L5: Principles, Heuristics, Feedback
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What are aspects of a good design?
innovative
useful
environmentally friendly
aethestic
as little design as possible
honest
long-lasting
consistent
Describe the role feedback plays
Feedback is essential part of interactive systems. The user has to be informed what has happened to decide next actions.
SHOULD be:
prompt
clear and easy to understand
CAN be:
visual
auditory
tactile
combo of the above
What are feedback cycles?
take an action, observe the results, and adjust the behavior
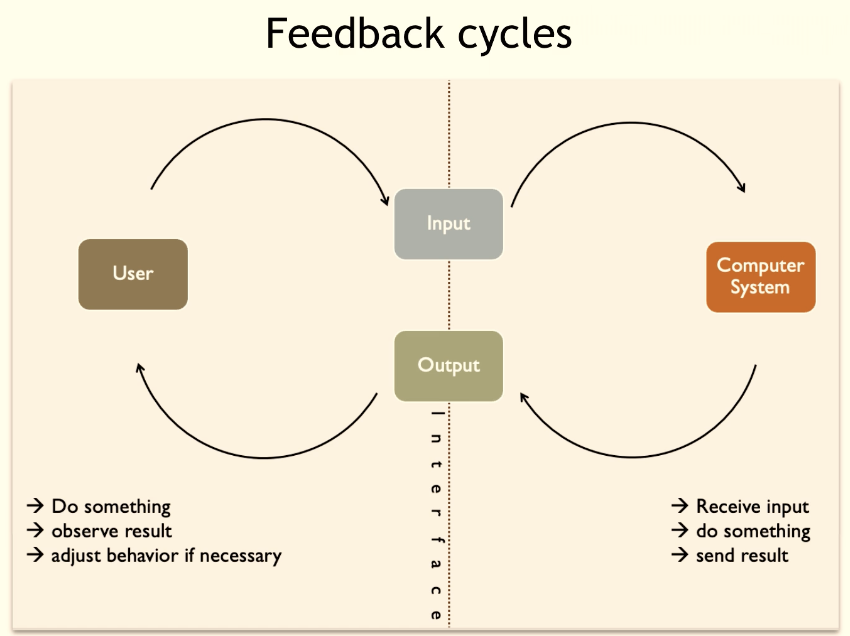
Are feedback cycles limited to human-computer interaction?
NO
Autonomous Systems
Feedback control
(Deep) reinforcement learning
Reward
Machine learning
Backpropagation
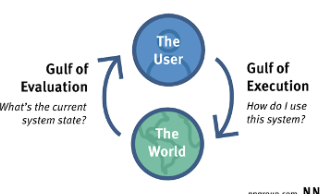
What is a gulf and what are the 2 gulfs?
Gulf of execution: How the system operates
Gulf of evaluation: Figure out how to change it
“With every interaction, users must overcome the twin challenges of understanding the current state of a system and figuring out how to change it.”
*DESIGNER’S RESPONSIBILITY TO BRIDGE/minimize THESE 2 GULFS
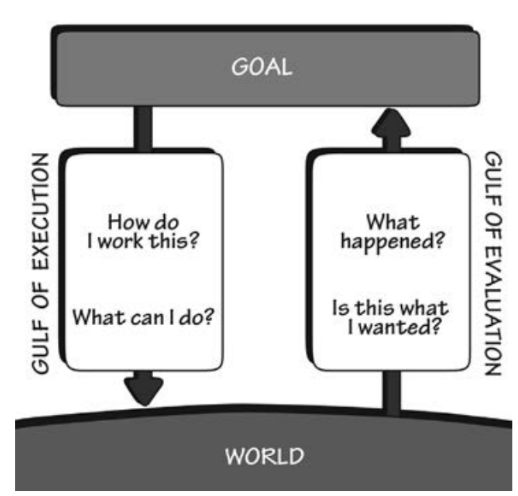
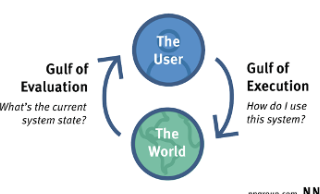
What is the gulf of execution?
The difference between the intentions of the users and what the system allows them to do (or how well the system supports those actions)
Describe an example of not bridging the gulf of execution
Your goal is to watch a movie in these three options. Soon you realize that the action that you performed does not yield the results that you want it.
You push a wrong button
You put DVD in a wrong way
You double-tap instead of holding once
How do you bridge the gulf of execution?
Use affordances (and signifiers only if necessary)
For novice users make actions visible/discoverable
For expert users reduce the number of steps (give them short cuts)
Provide feedforward (show user what will happen if the action continue)
Minimize effort need to execute each action
What is skeuomorphism? - gulf of execution
“a term most often used in graphical user interface design to describe interface objects that mimic their real-world counterparts in how they appear and/or how the user can interact with them.”
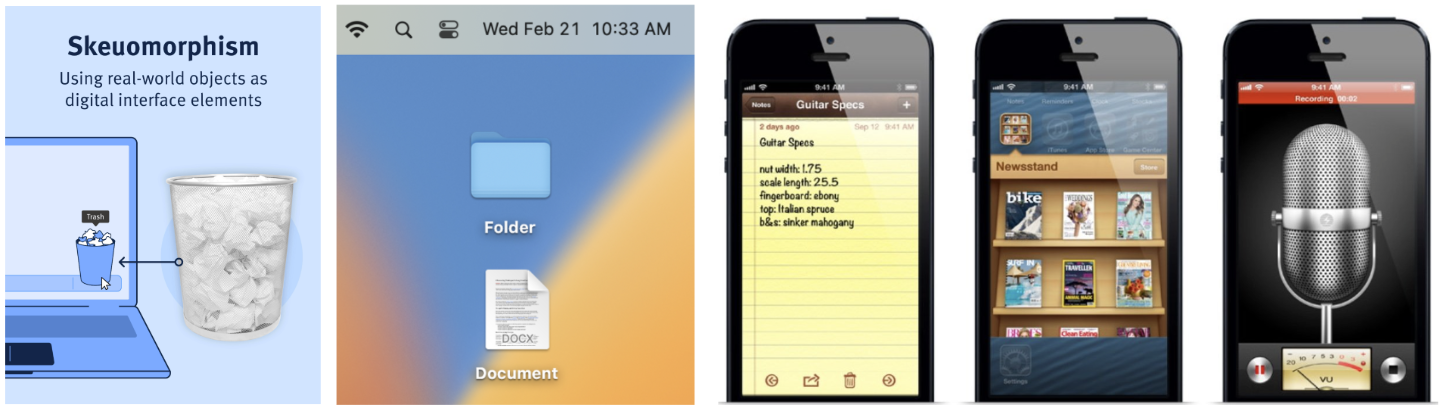
What is the gulf of evaluation?
The difficulty of assessing the state of the system and how well the artifact supports the discovery and interpretation of that state
Describe an example of not bridging the gulf of evaluation
Problem: after you performed an action there is no understandable feedback by the app. So the designers failed to bridge the gulf of evaluation.
ex. You downloaded a software from an app store, when you click on a button you continuously see the screen on on the right.
What is going on here?
What do rotating sticks represent?
What will be a purpose of this kind of feedback?

How do you bridge the gulf of evaluation?
Give feedback frequently
Give feedback immediately
Balance feedback with actions
Vary the feedback (audio vs. visual)
Use direct manipulation
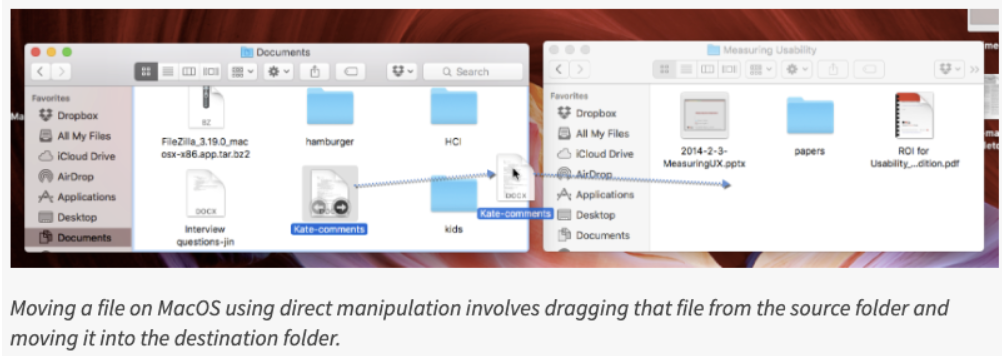
What is direct manipulation? - gulf of evaluation
Direct manipulation (DM) is an interaction style in which users act on displayed objects of interest using physical, incremental, reversible actions whose effects are immediately visible on the screen.
The performed action should be similar to the natural one
What are the 3 design principles/heuristics (shortcuts)?
Shneiderman’s 8 golden rules
Norman’s 7 principles
Nielsen’s usability Heuristics
At this stage, you can assume you already developed a high-fidelity prototype

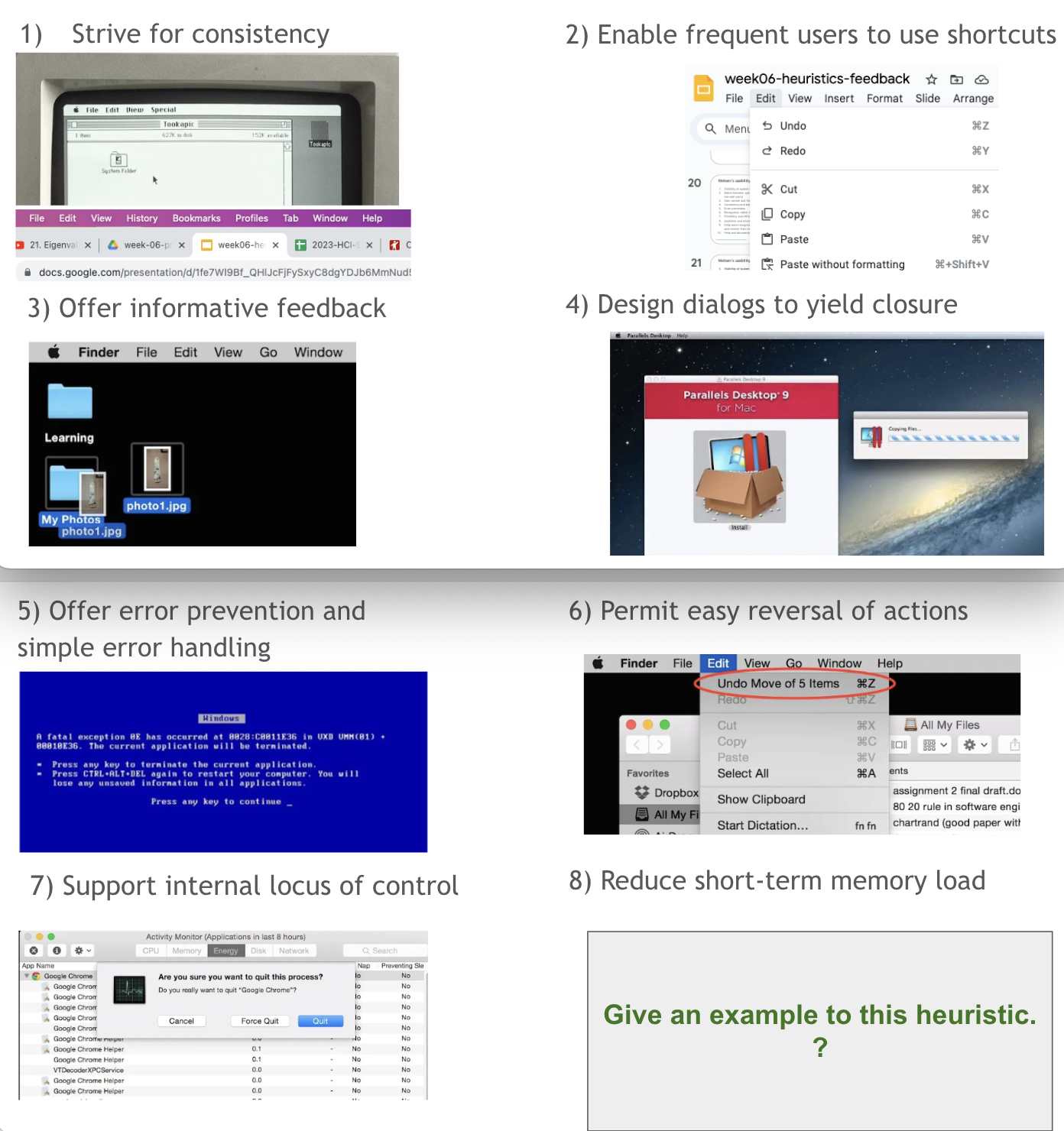
What are Shneiderman’s 8 golden rules?
Strive for consistency
Enable frequent users to use shortcuts
Offer informative feedback
Design dialogs to yield closure
Offer error prevention and simple error handling
Permit easy reversal of actions
Support internal locus of control
Reduce short-term memory load

What are Norman’s 7 Principles?
Use both knowledge in the world and knowledge in the head.
Simplify the structure of tasks.
Make things visible.
Get the mappings right.
Exploit the power of constraints, both natural and artificial.
Design for error.
When all else fails, standardize.

What are Nielsen’s 10 usability heuristics?
They are called "heuristics" because they are broad rules of thumb and not specific usability guidelines
Visibility of system status
The design should always keep users informed about what is going on, through appropriate feedback within a reasonable amount of time.
Match between system and the real world
The design should speak the users' language. Use words, phrases, and concepts familiar to the user, rather than internal jargon. Follow real-world conventions, making information appear in a natural and logical order.
User control and freedom
Users often perform actions by mistake. They need a clearly marked "emergency exit" to leave the unwanted action without having to go through an extended process.
Consistency and standards
Users should not have to wonder whether different words, situations, or actions mean the same thing. Follow platform and industry conventions.
Error prevention
Good error messages are important, but the best designs carefully prevent problems from occurring in the first place. Either eliminate error-prone conditions, or check for them and present users with a confirmation option before they commit to the action.
Recognition rather than recall
Minimize the user's memory load by making elements, actions, and options visible. The user should not have to remember information from one part of the interface to another.
Flexibility and efficiency of use
Shortcuts — hidden from novice users — may speed up the interaction for the expert user so that the design can cater to both inexperienced and experienced users. Allow users to tailor frequent actions.
Aesthetic and minimalist design
Interfaces should not contain information that is irrelevant or rarely needed. Every extra unit of information in an interface competes with the relevant units of information and diminishes their relative visibility.
Help users recognize, diagnose, and recover from errors
Error messages should be expressed in plain language (no error codes), precisely indicate the problem, and constructively suggest a solution.
Help and documentation
It’s best if the system doesn’t need any additional explanation. However, it may be necessary to provide documentation to help users understand how to complete their tasks.
