AP World-Chapter 10
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
What type of Christianity did the Byzantine Empire create?
Eastern Orthodox
What type of Christianity did Western Europe adopt during and after the fall of the western half of the Roman Empire?
Roman Catholic
What caused Christianity to all but disappear from Africa and Asia and become a more exclusively European faith?
The Islamic religion
What is significant about the site of the Dome of the Rock to Jews and Christians?
Jews: contained the stone on which Abraham prepared to offer Isaac as a sacrifice to God, the site of the first two Jewish temples
Christians: place visited by Jesus when he was young, the site where money changers were driven out
How were the Christians and Muslims in Syria and Persia treated?
-allowed to practice their religion in private for a special tax
-destroyed churches, villages and fields
-forced to wear distinctive clothing
-Nestorian Christians survived
How did Christians try to spread their faith within China?
-incorporated Buddhist and Daoist concepts
-the Mongols supported/practiced Christianity
What are dhimmis?
Legally inferior but protected peoples paying a special tax to practice their religion
Why did Christianity in Egypt, that was once the majority religion, being to die out?
As Christian crusaders and Mongols invaded Muslims began to question the loyalty of Christians. They ordered the removal of Christians and those who stayed converted to Islam
Why did Nubian Christianity quickly collapse by 1500?
-Egypt adopted a hostile stance toward Christians
-Islamic tribes and Arab migrants pushed against Nubia
Why did Christianity in Ethiopia persist whereas everywhere else in Africa it was dying out?
-Christian island protected by its geographic mountains and distance from Islamic power
-sheltered persecuted followers of Muhammad in the past
How do most historians describe the beginnings of the Byzantine Empire?
-no clear starting point
-continuation of the Roman Empire
-330 CE is the predicted starting year
Why did the eastern half of the Roman Empire able to protect itself from invasion by the Huns and Germanic barbarian tribes, whereas the Western half could not?
-wealthier
-more urbanized
-more cosmopolitan
-defensive capital of Constantinople
-clever diplomacy
-shorter frontier to guard
-access to Black Sea
-strong army, navy and merchant marine
In what ways was the Byzantium trying to preserve elements of Roman culture and politics?
-referred to themselves as Romans
-forbidden to wear boots, trousers, clothing from animal skins, long hairstyles
-insisted on Roman style robes and sandals
Describe the general location of the Byzantine Empire:
-northern Egypt
-east of the Alps
-through Greece
-up to the Black Sea and down to the Red Sea
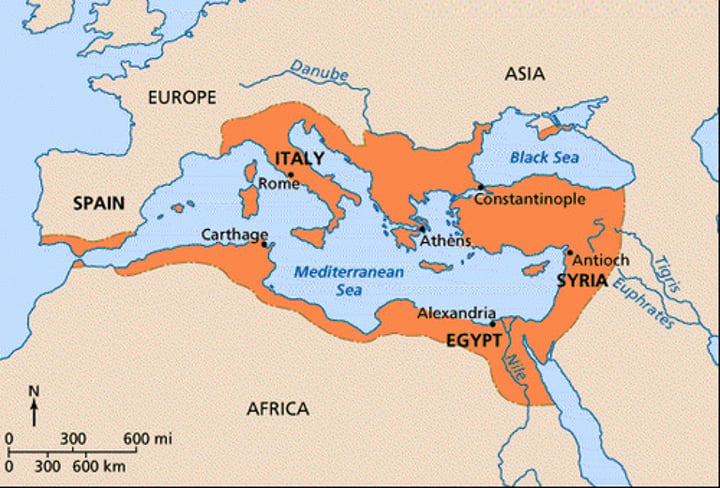
Describe the government of the Byzantine Empire:
-administrative system
-appointed general's avil authority in the empire's provinces and were allowed to raise armies
-centralized in Constantinople
What methods did the emperor employ to establish himself and the royal officials as "elites" within the empire?
-claimed to govern all creation as God's worldly representative
-imperial court tried to imitate God's heavenly court
-aristocrats trained in Greek rhetoric and occupied high positions in the administrations
-parades and court ceremonies maintained their elite status
What is caearopapism?
The relationship between a state and the church in which the state is supreme over the church in ecclesiastical matters
What is a patriarch?
Leader of the Orthodox church
How did Eastern Orthodox Christianity legitimize the emperor's authority?
-God appointed ruler
-reflections of God's glory on Earth
What are icons?
Religious artworks of Jesus, Mary and various saints that many believed conveyed the Divine Presence of the faithful
What language did the Eastern Orthodox religion used for their rituals and holy texts?
Greek
What language did the Roman Catholicism religion used for their rituals and holy texts?
Latin
What were distinctive rituals/practices the Eastern Orthodox religion participated in?
-priests had long hair and were allowed to marry
-used leavened bread in communion
What were distinctive rituals/practices the Roman Catholicism religion participated in?
-priests shaved and remained single
-used unleavened bread in communion
Who is the ultimate authority in the Eastern Orthodox church?
God
Who is the ultimate authority in the Roman Catholicism church?
Roman popes
What happened in 1054 that is often regard to as the "First Great Schism" or great split between the two branches of Christianity?
Representatives from both churches mutually excommunicated (excluded) each other, declaring that those who participated in the opposite religion were not true Christians
Explain how the crusades only made the relationship between the two branches of Christianity worse:
The crusaders often got into conflicts with the local people, which only depended the distrust between the religions and churches
What military technology did the Byzantines develop to protect themselves from Arabs encroaching on their territory?
"Greek Fire"-a combination of oil, sulfur and lime that was launched from bronze tubes to hold off the Arabs

What places did the Byzantine Empire have close links with when it came to trading?
-Western Europe
-Europe
-Russia
-Central Asia
-the Islamic world
-China
The gold coin, the bezant, was created in the Byzantine Empire and used in the Mediterranean basin for more than 500 years. What did wearing such coins show?
Wearing this coins as pendants shows a high-status symbol in the less developed kingdoms of Western Europe

What goods/products was Byzantium trading with other societies?
-jewelry
-gemstones
-silver and gold work
-linen
-silk
-woolen textiles
-purple dye
How did Byzantium helped preserve Greek learning?
It transmitted classical heritage to the Islamic World and the Christian West
Where did Byzantine missionaries go to seek converts since Islam was rapidly spreading south and east of the Byzantine Empire?
Looked to the northern Slavic-speaking peoples in the Balkans and Russia
What two Byzantine missionaries created an alphabet that was based on Greek letters to help Slavic languages understand the religion?
Cyril and Methodius
What did the Cyrillic script make possible?
It made it possible to translate the Bible and other religious texts into their languages and aid the process of conversion
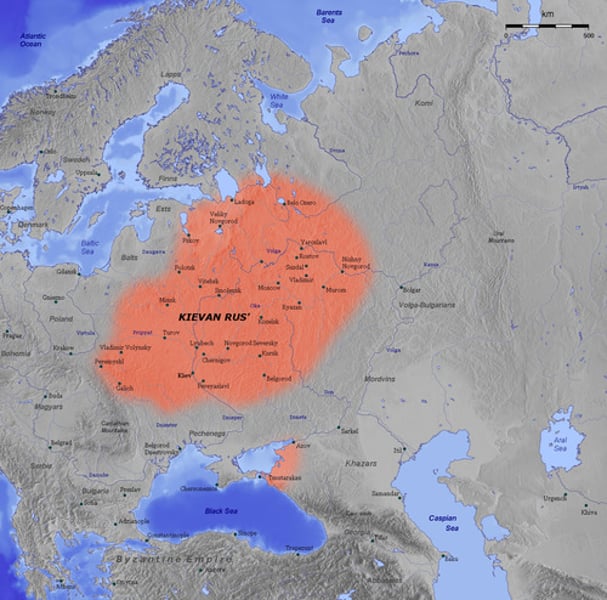
What new state was emerging in Russia around this time?
The state of Kievan Rus was emerging. This state emergence was stimulated by trade along the Dnieper River that linked Scandinavia and Byzantium.
Who was the most prominent nature god?
Perun:the god of thunder

What were Prince Vladimir's motivations for affiliating with one major religion specifically?
He wanted a unifying religion for the diverse people of his region, while linking Rus to wider networks of communication and exchange
Which religion did Prince V ultimately choose?
Christianity
What are some examples of the Russians borrowing Byzantine culture?
-architectural styles
-Cyrillic alphabet
-use of icons
-monastic tradition of stressing prayer and service
-political ideals of imperial control of the church
Why was Western Europe mostly cut off from the rest of the world during the time period after the fall of Rome?
Geographically it was cut off from the Eurasian region with its large mountain areas and dense forests. They were not exposed to the Silk Road, Sand Roads or Indian Ocean trade routes
What facilitated exchange within Europe?
-extensive coastlines
-interior river systems
What enabled Europe's productive agriculture?
-moderate climate
-plentiful rainfall
-fertile soils
What is the official date of the fall of the Roman Empire?
476-when the German general Odoacer overthrew the last Roman Empire in the west
Describe some ways that Roman influence declined immediately after the fall of the empire:
-large scale centralized rule disappeared
-disease and warfare killed 25%+ of the population
-largely rural existence developed
-long distance trade vanished
-barbarians became dominant
-center of gravity moved from the Mediterranean to the north and west
How was Western Europe organized politically?
Regional kingdoms ruled:
-Spain led by Visigoths
-France led by Franks
-Italy led by Lombards
-England led by Angles and Saxons
Who was Charlemagne and what were some of his accomplishments?
Charlemagne was the ruler of the Carolingian Empire who erected an imperial bureaucracy, implemented a system of standardized weights and measurements and acted like an imperial ruler

What is feudalism?
a social system which people worked and fought for nobles who gave them protection and the use of land in return
Describe the relationship between lords and vassals:
-lesser lords/knights swore allegiance to greater loss and became their vassals
-often received lands and plunder in return for military service
What is the difference between and a slave and a serf?
-serfs were not personal property of their masters
-serfs could not be thrown off their land
-serfs could live in families
they were bound to their masters' estate as peasant laborers
-owed payments and services to the lord of the manor
What did serfs provide to their lords? What did serfs receive in return?
-women provided cloth weaving and clothes
-men worked in the fields
-received a small farm and as much protection as the lord could provide
Why would families want to be serfs?
The only security was made possible by these ties to kin, manor and lord which constituted the primary human loyalties
What other institution provided Western Europe with a sense of unity and connection to the Old Roma world, besides feudalism?
The Roman Catholic church provided a hierarchical organization of popes, bishops, priests and monasteries that took over some of the political, administrative, educational and welfare functions
What was the missionary strategy of Christians trying to convert the "pagan" barbarians within their religion?
They would fan out across Europe and imply a "top down" strategy that employed a "wealth and protection of the powerful" message to ordinary people
In what ways did the church and the nobility of Europe cooperate and compete with each other?
Cooperated:
-rulers provided protection for the papacy and a strong encouragement for the faith
-the church offered religious legitimacy for the powerful and the prosperous
Competed:
-the argument between who had the right to appoint bishops/popes (known as inventive conflict)
-church won
What two occurrences most likely helped launch Europe into the High Middle Ages- a period of expansion and growth?
1. a number of invaders were settled into society
2. warm climate
How were Europeans changing their environment?
-new lands opened for cultivation
-marshes were drained
-religious orders organized new villages
-land reclaimed from sea (North Sea coast)
What products were Europeans getting from the Baltic Coast?
-wood
-beeswax
-furs
-rye
-wheat
-salt
-cloth
-wine
What products were Europeans now importing from the Islamic and Byzantine empires?
-silks
-drugs
-precious stones
-spices from Asia
What was happening to European cities during this period?
-population grew on the sites of the older Roman towns, cathedrals and trading crossroads
-complex division of labor
-urbanization was increasing
-attracted merchants, bankers, artisans, lawyers, doctors and scholars
What are guilds?
Associations of peoples pursuing the same line of work
What began to happen politically in Western Europe between the 11th and 13th centuries?
-territorial states developed more effected government institutions that insisted on the loyalty and obedience of their subjects
-nominal monarchs of Europe consolidated their authority
-the outlines of the French, English, Spanish and Scandinavian states appeared
Who was the widow of the great merchant who continued her husbands' business and lent a large sum of money to the king of England to finance a war against Scotland in 1318?
Rose Burford
By the 15th century women's roles in the economy drastically eroded-why?
-technological progress: water and animal powered grain mills replaced hand grinding, larger looms replaced manual looms
Which abbess won wide acclaim for her writings on theology, medicine botany and music?
Hildegard of Bingen

What are some of the limitations placed on women within the church during this time?
-restrictions on hearing confessions, preaching and chanting the Gospel
-monastic universities where only ordained men could study and teach became prominent
What were some of the arguments as to why women were no longer allowed to be priests in the church?
The earlier ideas of the impurity of the menstruation cycle and a woman's role as a sexual temptress were being brought back
Who were the Beguines?
A group of poorer laywomen in Northern Europe who lived together, practiced celibacy and devoted themselves to weaving and to working with the sick, the old and the poor

What is an anchoress?
A woman who withdrawals herself to a locked cell, usually attached to the church, and devotes herself to prayer and fasting
What did crusaders get in return for their willingness to go on a crusade?
-removed penalties for confessed sins
-immunity from lawsuits
-moratorium on the repayment of taxes
What were some of the religious and political motivations for the crusades?
Religious: amazing support, no penalties for confessed sins, provided security for those threading the spiritual health of Christians
Political: drew on warrior values of the elite, lawsuit and debt repayment immunity
What was the impact of the crusades on the Middle East and Europe?
Middle East: demonstrated organization, finance, transportation, recruitment and cruelty, developed 4 small Christian states, little lasting political or religious impact
Europe: Spain, Sicily and the Baltic region brought to Christianity permanently, popes strengthened their positions, picked up luxury Islamic goods, learned to use slave labor for the production of sugar
At this point, is Europe considered a major player in the global arena of trade and political influence?
No
How did the outside world view Western Europe?
-barbaric
-large bodies
-harsh manners
-dull understanding
-heavy tongues
-smaller cities
-weak political authorities
-less commercialized economy
-inferior technology
How did Europeans view themselves compared to the world?
They acknowledged their own comparative backwardness
How did Europe "catch up" to the rest of the world?
-borrowed from eastern advanced civilizations
-reconnected with the Eurasian trading system
-merchants made the journey on the road to China
-sought out African and Asian wealth on the seas
-advanced in technology (innovations)
What are some innovations to agriculture that Europeans employed?
-heavy wheeled plows
-relied on horses instead of oxes/cattle and used iron horseshoes
-three field corp rotation
-water driven mill
-experimented with perpetual motion machines

What technologies (borrowed from China and the Arab World) helped Europeans modernize their military power?
Borrowed from China:
-gunpowder for cannons
-magnetic compass
-sternpost rudder
Borrowed from Arab:
-lateen sail
Why was Europe unable to unify into one centralized empire?
-geographic barriers
-ethnic and linguistic diversity
-shifting balances of power among states
How did this lack of political unity affect all of the following in Europe?
Economy: capital, labor and goods made their way around political barriers-provided enough competition to stimulate innovation but preserved enough to allow the economy to grow
Politics: frequent wars-enhanced men's military status-drove "gunpowder revolution"
Cities: weaker rulers-Roman Catholic Church remained independent from state authority-vassals had certain rights-merchants exercised power-had their own courts, lawsuits and governments while paying their own taxes
What are some examples of events that occurred in the history of Post-Classical Europe that ended up contributing to events that occurred later in history?
~European crusades --> Spanish and Portuguese motives for exploring
~Europe's merchant freedom--> growth of capitalism and industrialization
~Controversy about faith --> resonates in the US still
Eastern Orthodox vs. Roman Catholicism still goes on today