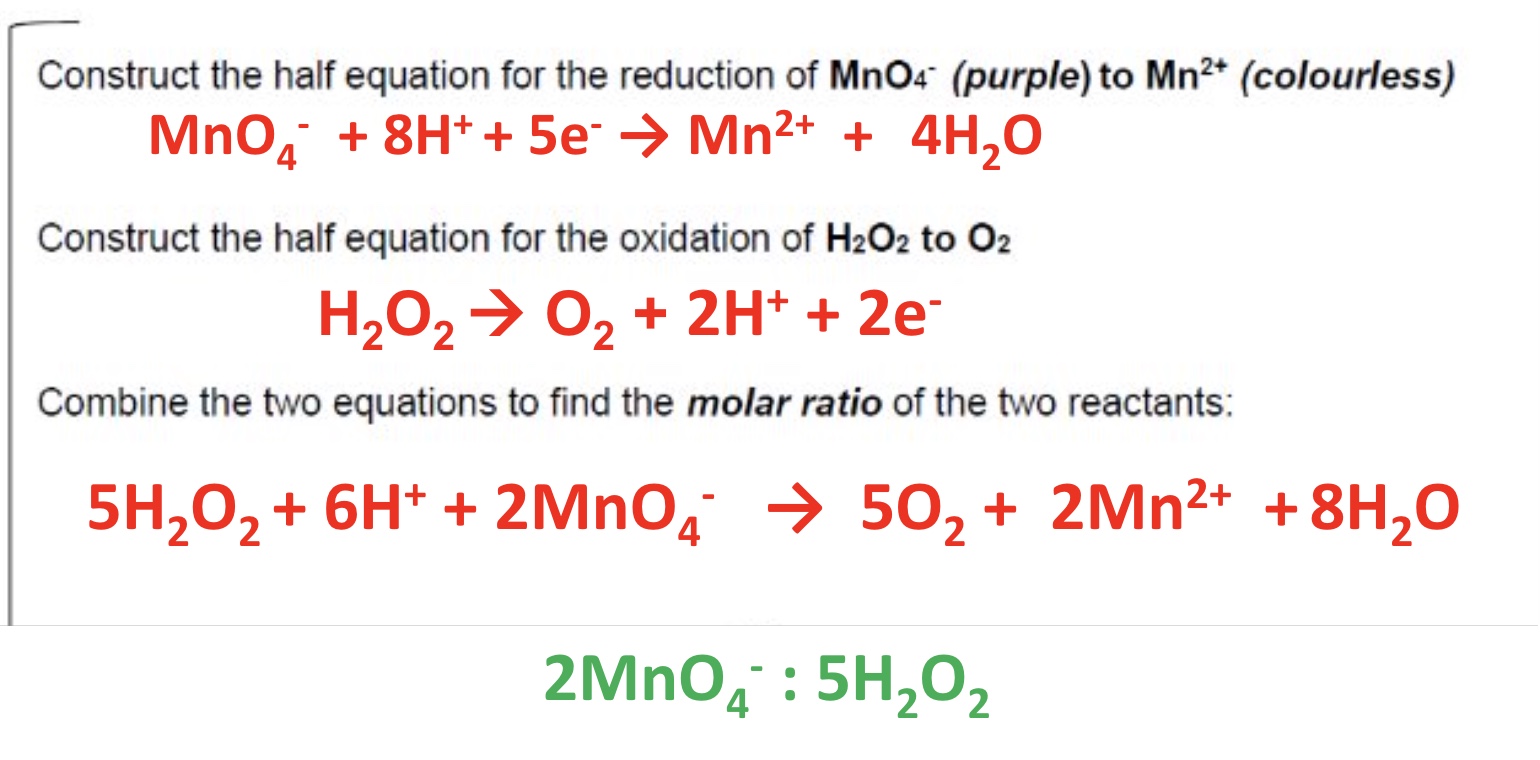
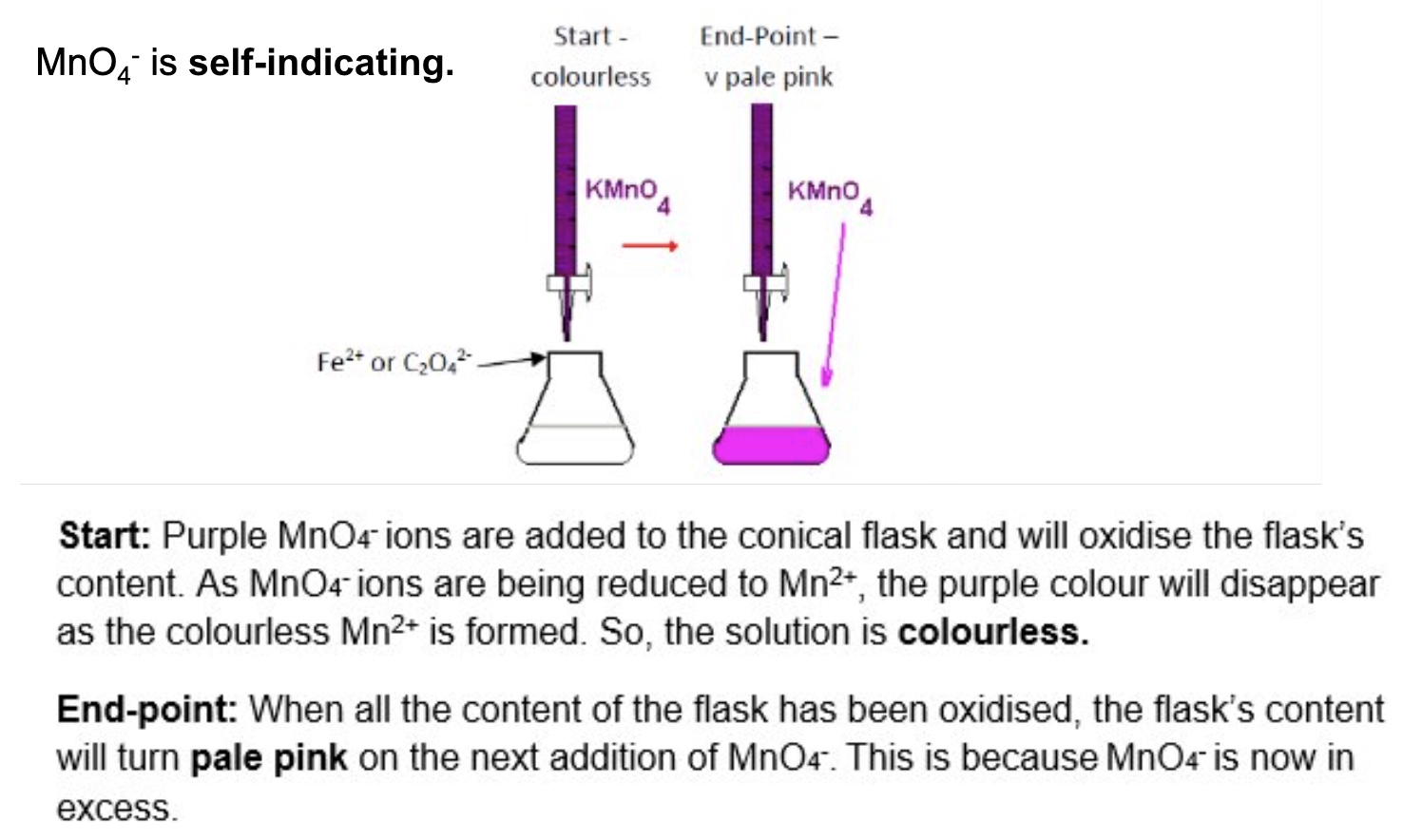
why dont we need an indicator for the redox titrations with MnO₄⁻?
due to the distinctive colour change, MnO₄⁻ is self-indicating
describe + explain the colour change that takes place during these redox titrations
what must the H+ ions be provided by? why?
by H₂SO₄ because if HCl is used the MnO₄⁻ will oxidise the Cl- ions