ORG CHEM LAB - Experiment 3, 4, 5 (Structural Effects)
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Experiment 3 - Structural Effects on Melting Point and Boiling Point, Experiment 4 - Structural Effects on Solubility, Experiment 5 - Structural Effects on Acidity and Basicity
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Melting and Boiling Points
Physical properties of a compound’s structure
Depend largely on which bonds can hold three atoms together in a molecule
Useful for synthesizing a new compound
Melting Point
The range of temperature at which a substance changes from solid to liquid phase.
Frequently followed by decomposition
The value may not be an equilibrium temperature but a temperature of transition from solid to liquid only.
Boiling Point
Corresponds to the temperature at which thermal energy of the molecule is great enough to overcome the cohesive forces that hold them in the liquid state.
Employed for compounds having low melting points and compounds that are usually liquid at room temperature.
The range of this constant should not exceed 5 C except for extremely high boiling compounds.
Thee constant may also be decreased or increased depending on the volatility of the impurity present.
Hydrogen Bonding
Attraction between a H atom that is bound to an electronegative atom and another molecule.
Functional groups: alcohols, amines (primary and secondary), carboxylic acids, amides (primary and secondary), and thiols
Dipole-Dipole Interaction
Stronger than Van der Waals Interaction, but not as strong as H bonds
The positive part of one molecule is attracted to the negative part of another molecule
Functional groups: all polar compounds (alcohols, ethers, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, amides, esters, alkyl halides, and thioethers)
Induced Dipole-Induced Dipole (Van der Waals/London Dispersion Forces)
Weakest of all the intermolecular forces
A temporary polarized molecular causes its neighbor to become temporary polarized as well
Every molecule exhibits this attraction
Increase in chain length increases the attraction, whereas increase in branching decreases the attraction.
Melting Point - Rough Method Procedure
Prepare capillary tubes with 1 mm diameter and about 5 cm in length.
Seal one end.
Powder a small amount of sample such that it will occupy 1 cm of the tube.
Attach this tube to the thermometer with a ring of rubber tubing.
Immerse the thermometer with the capillary tube in the oil bath and heat the bath.
Record the temperature range at which the substance begins to liquefy until it has completely melted.
Note any sintering, coloring, softening or any signs of decomposition.
Melting Point - Accurate Method Procedure
Heat the Mel-temp® apparatus to a temperature 30o below the lowest point obtained in the rough method.
Then raise the temperature slowly at the rate of 1-2 degrees per minute.
If the solid melts with decomposition, introduce the capillary tube when the temperature is 5-6 degrees below the melting point.
Use a charged capillary tube only once.
Boiling Point - Rough Method Procedure
Place about 50 mL of the assigned liquid into a clean and dry distilling flask.
Attach the thermometer.
Connect the side-arm to a water-jacketed condenser and place a receiver at the other end.
Heat gently at first and allow the liquid to boil.
Discard the first few drops of the distillate.
At this stage, take the boiling point range.
Then, save a few mL of the distillate for the next step.
Boiling Point - Accurate Method Procedure
Two tubes are required and both should be sealed at one end.
One tube is made of glass tubing, 6 cm long and 5 mm in diameter. (You could also use a thin-walled bulblet.)
The other is a capillary tube about 5 cm long.
Place about 2 drops of the test compound into the bulblet.
Place the capillary tube into the bulblet containing the test compound with the sealed end topmost.
Fasten the bulblet to the thermometer and immerse them in the oil bath.
Raise the temperature of the bath gradually until a rapid and continuous stream of bubbles comes out of the capillary and passes through the liquid.
Remove the heat and allow the bath to cool by stirring continuously.
Take note of the temperature at the instant the bubbles cease to come out of the capillary and just before the liquid enters it.
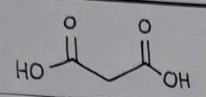
malonic acid
Melting Point Results
Theoretical Range: 132-135°C
malonic acid Structural Formula
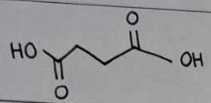
succinic acid
Melting Point Results
Theoretical Range: 185-187°C
succinic acid Structural Formula
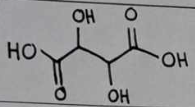
tartaric acid
Melting Point Results
Theoretical Range: 171-174°C
tartaric acid Structural Formula
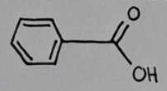
benzoic acid
Melting Point Results
Theoretical Range: 121-123°C
benzoic acid Structural Formula
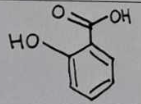
salicylic acid
Melting Point Results
Theoretical Range: 157-159°C
salicylic acid Structural Formula
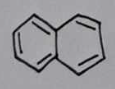
naphthalene
Melting Point Results
Theoretical Range: 80.1-80.26°C
naphthalene Structural Formula
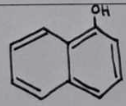
1-naphthol
Melting Point Results
Theoretical Range: 94-96°C
1-naphthol Structural Formula
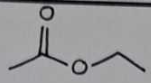
ethyl acetate
Boiling Point Results
Theoretical Range: 75-77°C
ethyl acetate Structural Formula
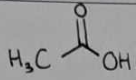
acetic acid
Boiling Point Results
Theoretical Range: 118°C
acetic acid Structural Formula
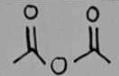
acetic anhydride
Boiling Point Results
Theoretical Range: 139°C
acetic anhydride Structural Formula
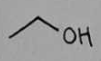
ethanol
Boiling Point Results
Theoretical Range: 78°C
ethanol Structural Formula
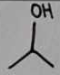
isopropyl alcohol
Boiling Point Results
Theoretical Range: 83°C
isopropyl alcohol Structural Formula
1-butanol
Boiling Point Results
Theoretical Range: 117°C
1-butanol Structural Formula
tert-butyl alcohol
Boiling Point Results
Theoretical Range: 82°C
tert-butyl alcohol Structural Formula
Solubility
A measure of the equilibrium between the pure substance and its solution.
Solubility Analysis
It is very useful in organic structure determination.
Dissolution
Involves separation of ions or molecules of a compound and the occupation of solvent molecules in the spaces between the solute ions or molecules.
Energy is supplied to overcome the intermolecular forces within the solute.
Solubility Test With Water
Compounds are first tested for solubility in water
A compound is soluble in water if about 3.3 g of it dissolves in 100 mL water
Solubility in Organic Solvents
Used for determination of solvents to be used in
Recrystallization
Analyses
Separation Techniques
Study of Chemical Reactions
Class A2
sodium benzoate Class
Class A2
benzoic acid Class
Class I
stearic acid Class
Class A2
p-aminophenol Class
Class SA
p-aminobenzoic acid Class
Class I
naphthalene Class
Class SA
formaldehyde Class
Class SA
formic acid Class
Class SB
diethanolamine Class
Class S2
triethanolamine Class
Class SB
diethylamine Class
Ranges of pH Paper
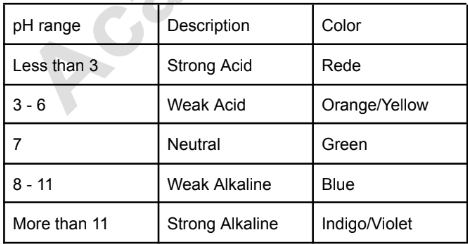
Phenol (Test Compound for Experiment 5)
for Experiment 5
pH paper: 12
pH meter: 13.07
isopropyl alcohol (Test Compound for Experiment 5)
for Experiment 5
pH paper: 8
pH meter: 6.8
acetic acid (Test Compound for Experiment 5)
for Experiment 5
pH paper: 3
pH meter: 3.31
chloroacetic acid (Test Compound for Experiment 5)
for Experiment 5
pH paper: 1
pH meter: 3.49
trichloroacetic acid (Test Compound for Experiment 5)
for Experiment 5
pH paper: 1
pH meter: 3.12
benzoic acid (Test Compound for Experiment 5)
for Experiment 5
pH paper: 4
pH meter: 4.87
salicylic acid (Test Compound for Experiment 5)
for Experiment 5
pH paper: 2
pH meter: 3.56
aniline (Test Compound for Experiment 5)
for Experiment 5
pH paper: 8
pH meter: 8.58
diethylamine (Test Compound for Experiment 5)
for Experiment 5
pH paper: 10
pH meter: 10.56