Lab 9- Post Lab Quiz: Staph, Strep, Water Quality,
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Streptococci
Gram positive, Mostly Pathogens
Hemolysis
is the breakdown of red blood cells to obtain iron within
using hemolysins which are considered virulence factors
3 types of hemolytic organisms
Alpha
Beta
Gamma
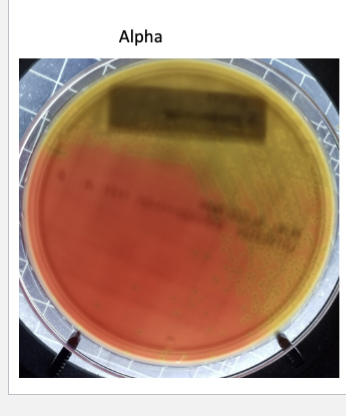
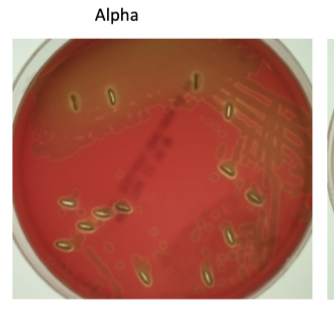
Alpha hemolysis
is the incomplete lysis which produces a greenish zone around the colony S. pneumoniae some other normal flora also do this

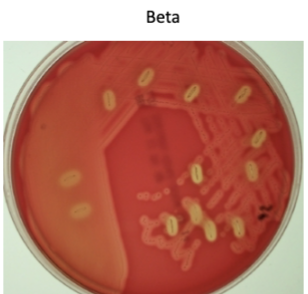
Beta (β) hemolysis
gets a clearing around the colonies due to compete lysis, S.
pyogenes which causes strep throat- it is a group A strep because it has the A carbohydrate
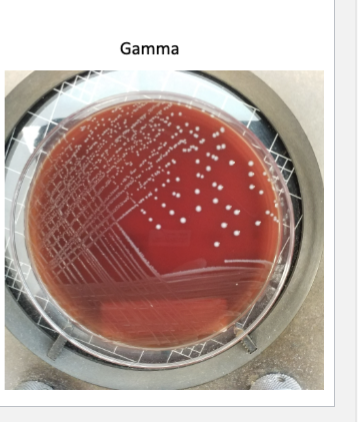
Gamma (γ) hemolysis
non-hemolytic - Streptococci that do not lyse red blood cells
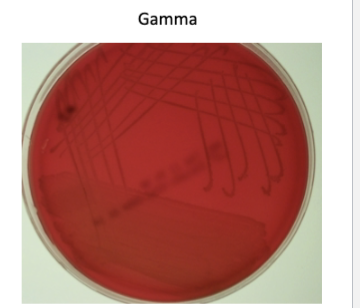
Medium used for looking at hemolytic patterns
Blood agar
Streptococci Sampling Procedure
You are going to take your own throat culture as close to tonsils as
possible make sure to roll swab around to get fully covered
– AVOID touching your teeth or tongue
• First quadrant streak the blood agar with the individually wrapped
swabs then finish quadrants 2-4 with loop
• Next week determine pattern of hemolysis and gram stain an
isolated colony
Staphylococci
Gram-Positive, mostly pathogens
gram positive organisms that tolerate high salt
concentrations and are frequent pathogens
Two main staphylococci
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus epidermidis
S. aureus
is frequently in the nose and there are many methicillin
resistant strains that cause nosocomial (hospital acquired) infections
S. epidermidis
is more of an opportunistic pathogen and infects burns sites, joint replacement site, and other human/medical device surfaces
Staphylococci 3 Media used
Staphylococci Medium 110 (SM110)
• Selective due to high salt concentration of ~7.5% due to NaCl
• Clear medium color allows us to observe colony color
– Mannitol Salts Agar (MSA)
• Selective due to high salt concentration of ~7.5% due to NaCl
• Differential for mannitol fermentation due to phenol red pH
indicator
– Fermenters turn plate yellow due to production of acid
– Rabbit Plasma- (Small foam stoppered tubes)
• Differential for coagulase production
– Enzyme produced by some organisms to clot blood
– Indicated by the medium solidifying after inoculation
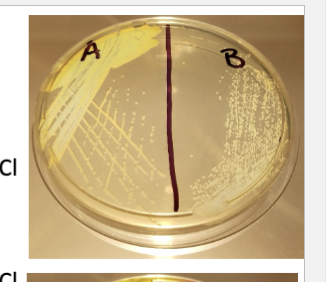
Staphylococci Medium 110 (SM110)
Selective due to high salt concentration of ~7.5% due to NaCl
Clear medium color allows us to observe colony color
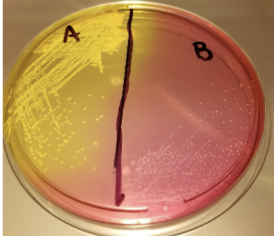
Mannitol Salts Agar (MSA)
• Selective due to high salt concentration of ~7.5% due to NaCl
• Differential for mannitol fermentation due to phenol red pH
indicator
– Fermenters turn plate yellow due to production of acid
Rabbit Plasma- (Small foam stoppered tubes
Differential for coagulase production
– Enzyme produced by some organisms to clot blood
– Indicated by the medium solidifying after inoculation
Staphylococcus aureus characteristics
+ plasma (solid)
+ (yellow plate)
Yellow colony
Staphylococcus epidermidis characteristics
- plasma (runny)
- Red plate)
White colony