QZLT Medical Surgical Nursing II: Acid-Base Balance & Fluid-Electrolyte Balance
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Blood and plasma are which type of fluid?
intravascular
Kussmaul respirations
very deep, labored breathing (usually associated with diabetic acidosis and renal failure)
Body's compensation for metabolic acidosis
Daily Weights
best indicator of fluid loss or retention
Tx for hyperkalemia
restricting potassium intake, loop diuretics, IV insulin +glucose(which forces K into the cells), Kayexelate(which binds to K), calcium gluconate through IV(which reduces membrane potential), or dialysis
food sources of calcium
-Milk
-Milk products
-Dark green leafy vegetables
-Salmon
-Calcium-fortified foods such as breads and cereals
signs of hyponatremia
Anorexia, nausea, cramps, fatigue, lethargy, muscle weakness, headache, confusion, seizures, decreased blood pressure
risk factors for hypocalcemia
smoking, lack of exercise, high alcohol consumption, anorexia, estrogen or testosterone deficiency, poor nutrition, obesity, post-menopausal women
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Hormone produced by the neurosecretory cells in the hypothalamus that stimulates water reabsorption from kidney tubule cells into the blood and vasoconstriction of arterioles.
Secreted to prevent further dehydration and encourage kidneys to retain fluids
Hypertonic
Having a higher concentration of solute than blood
Isotonic
Having the same solute concentration as blood.
Hypotonic
Having a lower concentration of solute than blood
Signs of hypocalcemia
-paresthesias followed by numbness
-hyperactive deep tendon reflexes
-a positive Trousseau's or Chvostek's sign
-neuromuscular excitability
-muscle cramps
-twitching
-tetany
-seizures, irritability, and anxiety
-increased gastric motility, hyperactive bowel sounds, abdominal cramping, and diarrhea.
sensible fluid losses
Measurable
Ex: from urination, defecation, & wounds
insensible fluid losses
Immeasurable
Ex: through the skin (affected by humidity & body surface area) & lungs (affected by respiratory rate and depth)
causes of hyponatremia
Fluid overload: heart failure, cirrhosis
Excessive water ingestion
Excessive infusion of D5W
SIADH
Dehydration
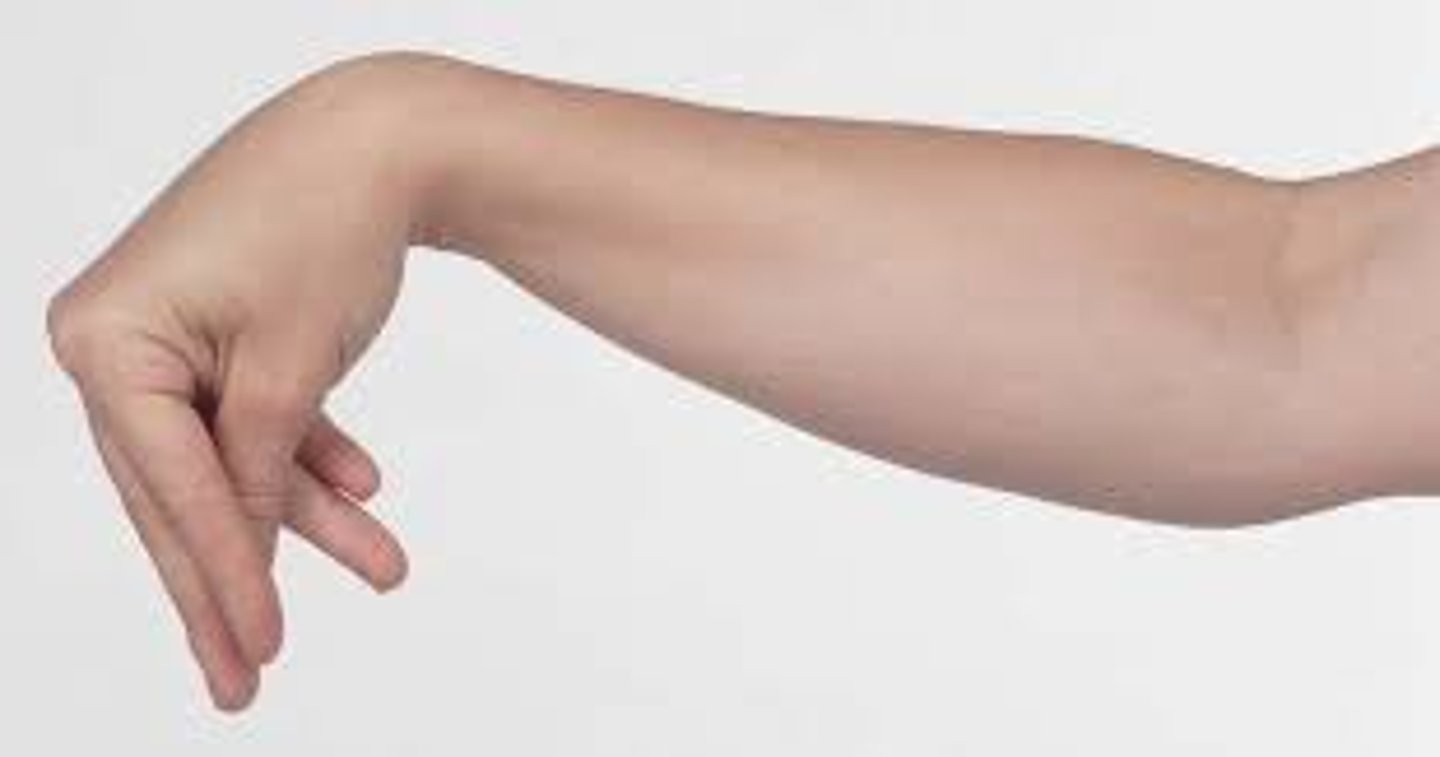
Trousseau sign
Spasmodic contractions caused by pressing the nerve supplying a muscle; seen in tetany

Chvostek's sign
Cheek, facial spasm when Cheek is tapped associates with hypocalcemia
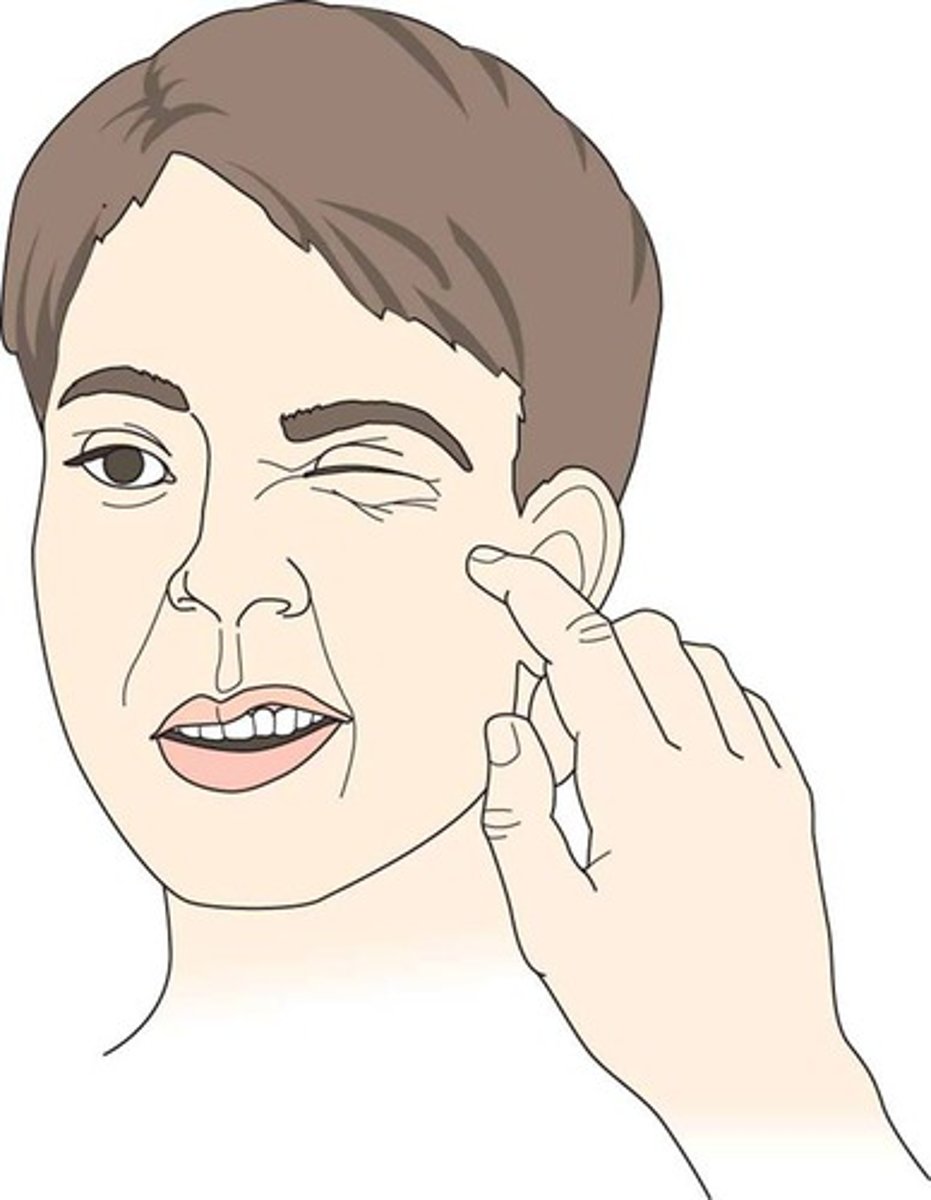
signs of hypovolemia
tachycardia, hypotension, weak pulse, loss of skin turgor, tachypnea, sunken eyes, orthostatic hypotension
treatment of hypovolemia
replace water and electrolytes with balanced IV solutions
Vitamin required to absorb calcium in the GI tract
Vitamin D
Electrolyte caused by hyperparathyroidism
hypercalcemia
Contraindications for IV fluid replacement
Heart Failure
possibly ESRD
food sources of potassium
Bananas
Oranges
Apricots
Figs
Dates
Carrots
Potatoes
Tomatoes
Spinach
Dairy products
Meats
Hypomagnesmia
lower than 1.5
causes: inadequate magnesium intake and absorption, increased excretion due to hypercalcemia or drugs such as furosemide, chronic alcoholism, malnutrition
signs/symptoms: lethargy, tremor, tetany, hyperreflexia, seizures, arrhythmias, *Torsades de pointes*
treatment: magnesium replacement
Hypermagnesmia
greater than 2.5
causes: acute renal failure, excess Mg/Al antacids
signs/symptoms: neuro and cardiac depression, drowsiness, hyporeflexia, decreased respiratory rate, cardiac arrest
treatment: saline and loop diuretics, possible hemodialysis
Hypercalcemia treatment
Treat underlying cause. Hydration, increasing salt intake, and forced diuresis (careful to prevent potassium or magnesium depletion), bisphosphonates and calcitonin
Edema is a sign of what fluid imbalance?
fluid volume overload
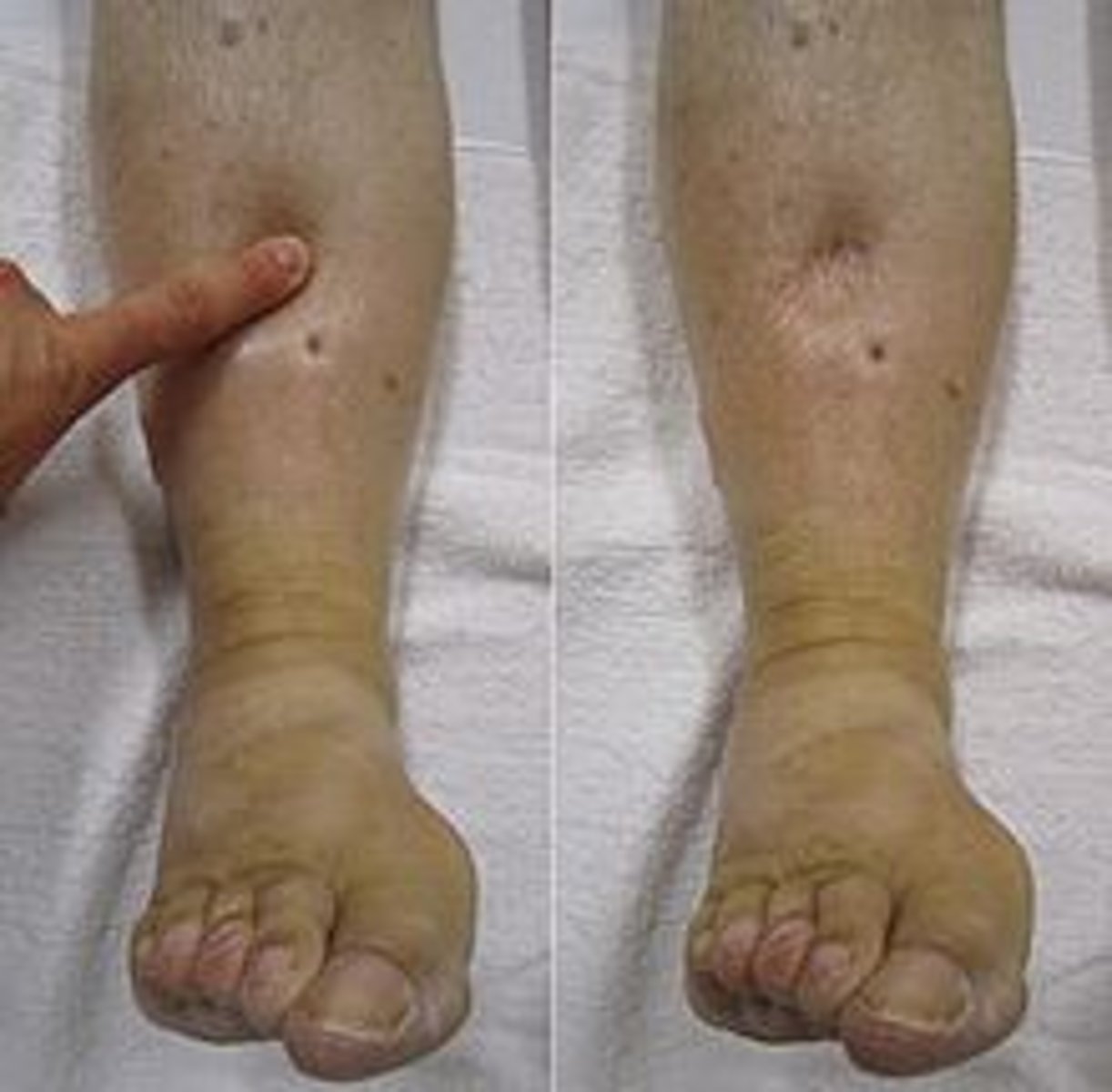
Interventions for fluid-volume overload
Raise head of bed
Stop IV fluid
Call doctor and get an order for Lasix ( furosemide)
Normal dose 20-40
Daily Weights
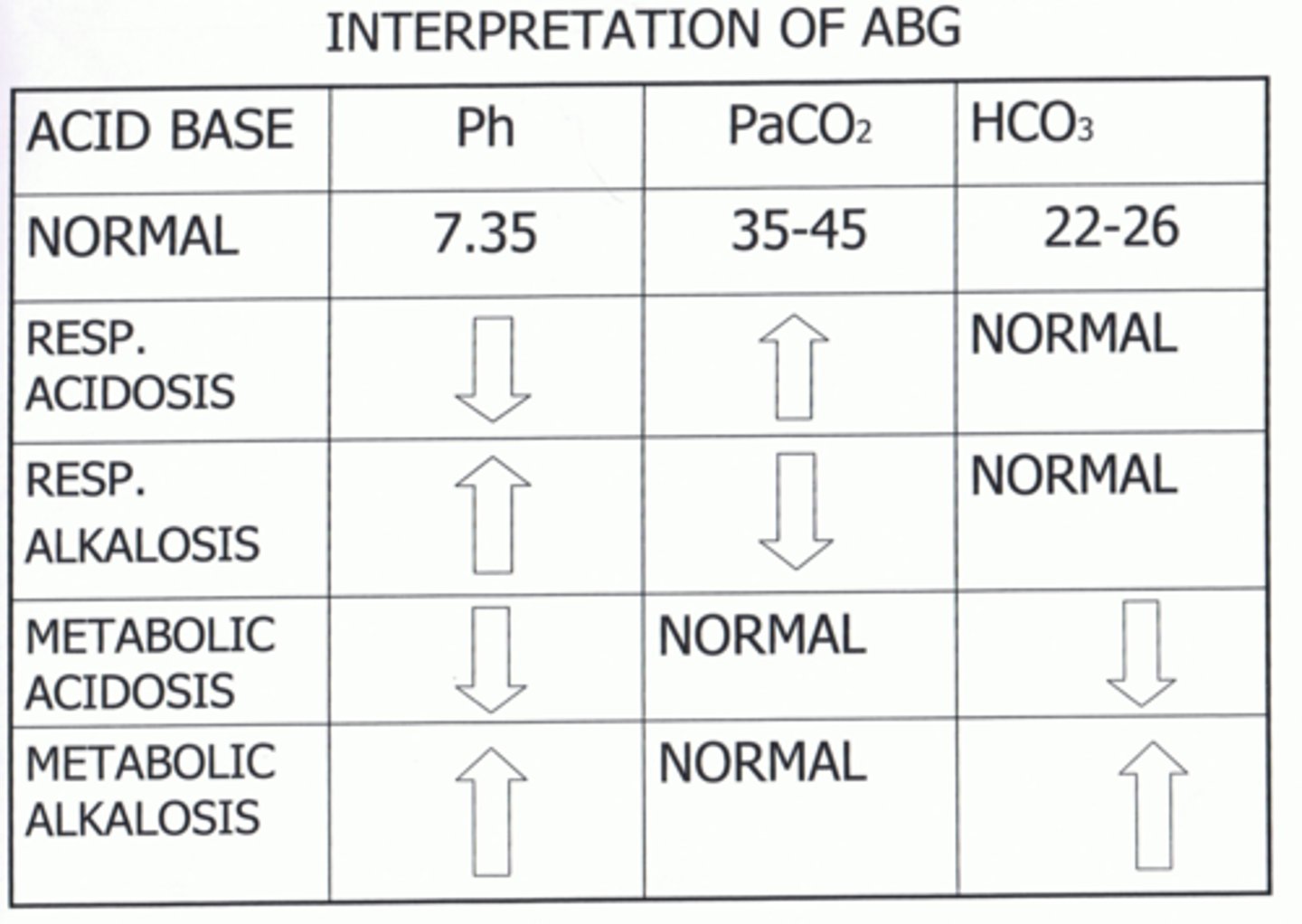
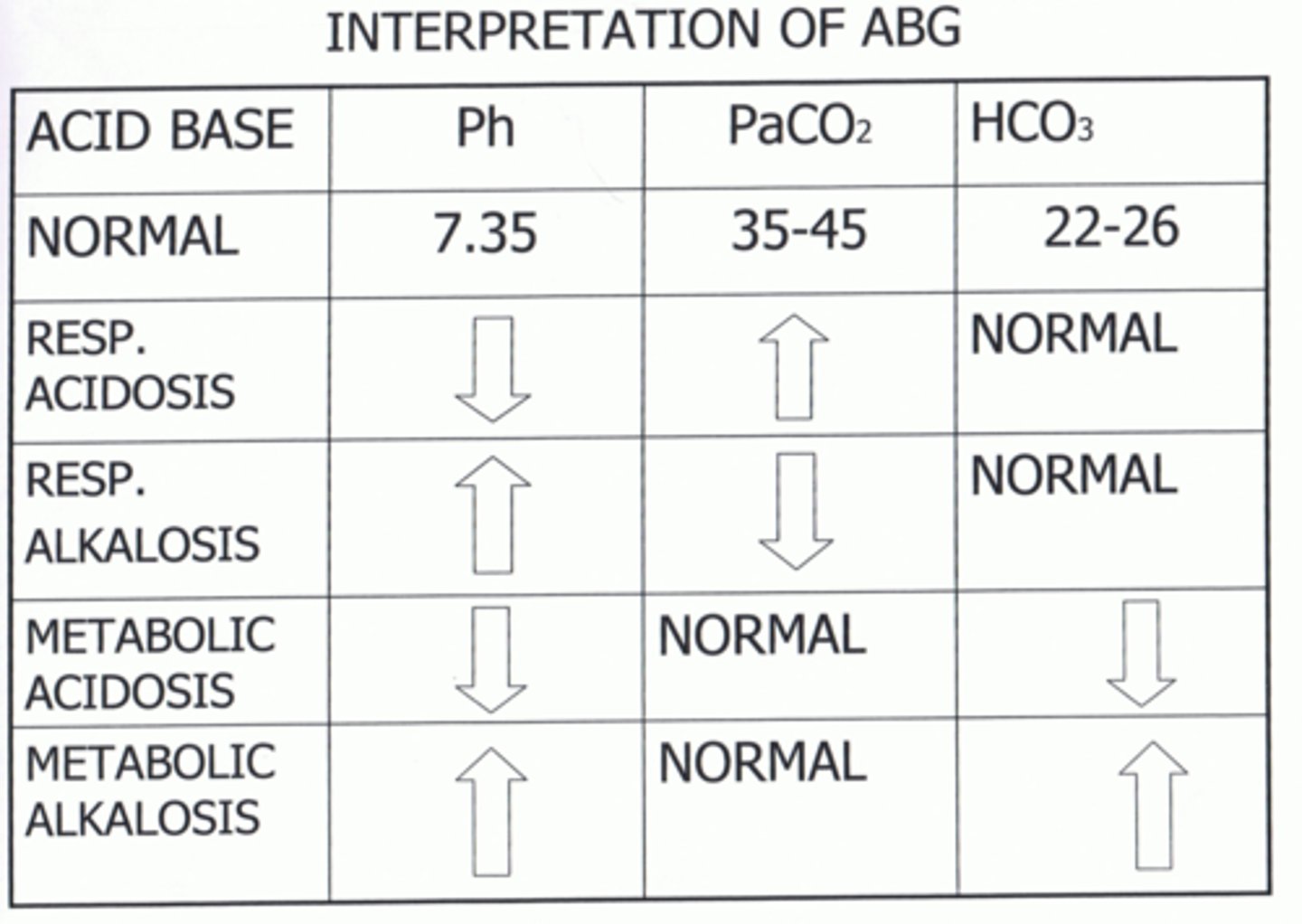
Interpret the ABGs and determine the Acid-Base Imbalance:
pH 7.46
pC02 31
pHC03 24
Respiratory Alkalosis
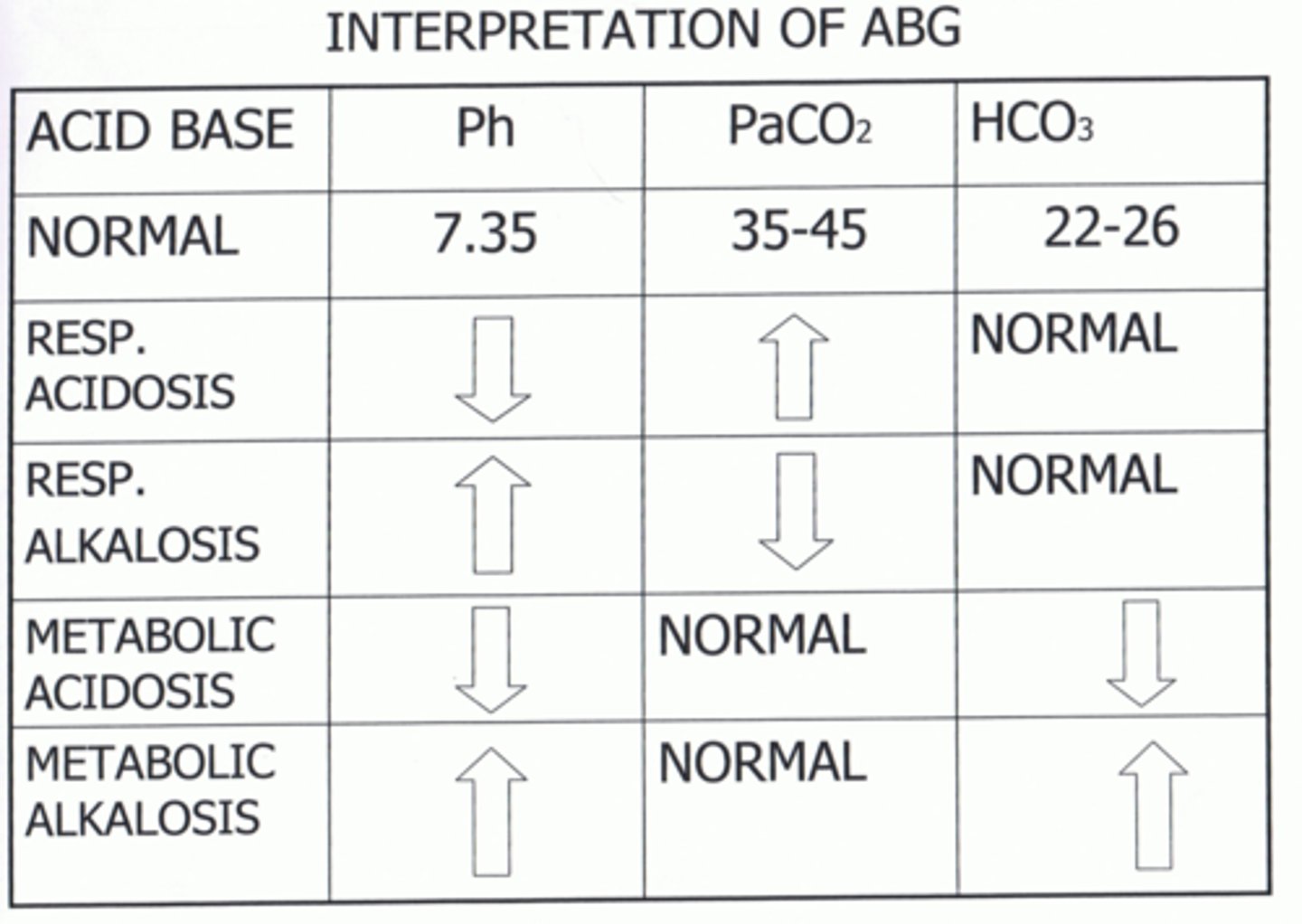
Interpret the ABGs and determine the Acid-Base Imbalance:
pH 7.30
pC02 47
pHC03 22
Respiratory Acidosis
Interpret the ABGs and determine the Acid-Base Imbalance
pH 7.49
pCO2 44
pHC03 29
Metabolic Alkalosis
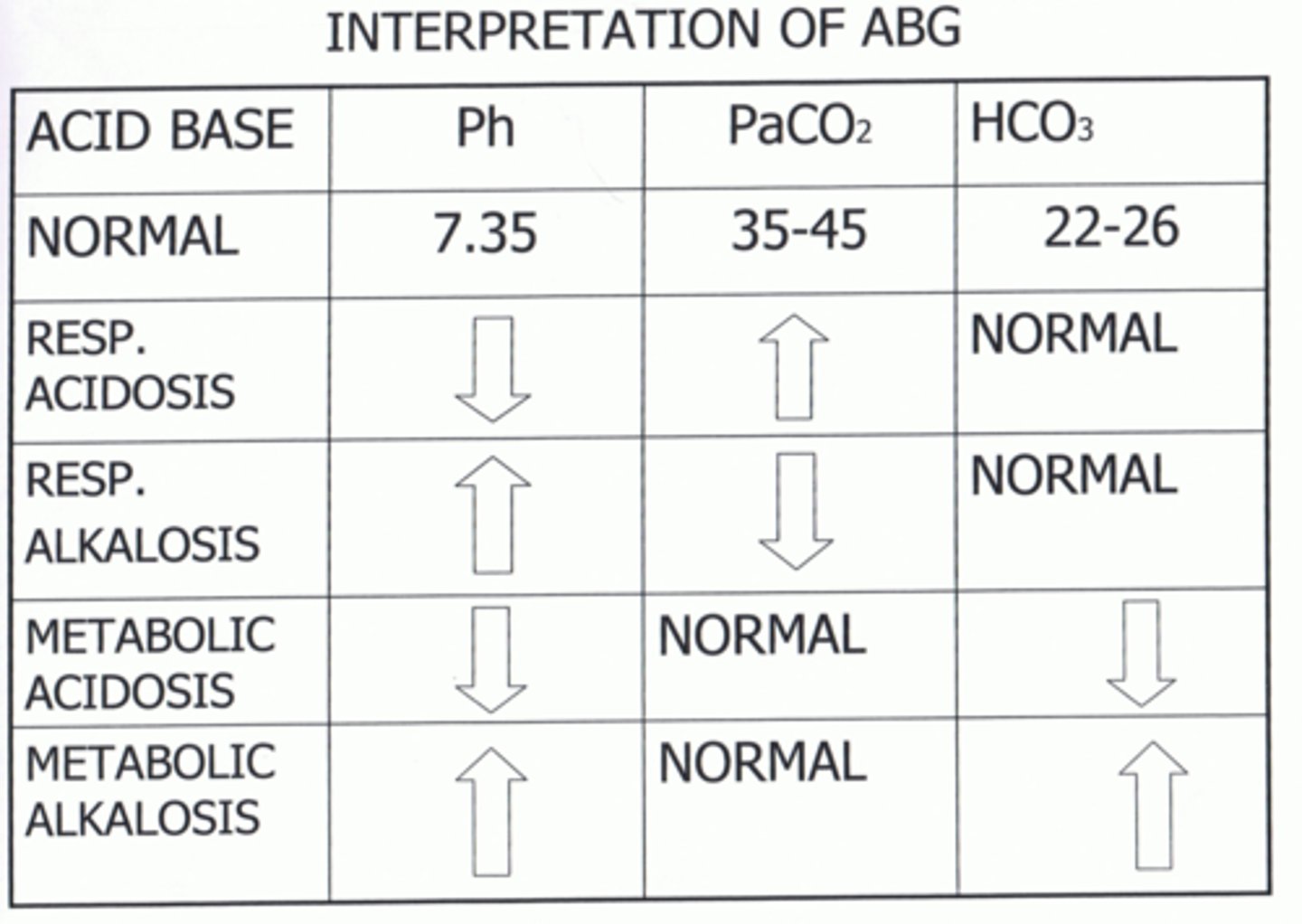
Interpret the ABGs and determine the Acid-Base imbalance
pH 7.32
pC02 43
pHCO3 19
Metabolic Acidosis
causes of hypokalemia
Actual total body potassium loss
~excessive use of meds such as diuretics and corticosteroids
~increased secretion of aldosterone (Cushing's Syndrome)
~Vomiting, diarrhea
~Wound drainage (gastrointestinal)
~Prolonged nasogastric suction
~Excessive diaphoresis
~Renal disease impairing reabsorption of potassium
Inadequate intake of potassium: NPO
Movement of potassium from the extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid
~alkalosis
~hyperinsulinism
Dilution of serum potassium
~Water intoxication
~IV therapy with potassium poor solutions
sources of sodium in diet
Processed foods have the most sodium and reduced potassium
Fresh fruits and vegetables have the least sodium
care for a patient with potassium imbalances
should always include a cardiac monitor
high risk of arrhythmia
Causes of respiratory acidosis
decreased respiratory stimuli (anesthesia, drug overdose), COPD, pneumonia, atelectasis
Causes of metabolic acidosis
Starvation, dehydration, diarrhea, shock, renal failure, and diabetic ketoacidosis.
Causes of respiratory alkalosis
hyperventilation (anxiety, PE, fear), mechanical ventilation
Causes of metabolic alkalosis
Loss of gastric juices, potassium wasting diuretics, overuse of antacids
Administration of potassium
-oral- DO NOT CRUSH
-IV (must be diluted)- DO NOT PUSH
-potassium chloride is most common
food sources of potassium
Bananas
Oranges
Apricots
Figs
Dates
Carrots
Potatoes
Tomatoes
Spinach
Dairy products
Meats
causes of hyperkalemia include
potassium supplements, ace inhibitors, renal failure, excessive loss from cells, potassium-sparing diuretics, burns, trauma, metabolic acidosis, infections
Hyperkalemia in DKA explanation
Acid in the blood is buffered by being drawn into cells, antiporting with potassium
Overall, though, the total body potassium is low, because it is lost in the urine, even though there is hyperkalemia in the blood