Systems Telencephalon
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
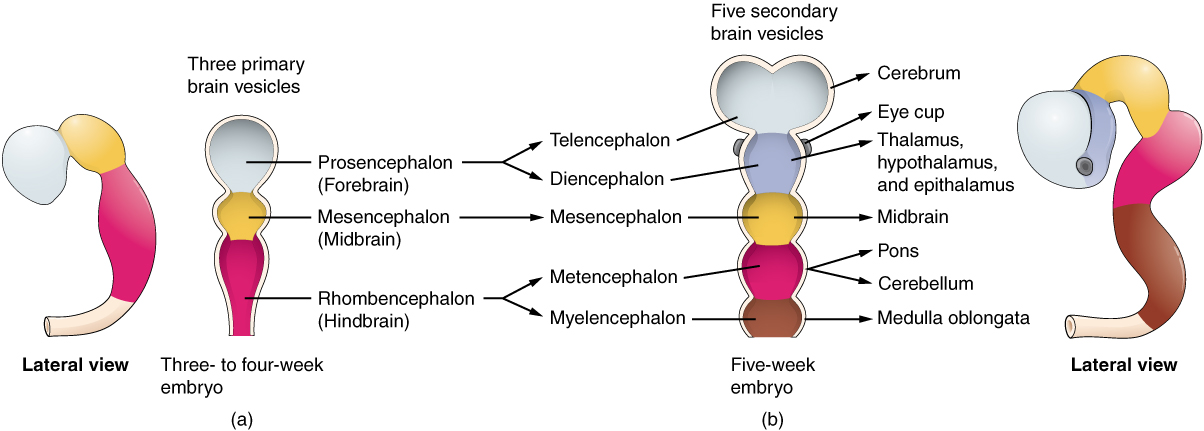
Embryonic → Adult brain → Associated Ventricle
Prosencephalon → Telencephalon → Lateral ventricles
Cerebral Cortex
Cerebral nuclei
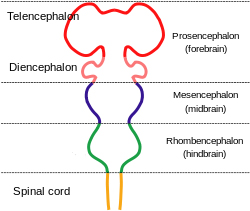
Prosencephalon
This is the most anterior of the three primary brain vesicles in early embryonic development, representing the forebrain.
Telencephalon
The largest portion of the central nervous system (CNS) and consists of the cerebral cortex, subcortical white matter (commissural, association, and projection fibers), and basal telencephalon.

Where is the telencephalon located?
It's bordered by the diencephalon and brainstem at the inferior boundary, and the cerebellum at the posterior boundary.
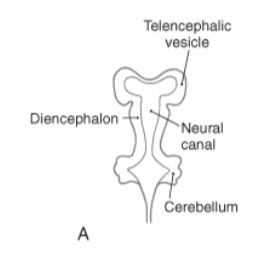
Telencephalic vesicles
The paired outpocketings of the anterior forebrain that eventually develop into the cerebral hemispheres, forming the most complex part of the brain.
What are the structures of and within the telencephalon?
Telencephalon development
Basal Telencephalon
Refers to the ventral part of the developing forebrain, which gives rise to several important structures including the basal ganglia, the hippocampus, and the amygdala.
→ Contributes to motor control.
Basal Ganglia (nuclei)
A group of nuclei including the caudate nucleus, putamen, and globus pallidus, important for motor control.
What are the different structures of the basal ganglia?
1. Corpus striatum
2. Caudate
Caudate nucleus
A C-shaped structure that forms the lateral wall of the lateral ventricle, surrounding the thalamus.
Putamen
A rounded structure that lies below the caudate nucleus.
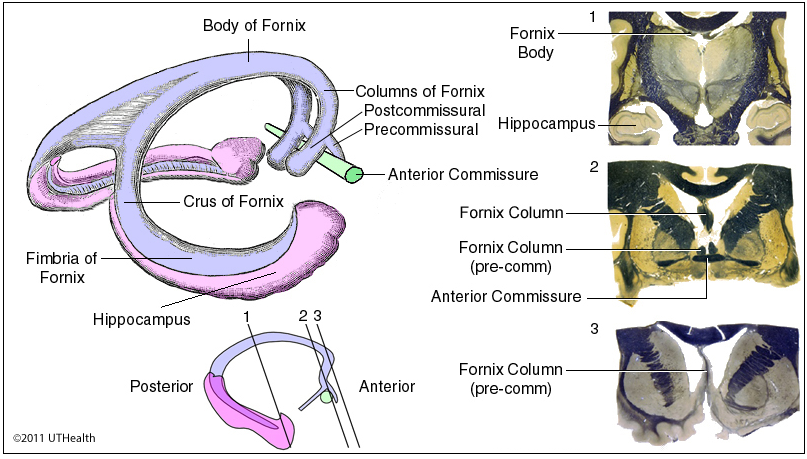
Hippocampus
The small subcortical region of the brain that helps with learning and memory, located in the temporal lobe; part of the limbic system, which controls emotions, smells, and memories.
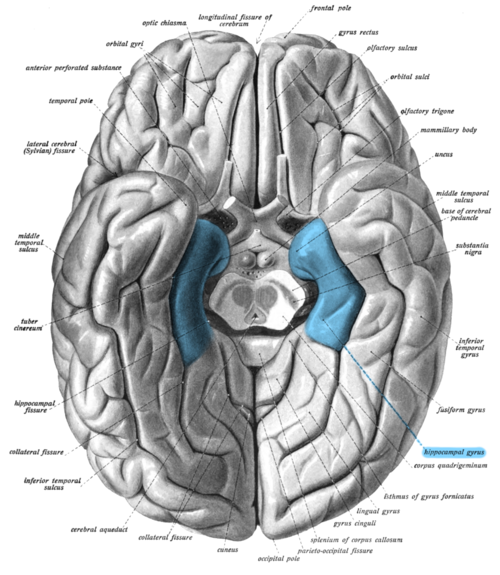
Parahippocampal Gyrus
A grey matter cortical region of the brain that surrounds the hippocampus and is part of the limbic system. The region plays an important role in memory encoding and retrieval.
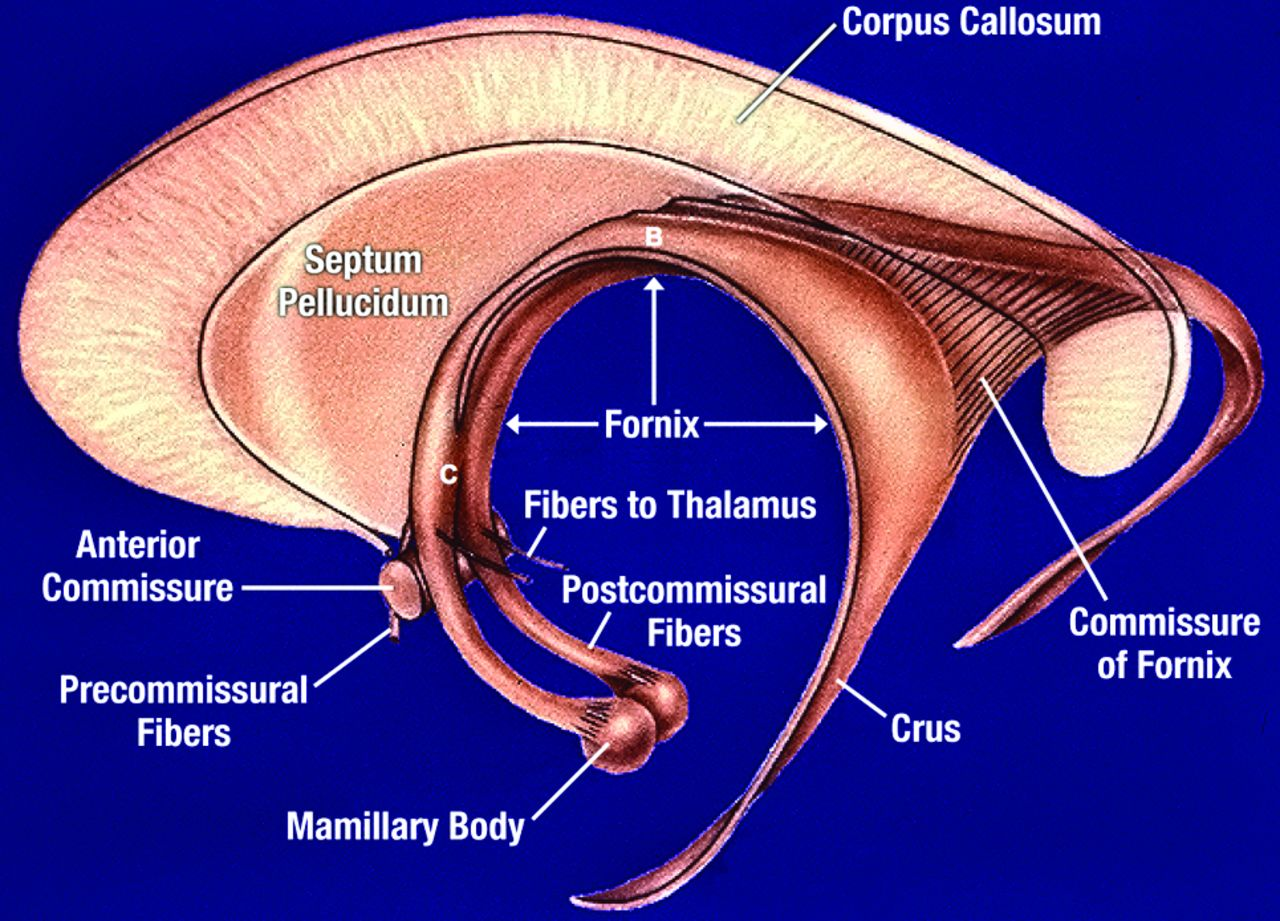
Fornix
A C-shaped, arched bundle of white matter fibers located deep within the brain, primarily functioning as the main output pathway of the hippocampus, connecting it to other limbic system structures like the mammillary bodies in the hypothalamus
Amygdala
Situated in the medial temporal lobe, plays a significant role in processing emotions, particularly fear.
Subcortical region
A group of neural structures located deep within the brain, below the cerebral cortex. These structures are made up of gray and white matter.