GAMETOGENESIS [EXAM LIKE QUESTIONS]
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
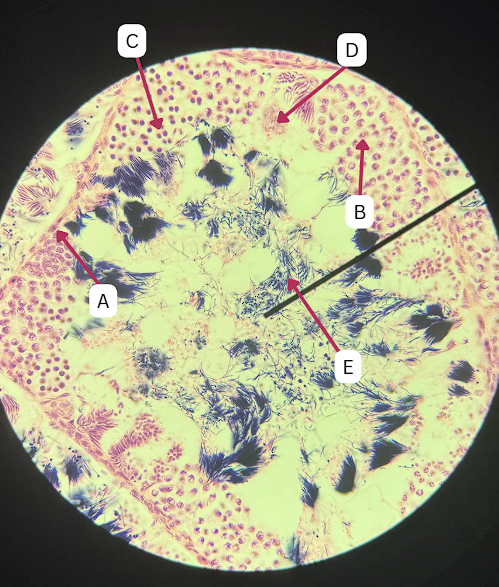
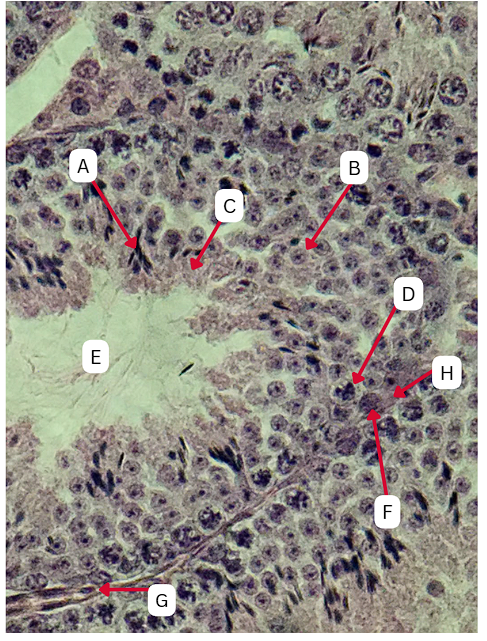
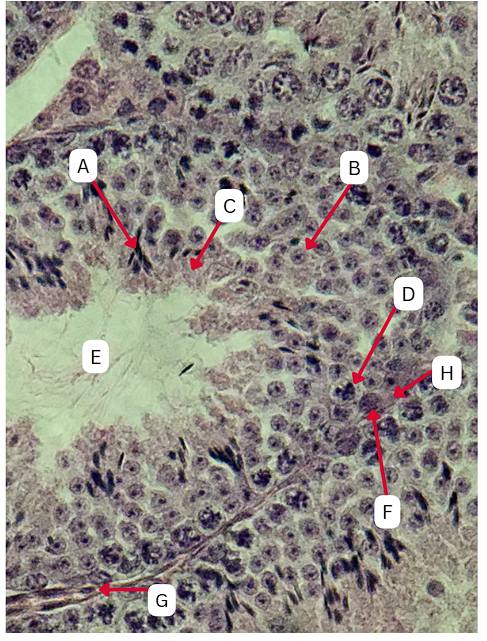
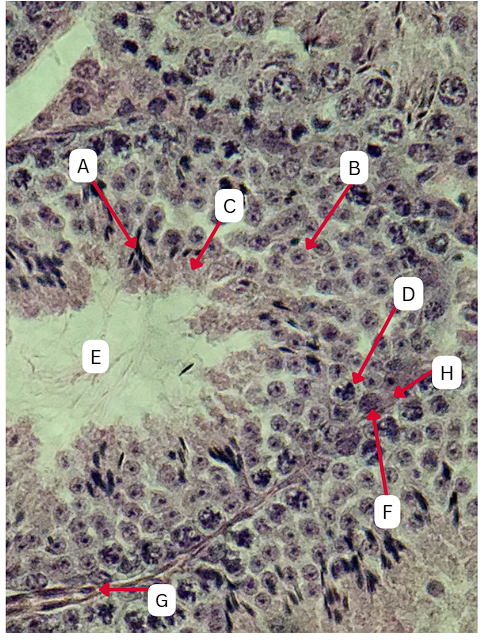
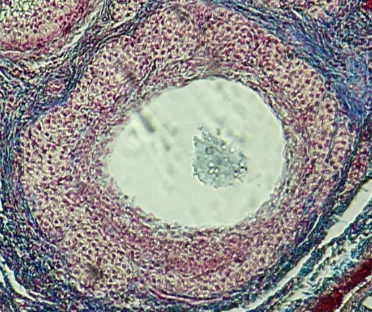
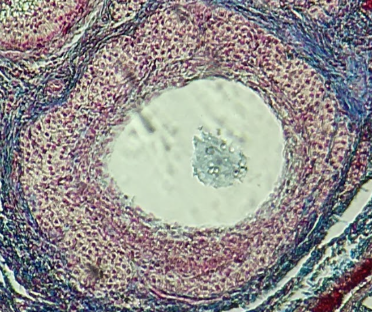
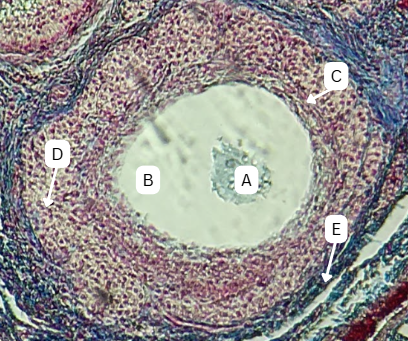
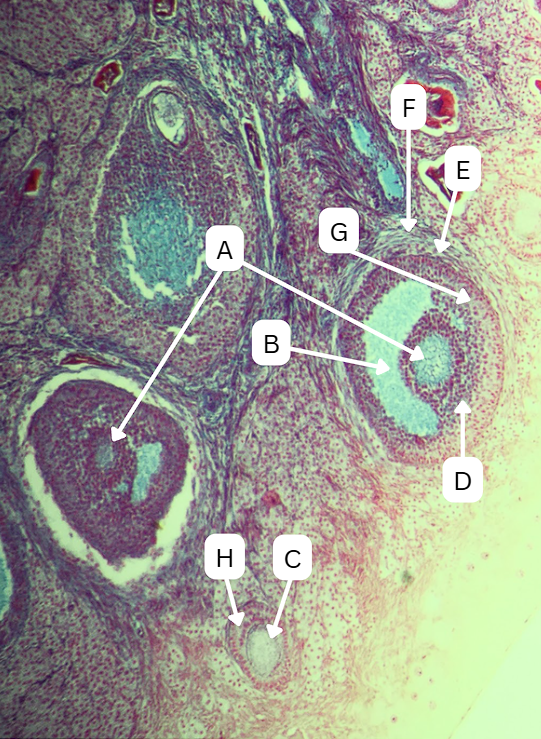
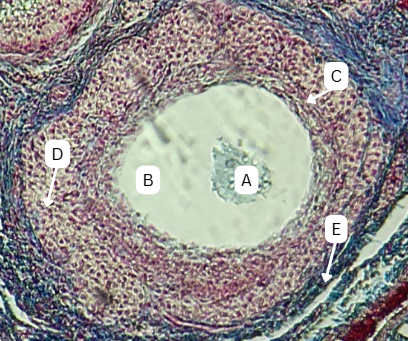
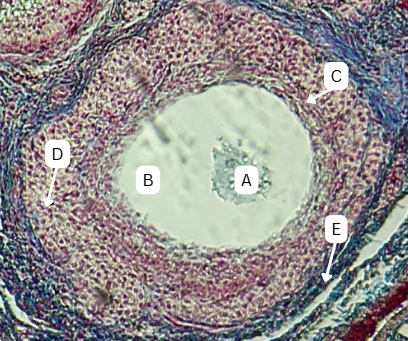
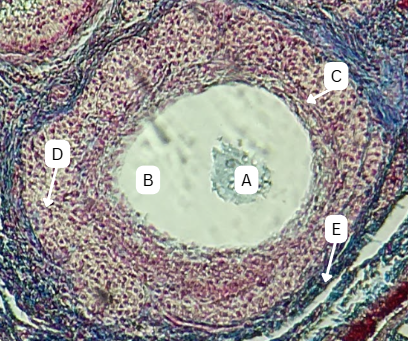
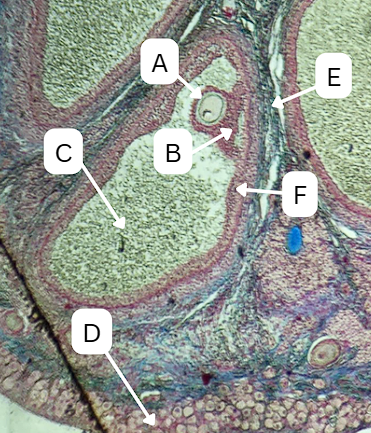
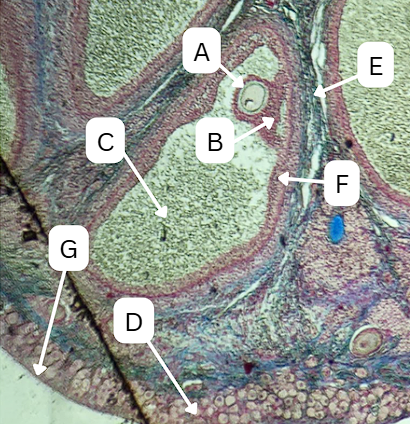
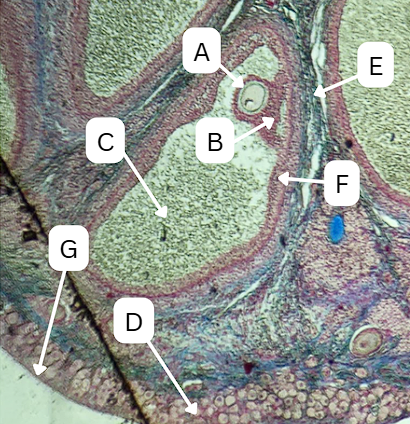
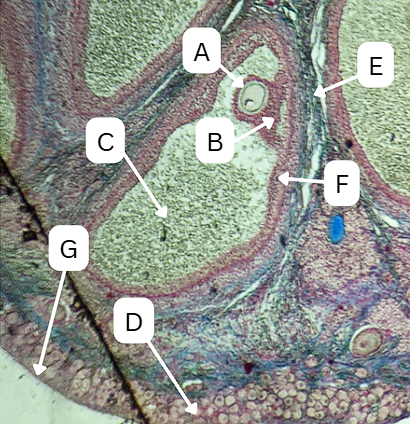
Seminiferous Tubules
Identify the whole structure presented in the image.
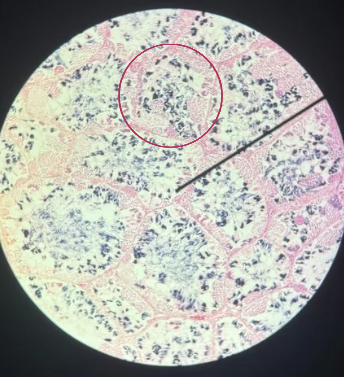
Lumen
What is the term used to describe the central, fluid-filled space within this structure where the process of spermatogenesis occurs in the male reproductive system?
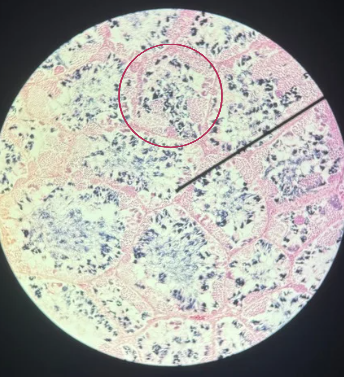
Spermatogenesis
What do you call the process of producing the sperm?
Frog
The specimen shows the testis of what animal?
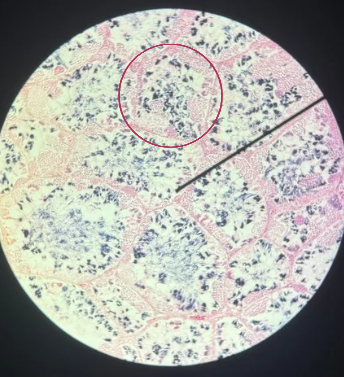
Mouse
The specimen shows the testis of what animal?
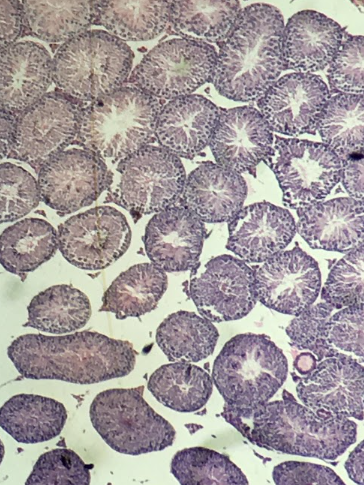
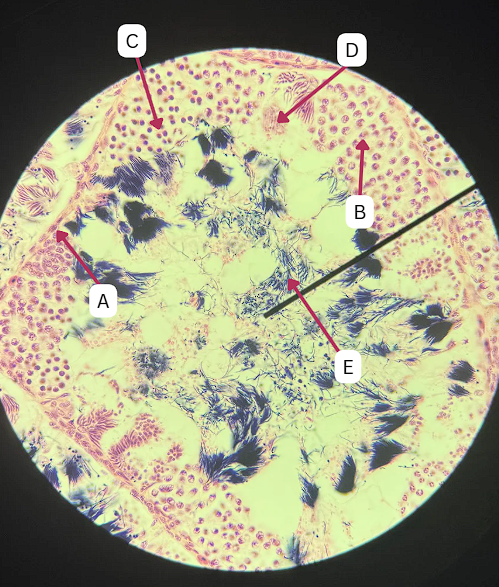
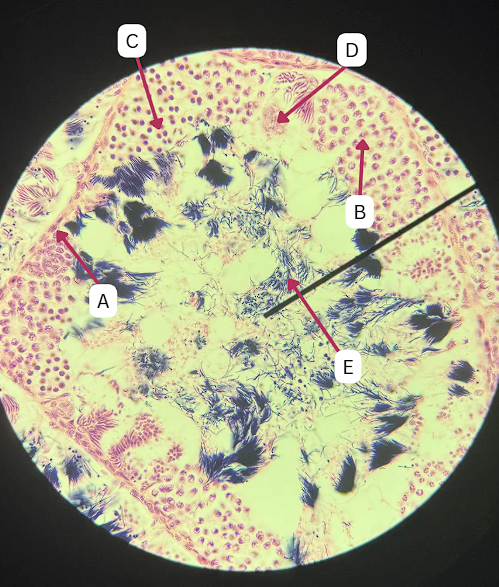
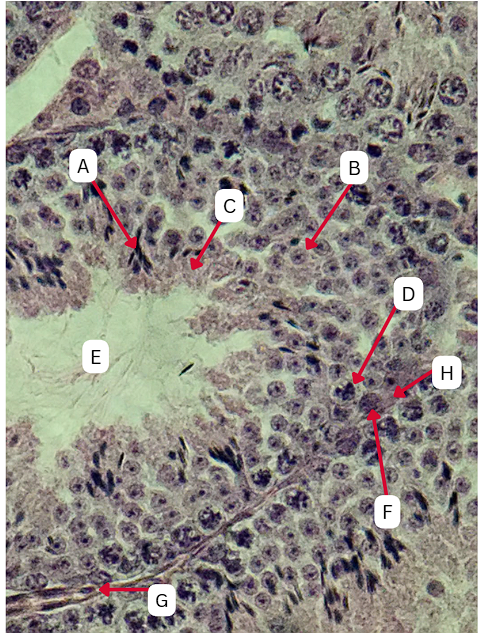
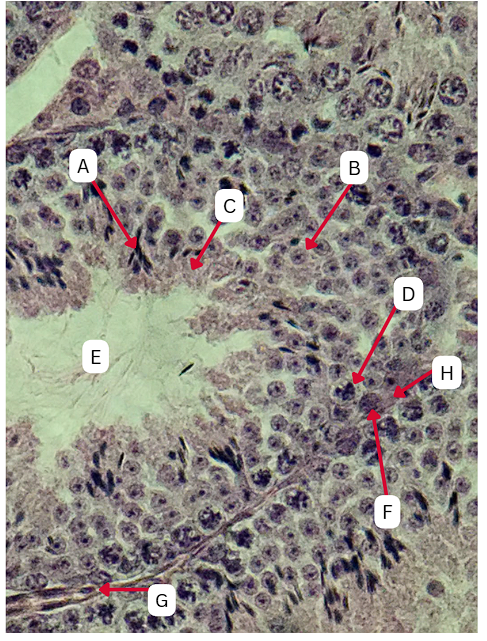
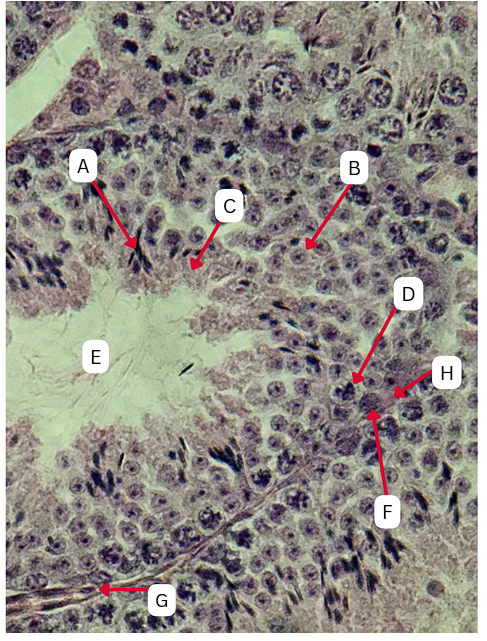
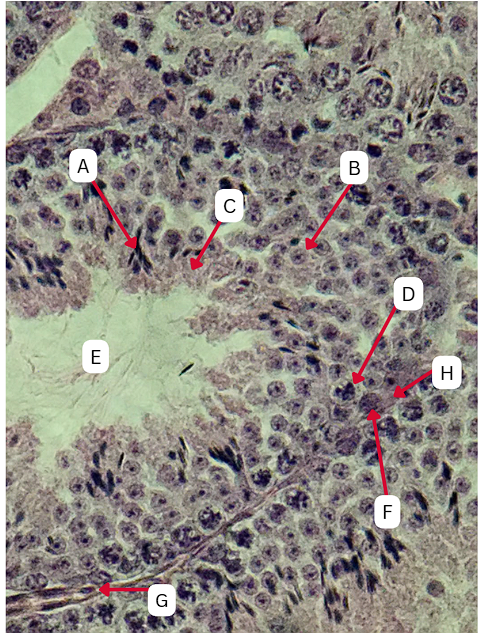
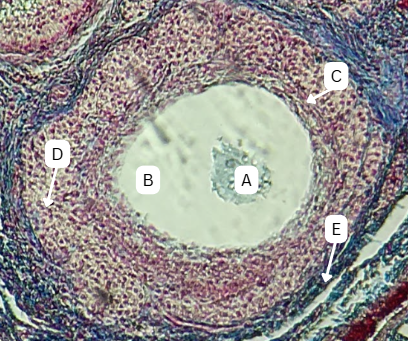
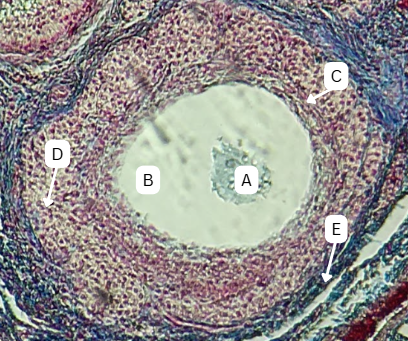
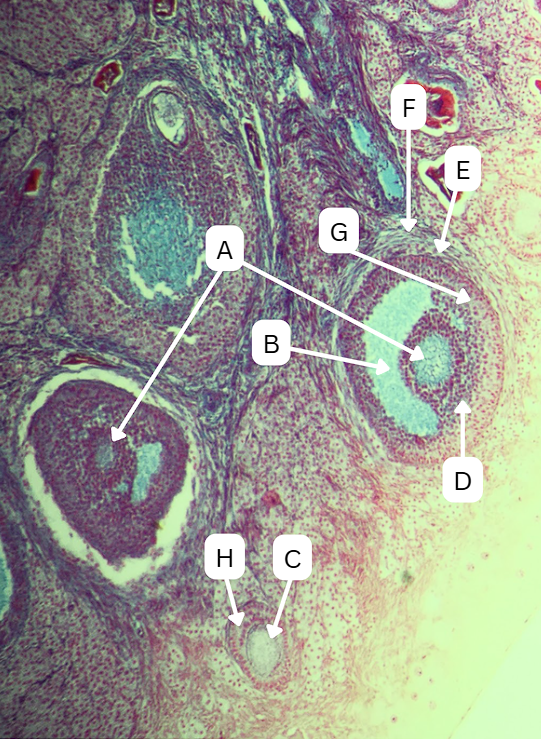
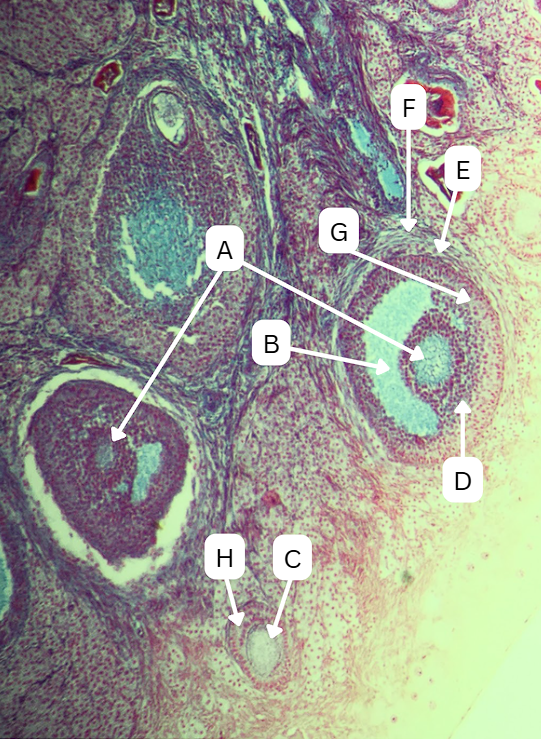
Spermatogonia
What is the cell stage at A
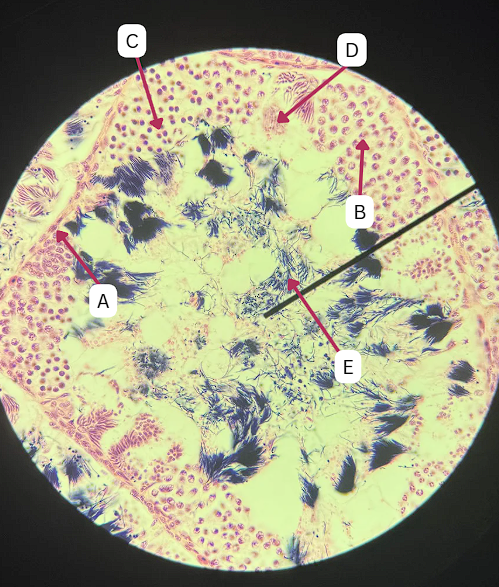
B
The stage after A is what letter?
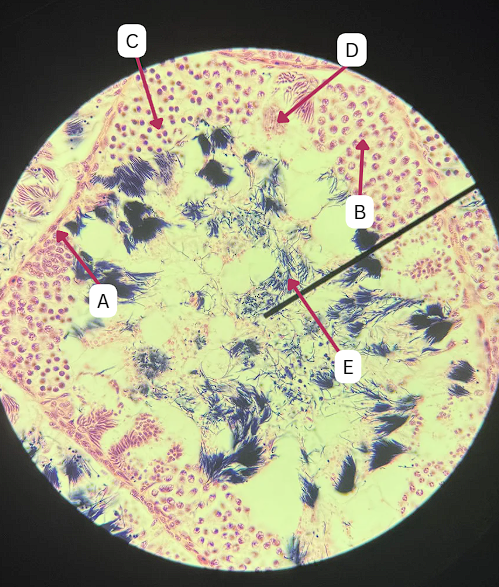
Primary Spermatocyte
What cell stage is B at?
FALSE
TRUE OR FALSE
A is a haploid cell
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE
B is a diploid cell
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE
Sperm cell development starts from outermost going towards to innermost
Spermatid
What is the cell stage of C?
A
What is the letter of the stage after C?
Secondary spermatocyte
What is the stage before C?
Spermiogenesis
What is the term used to describe the final stage of sperm cell development, during which C undergoes significant structural and functional changes to become A?
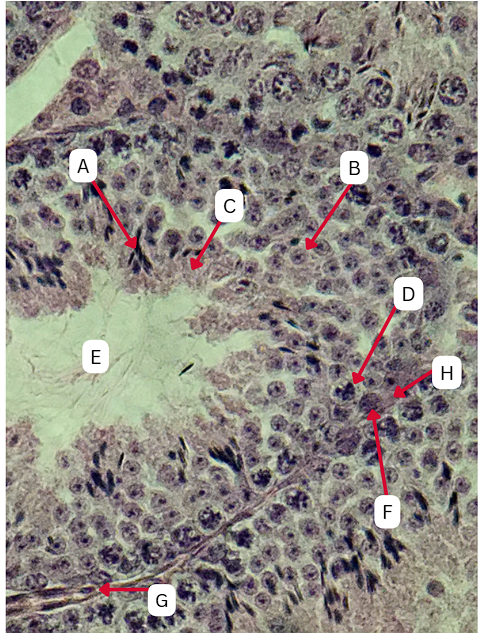
Sertoli cells
What cellular structures provide physical and nutritional support to cells during spermatogenesis?
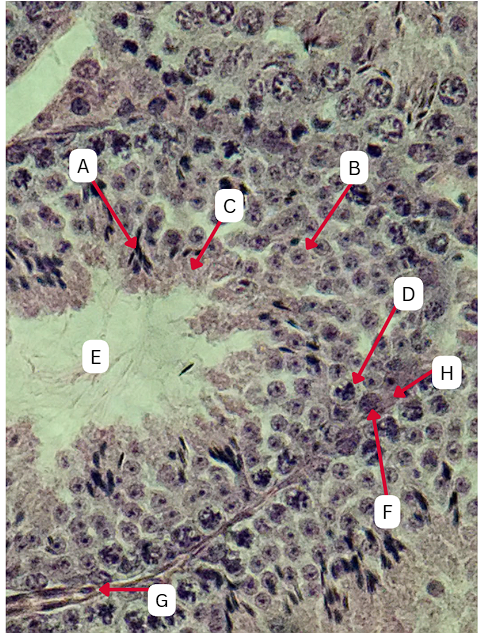
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE
F is the first stage of maturation in the sperm
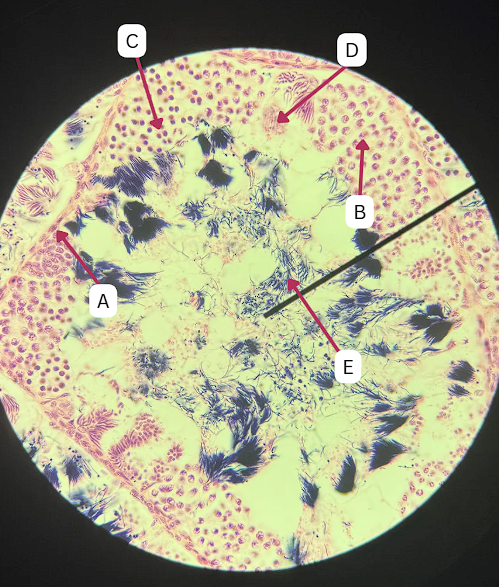
Spermatozoa
What is the cell stage of E?
Functional male gamete
What is the fate of A?
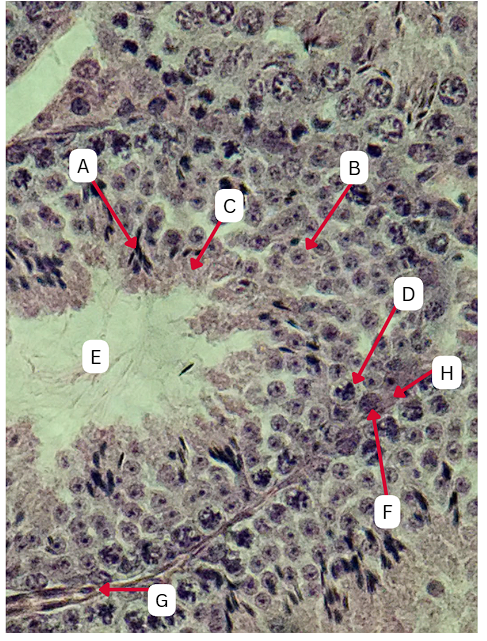
Endoderm
What is the origin germ layer of A?
Spermatid
What is the fate of B?
Endoderm
What is the origin germ layer of B?
Spermatozoa
What is the fate of C?
Endoderm
What is the origin germ layer of C?
Secondary Spermatocyte
What is the fate of D?
Endoderm
What is the origin germ layer of D?
Primary Spermatocyte
What is the fate of G?
Endoderm
What is the origin germ layer of G?
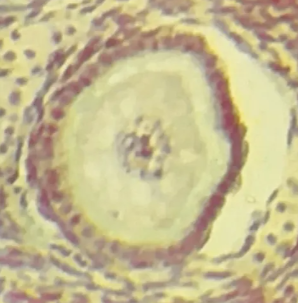
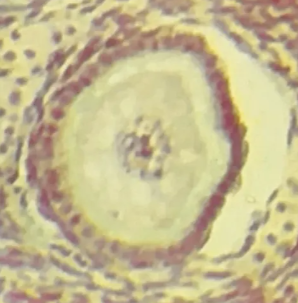
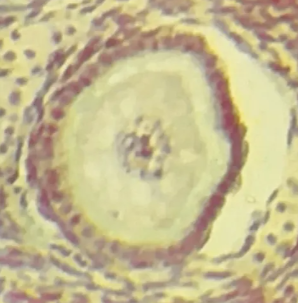
Primary follicle
Identify the whole structure presented in the image.
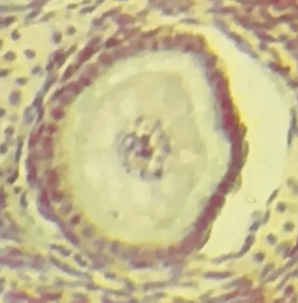
Follicle cells
What type of cells are surrounding the structure?
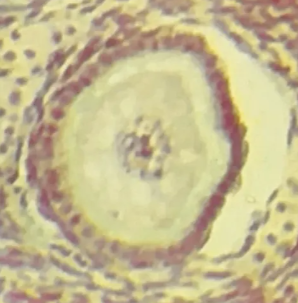
One
How many layer/s of follicle cells are present in this picture?
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE
This is the earliest stage of ovarian follicle development.
Cat
What specimen is this?
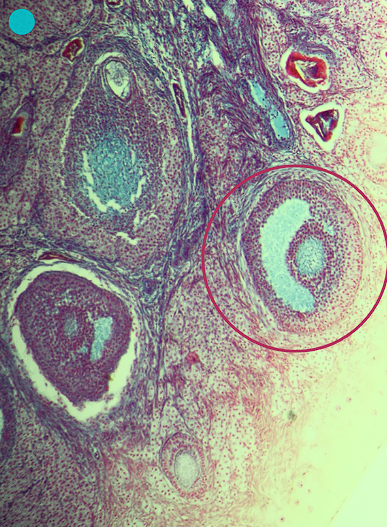
Secondary Follicle
Identify the whole structure presented in the image.
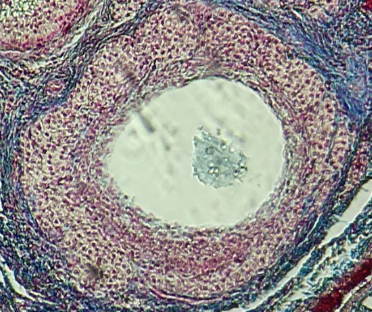
Atresia or tertiary follicle
What is the fate of this structure?
Mesoderm
What is the germ layer origin of this structure?
Oocyte
What is structure A?
Zona Pellucida
What is the thick acidophilic-staining glycoprotein layer surrounding A that encloses the vitelline membrane?
Stratum Granulosa
What is the structure that surrounds A with multiple layers?
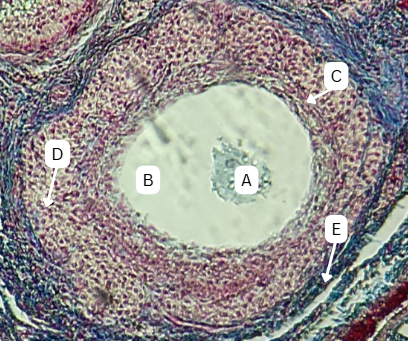
Corona Radiata
What is the fate of C?
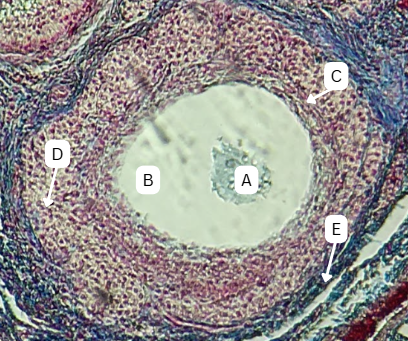
Mesoderm
What is the origin germ layer of C?
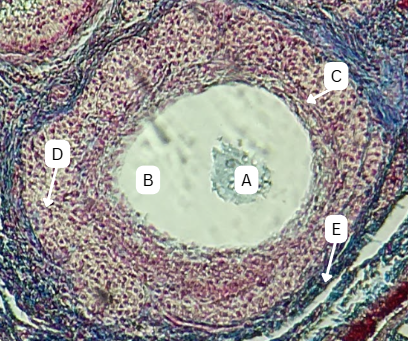
Persists until Fertilization
What is the fate of B?
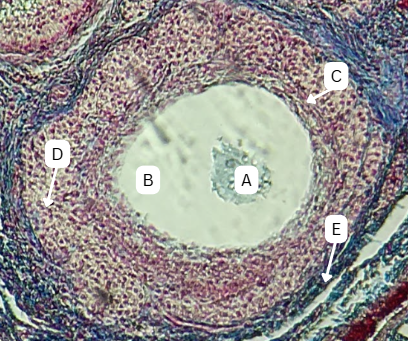
Endoderm
What is the origin germ layer of B?
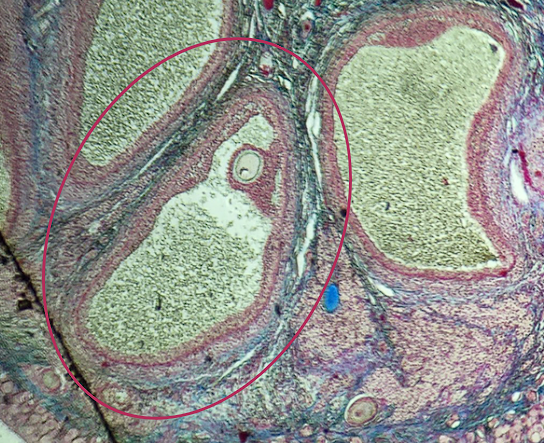
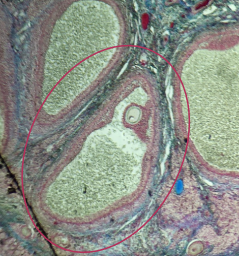
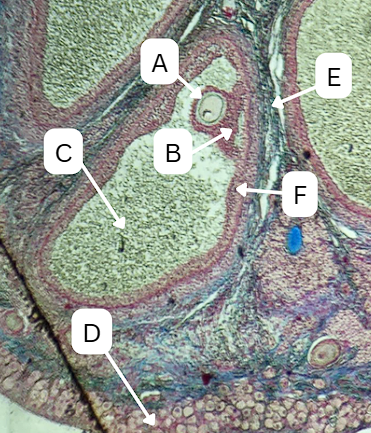
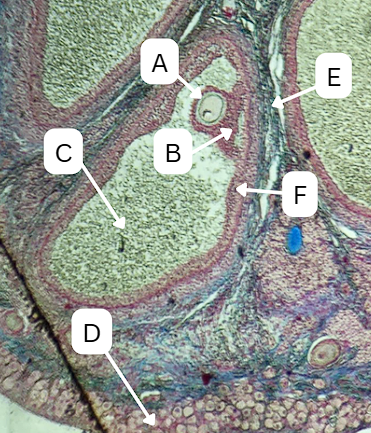
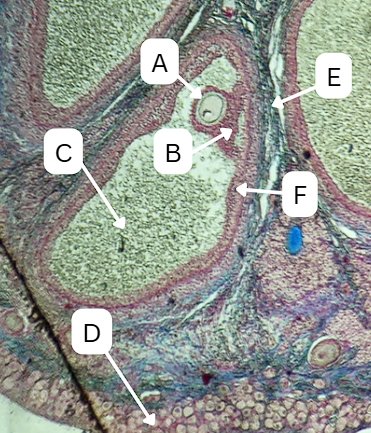
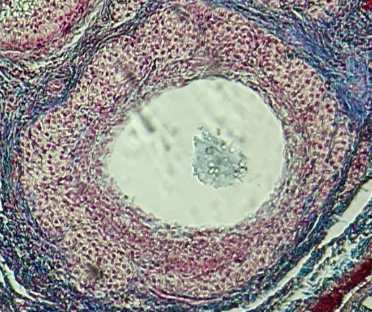
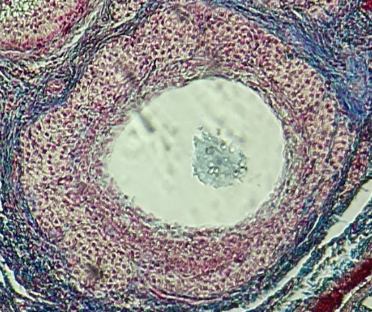
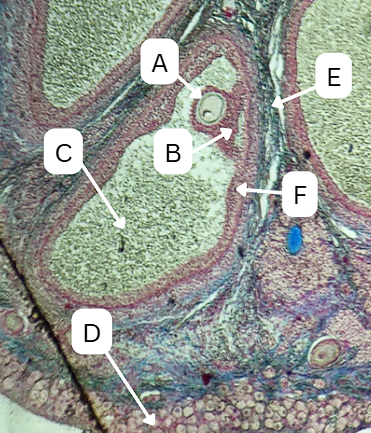
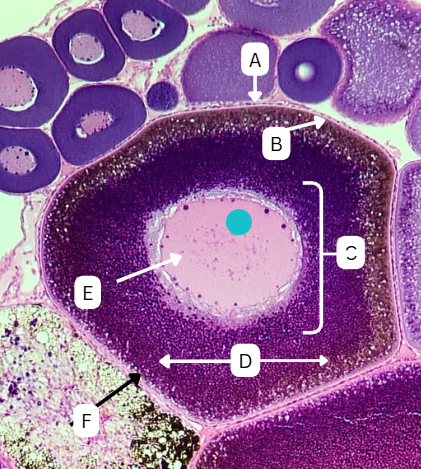
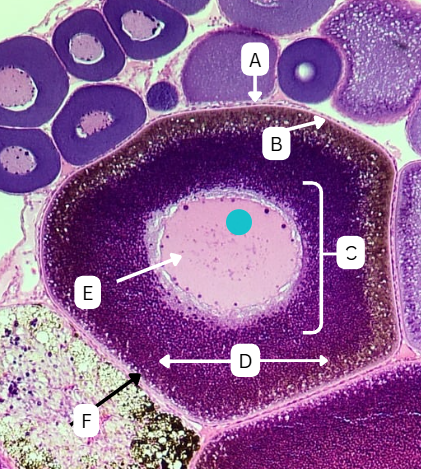
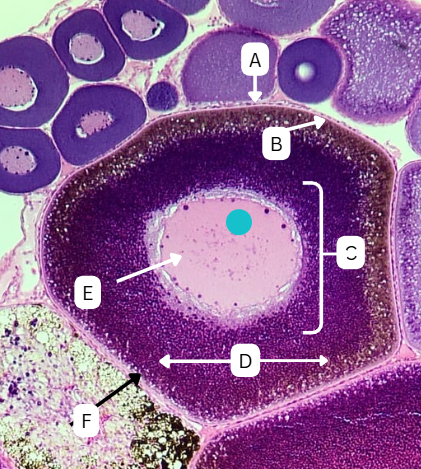
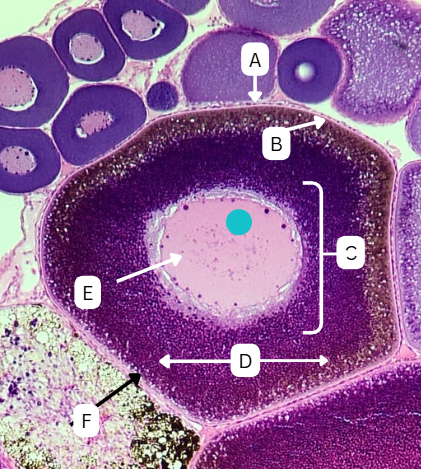
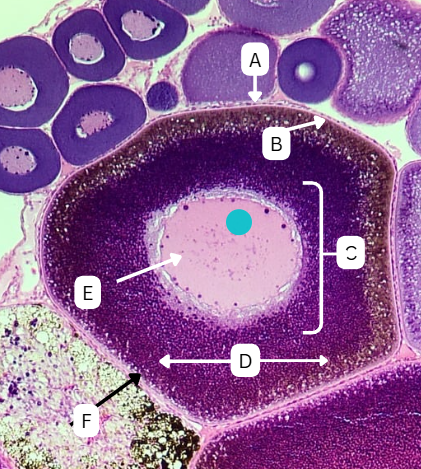
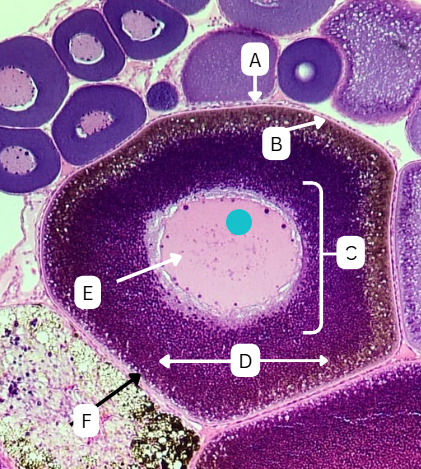
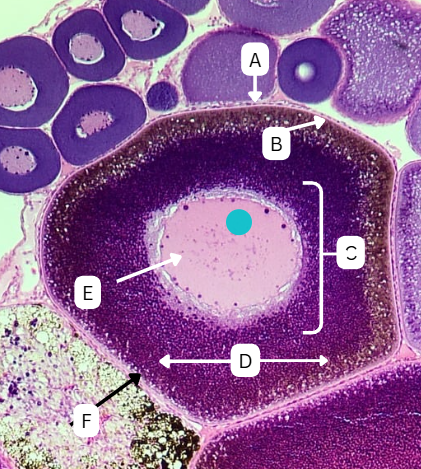
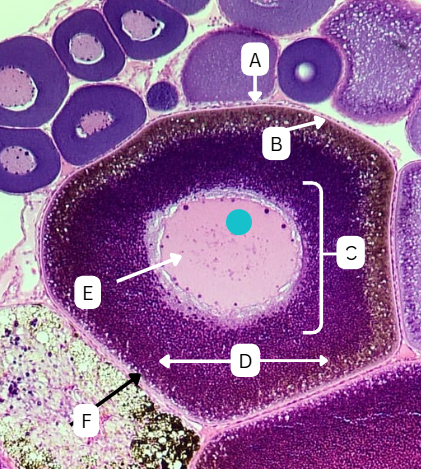
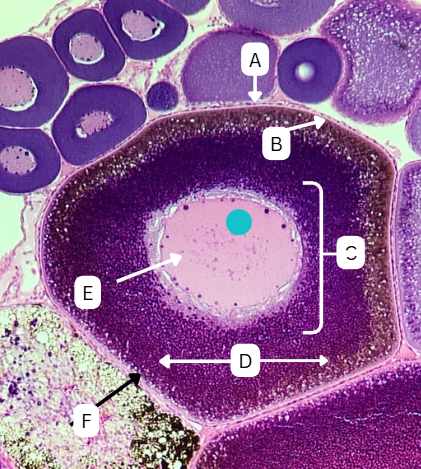
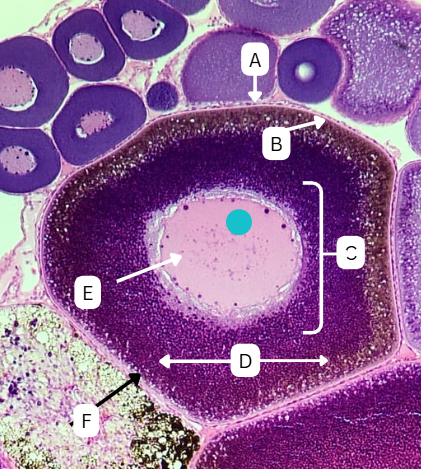
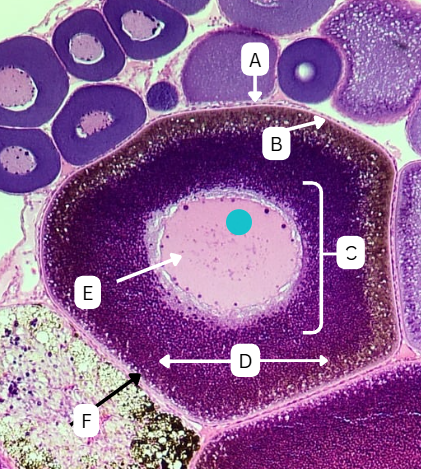
Tertiary Follicle
Identify the encircled structure presented in the image.
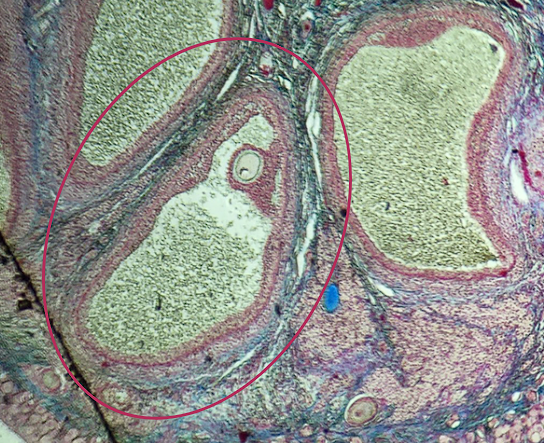
Corpus luteum
What term describes the structure consisting of the remnants of the ruptured encircled structure after ovulation?
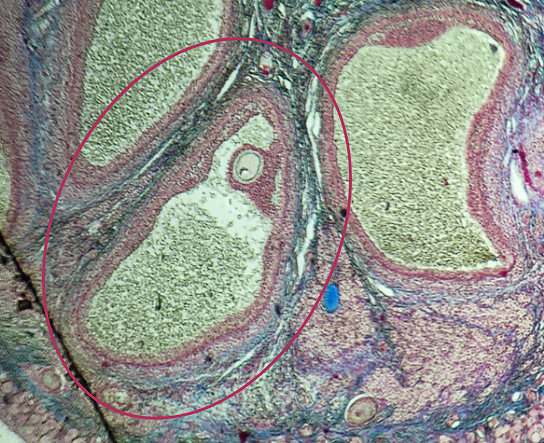
Ovulation
The secondary oocyte is usually located at the side of the encircled structure in preparation for which process?
Antrum
What is the fluid-filled cavity surrounding A?
Atresia or Ovulation
What is the fate of this structure?
Mesoderm
What is the origin germ layer of this structure?
Collapses during ovulation
What is the fate of the fluid-filled cavity surrounding A?
Mesoderm
What is the origin germ layer of B?
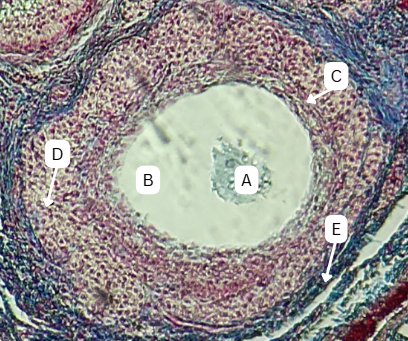
Corona Radiata
Identify the layer of cells in structure A directly adjacent or immediately surrounding the zona pellucida of a secondary oocyte
Cumulus Oophorus
Identify the thickened cluster of cells in structure B surrounding the oocyte.
Granulosa Cells
What type of cells comprise A and B?
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE
"Structure B" facilitates the transport of the oocyte from the ovary to the fallopian tube after ovulation.
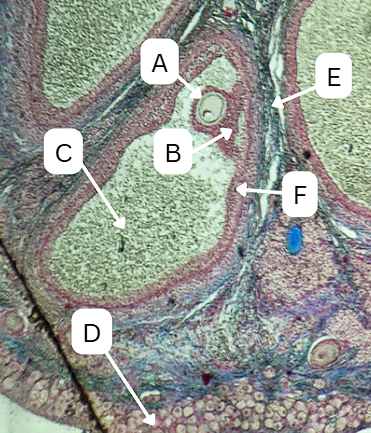
Theca cells
During this stage, what type of cells start to form around the follicle which plays a crucial role in the production of androgens and supporting the development of the growing follicle?
False
TRUE OR FALSE
The antrum is absent in this stage of oogenesis.
Theca Externa
Theca cell E is the outer layer made up of collagen fibers
Theca Interna
Theca cell D is the inner layer secreting androgens
Degenerates after ovulation
What is the fate of theca cells?
Mesoderm
What are the origin germ layers of theca cells?
ovulated together with oocyte
What is the fate of structure A and B?
Mesoderm
What is the origin germ layer of structure A and B?
Primordial Follicles
Structure D contains the primary oocyte surrounded by a thin layer of squamous follicle (granulosa) cells and an extemal basal lamina
Tunica Albuginea
What is the thin, fibrous connective tissue capsule located directly beneath structure D?
Mesoderm
What is the germ layer origin of structure D?
Frog
What ovary specimen is this?
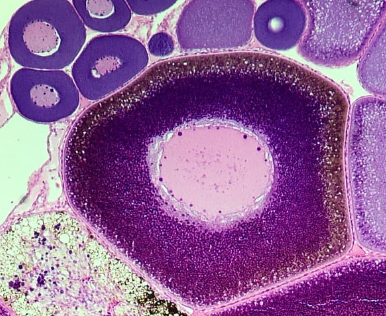
C
What letter is the food source of the embryo?
Cytoplasm
What is the fate of structure C?
Endoderm
What is the germ origin layer of structure C?
Germinal Vesicle
What is the structure that C is surrounding?
Nucleus
What is the fate of the structure that C is surrounding?
Endoderm
What is the germ origin layer of the structure that C is surrounding?
Vitelline Membrane
What is the dark thin line surrounding the plasma membrane?
Egg Membrane
What is the fate of structure F?
Endoderm
What is the germ origin layer of structure F?
Follicle cells
What do you call the cluster of spherical cells that help with the egg’s maturation inside the structure?
Degenerates after ovulation
What is the fate of the cluster of spherical cells?
Mesoderm
What is the germ origin layer of structure D?
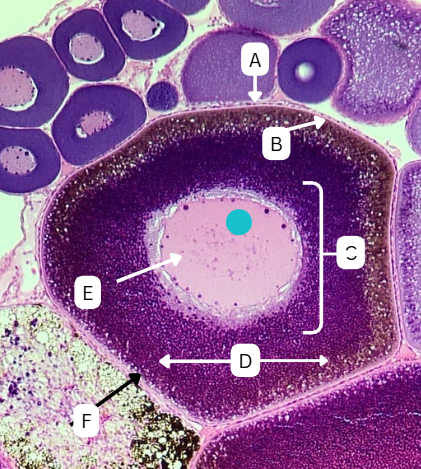
Primary Oocyte
What is the large cell surrounded by follicle cells with small centrally located nucleus?
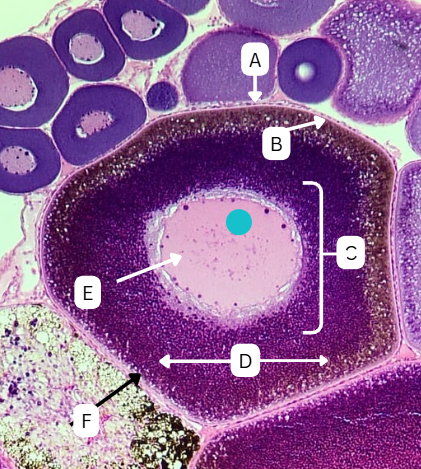
Secondary Oocyte or Ovum
What is the fate of the primary oocyte?
Endoderm
What is the germ origin layer of the primary oocyte?