Introduction to Genetics- Meiosis and Gamete cells
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
what does heredity mean?
traits passed down from parents to offspring
list examples of character traits passed from parents to offspring
shape of eye, nose hair etc
do plants have heredity?
yes, they inherit traits from their parent plants through genetic material.
every species has a certain number of chromosomes in each cell nucleus.
true
how many chromosomes does humans have?
46 chromosomes
how many chromosomes will the offspring get from its parents?
23 from dad
23 from mom
what are homologous chromosomes?
pairs of chromosomes, that carry the same gene
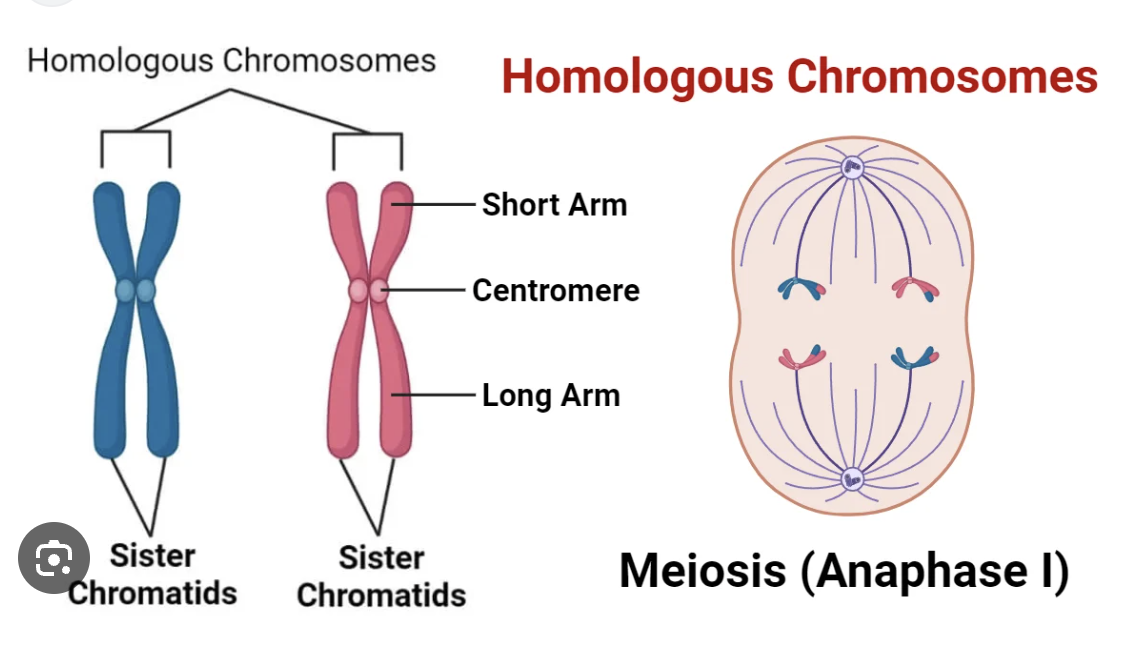
a cell that contain both sets of homologous chromosomes are called..
diploid
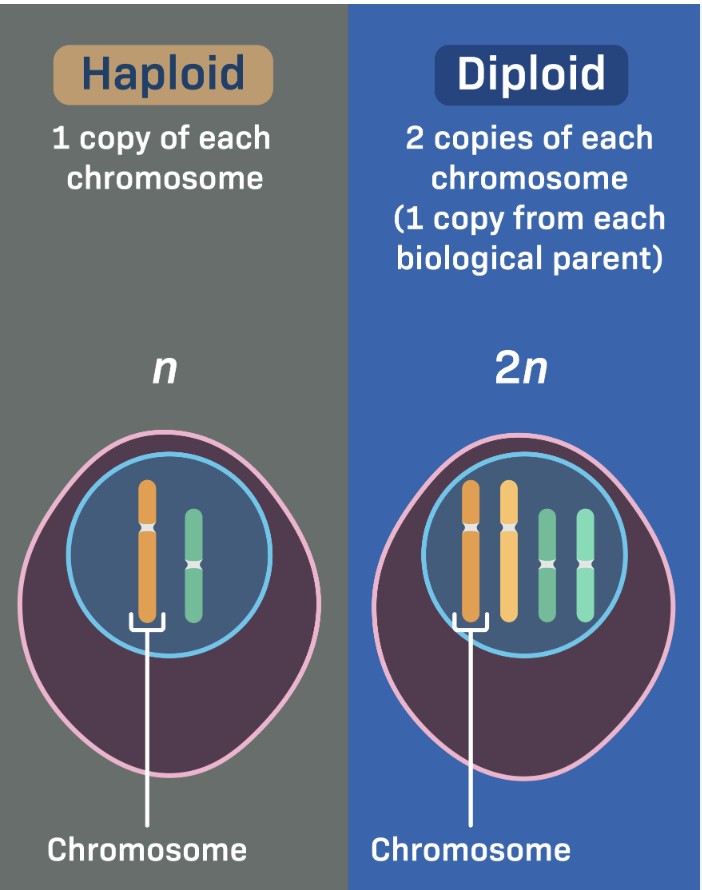
What is the number of chromosomes in a diploid cell represented by?
2n
gametes are what type of cells?
sex cells
how many chromosomes do gametes cells have?
half the number of chromosomes
ex) we each have 46 chromosomes, so half of that would be 23
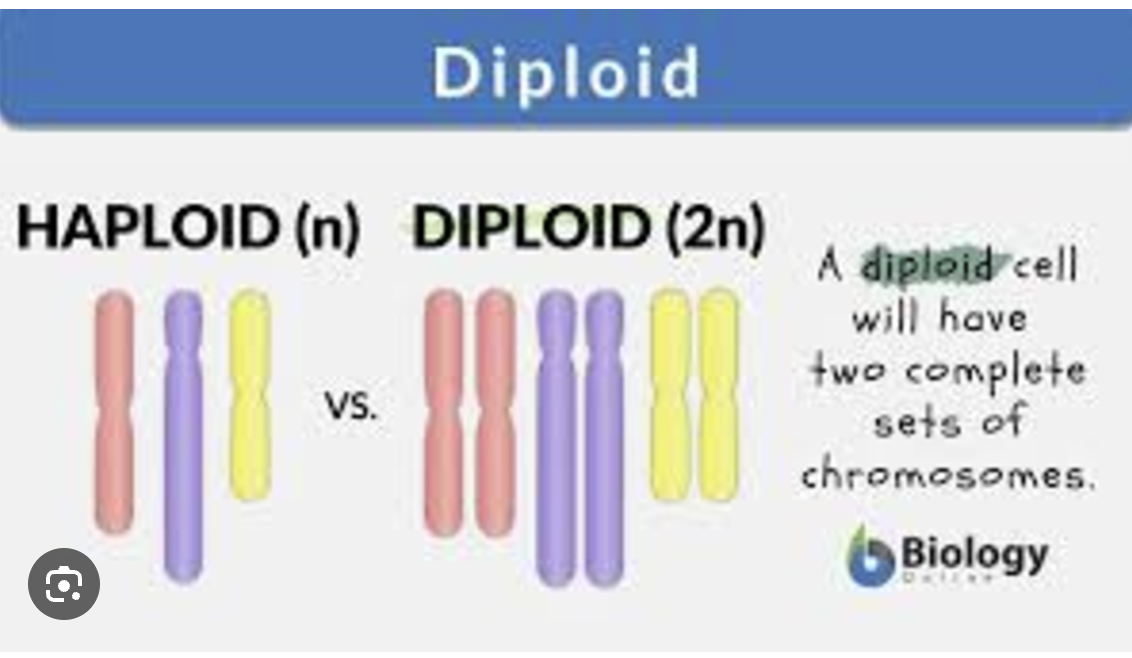
if a cell only has 1 set, what is it called?
haploid
what is the symbol for haploid?
N
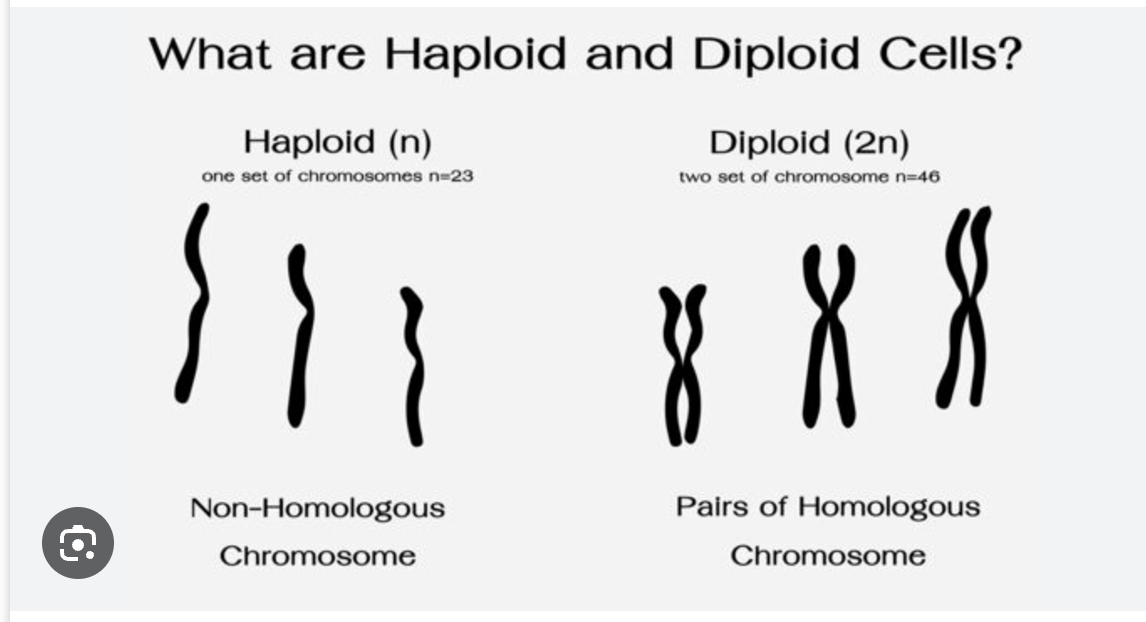
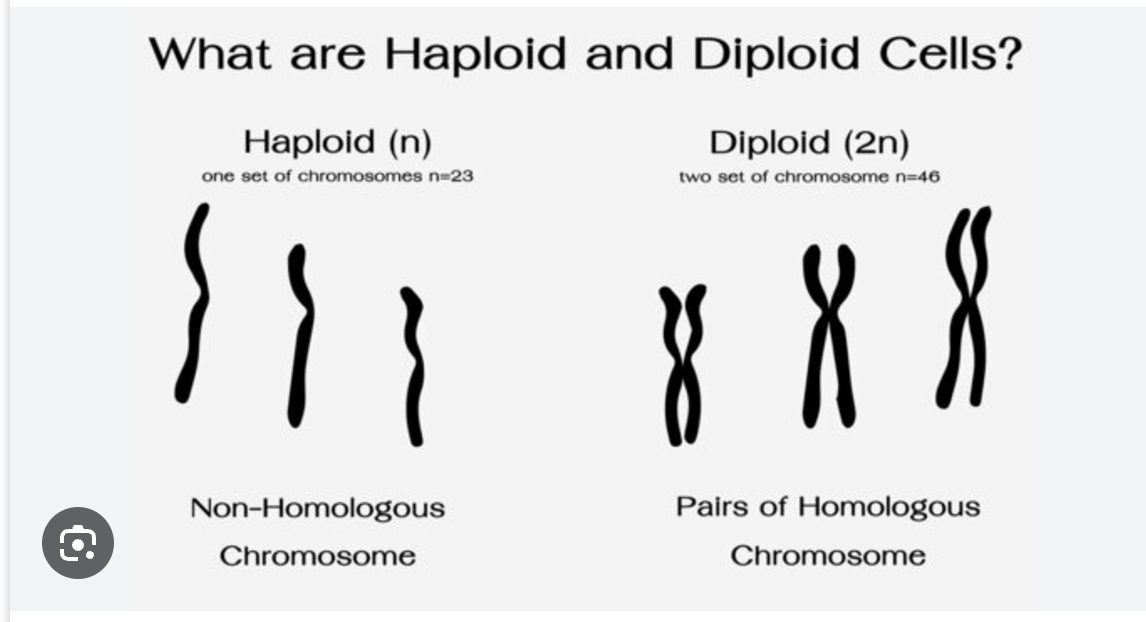
haploid (N) cells are also known as gametes
true
gamete cells are produced from a diploid cell by the process of what?
Meiosis
what happens in Meiosis 1 & 2 ?
4 daughter haploid cells are made
what happens in prophase 1
each chromosome pairs up with a homologous chromosome to form a tetrad
they cross-over chromatids
produce new combinations of alleles
what happens in metaphase1
tetrads meet at the middle
homologous chromosomes line up along the middle of the cell by spindle fibers
what happens in Anaphase 1
spindle fibers pull apart tetrads to opposite ends of the cell
sister chromatids still remain attatched
what happens in Telophase 1 and cytokinesis?
nuclear membranes form
cell separates into two cells
2 cells are produced
What happens in Meiosis 2?
cells produced by meiosis 1 do not go through dna replication
what happens in Metaphase 2
sister tetrads line up in the center of the cell
what happens in anaphase 2
the sister chromatids separate and move toward opposite ends of the cell
what happens in telophase 2 and cytokinesis?
Meiosis 2 results in four haploid (N) daughter cells
in male animals, meiosis results in how many gametes?
4 gametes
male gametes are called …
sperm
In female animals, meiosis only results in how many eggs?
1 egg
the scientific study of heredity began with an Austrian monk named..
Gregor Mendel
Mendel was the first to develop rules that accurately predicted patterns of heredity, he achieved these by carrying out experiments with garden peas.
true
during reproduction, sperm and egg cells join in a process called..
fertilization
what does fertilization produce?
a new cell
peas and most plants are..
self- pollinating ( meaning they get themselves pregnant)
what does it mean if a plant is true-breeding?
parent plants that produce offspring that are identical to themselves.
what is cross- pollination?
the process of transferring pollen from one plant to another
Each original pair of true breeding plants is called the..
P ( parental) generation
The offspring are called the..
F1 or “first filial generation
what are the 4 mendelian concepts?
1- alles have alternative versions, each gene resides at a specific locus or on a specific chromosome
2- there are 2 alleles, one from each parent
4- dominant alles determine the organism’s appearance, the recessive allele has no noticeable effect on the appearance
5- law of segregation- two alleles separate during gamete formation and end up in different gametes (anaphase)
organisms that have two identical alleles for a particular trait are said to be
homozygous
TT
homozygous
Organisms that have two differenta alleles for the same trait are ..
heterozygous
heterozygous
Tt
the physical appearance of a character/trait is called its..
phenotype
The set of alleles that an individual has for a trait or the genetic makeup of an organism is called
genotype
crosses between 2 organisms or single traits are called…
monohybrid crosses
crosses that examine the inheritance of two different traits are called
dihybrid crosses
when one allele is not completely dominant over another it is caled..
incomplete domianace
in incomplete dominance an offspring will have an blend
for example - mixed kids, they’re not fully white or black.
if a red and white flower mix- the flower will be pink
neither one phenotype is dominant so it blends
when both traits are fully expressed it is called..
codominance
in codominant alleles both traits are expressed
example- white and black cow offspring would not be mixed but may be black with white spots
what is an example of multiple allele inheritance?
human blood type
how many possible phenotypes do blood types have?
4 phenotypes
there are 3 alleles for the gene that determines blood type
true
what are the 3 alleles that determine blood type?
Ia, Ib, i
the blood type AB is a
universal recipient
the blood type O is a
universal donor
what is the most common blood type?
O+
what percent of the U.S population are 0+
37%
what is the second most frequently occurring blood type?
A+
what percent of the U.S population are type A+
34%
what blood type is the most rarerest?
AB negative
what percent of the U.S population are AB negative?
0.6%
what are traits that are controlled by two or more genes called?
polygenic traits
the genes for a polygenic trait may be scattered along the same chromosome or located on different chromsomes.
true
skin color in humans is a polygenic trait controlled by more than 4 different genes
true