Upper Limb Special Orthopedic tests
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Shoulder Stability Tests
Anterior Drawer
Posterior Drawer
Apprehension/ Crank Test
Push Pull Test
Sulcus Sign

Anterior Drawer Test
Purpose: tests for anterior GH instability
Positive signs: Hypermobility, clicking, apprehension
Method:
Patient lies supine
Abduct shoulder to 80-120 degrees, flexed forward to 20 degrees, laterally rotated up to 30 degrees
Therapist stabilizes scapula
Draws humerus forward

Posterior Drawer Test
Purpose: Tests for posterior instability
Positive Signs: Hypermobility, pain, apprehension
Method:
Start same position as anterior drawer- supine
Medially rotate arm and flex forward to 60-80°
Apply posterior force
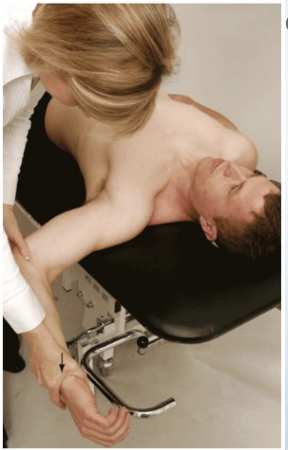
Apprehension/Crank Test
Purpose: Tests for gross instability of GH joint
Positive Signs: Apprehension, muscle spasm
Method:
Patient supine- at edge of table so arm can go off edge
Abduct to 90 degrees and fully externally rotate
Apply overpressure if no pain (push down on their arm)
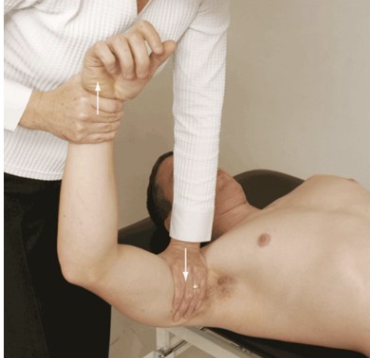
Push Pull Test
Purpose: Tests for posterior instability
Positive Signs: Hypermobility, pain, apprehension
Method:
Patient supine
Abduct arm to 90 degrees, flex to 30 degrees
Downward push at shoulder and upward pull at wrist
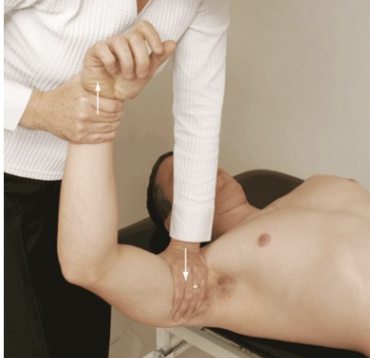
Sulcus Sign
Purpose: Tests for inferior instability
Positive Signs: Hypermobility, sulcus sign, with pain/apprehension
Method:
Arm relaxed at side
Distal pull of humerus
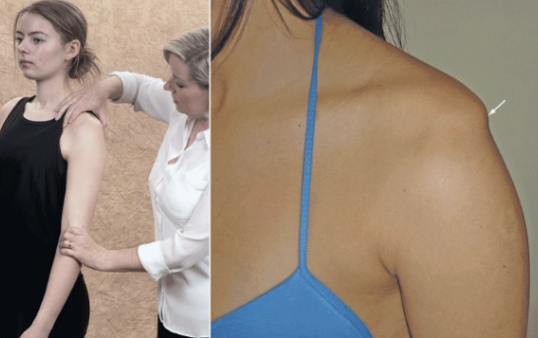
Impingement Tests
Hawkins- kennedy Test
Neer Impingement Test
Painful Arc
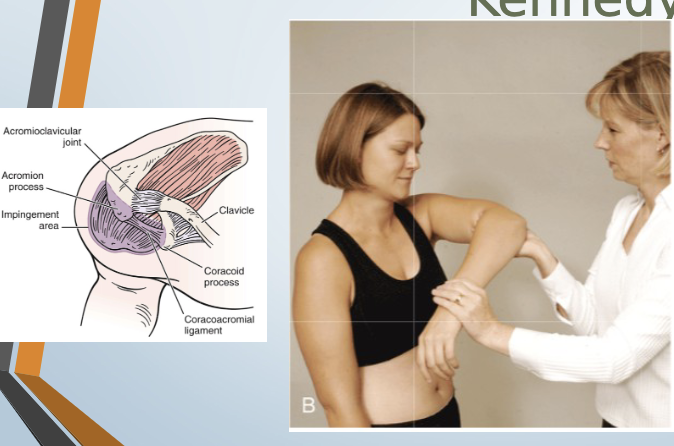
Hawkins-Kennedy Test
Purpose: Tests for supraspinatus tendinopathy/impingement
Positive Signs: Pain, apprehension
Method:
Seated or standing
Forward flex arm to 90 degrees, medially rotate
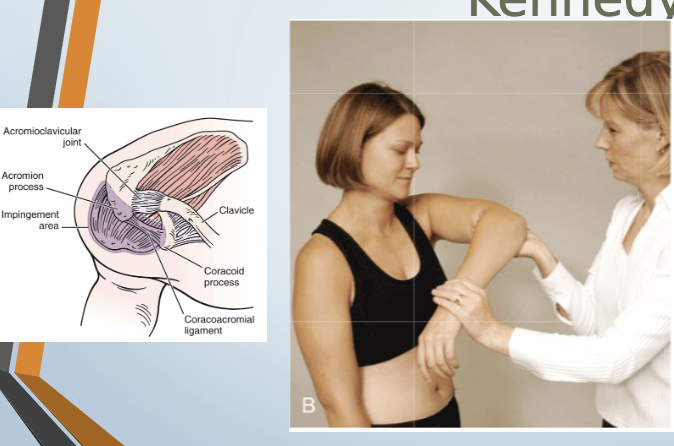

Neer Impingement Test
Purpose: Tests for supraspinatus overuse injury
Positive Signs: Pain, apprehension
Method:
Seated or standing
Abduct arm in scaption, medially rotated

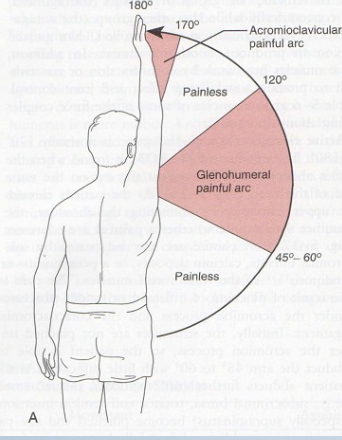
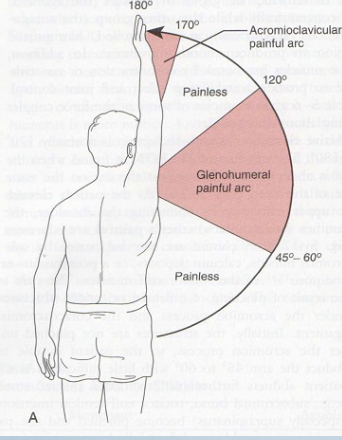
Painful Arc
Purpose: Tests for compression of subacromial structures
Positive Signs: Pain during mid-arc, pain at 170-180° indicates AC injury
Method:
AFROM abduction
Shoulder Motion Tests
Apley’s Scratch test
AC Shear test
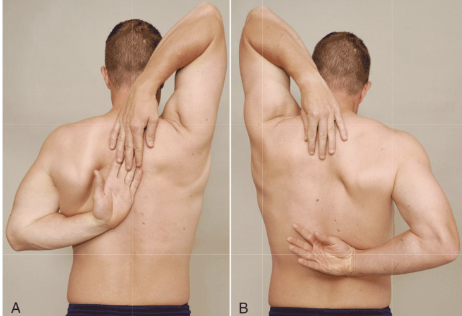
Apley’s Scratch Test
Purpose: Tests combined shoulder movements- internal and external rotation
Positive Signs: Normal fingertip touching range
Method:
Demonstrate to client to mimic
one arm over and behind shoulder
One arm reaching under and up to touch other hanf
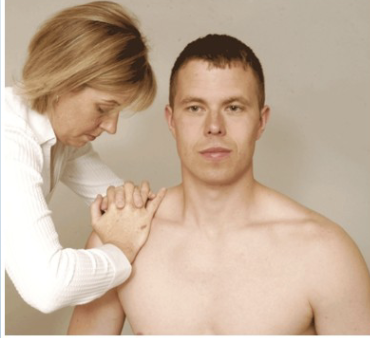
AC Shear Test
Purpose: Tests acromioclavicular joint pathology
Positive Signs: Pain, hypermobility
Method:
Seated
Hands on clavicle and spine of scapula
Interlock fingers one hand on each side of shoulder
Squeeze together
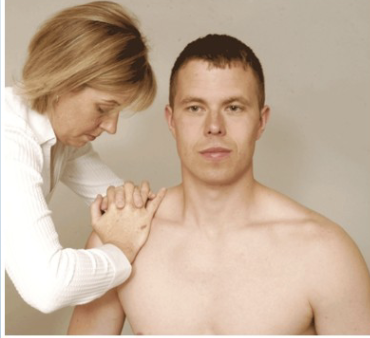
Rotator Cuff Injury Tests
Drop Arm Test
Speed’s Test
Supraspinatus Test (Empty Can Test)
Yergason’s Test
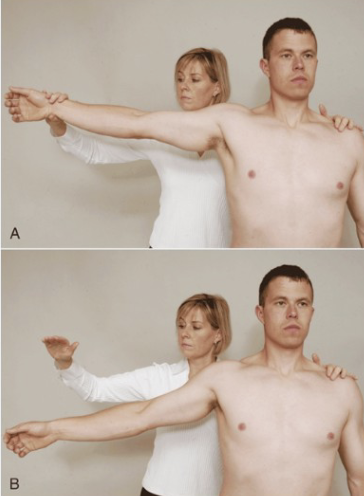
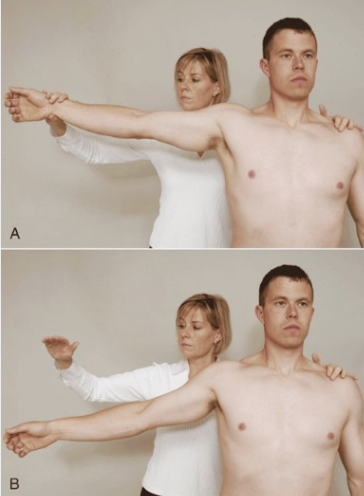
Drop Arm Test
Purpose: Tests for rotator cuff tear
Positive Signs: Inability to slowly lower arm, pain
Method:
Abduct shoulder to 90 degrees
Client lowers arm slowly to side
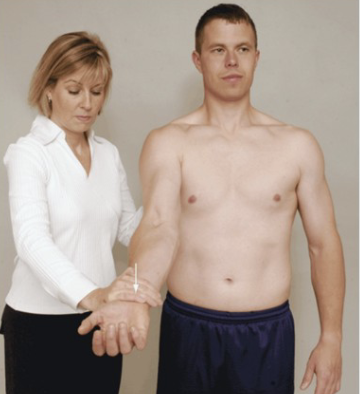
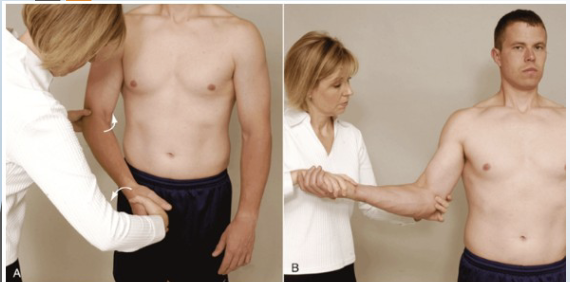
Speed’s Test
Purpose: Tests for bicipital tendinopathy
Positive Signs: Pain in bicipital groove
Method:
Seated
Resists shoulder forward flexion in supination then pronation
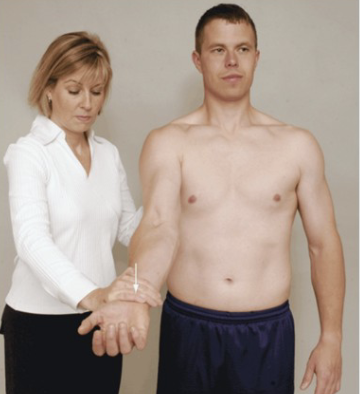
Supraspinatus Test (Empty Can Test) Jobes
Purpose: Tests for supraspinatus muscle/tendon tear
Positive Signs: Muscle weakness, pain
Method:
Abducted arm to 90 degrees in neutral, resist
Rotate medially into scaption and resist again
Resist at wrists pushing downward
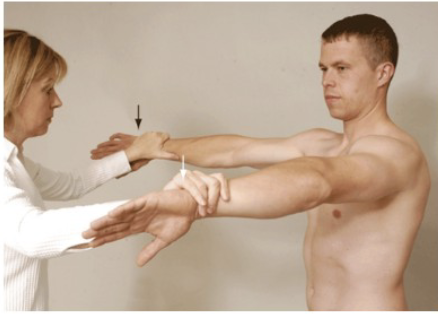
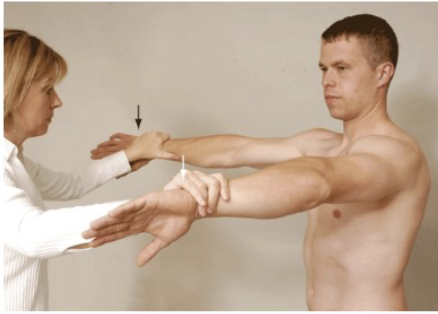
Yergason’s Test
Purpose: Tests for transverse humeral ligament integrity
Positive Signs: Biceps tendon pops out, pain in biccipital groove
Method:
Seated
Palpate biccipital groove
Elbow flexed medially and pronated then
Resist supination and lateral rotation with elbow flexed
Like a hitchhiker
Thoracic outlet Syndrome Tests (TOS)
Adson’s Test
Wright’s Hyperabduction Test
Halstead Test
Eden’s Costoclavicular Test (Military Brace)
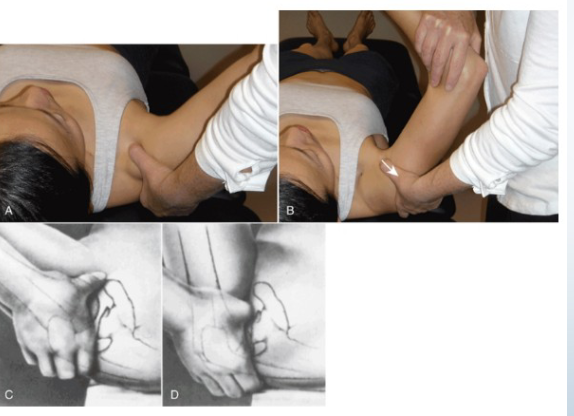
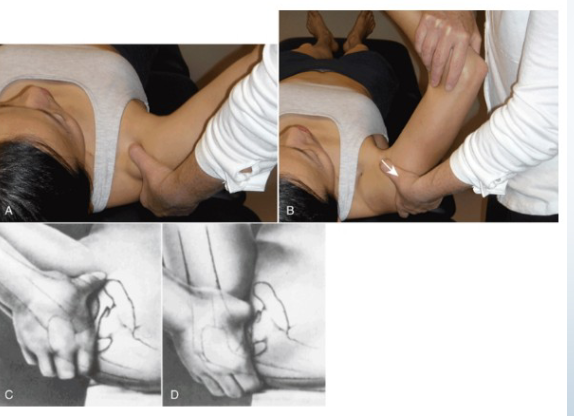
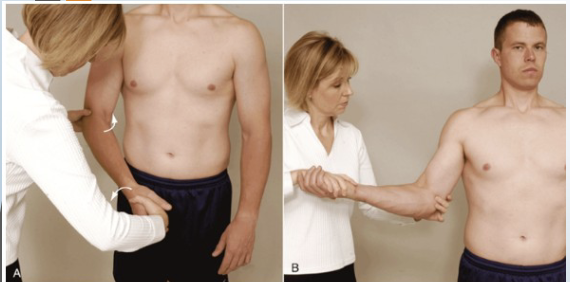
Adson’s Test
Purpose: Tests for anterior scalene-related TOS
Positive Signs: Pain into arm, loss of pulse
Method:
Seated
Palpate radial pulse, rotate head towards test shoulder
Extend head
Therapist externally rotates and extends shoulder
Patient takes deep breath and holds
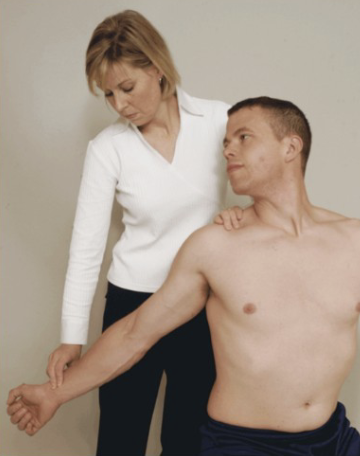
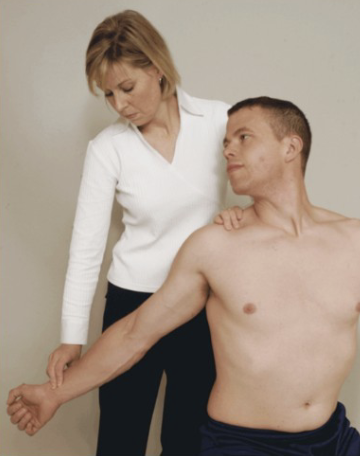
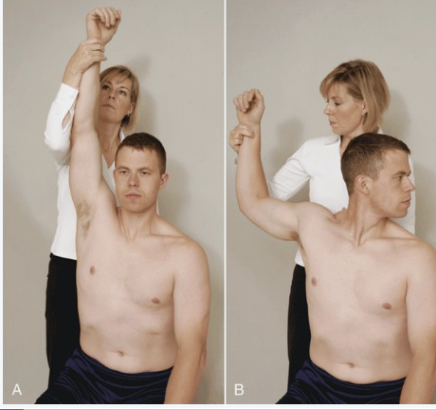
Wright’s Hyperabduction Test
Purpose: Tests for pec minor-related TOS
Positive Signs: Increased symptoms, decreased radial pulse
Method:
Seated
Passively fully abduct arm to 180 degrees with slight extension
Monitor the radial pulse
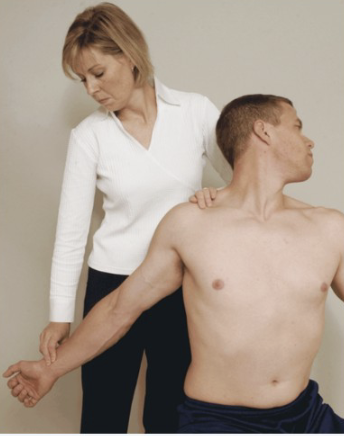
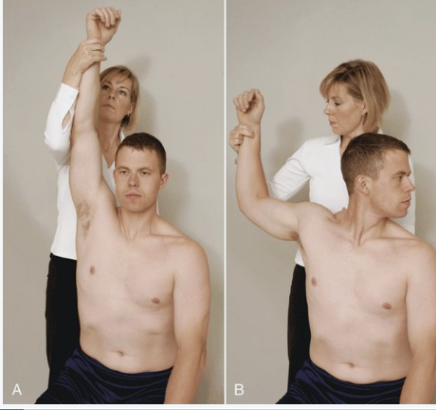
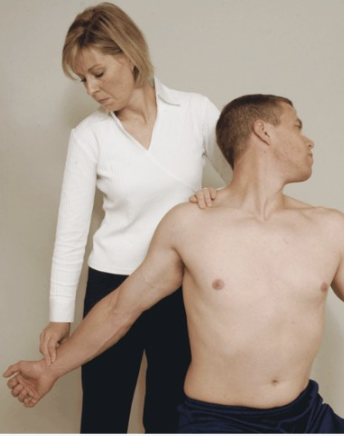
Halstead Test
Purpose: Tests for scalene-related TOS
Positive Signs: Pain into arm, neurological symptoms
Method:
Seated
Rotate head AWAY from test shoulder then extend head
Therapist externally rotates and extends shoulder with downward traction
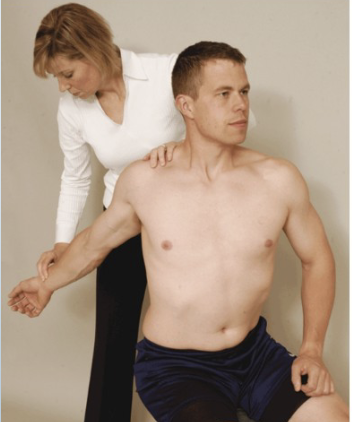
Eden’s Costoclavicular Test (Military Brace)
Purpose: Tests for costoclavicular-related TOS
Positive Signs: Increased neurological symptoms, decreased radial pulse
Method:
Monitor radial pulse,
Therapist depress and retract affected arm
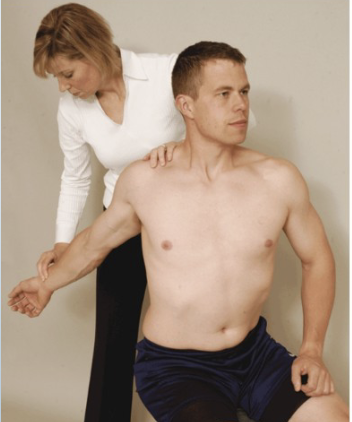
Compression Tests
Shoulder depression test
Shoulder Abduction/ Brakody’s
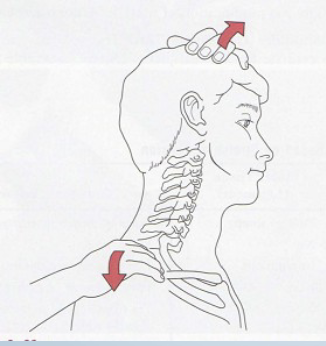
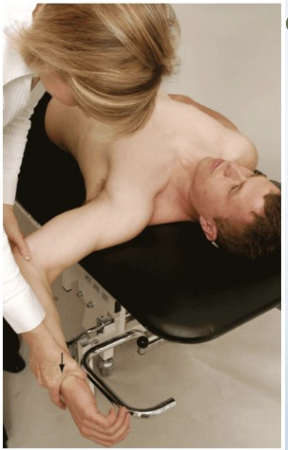
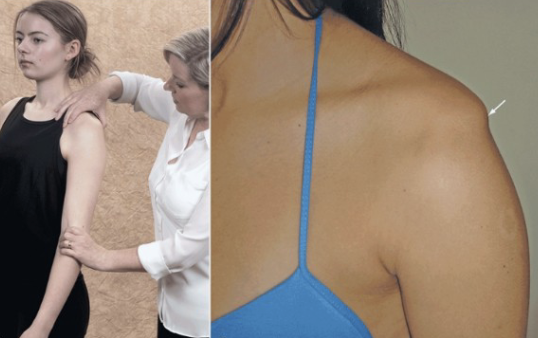
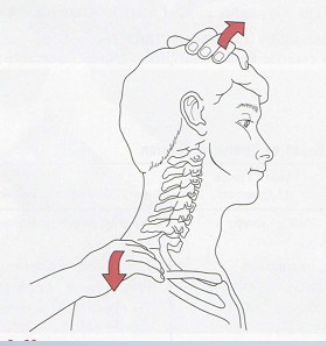
Shoulder Depression Test
Tests for:
• Brachial plexus
compression/irritation
• Multiple cervical nerve root
irritation
• Foraminal encroachment on
compressed side (osteophytes)
• Hypomobile joint capsule on
elongated side
•Positive sign:
• Increased pain and neurological
symptoms
•Method:
• Patient seated
• Therapist applies downward
pressure to shoulder while side
flexing head to opposite side
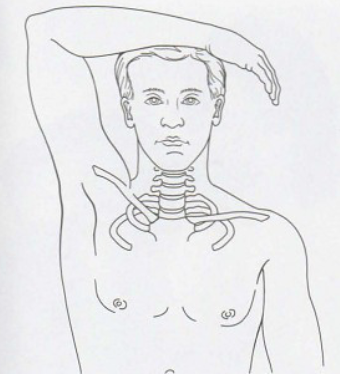
Shoulder Abduction/ Brakody’s
•Tests for:
• C4, C5, C6 nerve root
compression
• Herniated disc
•Positive sign:
• Decreased pain and
neurological symptoms (also
known as Brakody’s sign)
•Method:
• Patient seated or lying down
• Therapist passively (or
patient actively) elevates
arm through abduction so
that the hand or forearm
rests on top of the head
Tests of the Elbow medial/ lateral epicondylitis
Mill’s/ Cozen’s/Lat
EpicondylitisMedial epicondylitis
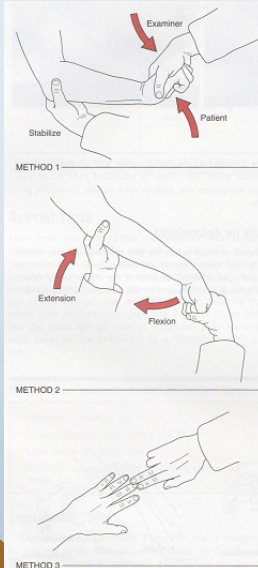
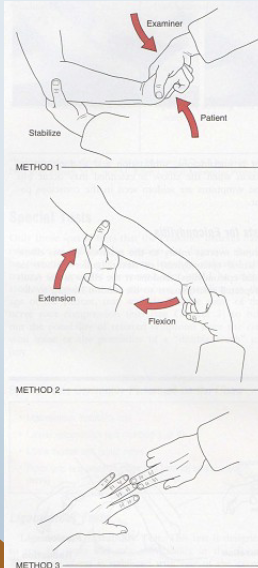
Mill”s Test, Cozens test
Tests for:
• Inflammation at the lateral epicondyle
• Commonly called tennis elbow
•Positive sign:
• Severe pain @ lateral epicondyle
•Method 1: (AKA- Cozen’s)
• Patients elbow stabilized by
therapists thumb resting on lateral
epicondyle
• Patient makes fist, pronates,
radially deviates, and extends the
wrist with the therapist resisting
•Method 2: (AKA- Mill’s)
• Therapist palpates the lateral
epicondyle , then passively
pronates, flexes wrist, and extends
elbow
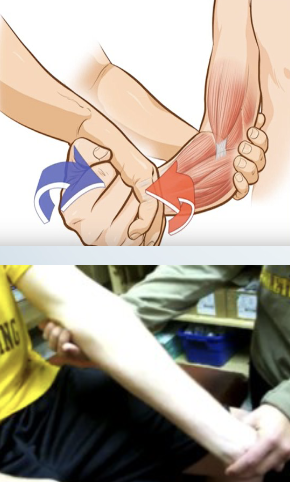
Medial epicondylitis: Reverse Cozen’s, Reverse Mill’s
•Tests for:
• Inflammation of the medial
Tests For:
epicondyle of the humerus
• Commonly called Golfer’s elbow
•Positive sign:
• Severe pain medial epicondyle
•Method:
• Reverse Cozen’s
• Patients elbow stabilized by
therapists thumb resting on medial
epicondyle
• Patient makes fist, supinates, ulnar
deviates, and flexes wrist with the
therapist resisting
• Reverse Mill’s
• Therapist palpates the medial
epicondyle
• Patients forearm is passively
supinated while the elbow and wrist
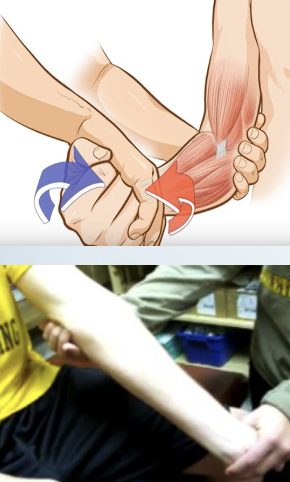
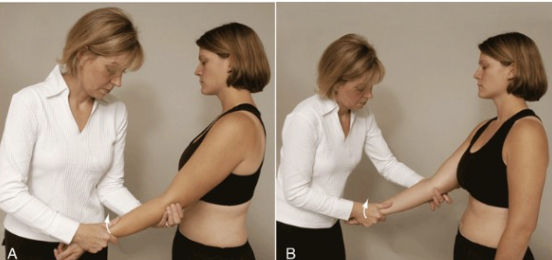
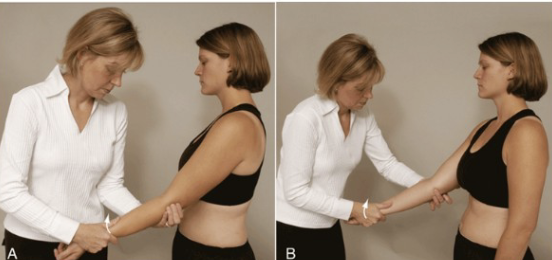
Instability: Varus/ Valgus stress test
•Tests for:
• Medial (ulnar) and lateral (radial) collateral ligament instability
• Varus stress also can stress the anular ligament of the radius
•Positive sign:
• Hypermobility/Pain
•Method:
• Patients elbow in slight flexion
• A varus (adduction) force is applied by the therapist to the distal forearm
to test the lateral collateral and a valgus (abduction) stress to test the
medial collateral
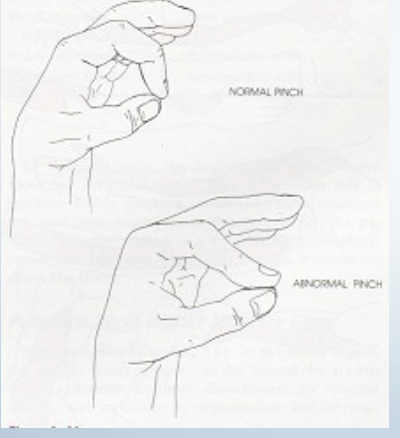
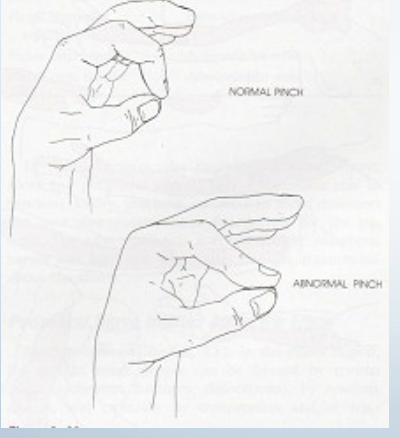
Neuro: pinch Grip test
•Tests for:
• Anterior interosseus
nerve (division of median
nerve) pathology/entrapment
between heads of pronator teres
•Positive sign: • Abnormal “pulp-to-pulp” pinch
•Method:
• Patient is asked to pinch
tips of thumb and index
fingers together
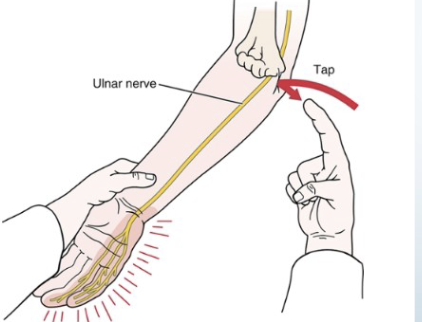
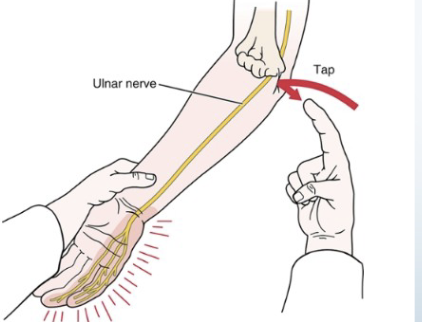
Tinel’s Sign
•Tests for:
• Ulnar nerve compression/
regeneration status
•Positive sign: • Tingling sensation in
ulnar distribution (the distribution of these
symptoms informs you how far the nerve has
regenerated/or the level of damage)
•Method:
• Tap the groove between
the olecranon and medial
epicondyle
Upper Wrist and Hand
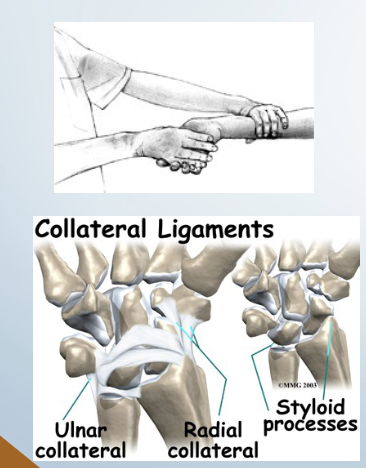
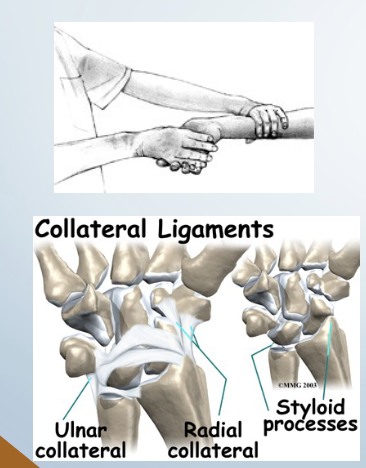
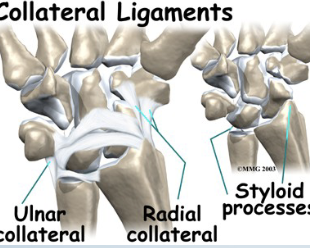
Instability: radial Ligamentous Stress Test
• Tests for: Ulnar collateral ligament
• Positive sign: • Pain and hypermobility
• Method:
• Place client in supination one
hand stabilizes proximal to
wrist
• Passively move hand into
radial deviation with
overpressure
Ulnar Ligamentous Stress Test
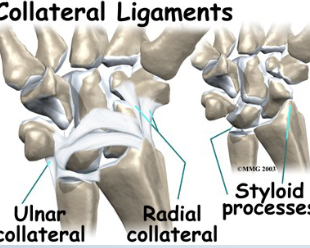
• Tests for:• Radial collateral ligament
• Positive sign: • Pain and hypermobility
• Method:
• Place client in supination one
hand stabilizes proximal to
wrist
• Passively move hand into ulnar
deviation with overpressure

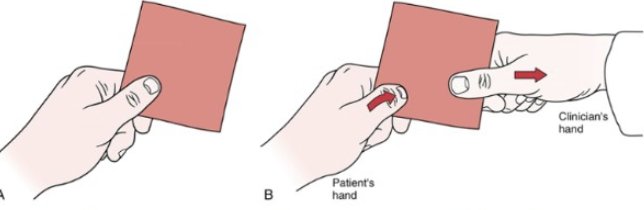
Tendon/ Muscle Pathology: Finklestein (Eichhoff)
•Tests for:
• DeQuervain’s
disease/tenosynovitis/paratenonitis
(APL/EPB)
•Positive sign:
• Pain over the abductor pollicis longus and
extensor pollicis brevis tendon at the
wrist
• Most people have some degree of
discomfort with this test, comparing
bilaterally confirms
•Method:
• Patient makes a fist with the thumb
inside the fingers
• Examiner stabilizes forearm and deviates
wrist toward ulnar side

Neuro: Fromet’s Test
•Tests for:
• Paralysis of adductor pollicis (ulnar nerve)
•Positive sign:
• Distal phalanx of the thumb flexes(Flexor pollicis
longus innervated by the median nerve)
•Method:
• Patient attempts to grasp a piece of paper between thumb
and index finger while therapist attempts to pull away the
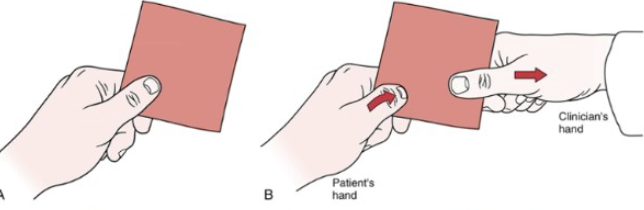
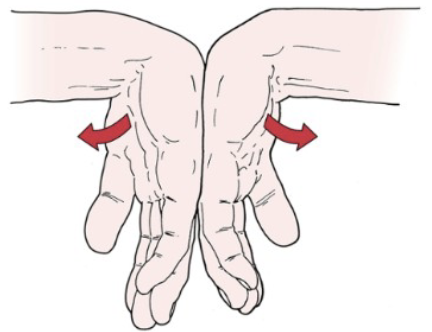
Neuro: Phalen’s (Wrist Flexion)
•Tests for: Carpal tunnel syndrome
•Positive sign:
• Tingling sensation in the
thumb index finger and
middle and lateral half
of ring finger (median
nerve distribution)
•Method:
• Examiner flexes patients
wrists maximally and
holds this position for 1 min pushing the wrists
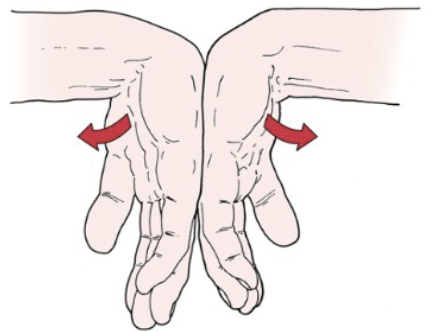
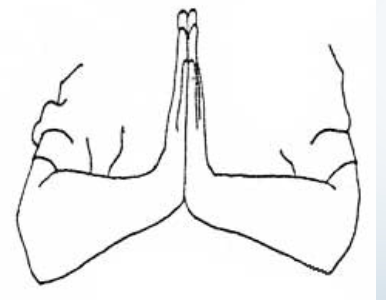
Neuro: Reverse Phalen’s Test
•Tests for: Median nerve
pathology
•Positive sign: Same as Phalen’s
•Tingling sensation in the
thumb index finger and
middle and lateral half
of ring finger (median
nerve distribution)
•Method:
• Therapist places
patients wrists in full
extension and then
draws downward
• Apply overpressure forst
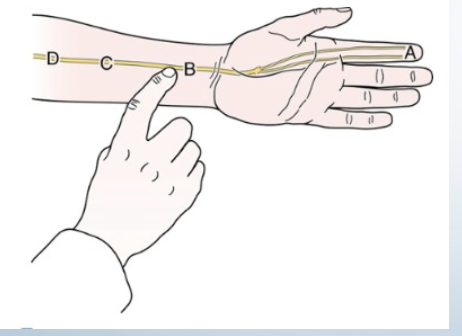
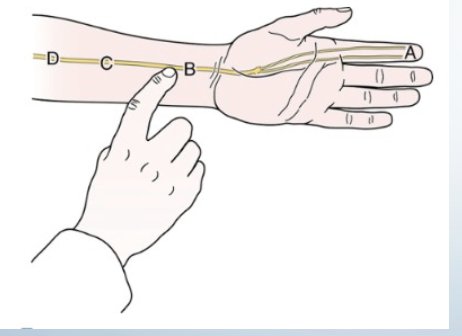
Tinel’s at the Wrist
•Tests for:
• Carpal tunnel syndrome
•Positive sign:
• Tingling sensation and
paraesthesia into thumb index
finger and middle and lateral
half of ring finger (median
nerve distribution)
• Must be felt distal to the
tapping
• Indicates rate of
regeneration of median
nerve
•Method:
Tap medial wrist
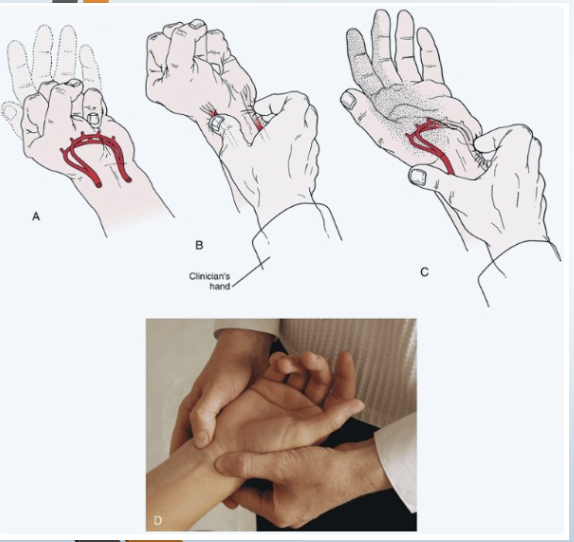
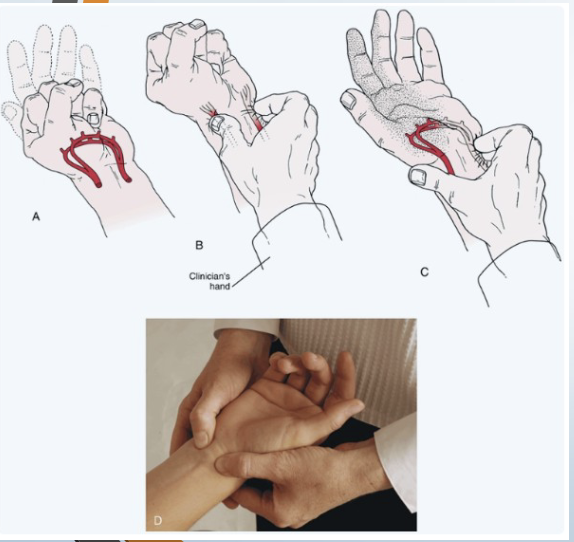
Circulation: Allen Test
• Tests for: Ulnar and radial artery
• Positive sign: Unequal or slow (6 seconds) flushing in
the hand when the blood flow is allowed to return
• Method:
• Patient is asked to open and close the hand
several times quickly
• Then patient squeezes hand tightly
• Therapist places thumb and index finger over
radial and ulnar arteries compressing them
• Patient opens hand while therapist maintains
pressure
• Then remove pressure from one artery and
watch for flushing
• Repeat for other artery