CSE13S Lecture 8 & 9
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
GDB
GNU Project Debugger, a command-line tool used to debug programs by controlling their execution and inspecting their state
cc –g hello.c –o hello
Add the –g option with the cc command to enable debugging
Two debugging tools
GNU Debugger (gdb) – for logical errors
○ Valgrind – for memory errors
Starting up gdb
Simply run gdb passing the executable in the argument
○ Example: gdb ./hello
The GNU Debugger (gdb)
What can you do with gdb?

What is an array?
The size may be determined either at compile time (static memory allocation) or at run
time (dynamic memory allocation).
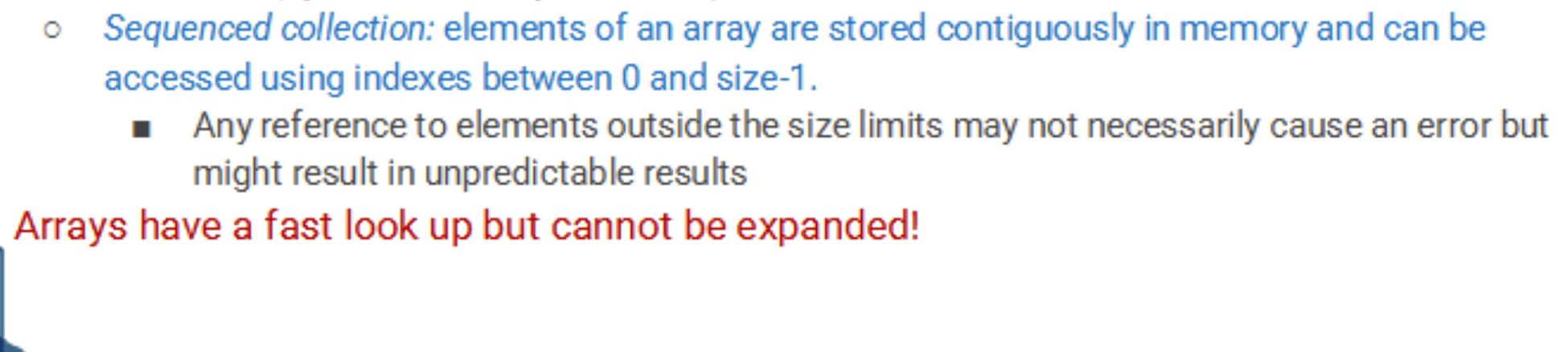
Static arrays:
declared using static memory allocation technique
○ Size is fixed and specified in the code
○ Memory is allocated at compile time on the
function stack frame
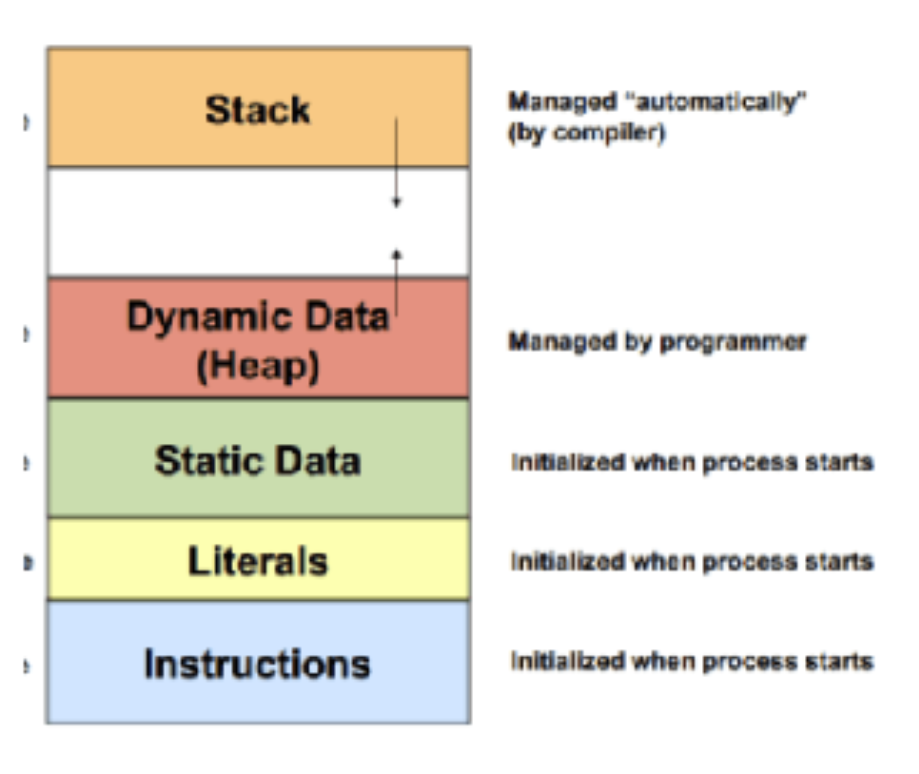
Dynamic arrays:
declared using dynamic
memory allocation technique
○ Size is specified at run-time
○ Memory is allocated at run time from the heap
○ Memory allocated using functions such as
malloc, calloc and realloc from the stdlib.h file
Array initialization:
type array-name[size] = {list of values};
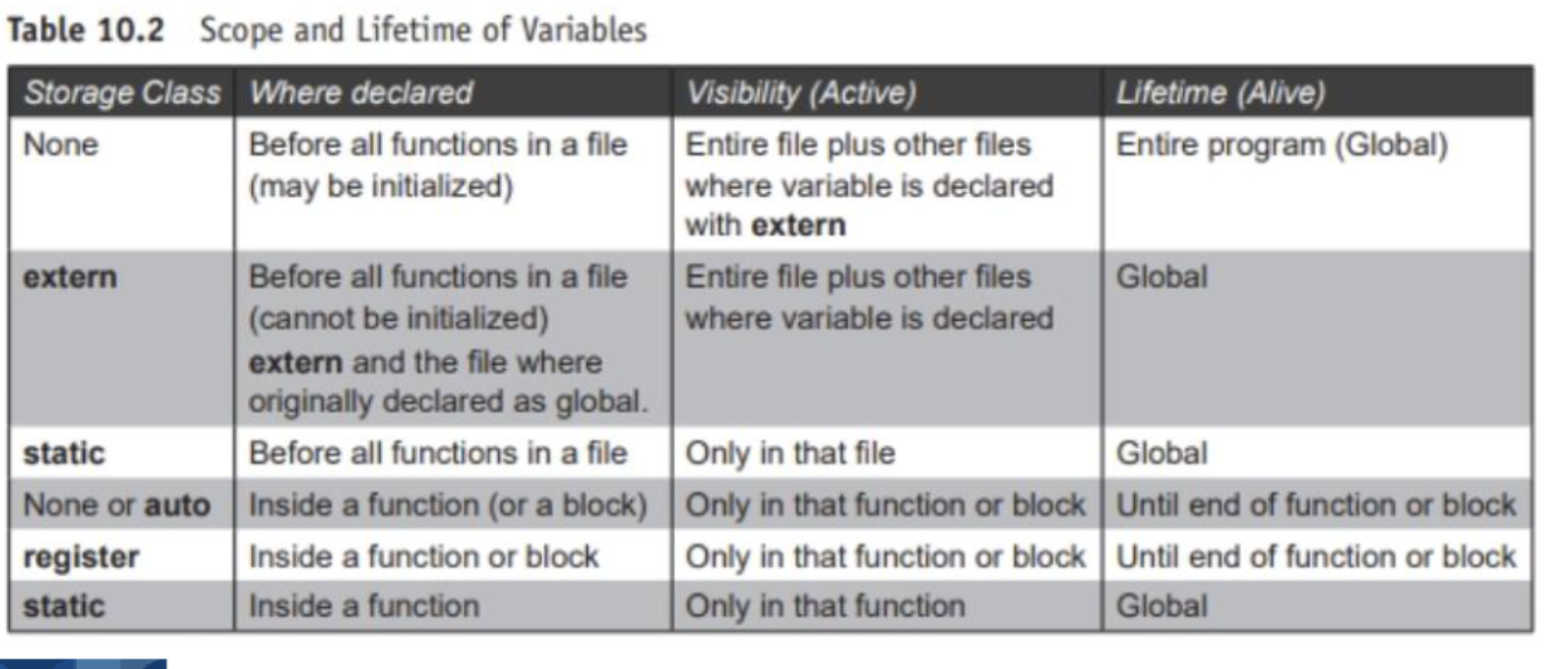
Summary of scope and lifetime of variables
Macros for functions
Example: #define MIN(x, y) ((x) < (y) ? (x) : (y))
Example: #define MAX(x, y) ((x) > (y) ? (x) : (y))
(condition) ? (expression_if_true) : (expression_if_false)
So it works like:
If condition is true → result = expression_if_true
If condition is false → result = expression_if_false
Passing 2-D arrays to functions
Function must be called by passing only the array name
○ Function declaration and definition must indicate that the array has 2 dimensions by including
2 sets of brackets
○ The size of the second dimension must be specified