The cerebrum
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lobes, fissures, and functions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Label the cerebrum
Label the cerebrum
Cerebrum
Responsible for brain cognitive function such as language, sensory info, conscious planning, movement, conscious interpreatation
What are the raised or shallow structures in the brain
Gyri- elevated ridges
Sulci- Shallow grooves
Increases brain surface area and makes it a more compact structure. It also increases the speed at which cerebral neuron communicate
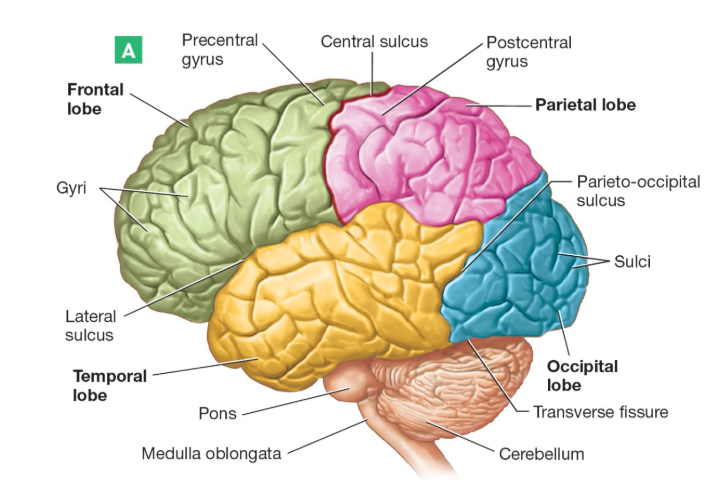
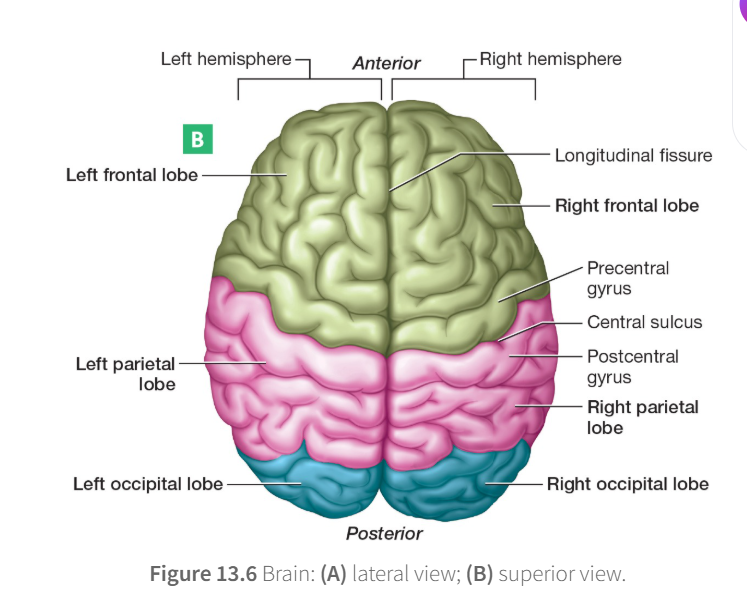
What are the five lobes?
Frontal Lobe: cognitive functions like thinking, planning, and decision-making
Parietal Lobe: processes sensory information and is involved in language, spatial navigation, and mathematical reasoning
Temporal Lobe: responsible for processing auditory information, memory, and language
Occipital Lobe: processing visual information
What are the two fissures and where do they separate
Longitudinal Fissure: Separated the two cerebral hemispheres
Transverse Fissure: Separates from the cerebellum
What are the sulcus?
Central Sulcus: separates central and parietal lobe
Lateral Sulcus: separates the frontal and temporal lobe
Parieto-occipital: Separates partieal and occiptal lobe
What are the gyrus?
Precentral gyrus: Houses primary motor cortex
Postcentral gyrus: soma sensory cortex
Pons
Controls rhythm of breathing and sleep cycle
Medulla oblongata
Controls blood pressure, heart rate, reflexes such as vomiting.
Cerebellum
Coordinate voluntary movements, ensuring they are smooth and balanced, and it also plays a crucial role in motor learning.
Diencephalon contains
Thalamus
Subthalamus
Hypothalamus
Thalamus
largest part; receives
input from most sensory neurons
in the body
Subthalamus
motor functions
Hypothalamus
major endocrine
tissue; homeostatically regulates
many important physiological
processes 37
Cerebral cortex:
Where complex information
processing occurs
Anatomically divided into 6 layers
Differences in function between
hemispheres (hemispheric
lateralization
Precentral gyrus
primary motor
cortex (M1)
Postcentral gyrus
somatosensory cortex (S1)
Hippocampus
is associated with memory
Homunculus:
a graphical representation of the amount of the S1 that receives
afferent sensory information from different parts of the body. 39