Chapter 5: Greenhouse Effect
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
What are the positive effects of global warming?
increase in productivity from _____ temperature
possibility of ____ new crops
Accelerated ____ rate for crops
____ growing seasons
Temporary benefit with ___ fertilization
warmer
growing
maturity
longer
CO2
what are the negative effects of global warming?
Crop damage from extreme ____
stronger ____, ____ rain, and ___
increase in _____ infestation and crop _____
increase in ____, ____ stress
Increase in ___ (bad plants)
decrease in ____ and ____ efficiency
heat
storms, torrential, flooding
insect, diseases
droughts, warming
weeds
insecticide and pesticide
The ___ is the main source of energy that keeps both Earth’s surface and the atmosphere warm
sun
what is a blackbody
an object that is 100% efficient in emitting and absorbing light
____’s displacement law describes one of the relations between the emission spectrum of a ____ and it’s ___
Wein’s blackbody, temperature
The peak of a blackbody radiation curve is _____ proportional to the ____ of the radiating object
inversely, temperature
wein’s displacement law states that the ____ the temperature, the lower the ____ ( λmax) for which the radiation curve reaches its _____.
higher, wavelength, maximum
Wein’s displacement (b) constant is?
2897 micrometers * K
λ𝑚𝑎𝑥= 𝑏 / T = ?
2897 micrometers (K)/ T(K)
Of the total incoming sunlight of all wavelengths that impinges upon the Earth, about 50% of them is absorbed at its surface by bodies of ___, __, ____, ____
water, soil, vegetation, buildings
Adding to the previous card, 20% of the incoming light is absorbed by ____ in the air (mainly in the form of clouds) and by molecular gases- the UV component by ________ and ________ and the IR by ____ __, and especially by ____.
water droplets, stratospheric ozone, diatomic oxygen, water vapor
A small amount of sunlight is absorbed by suspended particulates of ____.
black soot
much of the sunlight absorbed at the surface become converted to ____ that evaporates water from ___, ___, ___, and from ___.
heat, oceans, lakes, rivers, vegetation,
the remaining 30% of incoming sunlight is reflected back into space by ____, suspended ___, __, ____, ___, and other reflecting bodies
clouds, particle, ice, snow, sand
The fraction of sunlight reflected into space by an object is called its ____, measure in scale from _ to 1 or __ to 100%
albedo, 0, 1
snow and ice are highly reflective surface for ___ light (meaning they have ____ albedos), whereas bare soil and bodies of water are poor reflectors (___ albedos)
visible, high, low
If the Earth acted like a body, according to Wein’s equation, its wavelength of maximum emission would be about __ micrometers
10
what is the range of the thermal infrared region?
5-100 micrometers
IR light is emitted both at the Earth’s ____ and at the _____
surface, atmosphere
The ____ a body, the ___ energy it emits per second.
warmer, more
The rate of release of energy as a light by a blackbody increases in proportion to the ____ power of its Kelvin temperature. K is the _____ constant
fourth, proportionality

The phenomenon of interception of outgoing _IR _ by atmospheric constituents and its dissipation as heat to increase the temperature of the atmosphere is called the?
IR, greenhouse effect
light is most likely to be absorbed by a molecule when its frequency almost ____ matches the frequency of an ____ within the molecule
exactly, internal motion
which of the following molecules will absorb infrared light due to internal vibrational motions:
a) H2
b) CO
c) Cl2
d) O3
e) CCl4
f) NO
CO, O3, NO, CCl4
The _____ energy of a molecule can be either slightly ___ or slightly ___ when __ light is absorbed.
rotational, increased, decreased IR
CO2 trapped in ice-core samples from Antarctica indicate that the atmospheric concentration of CO2 during preindustrial times was about ___ ppm. By 2010, the concentration had increased by almost ___%, to ___ppm.
280ppm, 40%, 390ppm
The rate of increase in the first decade on the twenty-first century rose to about __ppm annually.
2.0ppm
Seasonal fluctuations in CO2 concentrations are due to the growth of ____ in the ____ and ____, which removes CO2 from the , and the vegetation cycle in ____and ___, which increased it.
vegetation, spring, summer, air, decay, fall, winter
The CO2 captured by the photosynthetic process is no longer free to function as _____ gas. The carbon that is trapped in this way is called ______.
The biological ____ of this plant material, is called the ____ reaction, which occurs mainly in the ____ and ____, frees the withdrawn CO2.
greenhouse, fixed carbon, decay, fall, winter
The increase of CO2 in the air is due to the ______, mostly ___, ____, and ____
combustion of fossil fuels, coal, oil, natural gas
A significant amount of carbon dioxide is added to the ______ when
forests are cleared, as well as the wood ____ in order to provide land for
______ use.
atmosphere, burned, agricultural
Carbon dioxide is also released into the atmosphere when _____ rock (limestone) is heated to produce ____, i.e. calcium oxide, used in the manufacturing of cement.
calcium carbonate, quicklime
The lifetime for a carbon dioxide molecule emitted into the atmosphere is
complex as it is not decomposed _____ or _______.
chemically, photochemically
The only permanent sink for CO2 is dissolution in the ____ of the ocean and/or _____ in the ocean as insoluble ____.
deep waters, precipitation, calcium carbonate
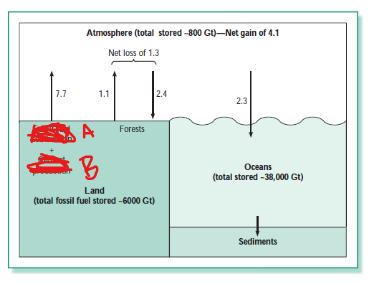
what are A and B (the major contributors)
A: fossil-fuel combustion
B: Cement production
The increase in growth rate of certain types of trees due to the increased concentration of carbon dioxide in the air is called CO2 _____
fertilization
water molecules are always ____ in air and absorb thermal ____ light through their HOH _____ vibration and absorption occurs at about __ micrometers
abundant, IR, bending, 6.3microcmeters
____ is the most important greenhouse gas in the Earth’s atmosphere.
water
the burning of fossil fuels produce ____ as a product
water
water in the ____ arises from the evaporation of ____ and solid ____ on Earth’s surface and in ____.
troposphere, liquid, water, clouds
positive feedback: the operation of a phenomenon produces a result that itself further _____ the result.
amplifies
After carbon dioxide and water , ____ is the next most important greenhouse gas,
methane
HCH bond-angle-bending vibrations absorb at __micrometers
7.7micrometers
Molecules of methane in the air have an average lifetime of slightly less than ____.
a decade
the dominant sink for atmospheric methane (almost 90%) is its reaction with molecules of ____
hydroxyl
about 70% of current methane emissions are ____.
anthropogenic
Most of the methane produced from plant decay results from the process of _____ decomposition, which is decomposition in the absence of ____.
anaerobic, oxygen
Anaerobic decomposition occurs on a huge scale where plant decay operates under ____-logged conditions.
water
_____ are the largest natural source of methan emissions.
Wetlands
Increase in rice production means increases in ___ emissions from the source.
methane
The expansion of wetlands that occurs by the ____ of land to produce more ____ power adds to the total natural emissions of _____ gas.
flooding, hydroelectric, methane
The anaerobic decomposition of the ____in garbage in landfills also contributes to the source of methane emissions into the air.
organic matter
The ____ of biomass is also a contributor to methan emissions.
brurning
Ruminant animals like cattle, sheep, and certain wild animals produce huge amounts of ___ as a by-product.
methane
The animals subsequently emit methane into the air by ___ or ___
belching, flatulence
methane is released into the air when ______ leak, when ____ is mined and when crude ___ is collected or refined.
gas pipelines, coal, oil
Nitrous oxide is also known as?
laughing gas